- 具身智能的视觉-语言导航综述
24年2月来自曲阜师范、华东师大和哈工大的论文“Vision-LanguageNavigationwithEmbodiedIntelligence:ASurvey”。作为人工智能领域的长期愿景,具身智能的核心目标是提升智体与环境的感知、理解和交互能力。视觉-语言导航(VLN)作为实现具身智能的重要研究路径,致力于探索智体如何利用自然语言与人进行有效沟通,接收并理解指令,并最终依靠视觉信息实现精准导
- 20181207
旅一30王思宁
1.在文章中我学到的重要概念:讲故事不要平铺直叙2.这篇中我学到的怦然心动词汇:facialrecognition刷脸smogfog雾霾3.本篇文章中我最喜欢的句子:Forgetthememories,continuetobelife,miss,justpassby.4.本周学习中我遇到的困难:东西太多,不知道从哪开始复习5.语伴给我的建议:好好复习吧,别挂科6.我的一些其他感受和收获:游戏的坑真
- python折半查找算法_python二分查找代码 试用递归法编写python程序实现折半查找算法...
python二分查找算法函数bi_search(),该函数实现检回忆,很美却很伤;回忆只是回不到过去的记忆。输入格式:第一行为正整数n接下来若干行为待查找的数字,每行输入一个总是女人为了天长地久而烦恼,男人却可以洒脱地出乎意料。defprime(n):ifnend:return-1mid=(start+end)//2ifprimelist[mid]==prime:returnmidelifprim
- 2022暑假总结
yanpinghappy
这个假期,娃都是按照每天的学习计划做事(10天日照旅游期间除外),大概是因为之前两三个寒暑假都是如此规律,所以娃也适应了这种按部就班的节奏。学习时间表,几乎都是我俩商量的结果,中间遇到时间紧张或者无法执行的情况,我们会再做调整。美中不足的是,复盘这一项我俩做得极少,这一点下次寒假时一定要加强起来。暑假第一个月,报了两个课程奥数和《水浒传》,时间排得满满的,把头一年报的游泳课挤出去了,到了第二个月才
- 小萝莉与猴神大叔
王刚画框
巴国”天使萝莉在“印国”境地与妈妈走失,巧遇“印国”憨厚大叔猴神,并由大叔一路艰辛护送回到自己的国家与家人团聚。在两国特殊的宗教、政治等大环境因素下,亲遇了社会的百态和人情的温暖。是她人生某个时间段最深刻的经历,应该是一辈子的记忆。她乖巧可爱,却不能发声,差点走失,却又在众人帮助下回到母亲的怀抱,他性格刚直,宗教信仰情怀浓厚,最后差点客死他乡。开始相遇,一个眼神的交汇后使两人的生活和命运开始了转折
- 不悲不怒 ,唯有自身心态放好
金椰子
一个人的心态真的很重要,不管遇到什么事都要以好的心态对待。每个人都缺点不可能十全十美,能做到是极少数。身边多少有单亲家庭的小孩,有些又能好好读书,而有些就想学坏主要是心态没放好、好坏不分,所以思想上出现分歧。在于写作上有每个人的想法,遇上就是对的能做到财富上收入、知识上的进步、认识好多知心朋友,写作能力更加有意义,能够深入投入写作。看一篇文章,内容丰富、真实、有带动性,写于她关于写作方面有很大的收
- Android UI 组件系列(五):CheckBox、RadioButton 与 Switch 控件详解
博客专栏:Android初级入门UI组件与布局源码:通过网盘分享的文件:Android入门布局及UI相关案例链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1EOuDUKJndMISolieFSvXXg?pwd=4k9n提取码:4k9n引言在Android开发中,用户与应用的交互往往离不开各种“选择”操作,例如:注册表单中选择兴趣爱好(可多选)设置界面中切换通知、Wi-Fi开关(开/关状态)
