Android-Accessibility(Android 8.0以上)
Accessibility Overview
Accessible design allows users of all abilities to navigate, understand, and use your UI successfully.Android Accessibility的目的在于让所有的用户都能更方便的使用Android设备,不仅为残障人士提供了便利,更是方便了all users,比如你在开车,在做饭的时候。
说个题外话,看Google I/O 2017或2018开发者大会视频,讲解Accessibility in Android的Product Manager(Patrick Clary)and Technical Program Manager(Victor Tsaran)是两位残障人士,由衷的敬佩。
Impact of Accessibility
- Increase your app’s reach.
- Improve your app’s versatility.
全世界约有15%的残障人士,如果能使你的APP more Accessibility,那么会有更多的人使用;另外Accessibility不仅仅方便了残障人士,也能方便所有人,比如你在开车的时候也能用语音代替手势或点击行为。也有可以做一些外挂,比如微信抢红包什么的。
Build accessibility services
在分析内部的AccessibilityService之前,我们先来看看构建accessibility service基础知识,先有个宏观上的认识,再去分析内部实现。
Manifest declarations and permissions
Accessibility service declaration
Accessibility Service也是一个服务,需要在AndroidManifest.xml中声明,注意这里必须有BIND_ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICE permission,让Android System知道可以绑定。
<application>
<service android:name=".MyAccessibilityService"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICE"
android:label="@string/accessibility_service_label">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.accessibilityservice.AccessibilityService" />
intent-filter>
service>
application>
Accessibility service configuration
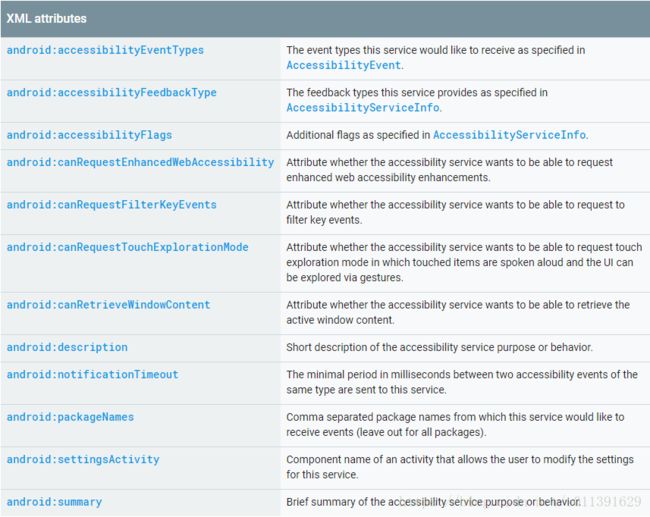
Accessibility Service还需要配置信息,指定服务处理时的accessibility events类型和关于服务的附加信息。配置信息可以通过AccessibilityServiceInfo类的setServiceInfo()方法配置。Android4.0后,可以在Manifest中包含 < meta-data> 元素。
For example:
AndroidManifest.xml
<service android:name=".MyAccessibilityService">
...
<meta-data
android:name="android.accessibilityservice"
android:resource="@xml/accessibility_service_config" />
service>
< project_dir>/res/xml/accessibility_service_config.xml
<accessibility-service xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:description="@string/accessibility_service_description"
android:packageNames="com.example.android.apis"
android:accessibilityEventTypes="typeAllMask"
android:accessibilityFlags="flagDefault"
android:accessibilityFeedbackType="feedbackSpoken"
android:notificationTimeout="100"
android:canRetrieveWindowContent="true"
android:settingsActivity="com.example.android.accessibility.ServiceSettingsActivity"
/>
Accessibility service methods
自己写的Accessibility Service必须从AccessibilityService继承,然后再重写里面的方法,这些方法都是被Android System调用。
- start service:
onServiceConnected() - running service:
onAccessibilityEvent(), onInterrupt() - close service:
onUnbind()
Register for accessibility events
Accessibility service configuration一个很重要的功能是告诉指定Accessibility Service可以处理哪些Accessibility Event,这些event可以靠两种方式判别:
- Package Names
- Event Types
Android Framework可能会把AccessibilityEvent分发给多个Accessibility Service,前提是这些Accessibility Service有不同的Feedback Types。如果多个Accessibility Service的Feedback Types相同,只有第一个注册的Accessibility Service会接收到这个Accessibility Event。
Accessibility volume
Android 8.0 (API level 26) 及以上,包含了STREAM_ACCESSIBILITYvolume category,可以独立于设备上其他的声音,只控制accessibility service的声音输出。通过调用AudioManager实例的 adjustStreamVolume()方法调节accessibility service的音量。
For example:
import static android.media.AudioManager.*;
public class MyAccessibilityService extends AccessibilityService {
private AudioManager mAudioManager =
(AudioManager) getSystemService(AUDIO_SERVICE);
@Override
public void onAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent accessibilityEvent) {
AccessibilityNodeInfo interactedNodeInfo =
accessibilityEvent.getSource();
if (interactedNodeInfo.getText().equals("Increase volume")) {
mAudioManager.adjustStreamVolume(AudioManager.STREAM_ACCESSIBILITY,
ADJUST_RAISE, 0);
}
}
}
Accessibility shortcut
用户可以通过长按两个音量键来启用和禁用他们喜欢的Accessibility Service。
Accessibility button
导航栏的右侧包括一个Accessibility button。当用户按下这个按钮时,可以根据屏幕上显示的内容调用几个启用的Accessibility Service。Accessibility Service需要add FLAG_REQUEST_ACCESSIBILITY_BUTTONflag(android:accessibilityFlags),然后调用registerAccessibilityButtonCallback()。
