Android PackageManagerService分析一:PMS的启动
从这一章开始,我们来分析Android的PackageManagerService,后面简称PMS。PMS用来管理所有的package信息,包括安装、卸载、更新以及解析AndroidManifest.xml以组织相应的数据结构,这些数据结构将会被PMS、ActivityMangerService等等service和application使用到。PMS有几个比较重要的命令可以用于我们debug中:
adb shell dumpsys package (dump出系统中所有的application信息)
adb shell dumpsys package “com.android.contacts" p (dump出系统中特定包名的application信息)
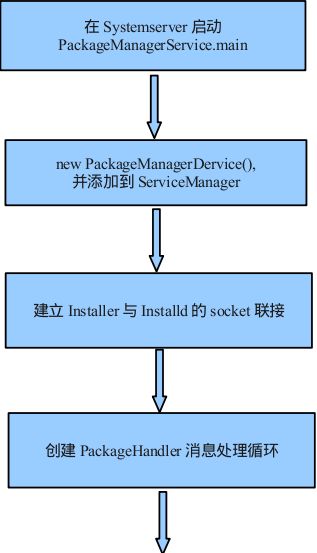
首先来看SystemServer中PMS的构造以及注册:
pm = PackageManagerService.main(context, installer,
factoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_OFF,
onlyCore);
try {
firstBoot = pm.isFirstBoot();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
try {
pm.performBootDexOpt();
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("performing boot dexopt", e);
}
try {
pm.systemReady();
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("making Package Manager Service ready", e);
}首先来看PMS的main方法:
public static final IPackageManager main(Context context, Installer installer,
boolean factoryTest, boolean onlyCore) {
PackageManagerService m = new PackageManagerService(context, installer,
factoryTest, onlyCore);
ServiceManager.addService("package", m);
return m;
}首先构造一个PMS对象,然后调用ServiceManager的addService注册这个服务。构造函数的第二个参数是一个Installer对象,用于和Installd通信使用,我们后面分析Installd再来介绍;第三个参数factoryTest为出厂测试,默认为false;第四个参数onlyCore与vold相关,我们以后再分析,这里也为false。PMS的构造函数比较长,我们首先来看一下大概的流程图,然后我们分段来分析代码:
public PackageManagerService(Context context, Installer installer,
boolean factoryTest, boolean onlyCore) {
mContext = context;
mFactoryTest = factoryTest;
mOnlyCore = onlyCore;
mNoDexOpt = "eng".equals(SystemProperties.get("ro.build.type"));
mMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
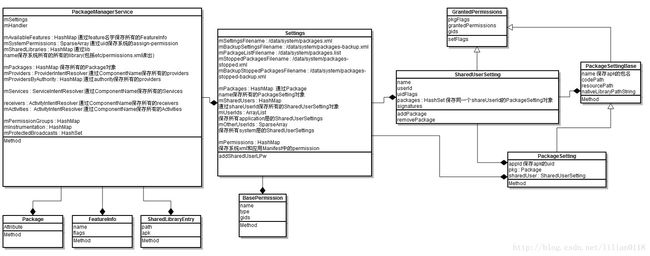
mSettings = new Settings(context);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.system", Process.SYSTEM_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM|ApplicationInfo.FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.phone", RADIO_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM|ApplicationInfo.FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.log", LOG_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM|ApplicationInfo.FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.nfc", NFC_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM|ApplicationInfo.FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.bluetooth", BLUETOOTH_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM|ApplicationInfo.FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.shell", SHELL_UID,
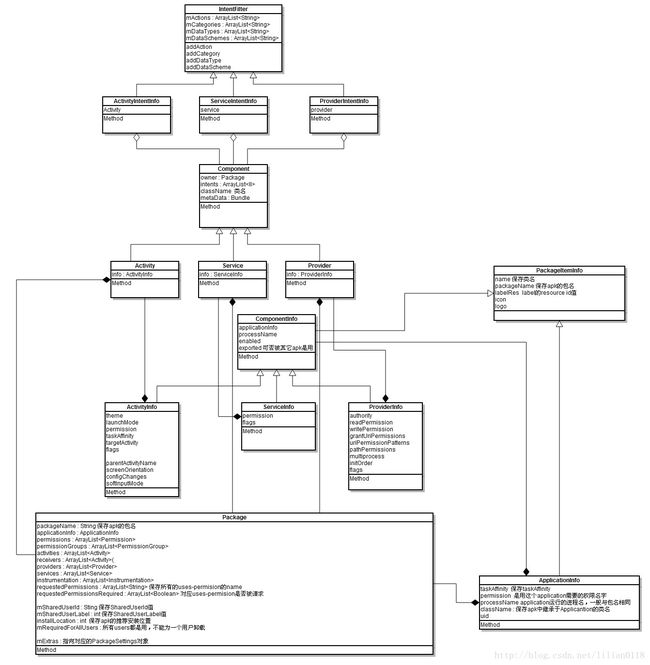
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM|ApplicationInfo.FLAG_PRIVILEGED);上面首先做一个变量的赋值,然后取出"ro.build.type"属性值,build版本分为user和eng两种,一种是面向user,一种是用于engineer debug版,这里假设mNoDexOpt为false。然后构造一个Settings对象,Settings是Android的全局管理者,用于协助PMS保存所有的安装包信息,PMS和Settings之间的类图关系如下:
来看一下Settings的构造函数:
Settings(Context context) {
this(context, Environment.getDataDirectory());
}
Settings(Context context, File dataDir) {
mContext = context;
mSystemDir = new File(dataDir, "system");
mSystemDir.mkdirs();
FileUtils.setPermissions(mSystemDir.toString(),
FileUtils.S_IRWXU|FileUtils.S_IRWXG
|FileUtils.S_IROTH|FileUtils.S_IXOTH,
-1, -1);
mSettingsFilename = new File(mSystemDir, "packages.xml");
mBackupSettingsFilename = new File(mSystemDir, "packages-backup.xml");
mPackageListFilename = new File(mSystemDir, "packages.list");
FileUtils.setPermissions(mPackageListFilename, 0660, SYSTEM_UID, PACKAGE_INFO_GID);
mStoppedPackagesFilename = new File(mSystemDir, "packages-stopped.xml");
mBackupStoppedPackagesFilename = new File(mSystemDir, "packages-stopped-backup.xml");
}Environment.getDataDirectory()返回/data目录,然后创建/data/system/目录,并设置它的权限,并在/data/system目录中创建mSettingsFilename、mBackupSettingsFilename、mPackageListFilename、mStoppedPackagesFilename和mBackupStoppedPackagesFilename几个文件。packages.xml就是保存了系统所有的Package信息,packages-backup.xml是packages.xml的备份,防止在写packages.xml突然断电等问题。回到PMS的构造函数,调用addSharedUserLPw将几种SharedUserId的名字和它对应的UID对应写到Settings当中。关于SharedUserId的使用,我们在后面介绍APK的安装过程中再来分析。这里先简单看一下Process中提供的UID列表:
public static final int SYSTEM_UID = 1000;
public static final int PHONE_UID = 1001;
public static final int SHELL_UID = 2000;
public static final int LOG_UID = 1007;
public static final int WIFI_UID = 1010;
public static final int MEDIA_UID = 1013;
public static final int DRM_UID = 1019;
public static final int VPN_UID = 1016;
public static final int NFC_UID = 1027;
public static final int BLUETOOTH_UID = 1002;
public static final int MEDIA_RW_GID = 1023;
public static final int PACKAGE_INFO_GID = 1032;
public static final int FIRST_APPLICATION_UID = 10000;
public static final int LAST_APPLICATION_UID = 19999;上面定义了一系列的UID,其中applicantion的uid从10000开始到19999结束。来看addSharedUserLPw函数的实现:
SharedUserSetting addSharedUserLPw(String name, int uid, int pkgFlags) {
SharedUserSetting s = mSharedUsers.get(name);
if (s != null) {
if (s.userId == uid) {
return s;
}
PackageManagerService.reportSettingsProblem(Log.ERROR,
"Adding duplicate shared user, keeping first: " + name);
return null;
}
s = new SharedUserSetting(name, pkgFlags);
s.userId = uid;
if (addUserIdLPw(uid, s, name)) {
mSharedUsers.put(name, s);
return s;
}
return null;
}
private boolean addUserIdLPw(int uid, Object obj, Object name) {