- 《一禅小和尚》经典语录
梦想写作者
(13)害怕孤独,却又不敢去轻易接近谁,渴望被爱,却又习惯了一个人,懒得去费尽心思讨好谁,从陌生到熟悉,最后回到陌生,如此小心翼翼,是因为知道,人生最大的遗憾不是错过最好的人,而是当你遇见更好的人时,却已经把最好的自己用完了!(14)太想要一样东西,是失去的开始,得不到会朝思暮想,得到了又害怕失去,一把沙抓得越紧,流失的越快,一个人抱的越紧,跑的越快,当你张开双臂,两手空空,你怀里拥抱的是整个世界
- 每周复盘——第十七周
马幸运
本周计划完成情况:本周除了补齐打卡,还有剩下收尾,别的都完了。而且弹琴有进步,还被老师夸奖了,很开心,以后继续保持。下周计划:1.练琴一个小时以上。2.准时完成日更。3.继续坚持跑步,一周一次起。4.给家人至少打一次电话。5.把之前的为了打卡的文章补齐。收获:通过和小伙伴交流,发现了自己在沟通表达上可以提高的地方,发现她好会和男朋友相处沟通交流呀,有学到很多。本周又是磕到糖的一周。其实,挺好的,可
- 多情的木匠
水星1975
一个木匠。身强体壮,体格健康。他喜欢村里大户人家的一个小姐。在他眼里,她的一举一动都是美的。这位小姐,美貌如花,娇生惯养。木匠到大户人家做活。每天可以看到小姐,他喜滋滋的。小姐聪明过人,早就发现木匠对她有意。活做完了,木匠要走了。小姐有些不舍,眼睛看着他,希望他能说点什么。木匠乌黑的大眼睛,读懂了小姐的心。他什么也没有说,只是走的时候背影稍微停留了一下。后来木匠经常从地道里,进入小姐的闺房,和她缠
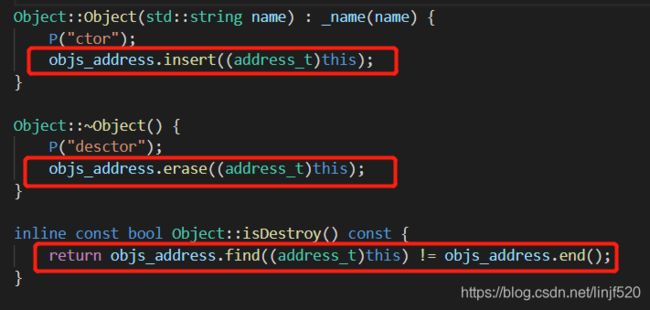
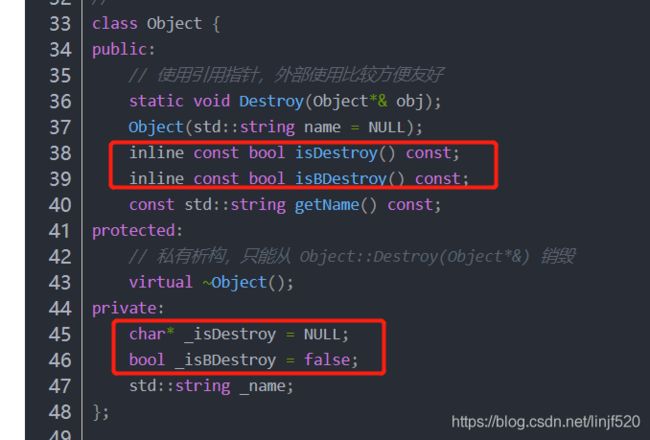
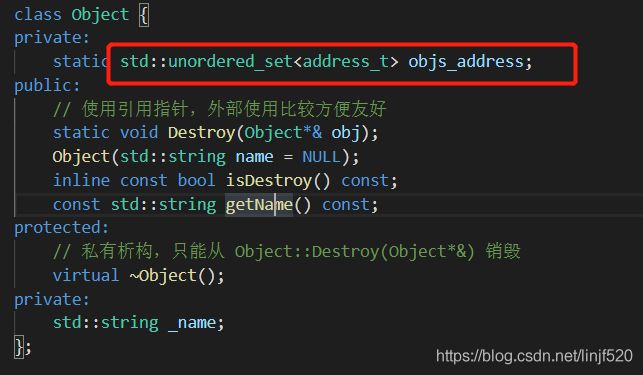
- HashMap和ConcurrentHashMap源码精讲
HashMap类结构图HashMap源码讲解//HashMap默认初始容量是2的4次方,也就是16;staticfinalintDEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY=1implementsMap.Entry{finalinthash;finalKkey;Vvalue;Nodenext;Node(inthash,Kkey,Vvalue,Nodenext){this.hash=hash;t
- BootstrapValidator表单验证效果无效,不验证
蓝色天空的银码星
技术问题表单验证网页前端
BootstrapValidator是一款非常好用的前端验证插件,但是因为很多问题,一直没有效果。果然不是代码问题,而是因为Bootstrap版本和BootstrapValidator的版本问题。下载地址:https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_37674052/11175279首先贴出来我的引用的文件代码表单代码:要用BootstrapValidato
- docker镜像加速器配置daemon.json不生效
蓝色天空的银码星
docker容器linux
现象安装docker26.1.4,启动服务拉取镜像发现超时,走的是官方镜像仓库地址,配置本地加速后/etc/docker/daemon.json,重启仍然走的官方地址加速器地址:https://docker.imgdb.de/dockerinfo|grep'RegistryMirrors'展示的是:io.docker,非我们配置的地址再继续测试:1、不通过系统服务systemctl启动docker
- 具身智能:从理论到实践的跨越
