Android-语言设置流程分析
Android手机语言切换行为,是通过设置-语言和输入法-语言来改变手机的语言,其实这个功能很少被用户使用。
以Android5.1工程源码为基础,从设置app入手来分析和学习语言切换的过程:
一、语言设置界面:
首先在设置app中找到语言设置这个Preference,目前设置中界面大多都是Fragment,先找到语言和输入法的PreferenceScreen,与其对应的Fragment是InputMethodAndLanguageSettings.java,在其onCreate()方法中,首先是增加语言设置的preference:
addPreferencesFromResource(R.xml.language_settings);
找到language_settings.xml,可发现如下代码:
于是断定LocalePicker就是语言设置的Fragment,它是ListFragment的子类,继承于framework中LocalePicker,并实现了父类的一个接口,其回调方法是onLocaleSelected(),Locale中文含义大致是语言环境,所以可推测这是设置语言后的一个回调方法,不确定的话,可打断点测试一下。然而此类中并没有关于语言设置界面数据适配的太多逻辑,
只是通过父类的方法创建了一个view:
@Override
public View onCreateView(
LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
final View view = super.onCreateView(inflater, container, savedInstanceState);
final ListView list = (ListView) view.findViewById(android.R.id.list);
Utils.forcePrepareCustomPreferencesList(container, view, list, false);
return view;
}
所以更多逻辑应该在framework中的LocalePicker.java中。既然是ListFragment,那就必须有Adapter,在此类中有构建了一个Adapter:
/**
* Constructs an Adapter object containing Locale information. Content is sorted by
* {@link LocaleInfo#label}.
*/
public static ArrayAdapter constructAdapter(Context context) {
return constructAdapter(context, R.layout.locale_picker_item, R.id.locale);
}
public static ArrayAdapter constructAdapter(Context context,
final int layoutId, final int fieldId) {
boolean isInDeveloperMode = Settings.Global.getInt(context.getContentResolver(),
Settings.Global.DEVELOPMENT_SETTINGS_ENABLED, 0) != 0;
//获取系统支持语言的信息
final List localeInfos = getAllAssetLocales(context, isInDeveloperMode);
final LayoutInflater inflater =
(LayoutInflater)context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
return new ArrayAdapter(context, layoutId, fieldId, localeInfos) {
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
View view;
TextView text;
if (convertView == null) {
view = inflater.inflate(layoutId, parent, false);
text = (TextView) view.findViewById(fieldId);
view.setTag(text);
} else {
view = convertView;
text = (TextView) view.getTag();
}
LocaleInfo item = getItem(position);
text.setText(item.toString());
text.setTextLocale(item.getLocale());
return view;
}
};
} public static List getAllAssetLocales(Context context, boolean isInDeveloperMode) {
final Resources resources = context.getResources();
//获取系统所支持的语言
final String[] locales = Resources.getSystem().getAssets().getLocales();
List localeList = new ArrayList(locales.length);
Collections.addAll(localeList, locales);
// Don't show the pseudolocales unless we're in developer mode.
if (!isInDeveloperMode) {
localeList.remove("ar-XB");
localeList.remove("en-XA");
}
Collections.sort(localeList);
final String[] specialLocaleCodes = resources.getStringArray(R.array.special_locale_codes);
final String[] specialLocaleNames = resources.getStringArray(R.array.special_locale_names);
final ArrayList localeInfos = new ArrayList(localeList.size());
for (String locale : localeList) {
final Locale l = Locale.forLanguageTag(locale.replace('_', '-'));
if (l == null || "und".equals(l.getLanguage())
|| l.getLanguage().isEmpty() || l.getCountry().isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
if (localeInfos.isEmpty()) {
if (DEBUG) {
Log.v(TAG, "adding initial "+ toTitleCase(l.getDisplayLanguage(l)));
}
localeInfos.add(new LocaleInfo(toTitleCase(l.getDisplayLanguage(l)), l));
} else {
// check previous entry:
// same lang and a country -> upgrade to full name and
// insert ours with full name
// diff lang -> insert ours with lang-only name
final LocaleInfo previous = localeInfos.get(localeInfos.size() - 1);
if (previous.locale.getLanguage().equals(l.getLanguage()) &&
!previous.locale.getLanguage().equals("zz")) {
if (DEBUG) {
Log.v(TAG, "backing up and fixing " + previous.label + " to " +
getDisplayName(previous.locale, specialLocaleCodes, specialLocaleNames));
}
previous.label = toTitleCase(getDisplayName(
previous.locale, specialLocaleCodes, specialLocaleNames));
if (DEBUG) {
Log.v(TAG, " and adding "+ toTitleCase(
getDisplayName(l, specialLocaleCodes, specialLocaleNames)));
}
localeInfos.add(new LocaleInfo(toTitleCase(
getDisplayName(l, specialLocaleCodes, specialLocaleNames)), l));
} else {
String displayName = toTitleCase(l.getDisplayLanguage(l));
if (DEBUG) {
Log.v(TAG, "adding "+displayName);
}
localeInfos.add(new LocaleInfo(displayName, l));
}
}
}
Collections.sort(localeInfos);
return localeInfos;
}
此方法中还会通过Resources.getSystem().getAssets().getLocales()去获得系统支持的语言信息,然后添加LocaleInfo里边,再通过Adapter适配到ListView中。getLocales()方法属于类AssetManager.java:
/**
* Get the locales that this asset manager contains data for.