For example:
private AccessibilityButtonController mAccessibilityButtonController;
private AccessibilityButtonController
.AccessibilityButtonCallback mAccessibilityButtonCallback;
private boolean mIsAccessibilityButtonAvailable;
@Override
protected void onServiceConnected() {
mAccessibilityButtonController = getAccessibilityButtonController();
mIsAccessibilityButtonAvailable =
mAccessibilityButtonController.isAccessibilityButtonAvailable();
if (!mIsAccessibilityButtonAvailable) {
return;
}
AccessibilityServiceInfo serviceInfo = getServiceInfo();
serviceInfo.flags
|= AccessibilityServiceInfo.FLAG_REQUEST_ACCESSIBILITY_BUTTON;
setServiceInfo(serviceInfo);
mAccessibilityButtonCallback =
new AccessibilityButtonController.AccessibilityButtonCallback() {
@Override
public void onClicked(AccessibilityButtonController controller) {
Log.d("MY_APP_TAG", "Accessibility button pressed!");
// Add custom logic for a service to react to the
// accessibility button being pressed.
}
@Override
public void onAvailabilityChanged(
AccessibilityButtonController controller, boolean available) {
if (controller.equals(mAccessibilityButtonController)) {
mIsAccessibilityButtonAvailable = available;
}
}
};
if (mAccessibilityButtonCallback != null) {
mAccessibilityButtonController.registerAccessibilityButtonCallback(
mAccessibilityButtonCallback, null);
}
}
Fingerprint gestures
Accessibility Service可以响应另一种输入机制,即在设备的指纹传感器上进行定向滑动(向上、向下、左、右)。配置一个Service来接收这些交互的回调,需要完成以下步骤:
- 声明
USE_FINGERPRINTpermission 和CAPABILITY_CAN_REQUEST_FINGERPRINT_GESTUREScapability. - 设置
FLAG_REQUEST_FINGERPRINT_GESTURESflag(android:accessibilityFlags). - 注册函数
registerFingerprintGestureCallback().
For example:
AndroidManifest.xml
<manifest ... >
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.USE_FINGERPRINT" />
...
<application>
<service android:name="com.example.MyFingerprintGestureService" ... >
<meta-data
android:name="android.accessibilityservice"
android:resource="@xml/myfingerprintgestureservice" />
service>
application>
manifest>
myfingerprintgestureservice.xml
<accessibility-service xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
...
android:accessibilityFlags=" ... |flagRequestFingerprintGestures"
android:canRequestFingerprintGestures="true"
... />
MyFingerprintGestureService.java
import static android.accessibilityservice.FingerprintGestureController.*;
public class MyFingerprintGestureService extends AccessibilityService {
private FingerprintGestureController mGestureController;
private FingerprintGestureController
.FingerprintGestureCallback mFingerprintGestureCallback;
private boolean mIsGestureDetectionAvailable;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
mGestureController = getFingerprintGestureController();
mIsGestureDetectionAvailable =
mGestureController.isGestureDetectionAvailable();
}
@Override
protected void onServiceConnected() {
if (mFingerprintGestureCallback != null
|| !mIsGestureDetectionAvailable) {
return;
}
mFingerprintGestureCallback =
new FingerprintGestureController.FingerprintGestureCallback() {
@Override
public void onGestureDetected(int gesture) {
switch (gesture) {
case FINGERPRINT_GESTURE_SWIPE_DOWN:
moveGameCursorDown();
break;
case FINGERPRINT_GESTURE_SWIPE_LEFT:
moveGameCursorLeft();
break;
case FINGERPRINT_GESTURE_SWIPE_RIGHT:
moveGameCursorRight();
break;
case FINGERPRINT_GESTURE_SWIPE_UP:
moveGameCursorUp();
break;
default:
Log.e(MY_APP_TAG,
"Error: Unknown gesture type detected!");
break;
}
}
@Override
public void onGestureDetectionAvailabilityChanged(boolean available) {
mIsGestureDetectionAvailable = available;
}
};
if (mFingerprintGestureCallback != null) {
mGestureController.registerFingerprintGestureCallback(
mFingerprintGestureCallback, null);
}
}
}
Multilingual text to speech