具身智能(EmbodiedAI)的概念起源与发展是一个跨越半个多世纪的学术探索历程,其核心思想在不同学科的交叉碰撞中逐渐成型。以下从理论源头、技术奠基、术语演进三个维度展开解析,揭示这一概念的学术脉络与产业价值:一、理论源头:从图灵的哲学构想到认知科学的具身化转向1.图灵的"感官机器"设想(1950年)在人工智能奠基性论文《计算机器与智能》中,图灵提出了两种智能发展路径:抽象计算路径:如国际象棋等
- 聊聊artemis的SlowConsumerReaperRunnable
go4it
序本文主要研究一下artemis的SlowConsumerReaperRunnableSlowConsumerPolicyactivemq-artemis-2.11.0/artemis-server/src/main/java/org/apache/activemq/artemis/core/settings/impl/SlowConsumerPolicy.javapublicenumSlowCo
- PyCharm高效入门指南:从零开始掌握Python开发利器
软考和人工智能学堂
Python开发经验强化学习PyCharm
引言PyCharm是JetBrains公司推出的一款强大的Python集成开发环境(IDE),被全球数百万Python开发者所青睐。无论你是Python初学者还是经验丰富的开发者,掌握PyCharm都能显著提升你的开发效率。本文将带你从零开始,全面了解PyCharm的核心功能和使用技巧。1.PyCharm的安装与配置1.1下载与安装首先访问JetBrains官网下载PyCharm。PyCharm有
- RK3588 编译 Android 13 镜像方法
YOYO--小天
RK35XX学习androidlinux
下载AndroidSDK源代码#下载完成后,在解压前先校验下MD5码:$md5sum-candroid*.txtandroid*_rk35xx_*_sdk.tar.gzaa:OKandroid*_rk35xx_*_sdk.tar.gzab:OKandroid*_rk35xx_*_sdk.tar.gzac:OKandroid*_rk35xx_*_sdk.tar.gzad:OKandroid*_rk3
- java开发安卓和kotlin对比
哈哈皮皮虾的皮
javaandroidkotlin
Java和Kotlin都是用于Android开发的编程语言,它们各自具有独特的特点和优势。以下是对Java和Kotlin在Android开发中的对比:一、语法与简洁性Java:Java的语法相对繁琐,需要编写较多的样板代码。例如,在Java中,每一行代码的末尾都需要一个分号来表示语句的结束。Kotlin:Kotlin的语法更为简洁,支持更多的语法糖,可以减少冗余的代码。在Kotlin中,换行符通常
- 今天是个好日子
走到底的花姑娘
大学闺蜜下午四点多发信息说她的儿砸提早来报道了。中午快十二点时本想发信息问她最近怎么样了,又考虑到这时间点她可能在吃饭,等下午迟点再联系她。因为她跟我当时怀孕一样有妊娠糖尿病,想了解一下她最近控糖效果如何。结果,我还没来得及问,她就直接告诉我生了,提早了一个月。好在小孩各项指标都比较正常,体重4.3斤,毕竟是早产儿为了保险起见得在保温箱中观察几天。真庆幸母子健康,真替她开心。他们夫妻俩年纪相对也比
- 漫漫追妻路上的第一百二十五封情书
光之予
桃花开了吗没春天尚在路上打包不易不要拆穿了谎言那么贵的运费南极到北极错写了一个字不适合邮寄梦在裂缝里挤游戏开始
- 忙碌的一天
b36731d3d324
