Android 应用进程启动流程
我们知道启动Activity时,在ActivityStackSupervisor.java中函数startSpecificActivityLocked里面会判断当前Activity所在application是否已经启动,如果启动,则直接创建Activity也即调用realStartActivityLocked,本篇讨论需要启动的Activity所属的application没有启动的情况,此时就会通过AMS来调用startProcessLocked创建新进程。
AMS获取请求
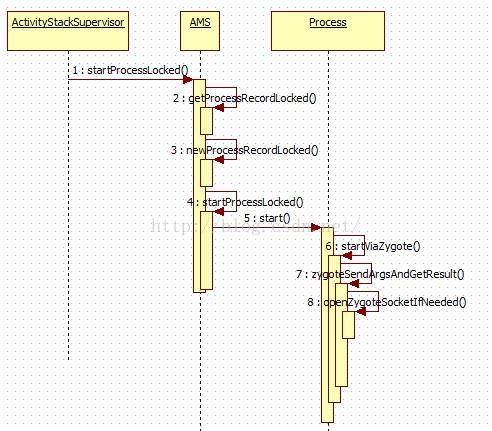
在ActivityStackSupervisor中分析完确定启动新进程,就会操作权交给AMS来处理,如图:
startSpecificActivityLocked分析是否要创建进程
void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
// Is this activity's application already running?
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo.uid, true);
r.task.stack.setLaunchTime(r);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
......
realStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig);
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
......
}
......
}
mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
"activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false, false, true);
}String hostingType, String hostingNameStr),如下:
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app,
String hostingType, String hostingNameStr) {
......
try {
......
// Start the process. It will either succeed and return a result containing
// the PID of the new process, or else throw a RuntimeException.
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start("android.app.ActivityThread",
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, app.info.seinfo, null);
......
if (app.persistent) {
Watchdog.getInstance().processStarted(app.processName, startResult.pid);
}
......
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// XXX do better error recovery.
app.setPid(0);
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting process " + app.processName, e);
}
} public static final ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
try {
return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
debugFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo, zygoteArgs);
} catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG,
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed");
throw new RuntimeException(
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed", ex);
}
} private static ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
final int uid, final int gid,
final int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String[] extraArgs)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
synchronized(Process.class) {
ArrayList argsForZygote = new ArrayList();
// --runtime-init, --setuid=, --setgid=,
// and --setgroups= must go first
argsForZygote.add("--runtime-init");
argsForZygote.add("--setuid=" + uid);
argsForZygote.add("--setgid=" + gid);
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_JNI_LOGGING) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-jni-logging");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_SAFEMODE) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-safemode");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-debugger");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_CHECKJNI) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-checkjni");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_ASSERT) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-assert");
}
if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_MULTIUSER) {
argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-multiuser");
} else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_MULTIUSER_ALL) {
argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-multiuser-all");
}
argsForZygote.add("--target-sdk-version=" + targetSdkVersion);
//TODO optionally enable debuger
//argsForZygote.add("--enable-debugger");
// --setgroups is a comma-separated list
if (gids != null && gids.length > 0) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("--setgroups=");
int sz = gids.length;
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
sb.append(',');
}
sb.append(gids[i]);
}
argsForZygote.add(sb.toString());
}
if (niceName != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--nice-name=" + niceName);
}
if (seInfo != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--seinfo=" + seInfo);
}
argsForZygote.add(processClass);
if (extraArgs != null) {
for (String arg : extraArgs) {
argsForZygote.add(arg);
}
}
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(argsForZygote);
}
} private static ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(ArrayList args)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
openZygoteSocketIfNeeded();
try {
/**
* See com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.readArgumentList()
* Presently the wire format to the zygote process is:
* a) a count of arguments (argc, in essence)
* b) a number of newline-separated argument strings equal to count
*
* After the zygote process reads these it will write the pid of
* the child or -1 on failure, followed by boolean to
* indicate whether a wrapper process was used.