if (uid > Process.LAST_APPLICATION_UID) {
return false;
}
if (uid >= Process.FIRST_APPLICATION_UID) {
int N = mUserIds.size();
final int index = uid - Process.FIRST_APPLICATION_UID;
while (index >= N) {
mUserIds.add(null);
N++;
}
if (mUserIds.get(index) != null) {
PackageManagerService.reportSettingsProblem(Log.ERROR,
"Adding duplicate user id: " + uid
+ " name=" + name);
return false;
}
mUserIds.set(index, obj);
} else {
if (mOtherUserIds.get(uid) != null) {
PackageManagerService.reportSettingsProblem(Log.ERROR,
"Adding duplicate shared id: " + uid
+ " name=" + name);
return false;
}
mOtherUserIds.put(uid, obj);
}
return true;
}mSharedUsers是一个HashMap,保存着所有的name和SharedUserSetting的映射关系。这里先调用addUserIdLPw将uid和SharedUserSetting添加到mOtherUserIds中,然后将name和SharedUserSetting添加到mSharedUsers中方便以后查找。接着来看PMS的构造函数:
mInstaller = installer;
WindowManager wm = (WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
Display d = wm.getDefaultDisplay();
d.getMetrics(mMetrics);
synchronized (mInstallLock) {
// writer
synchronized (mPackages) {
mHandlerThread.start();
mHandler = new PackageHandler(mHandlerThread.getLooper());
Watchdog.getInstance().addThread(mHandler, mHandlerThread.getName(),
WATCHDOG_TIMEOUT);
File dataDir = Environment.getDataDirectory();
mAppDataDir = new File(dataDir, "data");
mAppInstallDir = new File(dataDir, "app");
mAppLibInstallDir = new File(dataDir, "app-lib");
mAsecInternalPath = new File(dataDir, "app-asec").getPath();
mUserAppDataDir = new File(dataDir, "user");
mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir = new File(dataDir, "app-private");
sUserManager = new UserManagerService(context, this,
mInstallLock, mPackages);
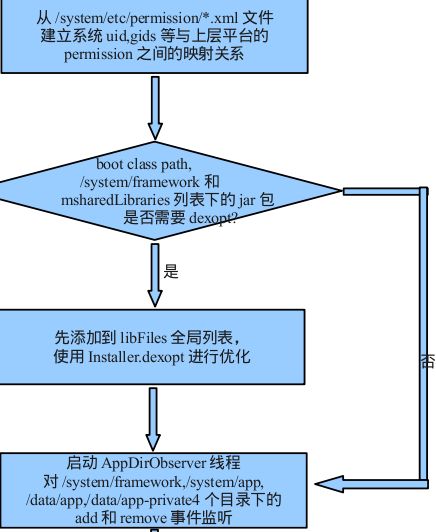
readPermissions();上面首先获得显示屏的相关信息并保存在mMetrics中。然后启动“PackageManager”的HandleThread并绑定到PackageHandler上,这就是最后处理所有的跨进程消息的handler。接着调用readPermissions()来处理系统的permissions相关的文件。在/etc/permissions的文件大多来源于代码中的framworks/native/data/etc,这些文件的作用是表明系统支持的feature有哪些,例如是否支持蓝牙、wifi、P2P等。文件目录如下:
- android.hardware.bluetooth.xml
- android.hardware.bluetooth_le.xml
- android.hardware.camera.autofocus.xml
- android.hardware.camera.flash-autofocus.xml
- android.hardware.camera.front.xml
- android.hardware.camera.xml
- android.software.sip.xml
- com.android.nfc_extras.xml
- com.nxp.mifare.xml
- handheld_core_hardware.xml
这里的文件内容很简单,例如android.hardware.bluetooth.xml的内容如下:
在/etc/permissions中有一个platform.xml,它是来源于frameworks/base/data/etc/中,其中的内容大致如下:
现在来看readPermissions()的实现:
void readPermissions() {
File libraryDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "etc/permissions");
if (!libraryDir.exists() || !libraryDir.isDirectory()) {
Slog.w(TAG, "No directory " + libraryDir + ", skipping");
return;
}
if (!libraryDir.canRead()) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Directory " + libraryDir + " cannot be read");
return;
}
for (File f : libraryDir.listFiles()) {
if (f.getPath().endsWith("etc/permissions/platform.xml")) {
continue;
}
if (!f.getPath().endsWith(".xml")) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Non-xml file " + f + " in " + libraryDir + " directory, ignoring");
continue;
}
if (!f.canRead()) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Permissions library file " + f + " cannot be read");
continue;
}
readPermissionsFromXml(f);
}
// Read permissions from .../etc/permissions/platform.xml last so it will take precedence
final File permFile = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(),
"etc/permissions/platform.xml");
readPermissionsFromXml(permFile);
}首先不断的读出/etc/permissions下面的文件,并依此处理除了platform.xml以外的其它xml文件,并最后处理platform.xml文件,来看readPermissionsFromXml()的实现,这个函数比较长,我们主要看处理feature、permission、assign-permission和library的代码:
private void readPermissionsFromXml(File permFile) {
FileReader permReader = null;
try {
permReader = new FileReader(permFile);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
}
try {
XmlPullParser parser = Xml.newPullParser();
parser.setInput(permReader);
XmlUtils.beginDocument(parser, "permissions");
while (true) {
XmlUtils.nextElement(parser);
if (parser.getEventType() == XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
break;
}
String name = parser.getName();
if ("group".equals(name)) {
} else if ("permission".equals(name)) {
String perm = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "name");
if (perm == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, " without name at "
+ parser.getPositionDescription());
XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser);
continue;
}
perm = perm.intern();
readPermission(parser, perm);
} else if ("assign-permission".equals(name)) {
String perm = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "name");
String uidStr = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "uid");
if (uidStr == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, " without uid at "
+ parser.getPositionDescription());
XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser);
continue;
}
int uid = Process.getUidForName(uidStr);
perm = perm.intern();
HashSet perms = mSystemPermissions.get(uid);
if (perms == null) {
perms = new HashSet();
mSystemPermissions.put(uid, perms);
}
perms.add(perm);
XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser);
} else if ("library".equals(name)) {
String lname = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "name");