text-to-speech (TTS) service可以在一个文本块识别和使用多种语言,要启用这种功能,需要将LocaleSpan对象中的所有字符串封装起来
For example:
TextView localeWrappedTextView = findViewById(R.id.my_french_greeting_text);
localeWrappedTextView.setText(wrapTextInLocaleSpan("Bonjour!", Locale.FRANCE));
private SpannableStringBuilder wrapTextInLocaleSpan(
CharSequence originalText, Locale loc) {
SpannableStringBuilder myLocaleBuilder =
new SpannableStringBuilder(originalText);
myLocaleBuilder.setSpan(new LocaleSpan(loc), 0,
originalText.length() - 1, 0);
return myLocaleBuilder;
}
Take action for users
从Android 4.0起,Accessibility Service可以代替用户做出Action,比如改变焦点(焦点就是当前正在处理事件的位置,比如有多个text输入框,同一时间内只能有一个输入框可以输入),模拟点击,模拟手势等等。
Listen for gestures
Accessibility Service可以监听特定的手势,然后代替用户做出反应。需要设置flags FLAG_REQUEST_TOUCH_EXPLORATION_MODE
public class MyAccessibilityService extends AccessibilityService {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
getServiceInfo().flags = AccessibilityServiceInfo.FLAG_REQUEST_TOUCH_EXPLORATION_MODE;
}
...
}
Continued gestures
可以通过Path表示手势的路径,然后用GestureDescription.StrokeDescription构造手势。
For example:
// Simulates an L-shaped drag path: 200 pixels right, then 200 pixels down.
private void doRightThenDownDrag() {
Path dragRightPath = new Path();
dragRightPath.moveTo(200, 200);
dragRightPath.lineTo(400, 200);
long dragRightDuration = 500L; // 0.5 second
// The starting point of the second path must match
// the ending point of the first path.
Path dragDownPath = new Path();
dragDownPath.moveTo(400, 200);
dragDownPath.lineTo(400, 400);
long dragDownDuration = 500L;
GestureDescription.StrokeDescription rightThenDownDrag =
new GestureDescription.StrokeDescription(dragRightPath, 0L,
dragRightDuration, true);
rightThenDownDrag.continueStroke(dragDownPath, dragRightDuration,
dragDownDuration, false);
}
Use accessibility actions
可以通过getSource()得到node,然后调用performAction做出Action。
public class MyAccessibilityService extends AccessibilityService {
@Override
public void onAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event) {
// get the source node of the event
AccessibilityNodeInfo nodeInfo = event.getSource();
// Use the event and node information to determine
// what action to take
// take action on behalf of the user
nodeInfo.performAction(AccessibilityNodeInfo.ACTION_SCROLL_FORWARD);
// recycle the nodeInfo object
nodeInfo.recycle();
}
...
}
Use focus types
可以用AccessibilityNodeInfo.findFocus()查找node有哪些元素具有Input Focus or Accessibility Focus,还可以使用focusSearch()选择Input Focus。最后使用performAction(AccessibilityNodeInfo.ACTION_SET_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUS)设置Accessibility Focus。
Gather information
Accessibility services also have standard methods of gathering and representing key units of user-provided information, such as event details, text, and numbers.
Get event details
AccessibilityEvent.getRecordCount()或getRecord(int)AccessibilityEvent.getSource()- 返回一个AccessibilityNodeInfo对象
Process text
Hint text
isShowingHintText()andsetShowingHintText()getHintText()
Locations of on-screen text characters
refreshWithExtraData()
Standardized one-sided range values
一些AccessibilityNodeInfo对象用AccessibilityNodeInfo.RangeInfo的实例表示UI元素的范围值。
- For ranges with no minimum,
Float.NEGATIVE_INFINITYrepresents the minimum value. - For ranges with no maximum,
Float.POSITIVE_INFINITYrepresents the maximum value.
Build an accessibility service
这一部分会介绍构建一个accessibility service的flow,从应用程序接收到的信息,然后该信息反馈给用户。
Create your accessibility service
create class
package com.example.android.apis.accessibility;
import android.accessibilityservice.AccessibilityService;
import android.view.accessibility.AccessibilityEvent;
public class MyAccessibilityService extends AccessibilityService {
...
@Override
public void onAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event) {
}
@Override
public void onInterrupt() {
}
...
}
AndroidManifest.xml
<application ...>
...