2019年11月23日星期日晴今天一上班就来了一个老顾客,磨一份养生粉190元,给这位大哥点赞!很懂的养生、舍得投资自己!跟这位大哥聊天、他说自己以前身体不好,经常感冒,从吃这个五谷磨粉后身休真的好多了,皮肤也好了,比吃补药好的多,还涚很多人都说他不像五十多岁的人。今天他来超市还穿短裤,我们都穿长袖了!,你们看这大哥多精神!万事开头难,万事开头难,今天开了个好头.这位大哥来开了一个头?从上班干活一
- 78岁老人有儿有女却住养老院,为让邻居来看她,每月给2000元
左颜时光
米亚契斯说:一个人,如果使自己的母亲伤心,无论他的地位多么显赫,无论他多么有名,他都是一个卑劣的人。老家有个李老太,78岁的年纪,当我们都以为她被儿女接去城里安享晚年时,一次巧合,在路过一家养老院门口时母亲认出她,于是陪着母亲下车,李老太看到母亲那一刻眼泪止不住地流,颤抖的双手紧紧握着母亲,激动地说“大妹子啊,我的大妹子,没想到还能见到你啊,没想到啊”。母亲和李老太坐在养老院门口的桥边,两位老人像
- 恋爱八年,我逃婚了(江苒顾现许曼)免费小说全集_阅读免费小说恋爱八年,我逃婚了江苒顾现许曼
喵喵美文
《恋爱八年,我逃婚了》主角:江苒顾现许曼简介:我和顾现恋爱八年。在婚期前三天,却发现他电脑里存了上万张同一个女生的照片。我偷偷订下婚礼当天出国的机票。静静看着他若无其事地表演。婚礼当天新娘逃婚,他却疯了。路上顾现的手机几次震动,都是许曼发来消息问他有没有安全到家。我解锁了屏幕,本来想礼貌性地回一句。却看见他和朋友的聊天记录。【假结婚是我最后的机会,如果她还是不回来,我就真的要放弃了。】【你在班级群
- Android Jetpack Compose + MVI 开发流程深度分析
你过来啊你
androidcomposemvi
MVI架构核心原理MVI(Model-View-Intent)是一种基于单向数据流的架构模式,其核心组件关系如下:[View]--Intents-->[ViewModel]--States-->[View]||用户交互事件处理业务逻辑||[View]=emptyList(),valisLoading:Boolean=false,valerror:String?=null,valnewTodoTit
- 【Android】UI布局工具及详解
米莱虾
#Androiduiandroid
ViewGroup1.简介ViewGroup是一种View,他是View容器,也就是里边可以包含其他View.分类:(1)layout布局类的ViewGroup(2)ScrollView带滚动条的ViewGroup(3)高级View容器(适配器View)(4)其他ViewGroup2.布局类的ViewGroup布局类的容器主要是用来控制子元素的排布方式和排列位置分类:(1)线性布局(2)相对布局(
- Android Room使用方法与底层原理详解
你过来啊你
androidroom
Room是一个强大的SQLite对象映射库,旨在提供更健壮、更简洁、更符合现代开发模式的数据库访问方式。核心价值:消除大量样板代码,提供编译时SQL验证,强制结构化数据访问,并流畅集成LiveData、Flow和RxJava以实现响应式UI。一、使用流程(Step-by-StepWorkflow)Room的使用遵循一个清晰的结构化流程:添加依赖://build.gradle(Module)depe
- Java中HashMap的实现原理详解
HashMap是Java集合框架中的核心类,基于哈希表实现键值对(Key-Value)存储,提供O(1)时间复杂度的快速查找。以下从数据结构、哈希机制、冲突解决、扩容策略等角度详细解析其实现原理(基于Java8)。一、核心数据结构:数组+链表+红黑树transientNode[]table;//哈希桶数组staticclassNode{//链表节点finalinthash;finalKkey;Vv
- 秒火|得大妈者得天下,这个APP是如何通广场舞闷声发大财的?