*/
sZygoteWriter.write(Integer.toString(args.size()));
sZygoteWriter.newLine();
int sz = args.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
String arg = args.get(i);
if (arg.indexOf('\n') >= 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(
"embedded newlines not allowed");
}
sZygoteWriter.write(arg);
sZygoteWriter.newLine();
}
sZygoteWriter.flush();
// Should there be a timeout on this?
ProcessStartResult result = new ProcessStartResult();
result.pid = sZygoteInputStream.readInt();
if (result.pid < 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");
}
result.usingWrapper = sZygoteInputStream.readBoolean();
return result;
} catch (IOException ex) {
try {
if (sZygoteSocket != null) {
sZygoteSocket.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex2) {
// we're going to fail anyway
Log.e(LOG_TAG,"I/O exception on routine close", ex2);
}
sZygoteSocket = null;
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex);
}
} private static void openZygoteSocketIfNeeded()
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
......
for (int retry = 0
; (sZygoteSocket == null) && (retry < (retryCount + 1))
; retry++ ) {
......
try {
sZygoteSocket = new LocalSocket();
sZygoteSocket.connect(new LocalSocketAddress(ZYGOTE_SOCKET,
LocalSocketAddress.Namespace.RESERVED));
sZygoteInputStream
= new DataInputStream(sZygoteSocket.getInputStream());
sZygoteWriter =
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
sZygoteSocket.getOutputStream()),
256);
Log.i("Zygote", "Process: zygote socket opened");
sPreviousZygoteOpenFailed = false;
break;
} catch (IOException ex) {
if (sZygoteSocket != null) {
try {
sZygoteSocket.close();
} catch (IOException ex2) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG,"I/O exception on close after exception",
ex2);
}
}
sZygoteSocket = null;
}
}
if (sZygoteSocket == null) {
sPreviousZygoteOpenFailed = true;
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("connect failed");
}
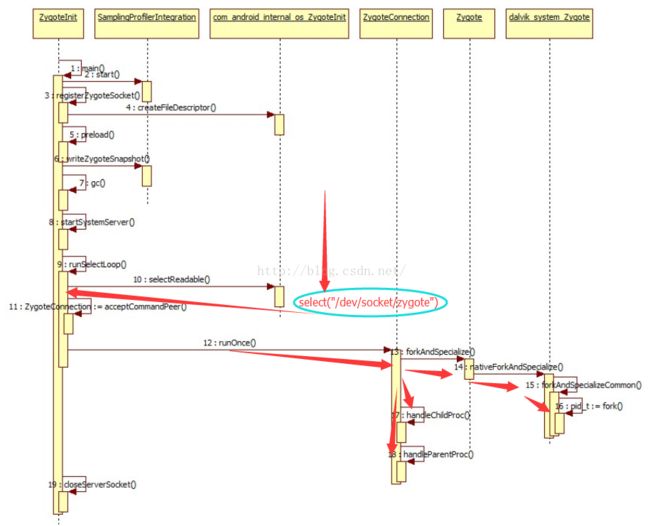
}Zygote服务进程会监听“/dev/socket/zygote”设备文件,一旦有读写动作,内部的轮询函授runSelectLoop就会创建ZygoteConnection,并运行runOnce
boolean runOnce() throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
String args[];
Arguments parsedArgs = null;
FileDescriptor[] descriptors;
try {
args = readArgumentList();
descriptors = mSocket.getAncillaryFileDescriptors();
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.w(TAG, "IOException on command socket " + ex.getMessage());
closeSocket();
return true;
}
if (args == null) {
// EOF reached.