String lfile = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "file");
if (lname == null) {
} else if (lfile == null) {
} else {
mSharedLibraries.put(lname, new SharedLibraryEntry(lfile, null));
}
XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser);
continue;
} else if ("feature".equals(name)) {
String fname = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "name");
if (fname == null) {
} else {
FeatureInfo fi = new FeatureInfo();
fi.name = fname;
mAvailableFeatures.put(fname, fi);
}
XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser);
continue;
} else {
XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser);
continue;
}
}
permReader.close();
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Got execption parsing permissions.", e);
} catch (IOException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Got execption parsing permissions.", e);
}
} 首先来看处理feature这个tag的代码,在fname中保存feature的名字,然后创建一个FeatureInfo,并把fname和FeatureInfo保存到mAvailableFeatures这个HashMap中。接着来看处理permission tag,首先读出permission的name,然后调用readPermission去处理后面的group信息:
void readPermission(XmlPullParser parser, String name)
throws IOException, XmlPullParserException {
name = name.intern();
BasePermission bp = mSettings.mPermissions.get(name);
if (bp == null) {
bp = new BasePermission(name, null, BasePermission.TYPE_BUILTIN);
mSettings.mPermissions.put(name, bp);
}
int outerDepth = parser.getDepth();
int type;
while ((type=parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT
&& (type != XmlPullParser.END_TAG
|| parser.getDepth() > outerDepth)) {
if (type == XmlPullParser.END_TAG
|| type == XmlPullParser.TEXT) {
continue;
}
String tagName = parser.getName();
if ("group".equals(tagName)) {
String gidStr = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "gid");
if (gidStr != null) {
int gid = Process.getGidForName(gidStr);
bp.gids = appendInt(bp.gids, gid);
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, " without gid at "
+ parser.getPositionDescription());
}
}
XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser);
}
} 在readPermission中首先构造BasePermission对象,并把name和BasePermission一起添加到Settings的mPermissions这个HashMap中。Android管理权限的机制其实就是对应相应的permission,用一个gid号来描述,当一个应用程序请求这个permission的时候,就把这个gid号添加到对应的application中去。Process.getGidForName方法通过JNI调用getgrnam系统函数去获取相应的组名称所对应的gid号,并把它添加到BasePermission对象的gids数组中。再来看处理assign-permission这个tag的代码,首先读出permission的名字和uid,保存在perm和uidStr中,Process.getUidForName方法通过JNI调用getpwnam系统函数获取相应的用户名所对应的uid号,并把刚解析的permission名添加到HashSet当中,最后把上面的uid和hashset添加到mSystemPermissions这个数组中。最后来看处理library这个tag的代码,这里把解析处理的library名字和路径保存在mSharedLibraries这个hashMap中。再回到PMS的构造函数中,接着往下来看:
mRestoredSettings = mSettings.readLPw(this, sUserManager.getUsers(false),
mSdkVersion, mOnlyCore);
String customResolverActivity = Resources.getSystem().getString(
R.string.config_customResolverActivity);
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(customResolverActivity)) {
customResolverActivity = null;
} else {
mCustomResolverComponentName = ComponentName.unflattenFromString(
customResolverActivity);
}
long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
int scanMode = SCAN_MONITOR | SCAN_NO_PATHS | SCAN_DEFER_DEX | SCAN_BOOTING;
if (mNoDexOpt) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Running ENG build: no pre-dexopt!");
scanMode |= SCAN_NO_DEX;
}
final HashSet alreadyDexOpted = new HashSet();
String bootClassPath = System.getProperty("java.boot.class.path");
if (bootClassPath != null) {
String[] paths = splitString(bootClassPath, ':');
for (int i=0; i 0) {
Iterator libs = mSharedLibraries.values().iterator();
while (libs.hasNext()) {
String lib = libs.next().path;
if (lib == null) {
continue;
}
try {
if (dalvik.system.DexFile.isDexOptNeeded(lib)) {
alreadyDexOpted.add(lib);
mInstaller.dexopt(lib, Process.SYSTEM_UID, true);
didDexOpt = true;
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Library not found: " + lib);
} catch (IOException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Cannot dexopt " + lib + "; is it an APK or JAR? "
+ e.getMessage());
}
}
} 这里首先调用Settings的readLPw函数去解析packages.xml和packages-backup.xml保存的安装列表信息,并把解析的pakcages信息添加到相应的数据结构中,这里我们先假设这是第一次开机,所有packages.xml和packages-backup.xml文件都还不存在。所以Settings的readLPw函数会直接返回。接着把boot class path里面的文件添加到alreadyDexOpted这个HashSet中,因为它们在zygote启动时已经进过Dex优化了。接着扫描mSharedLibraries中的文件,这些文件是在解析platfrom.xml中的library tag添加进来的,如果它们需要做dex优化,则调用Installd的的dexopt方法,关于installd的调用流程,我们后面在安装apk的时候再来分析。接着来看PMS的构造函数:
File frameworkDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "framework");
alreadyDexOpted.add(frameworkDir.getPath() + "/framework-res.apk");
alreadyDexOpted.add(frameworkDir.getPath() + "/core-libart.jar");
String[] frameworkFiles = frameworkDir.list();
if (frameworkFiles != null) {
for (int i=0; i这里扫描所有的/system/framework下面除framework-res以外的apk和jar包(因为framework-res只有resource文件),然后依次对它们做Dex优化。在上面如果有对文件做过Dex优化,就要去删除dalvi-cache下面所有的dex文件,以防止cache文件和现在的文件不相符。接着来看PMS的构造函数:
mFrameworkInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver(
frameworkDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, true, false);
mFrameworkInstallObserver.startWatching();
scanDirLI(frameworkDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_PRIVILEGED,
scanMode | SCAN_NO_DEX, 0);
// Collected privileged system packages.
File privilegedAppDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "priv-app");
mPrivilegedInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver(
privilegedAppDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, true, true);
mPrivilegedInstallObserver.startWatching();
scanDirLI(privilegedAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_PRIVILEGED, scanMode, 0);
// Collect ordinary system packages.
File systemAppDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "app");
mSystemInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver(
systemAppDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, true, false);
mSystemInstallObserver.startWatching();
scanDirLI(systemAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanMode, 0);
// Collect all vendor packages.
File vendorAppDir = new File("/vendor/app");
mVendorInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver(
vendorAppDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, true, false);
mVendorInstallObserver.startWatching();
scanDirLI(vendorAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanMode, 0);
if (DEBUG_UPGRADE) Log.v(TAG, "Running installd update commands");
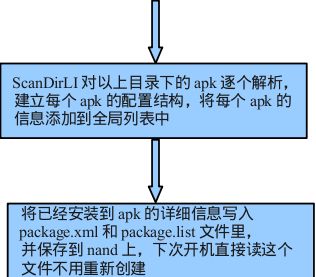
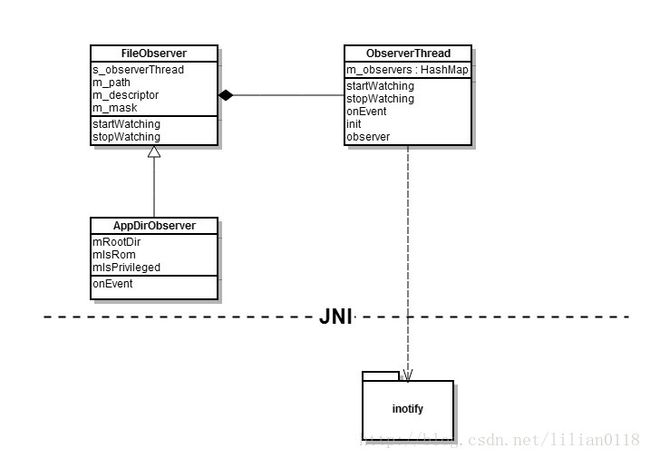
mInstaller.moveFiles();这里首先会/system/framework、/system/priv-app、/system/app、/vendor/app四个目录建立AppDirObserver去监听它们的add、delete等操作,AppDirObserver是继承于FileObserver,它的底层是通过linux内核的inotify机制实现的。接着调用scanDirLI去扫描上面的四个目录。我们来看一下AppDirObserver的架构:
接着来看scanDirLI的代码:
private void scanDirLI(File dir, int flags, int scanMode, long currentTime) {
String[] files = dir.list();
int i;
for (i=0; iscanDirLI调用scanPackageLI依次扫描并解析上面四个目录的目录下所有的apk文件:
private PackageParser.Package scanPackageLI(File scanFile,
int parseFlags, int scanMode, long currentTime, UserHandle user) {
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;
String scanPath = scanFile.getPath();
parseFlags |= mDefParseFlags;
PackageParser pp = new PackageParser(scanPath);
//首先解析出一个Package对象
final PackageParser.Package pkg = pp.parsePackage(scanFile,
scanPath, mMetrics, parseFlags);
PackageSetting ps = null;
PackageSetting updatedPkg;
synchronized (mPackages) {
String oldName = mSettings.mRenamedPackages.get(pkg.packageName);
if (pkg.mOriginalPackages != null && pkg.mOriginalPackages.contains(oldName)) {
ps = mSettings.peekPackageLPr(oldName);
}
if (ps == null) {
ps = mSettings.peekPackageLPr(pkg.packageName);
}
updatedPkg = mSettings.getDisabledSystemPkgLPr(ps != null ? ps.name : pkg.packageName);
if (DEBUG_INSTALL && updatedPkg != null) Slog.d(TAG, "updatedPkg = " + updatedPkg);
}
if (updatedPkg != null && (parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) != 0) {
//与update app相关的
}
if (updatedPkg != null) {
parseFlags |= PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM;
}
if (!collectCertificatesLI(pp, ps, pkg, scanFile, parseFlags)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed verifying certificates for package:" + pkg.packageName);
return null;
}
//处理system与非system的app同名的问题
boolean shouldHideSystemApp = false;
if (updatedPkg == null && ps != null
&& (parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR) != 0 && !isSystemApp(ps)) {
if (compareSignatures(ps.signatures.mSignatures, pkg.mSignatures)
!= PackageManager.SIGNATURE_MATCH) {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "Signature mismatch!");
deletePackageLI(pkg.packageName, null, true, null, null, 0, null, false);
ps = null;
} else {
if (pkg.mVersionCode < ps.versionCode) {
shouldHideSystemApp = true;
} else {
InstallArgs args = createInstallArgs(packageFlagsToInstallFlags(ps),
ps.codePathString, ps.resourcePathString, ps.nativeLibraryPathString);
synchronized (mInstallLock) {
args.cleanUpResourcesLI();
}
}
}
}
if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR) == 0) {
if (ps != null && !ps.codePath.equals(ps.resourcePath)) {
parseFlags |= PackageParser.PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK;
}
}
String codePath = null;
String resPath = null;
if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK) != 0) {
if (ps != null && ps.resourcePathString != null) {
resPath = ps.resourcePathString;
} else {
}
} else {
resPath = pkg.mScanPath;
}
codePath = pkg.mScanPath;
setApplicationInfoPaths(pkg, codePath, resPath);
//
PackageParser.Package scannedPkg = scanPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanMode
| SCAN_UPDATE_SIGNATURE, currentTime, user);
if (shouldHideSystemApp) {
synchronized (mPackages) {
grantPermissionsLPw(pkg, true);
mSettings.disableSystemPackageLPw(pkg.packageName);
}
}
return scannedPkg;
}scanPackageLI首先调用PackageParser的parsePackage去解析扫描的文件,注意这里有两个parsePackage函数,但它们的参数不同,我们来看以File为第一个参数的parsePackage方法:
public Package parsePackage(File sourceFile, String destCodePath,
DisplayMetrics metrics, int flags) {
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;
mArchiveSourcePath = sourceFile.getPath();
XmlResourceParser parser = null;
AssetManager assmgr = null;
Resources res = null;
boolean assetError = true;
try {
assmgr = new AssetManager();
int cookie = assmgr.addAssetPath(mArchiveSourcePath);
if (cookie != 0) {
res = new Resources(assmgr, metrics, null);
assmgr.setConfiguration(0, 0, null, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
Build.VERSION.RESOURCES_SDK_INT);
parser = assmgr.openXmlResourceParser(cookie, ANDROID_MANIFEST_FILENAME);
assetError = false;
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed adding asset path:"+mArchiveSourcePath);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to read AndroidManifest.xml of "
+ mArchiveSourcePath, e);
}
if (assetError) {
if (assmgr != null) assmgr.close();
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_BAD_MANIFEST;
return null;
}
String[] errorText = new String[1];
Package pkg = null;
Exception errorException = null;
try {
// XXXX todo: need to figure out correct configuration.