*
* On SDK 21 (Android 5.0: Lollipop) and above, Locale strings are valid
* BCP-47 language tags and can be
* parsed using {@link java.util.Locale#forLanguageTag(String)}.
*
*
On SDK 20 (Android 4.4W: Kitkat for watches) and below, locale strings
* are of the form {@code ll_CC} where {@code ll} is a two letter language code,
* and {@code CC} is a two letter country code.
*/
public native final String[] getLocales();
乍一看,是个native方法,那不就是跟JNI有关系了,所以只能到相应JNI目录下去找了,路径:android5.1\frameworks\base\core\jni,对应文件:android_util_AssetManager.cpp(浏览下这个文件,发现这个家伙有点不得了啊,什么resource,theme等都跟它有关系,看样子还的加油学学JNI啊!),然后找到对应的native方法:
static jobjectArray android_content_AssetManager_getLocales(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{
Vector locales;
AssetManager* am = assetManagerForJavaObject(env, clazz);
if (am == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
am->getLocales(&locales);
const int N = locales.size();
jobjectArray result = env->NewObjectArray(N, g_stringClass, NULL);
if (result == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
for (int i=0; iNewStringUTF(locales[i].string());
if (str == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
env->SetObjectArrayElement(result, i, str);
env->DeleteLocalRef(str);
}
return result;
}
二、语言设置功能实现过程:
上面提到了设置中的LocalePicker类实现了父类接口中的onLocaleSelected()方法:
public static interface LocaleSelectionListener {
// You can add any argument if you really need it...
public void onLocaleSelected(Locale locale);
}
@Override
public void onLocaleSelected(final Locale locale) {
if (Utils.hasMultipleUsers(getActivity())) {
mTargetLocale = locale;
showDialog(DLG_SHOW_GLOBAL_WARNING);
} else {
getActivity().onBackPressed();
LocalePicker.updateLocale(locale);
}
}
此方法中最终调用了其父类的updateLocale()方法来更新系统的语言环境:
/**
* Requests the system to update the system locale. Note that the system looks halted
* for a while during the Locale migration, so the caller need to take care of it.
*/
public static void updateLocale(Locale locale) {
try {
IActivityManager am = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
Configuration config = am.getConfiguration();
// Will set userSetLocale to indicate this isn't some passing default - the user
// wants this remembered
config.setLocale(locale);
am.updateConfiguration(config);
// Trigger the dirty bit for the Settings Provider.
BackupManager.dataChanged("com.android.providers.settings");
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// Intentionally left blank
}
}
又看到ActivityManagerNative.getDefault(),所以可以直接到ActivityManagerService.java中找对应的方法,此方法中先是把选择的语言设置到Configuration中,记录下来。设置了不代表系统就知道这档子事,所以还需要am去更新一下,说的俗气一点:am老大知道了这档子事,然后大吼一声,我这里有个东西改变了,小伙伴们刷新一下!在ActivityManagerService中找到updateConfiguration()方法:
public void updateConfiguration(Configuration values) {
enforceCallingPermission(android.Manifest.permission.CHANGE_CONFIGURATION,
"updateConfiguration()");
synchronized(this) {
if (values == null && mWindowManager != null) {
// sentinel: fetch the current configuration from the window manager
values = mWindowManager.computeNewConfiguration();
}
if (mWindowManager != null) {
mProcessList.applyDisplaySize(mWindowManager);
}
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (values != null) {
Settings.System.clearConfiguration(values);
}
updateConfigurationLocked(values, null, false, false);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
看到Settings.System.clearConfiguration(values)不要以为这里把values清除了额,其实这个方法只是把系统字体的特效清除了,比如字体的大小:
/**
* @hide Erase the fields in the Configuration that should be applied
* by the settings.