秒火炎焱燚
知乎上有一个问题非常火:互联网行业有哪些闷声发大财的公司。结果排名第一的公司竟然是一个广场舞视频教学APP——糖豆。可能你的手机上并没有它的身影,但是妈妈们的手机上似乎都安装了它。而且如今的糖豆已经完成了c轮融资,直至今日已经获得包括腾讯在内的1亿美金的支持,这时候人们才发现原来糖豆网真的在闷声发大财。一个广场舞视频教学软件,究竟是如何快速如今大妈市场?今天我们就来聊聊糖豆网是如何做到得大妈者得天
- 2023-05-09
论文小天才
2023年社会科学、人文艺术与文化国际会议(SSHAC2023)大会简介2023年社会科学、人文、艺术和文化国际会议(SSHAC2023)将在四川省成都市举行。会议旨在为从事“社会科学”和“人文艺术”研究的专家学者提供一个平台,分享科研成果和前沿技术,了解学术发展趋势,拓宽研究思路,加强学术研究和讨论,促进学术成果产业化合作。大会邀请了来自国内外高校和研究机构的专家、学者、企业家等相关人员。热忱欢
- 三观,三观,到底什么是三观
星星的彼岸
无论是在网上还是在和同学交流,当对于一个问题的答案有争论的时候,总会听到一句话:“我们三观不合,所以,答案不同”,这句话听多了也就习以为常了,但是“三观”这个词真的知道是什么意思吗?三观究竟是一个什么东西?这个问题我们并没有去探讨过。在高中的时候,我们会听老师说:“三观,三观,就是人生观,价值观,世界观的统称”,然而,什么是人生观,什么是价值观和世界观,都不知道,于是今天就和我爸在交流这个问题。世
- 项目中 枚举与注解的结合使用
飞翔的马甲
javaenumannotation
前言:版本兼容,一直是迭代开发头疼的事,最近新版本加上了支持新题型,如果新创建一份问卷包含了新题型,那旧版本客户端就不支持,如果新创建的问卷不包含新题型,那么新旧客户端都支持。这里面我们通过给问卷类型枚举增加自定义注解的方式完成。顺便巩固下枚举与注解。
一、枚举
1.在创建枚举类的时候,该类已继承java.lang.Enum类,所以自定义枚举类无法继承别的类,但可以实现接口。
- 【Scala十七】Scala核心十一:下划线_的用法
bit1129
scala
下划线_在Scala中广泛应用,_的基本含义是作为占位符使用。_在使用时是出问题非常多的地方,本文将不断完善_的使用场景以及所表达的含义
1. 在高阶函数中使用
scala> val list = List(-3,8,7,9)
list: List[Int] = List(-3, 8, 7, 9)
scala> list.filter(_ > 7)
r
- web缓存基础:术语、http报头和缓存策略
dalan_123
Web
对于很多人来说,去访问某一个站点,若是该站点能够提供智能化的内容缓存来提高用户体验,那么最终该站点的访问者将络绎不绝。缓存或者对之前的请求临时存储,是http协议实现中最核心的内容分发策略之一。分发路径中的组件均可以缓存内容来加速后续的请求,这是受控于对该内容所声明的缓存策略。接下来将讨web内容缓存策略的基本概念,具体包括如如何选择缓存策略以保证互联网范围内的缓存能够正确处理的您的内容,并谈论下
- crontab 问题
周凡杨
linuxcrontabunix
一: 0481-079 Reached a symbol that is not expected.
背景:
*/5 * * * * /usr/IBMIHS/rsync.sh
- 让tomcat支持2级域名共享session
g21121
session
tomcat默认情况下是不支持2级域名共享session的,所有有些情况下登陆后从主域名跳转到子域名会发生链接session不相同的情况,但是只需修改几处配置就可以了。
打开tomcat下conf下context.xml文件
找到Context标签,修改为如下内容
如果你的域名是www.test.com
<Context sessionCookiePath="/path&q
- web报表工具FineReport常用函数的用法总结(数学和三角函数)
老A不折腾
Webfinereport总结
ABS
ABS(number):返回指定数字的绝对值。绝对值是指没有正负符号的数值。
Number:需要求出绝对值的任意实数。
示例:
ABS(-1.5)等于1.5。
ABS(0)等于0。
ABS(2.5)等于2.5。
ACOS
ACOS(number):返回指定数值的反余弦值。反余弦值为一个角度,返回角度以弧度形式表示。
Number:需要返回角
- linux 启动java进程 sh文件
墙头上一根草
linuxshelljar
#!/bin/bash
#初始化服务器的进程PId变量
user_pid=0;
robot_pid=0;
loadlort_pid=0;
gateway_pid=0;
#########
#检查相关服务器是否启动成功
#说明:
#使用JDK自带的JPS命令及grep命令组合,准确查找pid
#jps 加 l 参数,表示显示java的完整包路径
#使用awk,分割出pid
- 我的spring学习笔记5-如何使用ApplicationContext替换BeanFactory
aijuans
Spring 3 系列
如何使用ApplicationContext替换BeanFactory?