closeSocket();
return true;
}
/** the stderr of the most recent request, if avail */
PrintStream newStderr = null;
if (descriptors != null && descriptors.length >= 3) {
newStderr = new PrintStream(
new FileOutputStream(descriptors[2]));
}
int pid = -1;
FileDescriptor childPipeFd = null;
FileDescriptor serverPipeFd = null;
try {
parsedArgs = new Arguments(args);
applyUidSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer, peerSecurityContext);
applyRlimitSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer, peerSecurityContext);
applyCapabilitiesSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer, peerSecurityContext);
applyInvokeWithSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer, peerSecurityContext);
applyseInfoSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer, peerSecurityContext);
applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
int[][] rlimits = null;
if (parsedArgs.rlimits != null) {
rlimits = parsedArgs.rlimits.toArray(intArray2d);
}
if (parsedArgs.runtimeInit && parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
FileDescriptor[] pipeFds = Libcore.os.pipe();
childPipeFd = pipeFds[1];
serverPipeFd = pipeFds[0];
ZygoteInit.setCloseOnExec(serverPipeFd, true);
}
pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid, parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mountExternal, parsedArgs.seInfo,
parsedArgs.niceName);
} catch (IOException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Exception creating pipe", ex);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Exception creating pipe", ex);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Invalid zygote arguments", ex);
} catch (ZygoteSecurityException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr,
"Zygote security policy prevents request: ", ex);
}
try {
if (pid == 0) {
// in child
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
serverPipeFd = null;
handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);
// should never get here, the child is expected to either
// throw ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller or exec().
return true;
} else {
// in parent...pid of < 0 means failure
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);
}
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
}
}forkAndSpecializeCommon,在到内核的fork函数,完成进程的创建,后面调用handleChildProc,handleParentProc对父子进程做相关处理。
private boolean handleParentProc(int pid,
FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, Arguments parsedArgs) {
if (pid > 0) {
setChildPgid(pid);
}
if (descriptors != null) {
for (FileDescriptor fd: descriptors) {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(fd);
}
}
boolean usingWrapper = false;
if (pipeFd != null && pid > 0) {
DataInputStream is = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(pipeFd));
int innerPid = -1;
try {
innerPid = is.readInt();
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.w(TAG, "Error reading pid from wrapped process, child may have died", ex);
} finally {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
}
}
// Ensure that the pid reported by the wrapped process is either the
// child process that we forked, or a descendant of it.
if (innerPid > 0) {
int parentPid = innerPid;
while (parentPid > 0 && parentPid != pid) {
parentPid = Process.getParentPid(parentPid);
}
if (parentPid > 0) {
Log.i(TAG, "Wrapped process has pid " + innerPid);
pid = innerPid;
usingWrapper = true;
} else {
Log.w(TAG, "Wrapped process reported a pid that is not a child of "
+ "the process that we forked: childPid=" + pid
+ " innerPid=" + innerPid);
}
}
}
try {
mSocketOutStream.writeInt(pid);
mSocketOutStream.writeBoolean(usingWrapper);
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error reading from command socket", ex);
return true;
}
return false;
} private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs,
FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, PrintStream newStderr)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
closeSocket();
ZygoteInit.closeServerSocket();
if (descriptors != null) {
try {
ZygoteInit.reopenStdio(descriptors[0],
descriptors[1], descriptors[2]);
for (FileDescriptor fd: descriptors) {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(fd);
}
newStderr = System.err;
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error reopening stdio", ex);
}
}
if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);
}
if (parsedArgs.runtimeInit) {
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
pipeFd, parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
} else {
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
}
} else {
String className;
try {
className = parsedArgs.remainingArgs[0];
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr,
"Missing required class name argument", null);
return;
}
String[] mainArgs = new String[parsedArgs.remainingArgs.length - 1];
System.arraycopy(parsedArgs.remainingArgs, 1,
mainArgs, 0, mainArgs.length);
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
WrapperInit.execStandalone(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.classpath, className, mainArgs);
} else {
ClassLoader cloader;
if (parsedArgs.classpath != null) {
cloader = new PathClassLoader(parsedArgs.classpath,
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
} else {
cloader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
}
try {
ZygoteInit.invokeStaticMain(cloader, className, mainArgs);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Error starting.", ex);
}
}
}
} static void invokeStaticMain(ClassLoader loader,
String className, String[] argv)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
Class cl;
try {
cl = loader.loadClass(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
Method m;
try {
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
/*
* This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
*/
throw new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}