pkg = parsePackage(res, parser, flags, errorText);
} catch (Exception e) {
errorException = e;
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_UNEXPECTED_EXCEPTION;
}
parser.close();
assmgr.close();
pkg.mPath = destCodePath;
pkg.mScanPath = mArchiveSourcePath;
pkg.mSignatures = null;
return pkg;
}
首先从apk文件中打开AndroidManifest.xml文件,然后调用以Resources为第一个参数的parsePackage方法,这个函数比较长,主要就是解析AndroidManifest.xml文件,建立一个Package对象,大概类图如下。最后设置Package对象的mPath和mScanPath为当前APK所在的全路径名。
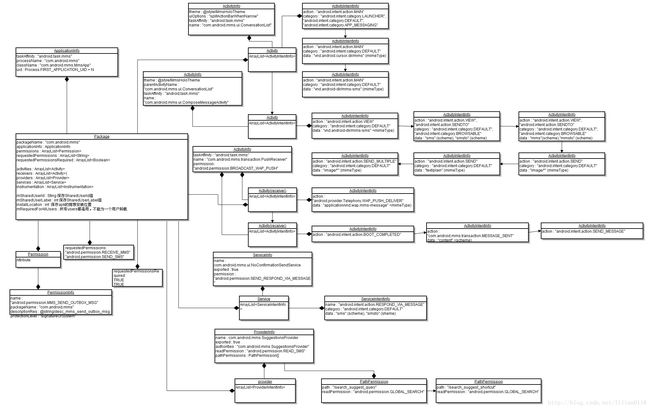
我们以Mms这个应用的Manifest文件来看分析解析后的结果,首先来看Mms的AndroidManifest.xml文件(这里只截取了一部分)
上面的AndroidManifest.xml文件中定义了2个Activity,2个receiver,1个service和1个provider,我们来看进过parsePackage得到的Package对象如下:
接着回到scanPackageLI方法,解析完AndroidManifest.xml文件后,再来检查是否是更新的APK,如果更新的APK版本比以前的版本还有低,则直接返回;如果更新的APK版本比以前的版本高,则去删除之前的APK以及resource文件。若不是更新APK,并且当前package是系统app,但之前安装了非系统的app,这里首先比较签名,如果签名不一致,则直接删除当前package;若签名文件一致,则首先比较当前package和之前的版本号,如果当前版本号比较新,则直接删除之前的APK以及resource文件。最后调用scanPackageLI方法让把当前package的信息归入到PMS中的数据结构:
private PackageParser.Package scanPackageLI(PackageParser.Package pkg,
int parseFlags, int scanMode, long currentTime, UserHandle user) {
File scanFile = new File(pkg.mScanPath);
mScanningPath = scanFile;
if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) != 0) {
pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM;
}
if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_PRIVILEGED) != 0) {
pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_PRIVILEGED;
}
if (mCustomResolverComponentName != null &&
mCustomResolverComponentName.getPackageName().equals(pkg.packageName)) {
setUpCustomResolverActivity(pkg);
}
if (pkg.packageName.equals("android")) {
synchronized (mPackages) {
if (mAndroidApplication != null) {
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_DUPLICATE_PACKAGE;
return null;
}
mPlatformPackage = pkg;
pkg.mVersionCode = mSdkVersion;
mAndroidApplication = pkg.applicationInfo;
if (!mResolverReplaced) {
mResolveActivity.applicationInfo = mAndroidApplication;
mResolveActivity.name = ResolverActivity.class.getName();
mResolveActivity.packageName = mAndroidApplication.packageName;
mResolveActivity.processName = "system:ui";
mResolveActivity.launchMode = ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_MULTIPLE;
mResolveActivity.flags = ActivityInfo.FLAG_EXCLUDE_FROM_RECENTS;
mResolveActivity.theme = com.android.internal.R.style.Theme_Holo_Dialog_Alert;
mResolveActivity.exported = true;
mResolveActivity.enabled = true;
mResolveInfo.activityInfo = mResolveActivity;
mResolveInfo.priority = 0;
mResolveInfo.preferredOrder = 0;
mResolveInfo.match = 0;
mResolveComponentName = new ComponentName(
mAndroidApplication.packageName, mResolveActivity.name);
}
}
}
File destCodeFile = new File(pkg.applicationInfo.sourceDir);
File destResourceFile = new File(pkg.applicationInfo.publicSourceDir);
SharedUserSetting suid = null;
PackageSetting pkgSetting = null;
if (!isSystemApp(pkg)) {
// Only system apps can use these features.