<service android:name=".MyAccessibilityService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.accessibilityservice.AccessibilityService" />
intent-filter>
. . .
service>
...
application>
Configure your accessibility service
告诉Android System,你想怎么运行,何时运行,你想对何种AccessibilityEvent做出回应,Service是否要监听所有Application,还是特定的Application,使用哪种feedback types。
有两种方法,一种是setServiceInfo(android.accessibilityservice.AccessibilityServiceInfo),然后重写onServiceConnected()。
For example:
@Override
public void onServiceConnected() {
// Set the type of events that this service wants to listen to. Others
// won't be passed to this service.
info.eventTypes = AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED |
AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_FOCUSED;
// If you only want this service to work with specific applications, set their
// package names here. Otherwise, when the service is activated, it will listen
// to events from all applications.
info.packageNames = new String[]
{"com.example.android.myFirstApp", "com.example.android.mySecondApp"};
// Set the type of feedback your service will provide.
info.feedbackType = AccessibilityServiceInfo.FEEDBACK_SPOKEN;
// Default services are invoked only if no package-specific ones are present
// for the type of AccessibilityEvent generated. This service *is*
// application-specific, so the flag isn't necessary. If this was a
// general-purpose service, it would be worth considering setting the
// DEFAULT flag.
// info.flags = AccessibilityServiceInfo.DEFAULT;
info.notificationTimeout = 100;
this.setServiceInfo(info);
}
另一种方法是使用xml方法
For example:
<accessibility-service
android:accessibilityEventTypes="typeViewClicked|typeViewFocused"
android:packageNames="com.example.android.myFirstApp, com.example.android.mySecondApp"
android:accessibilityFeedbackType="feedbackSpoken"
android:notificationTimeout="100"
android:settingsActivity="com.example.android.apis.accessibility.TestBackActivity"
android:canRetrieveWindowContent="true"
/>
同时在AndroidManifest.xml中添加< meta-data>,假设XML file 在res/xml/serviceconfig.xml
<service android:name=".MyAccessibilityService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.accessibilityservice.AccessibilityService" />
intent-filter>
<meta-data android:name="android.accessibilityservice"
android:resource="@xml/serviceconfig" />
service>
Respond to accessibility events
当监听有AccessibilityEvent时,使用onAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent)方法做出回应。用getEventType()获取AccessibilityEvent Type,getContentDescription()提取与触发事件的视图有关的标签文本。
For example:
@Override
public void onAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event) {
final int eventType = event.getEventType();
String eventText = null;
switch(eventType) {
case AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED:
eventText = "Clicked: ";
break;
case AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_FOCUSED:
eventText = "Focused: ";
break;
}
eventText = eventText + event.getContentDescription();
// Do something nifty with this text, like speak the composed string
// back to the user.
speakToUser(eventText);
...
}
Query the view hierarchy for more context
有时候,需要得到视图的相关信息,可以查看视图的层次关系,为了做到这一点,需要现在xml中配置。
android:canRetrieveWindowContent="true"
使用getSource()获得AccessibilityNodeInfo对象,当接收到一个AccessibilityEvent时,它会做以下事情:
1.抓住该事件视图的父节点。
2.在该视图(父节点)寻找label and check box作为子视图。
3.如果它找到了它们,就创建一个字符串来向用户报告,指示标签,以及是否检查了它。
4.如果在遍历视图层级时返回null(不管什么时候),那么该方法就会放弃。
For example:
// Alternative onAccessibilityEvent, that uses AccessibilityNodeInfo
@Override
public void onAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event) {
AccessibilityNodeInfo source = event.getSource();
if (source == null) {
return;
}
// Grab the parent of the view that fired the event.
AccessibilityNodeInfo rowNode = getListItemNodeInfo(source);
if (rowNode == null) {
return;
}
// Using this parent, get references to both child nodes, the label and the checkbox.
AccessibilityNodeInfo labelNode = rowNode.getChild(0);
if (labelNode == null) {
rowNode.recycle();
return;
}
AccessibilityNodeInfo completeNode = rowNode.getChild(1);
if (completeNode == null) {
rowNode.recycle();
return;
}
// Determine what the task is and whether or not it's complete, based on
// the text inside the label, and the state of the check-box.
if (rowNode.getChildCount() < 2 || !rowNode.getChild(1).isCheckable()) {
rowNode.recycle();
return;
}
CharSequence taskLabel = labelNode.getText();
final boolean isComplete = completeNode.isChecked();
String completeStr = null;
if (isComplete) {
completeStr = getString(R.string.checked);
} else {
completeStr = getString(R.string.not_checked);
}
String reportStr = taskLabel + completeStr;
speakToUser(reportStr);
}
以上基本是Android官网的学习资料,下一篇会学习AccessibilityService的源码,看看内部是怎么实现的。
请看Android 9.0源码学习-AccessibilityManager