android input子系统分析---事件层
3 核心层
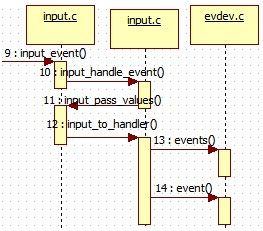
核心层主要都是在input.c中处理。这里会处理各种Event,各种sensor,触摸事件,按键事件等等。流程图如下,
input_event方法直接调用input_handle_event方法进行处理,
void input_event(struct input_dev *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
unsigned long flags;
//判断是否是注册时的event类型,驱动probe时注册input_dev时设置了能响应的event类型
if (is_event_supported(type, dev->evbit, EV_MAX)) {
spin_lock_irqsave(&dev->event_lock, flags); //自旋锁枷锁
input_handle_event(dev, type, code, value);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&dev->event_lock, flags); //解锁
}
}
input_handle_event首先调用input_get_disposition方法获取发送Event的类型,然后根据类型分别处理。
在上个小节中,发送加速度值的类型时EV_ABS,发送时间的值是EV_SYN。
input_get_disposition方法有关sensor代码如下,
case EV_SYN:
switch (code) {
case SYN_CONFIG:
case SYN_TIME_SEC:
case SYN_TIME_NSEC:
disposition = INPUT_PASS_TO_ALL;
break;
•••
case EV_ABS:
if (is_event_supported(code, dev->absbit, ABS_MAX))
disposition = input_handle_abs_event(dev, code, &value);
break;
由此可见,sensor的时间事件返回的是INPUT_PASS_TO_ALL
对于sensor事件, input_handle_abs_event 一般返回INPUT_PASS_TO_HANDLERS。
这些值的定义如下,
#define INPUT_IGNORE_EVENT 0
#define INPUT_PASS_TO_HANDLERS 1
#define INPUT_PASS_TO_DEVICE 2
#define INPUT_SLOT 4
#define INPUT_FLUSH 8
#define INPUT_PASS_TO_ALL (INPUT_PASS_TO_HANDLERS | INPUT_PASS_TO_DEVICE)
input_handle_event方法最后会调用input_pass_values方法进行处理,
input_pass_values(dev, dev->vals, dev->num_vals);最后的input_to_handler主要逻辑如下,
if (handler->events)
handler->events(handle, vals, count);
else if (handler->event)
for (v = vals; v != end; v++)
handler->event(handle, v->type, v->code, v->value);
input_to_handler()调用handler->events()和handler->event(),不同的handler,handler->event()函数不同,
这样input_event()就把事件上报给device或handler处理了,整个inputcore层的工作完成了。具体的处理是
handler做的事情。
4 事件层
4.1 evdev
evdev是/kernel/drivers/input下众多事件处理器handler其中的一个,其对应的init方法是evdev_init,如下,
static int __init evdev_init(void)
{
return input_register_handler(&evdev_handler);
}
初始化就是往input核心中注册一个input_handler类型的evdev_handler,定义如下,
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
.event = evdev_event,
.events = evdev_events,
.connect = evdev_connect,
.disconnect = evdev_disconnect,
.legacy_minors = true,
.minor = EVDEV_MINOR_BASE,
.name = "evdev",
.id_table = evdev_ids,
};
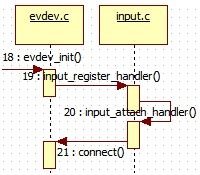
基本是一个input和evdev方法的对应关系。整个调用流程图如下,
input.c的input_register_handler方法如下,
int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler)
{
struct input_dev *dev;
int error;
error = mutex_lock_interruptible(&input_mutex);
if (error)
return error;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&handler->h_list);
list_add_tail(&handler->node, &input_handler_list); //添加进handler 链表
//遍历input_dev这个链表,依次调用下面的input_attach_handler去匹配input_dev
list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node)
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);
input_wakeup_procfs_readers();
mutex_unlock(&input_mutex);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(input_register_handler);
最后input_attach_handler会回调evdev.c的connect方法, connect指向的函数为evdev_connect,在该方法中,
会初始化evdev结构,
evdev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct evdev), GFP_KERNEL);
•••
dev_set_name(&evdev->dev, "event%d", dev_no);
evdev->handle.dev = input_get_device(dev);
evdev->handle.name = dev_name(&evdev->dev);
evdev->handle.handler = handler;
evdev->handle.private = evdev;
evdev->dev.devt = MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, minor);
evdev->dev.class = &input_class;
evdev->dev.parent = &dev->dev;
evdev->dev.release = evdev_free;
device_initialize(&evdev->dev);
初始化完成之后,将handle 注册到input核心中去
error = input_register_handle(&evdev->handle);最后将device 添加到/sys/class/input/下面,所以可以看到/dev/input下面看到:event0等 字样字符设备文件,
error = device_add(&evdev->dev);evdev结构体如下,
struct evdev {
int open; //打开标志
struct input_handle handle; //包含的handle结构