pkg.mOriginalPackages = null;
pkg.mRealPackage = null;
pkg.mAdoptPermissions = null;
}
// writer
synchronized (mPackages) {
if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR) == 0) {
if (!updateSharedLibrariesLPw(pkg, null)) {
return null;
}
}
if (pkg.mSharedUserId != null) {
suid = mSettings.getSharedUserLPw(pkg.mSharedUserId, 0, true);
if (suid == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Creating application package " + pkg.packageName
+ " for shared user failed");
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE;
return null;
}
if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) {
if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0)
Log.d(TAG, "Shared UserID " + pkg.mSharedUserId + " (uid=" + suid.userId
+ "): packages=" + suid.packages);
}
}
这里的mCustomResolverComponentName默认是空,采用framework是本身的ResolverActivity去解析intent。mAndroidApplication在Android系统中只有一个这样的application,就是framework-res.apk,它的packageName是"android"。然后在mResolveActivity和mResolveInfo保存ResolverActivity的信息,ResolverActivity用于在启动Activity的时候,如果有多个activity符合条件,弹出对话框给用户选择,这部分我们在以后分析AcitivityManagerService的时候再来分析。如果在Manifest中指定了ShareUserId,则首先获取一个关联的SharedUserSetting对象:
SharedUserSetting getSharedUserLPw(String name,
int pkgFlags, boolean create) {
SharedUserSetting s = mSharedUsers.get(name);
if (s == null) {
if (!create) {
return null;
}
s = new SharedUserSetting(name, pkgFlags);
s.userId = newUserIdLPw(s);
Log.i(PackageManagerService.TAG, "New shared user " + name + ": id=" + s.userId);
// < 0 means we couldn't assign a userid; fall out and return
// s, which is currently null
if (s.userId >= 0) {
mSharedUsers.put(name, s);
}
}
return s;
}在开始PMS的构造函数里面我们知道,系统会首先添加一系列的sysem的user id到mSharedUsers,所以如果能够从mSharedUsers获得到就直接返回;如果不能,则首先构造一个SharedUserSetting,并指派一个没有使用的APPLICATION UID,当然APPLICATION UID的值是在FIRST_APPLICATION_UID到LAST_APPLICATION_UID之间。最后把创建的SharedUserSetting添加到mSharedUsers和mUserIds数组当中。接着来看scanPackageLI函数:
PackageSetting origPackage = null;
String realName = null;
if (pkg.mOriginalPackages != null) {
//关于应用命名和更新的代码
}
pkgSetting = mSettings.getPackageLPw(pkg, origPackage, realName, suid, destCodeFile,
destResourceFile, pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir,
pkg.applicationInfo.flags, user, false);
if (pkgSetting == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Creating application package " + pkg.packageName + " failed");
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE;
return null;
}
if (pkgSetting.origPackage != null) {
pkg.setPackageName(origPackage.name);
String msg = "New package " + pkgSetting.realName
+ " renamed to replace old package " + pkgSetting.name;
reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg);
mTransferedPackages.add(origPackage.name);
pkgSetting.origPackage = null;
}
if (realName != null) {
mTransferedPackages.add(pkg.packageName);
}
if (mSettings.isDisabledSystemPackageLPr(pkg.packageName)) {
pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_UPDATED_SYSTEM_APP;
}
if (mFoundPolicyFile) {
SELinuxMMAC.assignSeinfoValue(pkg);
}
pkg.applicationInfo.uid = pkgSetting.appId;
pkg.mExtras = pkgSetting;
if (!verifySignaturesLP(pkgSetting, pkg)) {
if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR) == 0) {
return null;
}
pkgSetting.signatures.mSignatures = pkg.mSignatures;
if (pkgSetting.sharedUser != null) {
if (compareSignatures(pkgSetting.sharedUser.signatures.mSignatures,
pkg.mSignatures) != PackageManager.SIGNATURE_MATCH) {
Log.w(TAG, "Signature mismatch for shared user : " + pkgSetting.sharedUser);
mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_INCONSISTENT_CERTIFICATES;
return null;
}
}
String msg = "System package " + pkg.packageName
+ " signature changed; retaining data.";
reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg);
}关于应用程序改名和更新的代码我们这里先忽略,首先来看构造PackageSetting的方法:
PackageSetting getPackageLPw(PackageParser.Package pkg, PackageSetting origPackage,
String realName, SharedUserSetting sharedUser, File codePath, File resourcePath,
String nativeLibraryPathString, int pkgFlags, UserHandle user, boolean add) {
final String name = pkg.packageName;
PackageSetting p = getPackageLPw(name, origPackage, realName, sharedUser, codePath,
resourcePath, nativeLibraryPathString, pkg.mVersionCode, pkgFlags,
user, add, true /* allowInstall */);
return p;
}
private PackageSetting getPackageLPw(String name, PackageSetting origPackage,
String realName, SharedUserSetting sharedUser, File codePath, File resourcePath,
String nativeLibraryPathString, int vc, int pkgFlags,
UserHandle installUser, boolean add, boolean allowInstall) {
PackageSetting p = mPackages.get(name);
if (p != null) {
//更新apk相关
}
if (p == null) {
if (origPackage != null) {
//更新apk相关
} else {
p = new PackageSetting(name, realName, codePath, resourcePath,
nativeLibraryPathString, vc, pkgFlags);
p.setTimeStamp(codePath.lastModified());
p.sharedUser = sharedUser;
if ((pkgFlags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM) == 0) {
List users = getAllUsers();
if (users != null && allowInstall) {
//多用户的部分
}
}
}
if (sharedUser != null) {
p.appId = sharedUser.userId;
} else {
//更新系统apk相关
}
if (add) {
// Finish adding new package by adding it and updating shared
// user preferences
addPackageSettingLPw(p, name, sharedUser);
}
} else {
//多用户的部分
}
return p;
} 关于PackageSetting结构可以看文章最开始的类图。在新建一个PackageSetting对象后,首先将得到的系统的uid值赋给applicationInfo.uid ,这就是当前APK以后运行时的UID了。然后就做数字签名验证,这里主要是对于更新APK来做验证。在做完数字签名验证后,还需要检查当前APK是否提供providers与系统已有的providers冲突,如果冲突,则提示安装失败。接着来看scanPackageLI函数:
synchronized (mPackages) {
// We don't expect installation to fail beyond this point,
if ((scanMode&SCAN_MONITOR) != 0) {
mAppDirs.put(pkg.mPath, pkg);
}
// Add the new setting to mSettings
mSettings.insertPackageSettingLPw(pkgSetting, pkg);
// Add the new setting to mPackages
mPackages.put(pkg.applicationInfo.packageName, pkg);
// Make sure we don't accidentally delete its data.
final Iterator iter = mSettings.mPackagesToBeCleaned.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
PackageCleanItem item = iter.next();
if (pkgName.equals(item.packageName)) {
iter.remove();
}
}
// Take care of first install / last update times.