package onlyfun.caterpillar.device;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import
- Linux 内存使用方法详细解析
annan211
linux内存Linux内存解析
来源 http://blog.jobbole.com/45748/
我是一名程序员,那么我在这里以一个程序员的角度来讲解Linux内存的使用。
一提到内存管理,我们头脑中闪出的两个概念,就是虚拟内存,与物理内存。这两个概念主要来自于linux内核的支持。
Linux在内存管理上份为两级,一级是线性区,类似于00c73000-00c88000,对应于虚拟内存,它实际上不占用
- 数据库的单表查询常用命令及使用方法(-)
百合不是茶
oracle函数单表查询
创建数据库;
--建表
create table bloguser(username varchar2(20),userage number(10),usersex char(2));
创建bloguser表,里面有三个字段
&nbs
- 多线程基础知识
bijian1013
java多线程threadjava多线程
一.进程和线程
进程就是一个在内存中独立运行的程序,有自己的地址空间。如正在运行的写字板程序就是一个进程。
“多任务”:指操作系统能同时运行多个进程(程序)。如WINDOWS系统可以同时运行写字板程序、画图程序、WORD、Eclipse等。
线程:是进程内部单一的一个顺序控制流。
线程和进程
a. 每个进程都有独立的
- fastjson简单使用实例
bijian1013
fastjson
一.简介
阿里巴巴fastjson是一个Java语言编写的高性能功能完善的JSON库。它采用一种“假定有序快速匹配”的算法,把JSON Parse的性能提升到极致,是目前Java语言中最快的JSON库;包括“序列化”和“反序列化”两部分,它具备如下特征:
- 【RPC框架Burlap】Spring集成Burlap
bit1129
spring
Burlap和Hessian同属于codehaus的RPC调用框架,但是Burlap已经几年不更新,所以Spring在4.0里已经将Burlap的支持置为Deprecated,所以在选择RPC框架时,不应该考虑Burlap了。
这篇文章还是记录下Burlap的用法吧,主要是复制粘贴了Hessian与Spring集成一文,【RPC框架Hessian四】Hessian与Spring集成
- 【Mahout一】基于Mahout 命令参数含义
bit1129
Mahout
1. mahout seqdirectory
$ mahout seqdirectory
--input (-i) input Path to job input directory(原始文本文件).
--output (-o) output The directory pathna
- linux使用flock文件锁解决脚本重复执行问题
ronin47
linux lock 重复执行
linux的crontab命令,可以定时执行操作,最小周期是每分钟执行一次。关于crontab实现每秒执行可参考我之前的文章《linux crontab 实现每秒执行》现在有个问题,如果设定了任务每分钟执行一次,但有可能一分钟内任务并没有执行完成,这时系统会再执行任务。导致两个相同的任务在执行。
例如:
<?
//
test
.php
- java-74-数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过了数组长度的一半,找出这个数字
bylijinnan
java
public class OcuppyMoreThanHalf {
/**
* Q74 数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过了数组长度的一半,找出这个数字
* two solutions:
* 1.O(n)
* see <beauty of coding>--每次删除两个不同的数字,不改变数组的特性
* 2.O(nlogn)
* 排序。中间
- linux 系统相关命令
candiio
linux
系统参数
cat /proc/cpuinfo cpu相关参数
cat /proc/meminfo 内存相关参数
cat /proc/loadavg 负载情况
性能参数
1)top
M:按内存使用排序
P:按CPU占用排序
1:显示各CPU的使用情况
k:kill进程
o:更多排序规则
回车:刷新数据
2)ulimit
ulimit -a:显示本用户的系统限制参
- [经营与资产]保持独立性和稳定性对于软件开发的重要意义
comsci
软件开发
一个软件的架构从诞生到成熟,中间要经过很多次的修正和改造
如果在这个过程中,外界的其它行业的资本不断的介入这种软件架构的升级过程中
那么软件开发者原有的设计思想和开发路线
- 在CentOS5.5上编译OpenJDK6
Cwind
linuxOpenJDK
几番周折终于在自己的CentOS5.5上编译成功了OpenJDK6,将编译过程和遇到的问题作一简要记录,备查。
0. OpenJDK介绍
OpenJDK是Sun(现Oracle)公司发布的基于GPL许可的Java平台的实现。其优点:
1、它的核心代码与同时期Sun(-> Oracle)的产品版基本上是一样的,血统纯正,不用担心性能问题,也基本上没什么兼容性问题;(代码上最主要的差异是
- java乱码问题
dashuaifu
java乱码问题js中文乱码