wait_queue_head_t wait;
struct evdev_client __rcu *grab;// evdev_client结构
//evdev_client 链表,这说明一个evdev设备可以处理多个evdev_client,可以有多个进程访问evdev设备
struct list_head client_list;
spinlock_t client_lock; /* protects client_list */
struct mutex mutex;
struct device dev;
struct cdev cdev;
bool exist;
};
evdev_client结构体如下,
struct evdev_client {
unsigned int head; //buffer数组的索引头
unsigned int tail; //buffer数组的索引尾
unsigned int packet_head; /* [future] position of the first element of next packet */
spinlock_t buffer_lock; /* protects access to buffer, head and tail */
struct wake_lock wake_lock;
bool use_wake_lock;
char name[28];
struct fasync_struct *fasync; //异步通知函数
struct evdev *evdev;
struct list_head node; //链表
int clkid;
unsigned int bufsize;
//input_event数据结构的数组,input_event代表一个事件,基本成员:类型(type),编码(code),值(value)
struct input_event buffer[];
};
4.2 处理流程
evdev.c 方法中的对应关系如下,
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
.event = evdev_event,
.events = evdev_events,
.connect = evdev_connect,
.disconnect = evdev_disconnect,
.legacy_minors = true,
.minor = EVDEV_MINOR_BASE,
.name = "evdev",
.id_table = evdev_ids,
};
event对应的evdev_event方法最后还是会调用evdev_events方法进行处理, evdev_events方法的处理流程图如下,
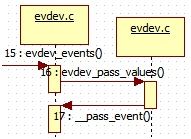
每当input device上报一个事件时,会将其交给和它匹配的handler的event函数处理.在evdev中这个event函数。
__pass_event 方法如下,
static void __pass_event(struct evdev_client *client,
const struct input_event *event)
{
client->buffer[client->head++] = *event;
client->head &= client->bufsize - 1;
if (unlikely(client->head == client->tail)) {
/*
* This effectively "drops" all unconsumed events, leaving
* EV_SYN/SYN_DROPPED plus the newest event in the queue.
*/
client->tail = (client->head - 2) & (client->bufsize - 1);
client->buffer[client->tail].time = event->time;
client->buffer[client->tail].type = EV_SYN;
client->buffer[client->tail].code = SYN_DROPPED;
client->buffer[client->tail].value = 0;
client->packet_head = client->tail;
if (client->use_wake_lock)
wake_unlock(&client->wake_lock);
}
if (event->type == EV_SYN && event->code == SYN_REPORT) {
client->packet_head = client->head;
if (client->use_wake_lock)
wake_lock(&client->wake_lock);
kill_fasync(&client->fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
}
}
这里的操作很简单.就是将event(上传数据)保存到client->buffer中.而client->head就是当前的数据位置.注意这里
是一个环形缓存区.写数据是从client->head写.而读数据则是从client->tail中读.
4.3 和HAL上层交互
和Framework进行交互一般都是evdev.c,对应的方法如下,
static const struct file_operations evdev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = evdev_read,
.write = evdev_write,
.poll = evdev_poll,
.open = evdev_open,
.release = evdev_release,
.unlocked_ioctl = evdev_ioctl,
•••
};
例如,上层调用read 方法读取对应sysfs文件节点的数据时,调用的是evdev_read方法,
static ssize_t evdev_read(struct file *file, char __user *buffer,
size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
//这个客户端结构在打开的时候分配并保存在file->private_data中
struct evdev_client *client = file->private_data;
struct evdev *evdev = client->evdev;
struct input_event event;
size_t read = 0;
int error;
if (count != 0 && count < input_event_size())
return -EINVAL;
for (;;) {
if (!evdev->exist)
return -ENODEV;
if (client->packet_head == client->tail &&
(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK))
return -EAGAIN;
/*
* count == 0 is special - no IO is done but we check
* for error conditions (see above).
*/
if (count == 0)
break;
while (read + input_event_size() <= count &&
evdev_fetch_next_event(client, &event)) {
//将事件复制到用户空间
if (input_event_to_user(buffer + read, &event))
return -EFAULT;
read += input_event_size();
}
if (read)
break;
if (!(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)) {
//如果设置了非阻塞操作,则会立刻返回
error = wait_event_interruptible(evdev->wait,
client->packet_head != client->tail ||
!evdev->exist);
if (error)
return error;
}
}
return read;
}
和上面__pass_event方法刚好相反。这样,通过read方法,就可以将数据从内核态复制到用户态。