if (currentTime != 0) {
if (pkgSetting.firstInstallTime == 0) {
pkgSetting.firstInstallTime = pkgSetting.lastUpdateTime = currentTime;
} else if ((scanMode&SCAN_UPDATE_TIME) != 0) {
pkgSetting.lastUpdateTime = currentTime;
}
} else if (pkgSetting.firstInstallTime == 0) {
// We need *something*. Take time time stamp of the file.
pkgSetting.firstInstallTime = pkgSetting.lastUpdateTime = scanFileTime;
} else if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR) != 0) {
if (scanFileTime != pkgSetting.timeStamp) {
// A package on the system image has changed; consider this
// to be an update.
pkgSetting.lastUpdateTime = scanFileTime;
}
}
// Add the package's KeySets to the global KeySetManager
KeySetManager ksm = mSettings.mKeySetManager;
try {
ksm.addSigningKeySetToPackage(pkg.packageName, pkg.mSigningKeys);
if (pkg.mKeySetMapping != null) {
for (Map.Entry> entry : pkg.mKeySetMapping.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue() != null) {
ksm.addDefinedKeySetToPackage(pkg.packageName,
entry.getValue(), entry.getKey());
}
}
}
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Could not add KeySet to " + pkg.packageName, e);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Could not add KeySet to malformed package" + pkg.packageName, e);
} 首先调用Settings的insertPackageSettingLPw将pkgSetting对象加入到Settings中的mPackages这个HashMap中。在insertPackageSettingLPw方法中,首先将Package中的一些信息赋予给PackageSetting,然后调用addPackageSettingLPw方法将PackageSetting对象添加到mPackages中,并将PackageSetting加入到SharedUserSetting中的packages这个HashSet中。接着将pkg对象加入到PMS的mPackages这个HashMap中,保存在mPackages中信息会被后面很多地方使用到。最后对apk的安装或者更新时间做相应的更新。接着来看scanPackageLI函数:
int N = pkg.providers.size();
StringBuilder r = null;
int i;
for (i=0; i permissionMap =
p.tree ? mSettings.mPermissionTrees
: mSettings.mPermissions;
p.group = mPermissionGroups.get(p.info.group);
if (p.info.group == null || p.group != null) {
BasePermission bp = permissionMap.get(p.info.name);
if (bp == null) {
bp = new BasePermission(p.info.name, p.info.packageName,
BasePermission.TYPE_NORMAL);
permissionMap.put(p.info.name, bp);
}
if (bp.perm == null) {
if (bp.sourcePackage != null
&& !bp.sourcePackage.equals(p.info.packageName)) {
if (isSystemApp(p.owner)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "New decl " + p.owner + " of permission "
+ p.info.name + " is system");
bp.sourcePackage = null;
}
}
if (bp.sourcePackage == null
|| bp.sourcePackage.equals(p.info.packageName)) {
BasePermission tree = findPermissionTreeLP(p.info.name);
if (tree == null
|| tree.sourcePackage.equals(p.info.packageName)) {
bp.packageSetting = pkgSetting;
bp.perm = p;
bp.uid = pkg.applicationInfo.uid;
if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) {
if (r == null) {
r = new StringBuilder(256);
} else {
r.append(' ');
}
r.append(p.info.name);
}
} else {
}
} else {
}
} else if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) {
if (r == null) {
r = new StringBuilder(256);
} else {
r.append(' ');
}
r.append("DUP:");
r.append(p.info.name);
}
if (bp.perm == p) {
bp.protectionLevel = p.info.protectionLevel;
}
} else {
}
}
if (r != null) {
if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) Log.d(TAG, " Permissions: " + r);
}
N = pkg.instrumentation.size();
r = null;
for (i=0; i
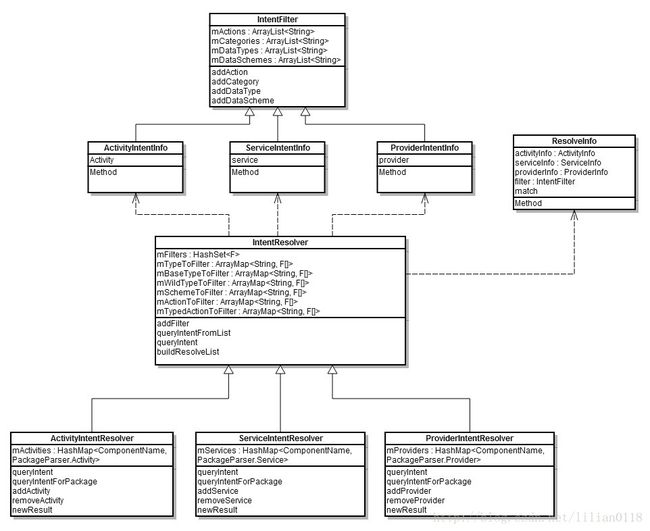
上面的代码比较长,但功能却比较简单,就是将前面从AndroidManifest里面Parse出来的providers、services、receivers、activities、permissionGroups、permissions和instrumentation添加到PMS的相应数据结构中。providers保存在ProviderIntentResolver对象中;services保存在ServiceIntentResolver对象中;receivers和activities保存在ActivityIntentResolver中;permissionGroups、permissions和permissions保存在HashMap中。ProviderIntentResolver、ServiceIntentResolver和ActivityIntentResolver都是继承于IntentResolver,它们的类图关系如下:
到这里,我们就把scanDirLI介绍完了,依次扫描完/system/framework、/system/priv-app、/system/app、/vendor/app这四个目录下面所有的APK文件,并解析成一个个Package对象,并把他们加入到PMS和Settings中的一些数据结构中。接着回到PMS的构造函数来分析:
final List possiblyDeletedUpdatedSystemApps = new ArrayList();
if (!mOnlyCore) {
Iterator psit = mSettings.mPackages.values().iterator();
while (psit.hasNext()) {
PackageSetting ps = psit.next();
if ((ps.pkgFlags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM) == 0) {
continue;
}
final PackageParser.Package scannedPkg = mPackages.get(ps.name);
if (scannedPkg != null) {
if (mSettings.isDisabledSystemPackageLPr(ps.name)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Expecting better updatd system app for " + ps.name
+ "; removing system app");
removePackageLI(ps, true);
}
continue;
}
if (!mSettings.isDisabledSystemPackageLPr(ps.name)) {
psit.remove();
String msg = "System package " + ps.name
+ " no longer exists; wiping its data";
reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg);
removeDataDirsLI(ps.name);
} else {
final PackageSetting disabledPs = mSettings.getDisabledSystemPkgLPr(ps.name);
if (disabledPs.codePath == null || !disabledPs.codePath.exists()) {
possiblyDeletedUpdatedSystemApps.add(ps.name);
}
}
}
} 上面的代码主要是处理在mSettings中保存了的System app,但在在刚刚的scanDirLI并没有找到对应的APK,这里分三种情况:一是在mSettings中有保存,刚刚的scanDirLI也有找到,这里判断它是否被disable的APK,如果是,说明这个apk是通过OTA升级后更新了的,所以清除相应的数据结构;二是在mSettings中有保存,但刚刚的scanDirLI没有找到对应的APK,并且不是被disable的APK就直接删除相应的数据结构;三是在mSettings中有保存,但刚刚的scanDirLI没有找到对应的APK,并且是被disable的APK,就通过查看它的codePath是否存在来判断它是否有可能被更新或者删除,并添加到possiblyDeletedUpdatedSystemApps链表里。接着来看PMS的构造函数:
ArrayList deletePkgsList = mSettings.getListOfIncompleteInstallPackagesLPr();
for(int i = 0; i < deletePkgsList.size(); i++) {
//clean up here
cleanupInstallFailedPackage(deletePkgsList.get(i));
}
deleteTempPackageFiles();
mSettings.pruneSharedUsersLPw();
if (!mOnlyCore) {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_PMS_DATA_SCAN_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
mAppInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver(
mAppInstallDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, false, false);
mAppInstallObserver.startWatching();
scanDirLI(mAppInstallDir, 0, scanMode, 0);
mDrmAppInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver(
mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, false, false);
mDrmAppInstallObserver.startWatching();
scanDirLI(mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir, PackageParser.PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK,
scanMode, 0);
for (String deletedAppName : possiblyDeletedUpdatedSystemApps) {
PackageParser.Package deletedPkg = mPackages.get(deletedAppName);
mSettings.removeDisabledSystemPackageLPw(deletedAppName);
String msg;
if (deletedPkg == null) {
msg = "Updated system package " + deletedAppName
+ " no longer exists; wiping its data";
removeDataDirsLI(deletedAppName);
} else {
msg = "Updated system app + " + deletedAppName
+ " no longer present; removing system privileges for "
+ deletedAppName;
deletedPkg.applicationInfo.flags &= ~ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM;
PackageSetting deletedPs = mSettings.mPackages.get(deletedAppName);
deletedPs.pkgFlags &= ~ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM;
}
reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg);
}
} else {
mAppInstallObserver = null;
mDrmAppInstallObserver = null;
} 首先去删除安装不完整的APK文件及其数据,然后清除安装的temp文件,并清除在mSharedUsers没有被使用的ShareUserSettins。接着去扫描/data/app和/data/app-private两个目录中的所有APK文件,并建立对应的FileObserver。最后处理通过OTA更新或者删除的APK文件。来看PMS构造函数的最后一部分:
updateAllSharedLibrariesLPw();
final boolean regrantPermissions = mSettings.mInternalSdkPlatform
!= mSdkVersion;
if (regrantPermissions) Slog.i(TAG, "Platform changed from "
+ mSettings.mInternalSdkPlatform + " to " + mSdkVersion
+ "; regranting permissions for internal storage");
mSettings.mInternalSdkPlatform = mSdkVersion;
updatePermissionsLPw(null, null, UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL
| (regrantPermissions
? (UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_REPLACE_PKG|UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_REPLACE_ALL)
: 0));
if (!mRestoredSettings && !onlyCore) {
mSettings.readDefaultPreferredAppsLPw(this, 0);
}
mSettings.writeLPr();
Runtime.getRuntime().gc();
} // synchronized (mPackages)
} // synchronized (mInstallLock)
}这一部分的代码量虽然很少,却做了比较多的事情,首先调用updateAllSharedLibrariesLPw为所有需要使用ShareLibrary的package找到对应的ShareLibrary路径,并把这些路径保存在package的usesLibraryFiles数组中。接着调用updatePermissionsLPw为需要使用权限的APK分配对应的权限:
private void updatePermissionsLPw(String changingPkg,
PackageParser.Package pkgInfo, int flags) {
Iterator it = mSettings.mPermissionTrees.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
final BasePermission bp = it.next();
if (bp.packageSetting == null) {
bp.packageSetting = mSettings.mPackages.get(bp.sourcePackage);
}
}
it = mSettings.mPermissions.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
final BasePermission bp = it.next();
if (bp.type == BasePermission.TYPE_DYNAMIC) {
if (bp.packageSetting == null && bp.pendingInfo != null) {
final BasePermission tree = findPermissionTreeLP(bp.name);
if (tree != null && tree.perm != null) {
bp.packageSetting = tree.packageSetting;
bp.perm = new PackageParser.Permission(tree.perm.owner,
new PermissionInfo(bp.pendingInfo));
bp.perm.info.packageName = tree.perm.info.packageName;
bp.perm.info.name = bp.name;
bp.uid = tree.uid;
}
}
}
if (bp.packageSetting == null) {
bp.packageSetting = mSettings.mPackages.get(bp.sourcePackage);
}
if (bp.packageSetting == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Removing dangling permission: " + bp.name
+ " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);
it.remove();
} else if (changingPkg != null && changingPkg.equals(bp.sourcePackage)) {
if (pkgInfo == null || !hasPermission(pkgInfo, bp.name)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Removing old permission: " + bp.name
+ " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);
flags |= UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL;
it.remove();
}
}
}
if ((flags&UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL) != 0) {
for (PackageParser.Package pkg : mPackages.values()) {
if (pkg != pkgInfo) {
grantPermissionsLPw(pkg, (flags&UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_REPLACE_ALL) != 0);
}
}
}
} updatePermissionsLPw中首先对mPermissionTrees和mPermissions两个Map中的permission的一些信息进行赋值,然后调用grantPermissionsLPw为每个package分配权限,Android分配权限其实就是分配对应的gid号。在grantPermissionsLPw有一系列的判断条件,如果请求分配的权限被允许,就会将对应的gid号码加入到GrantedPermissions的gids数组当中。回到PMS的构造函数函数,最后调用readDefaultPreferredAppsLPw去设置对于处理Intent默认的Activity信息,关于这部分,我们在ActivityMangerService中再来介绍。在PMS构造函数的最后调用mSettings.writeLPr将所有的package、permission、ShareUserID等信息全部写到/data/system/packages.xml中。到这里PMS的构造函数就介绍完了。