swfupload上传文件参数值为中文传递到后台接收中文乱码 在js中用setPostParams({"tag" : encodeURI( document.getElementByIdx_x("filetag").value,"utf-8")});
然后在servlet中String t
- cygwin很多命令显示command not found的解决办法
dcj3sjt126com
cygwin
cygwin很多命令显示command not found的解决办法
修改cygwin.BAT文件如下
@echo off
D:
set CYGWIN=tty notitle glob
set PATH=%PATH%;d:\cygwin\bin;d:\cygwin\sbin;d:\cygwin\usr\bin;d:\cygwin\usr\sbin;d:\cygwin\us
- [介绍]从 Yii 1.1 升级
dcj3sjt126com
PHPyii2
2.0 版框架是完全重写的,在 1.1 和 2.0 两个版本之间存在相当多差异。因此从 1.1 版升级并不像小版本间的跨越那么简单,通过本指南你将会了解两个版本间主要的不同之处。
如果你之前没有用过 Yii 1.1,可以跳过本章,直接从"入门篇"开始读起。
请注意,Yii 2.0 引入了很多本章并没有涉及到的新功能。强烈建议你通读整部权威指南来了解所有新特性。这样有可能会发
- Linux SSH免登录配置总结
eksliang
ssh-keygenLinux SSH免登录认证Linux SSH互信
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2187265 一、原理
我们使用ssh-keygen在ServerA上生成私钥跟公钥,将生成的公钥拷贝到远程机器ServerB上后,就可以使用ssh命令无需密码登录到另外一台机器ServerB上。
生成公钥与私钥有两种加密方式,第一种是
- 手势滑动销毁Activity
gundumw100
android
老是效仿ios,做android的真悲催!
有需求:需要手势滑动销毁一个Activity
怎么办尼?自己写?
不用~,网上先问一下百度。
结果:
http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming/article/details/20934541
首先将你需要的Activity继承SwipeBackActivity,它会在你的布局根目录新增一层SwipeBackLay
- JavaScript变换表格边框颜色
ini
JavaScripthtmlWebhtml5css
效果查看:http://hovertree.com/texiao/js/2.htm代码如下,保存到HTML文件也可以查看效果:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>表格边框变换颜色代码-何问起</title>
</head>
<body&
- Kafka Rest : Confluent
kane_xie
kafkaRESTconfluent
最近拿到一个kafka rest的需求,但kafka暂时还没有提供rest api(应该是有在开发中,毕竟rest这么火),上网搜了一下,找到一个Confluent Platform,本文简单介绍一下安装。
这里插一句,给大家推荐一个九尾搜索,原名叫谷粉SOSO,不想fanqiang谷歌的可以用这个。以前在外企用谷歌用习惯了,出来之后用度娘搜技术问题,那匹配度简直感人。
环境声明:Ubu
- Calender不是单例
men4661273
单例Calender
在我们使用Calender的时候,使用过Calendar.getInstance()来获取一个日期类的对象,这种方式跟单例的获取方式一样,那么它到底是不是单例呢,如果是单例的话,一个对象修改内容之后,另外一个线程中的数据不久乱套了吗?从试验以及源码中可以得出,Calendar不是单例。
测试:
Calendar c1 =
- 线程内存和主内存之间联系
qifeifei
java thread
1, java多线程共享主内存中变量的时候,一共会经过几个阶段,
lock:将主内存中的变量锁定,为一个线程所独占。
unclock:将lock加的锁定解除,此时其它的线程可以有机会访问此变量。
read:将主内存中的变量值读到工作内存当中。
load:将read读取的值保存到工作内存中的变量副本中。
- schedule和scheduleAtFixedRate
tangqi609567707
javatimerschedule
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/weidan1121/article/details/527307
import java.util.Timer;import java.util.TimerTask;import java.util.Date;
/** * @author vincent */public class TimerTest {
- erlang 部署
wudixiaotie
erlang
1.如果在启动节点的时候报这个错 :
{"init terminating in do_boot",{'cannot load',elf_format,get_files}}
则需要在reltool.config中加入
{app, hipe, [{incl_cond, exclude}]},
2.当generate时,遇到:
ERROR