*/
public static void clearConfiguration(Configuration inoutConfig) {
inoutConfig.fontScale = 0;
}
然后调用updateConfigurationLocked()方法:
/**
* Do either or both things: (1) change the current configuration, and (2)
* make sure the given activity is running with the (now) current
* configuration. Returns true if the activity has been left running, or
* false if starting is being destroyed to match the new
* configuration.
* @param persistent TODO
*/
boolean updateConfigurationLocked(Configuration values,
ActivityRecord starting, boolean persistent, boolean initLocale) {
int changes = 0;
if (values != null) {
Configuration newConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
changes = newConfig.updateFrom(values);
if (changes != 0) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Updating configuration to: " + values);
}
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED, changes);
if (values.locale != null && !initLocale) {
saveLocaleLocked(values.locale,
!values.locale.equals(mConfiguration.locale),
values.userSetLocale);
}
mConfigurationSeq++;
if (mConfigurationSeq <= 0) {
mConfigurationSeq = 1;
}
newConfig.seq = mConfigurationSeq;
mConfiguration = newConfig;
Slog.i(TAG, "Config changes=" + Integer.toHexString(changes) + " " + newConfig);
mUsageStatsService.reportConfigurationChange(newConfig, mCurrentUserId);
//mUsageStatsService.noteStartConfig(newConfig);
final Configuration configCopy = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
// TODO: If our config changes, should we auto dismiss any currently
// showing dialogs?
mShowDialogs = shouldShowDialogs(newConfig);
AttributeCache ac = AttributeCache.instance();
if (ac != null) {
ac.updateConfiguration(configCopy);
}
// Make sure all resources in our process are updated
// right now, so that anyone who is going to retrieve
// resource values after we return will be sure to get
// the new ones. This is especially important during
// boot, where the first config change needs to guarantee
// all resources have that config before following boot
// code is executed.
mSystemThread.applyConfigurationToResources(configCopy);
if (persistent && Settings.System.hasInterestingConfigurationChanges(changes)) {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(UPDATE_CONFIGURATION_MSG);
msg.obj = new Configuration(configCopy);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
for (int i=mLruProcesses.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ProcessRecord app = mLruProcesses.get(i);
try {
if (app.thread != null) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Sending to proc "
+ app.processName + " new config " + mConfiguration);
app.thread.scheduleConfigurationChanged(configCopy);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY
| Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REPLACE_PENDING
| Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
broadcastIntentLocked(null, null, intent, null, null, 0, null, null,
null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, false, false, MY_PID,
Process.SYSTEM_UID, UserHandle.USER_ALL);
if ((changes&ActivityInfo.CONFIG_LOCALE) != 0) {
intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
broadcastIntentLocked(null, null, intent,
null, null, 0, null, null, null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE,
false, false, MY_PID, Process.SYSTEM_UID, UserHandle.USER_ALL);
}
}
}
boolean kept = true;
final ActivityStack mainStack = mStackSupervisor.getFocusedStack();
// mainStack is null during startup.
if (mainStack != null) {
if (changes != 0 && starting == null) {
// If the configuration changed, and the caller is not already
// in the process of starting an activity, then find the top
// activity to check if its configuration needs to change.
starting = mainStack.topRunningActivityLocked(null);
}
if (starting != null) {
kept = mainStack.ensureActivityConfigurationLocked(starting, changes);
// And we need to make sure at this point that all other activities
// are made visible with the correct configuration.
mStackSupervisor.ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(starting, changes);
}
}
if (values != null && mWindowManager != null) {
mWindowManager.setNewConfiguration(mConfiguration);
}
return kept;
}
有了新的数据就要保存,保存在configuration中不是个事。对于Android系统而言,改变语言,有两个地方的数据需要更新,一个是SystemProperties,另一个是数据库。前者以键值对的形式存放数据,多用于System,后者保存于DataBase中,多用于应用程序获取,算是对外开放的数据。上面方法中对这两个地方都进行了数据保存操作:
1)SystemProperties:调用saveLocaleLocked()方法:
/**
* Save the locale. You must be inside a synchronized (this) block.
*/
private void saveLocaleLocked(Locale l, boolean isDiff, boolean isPersist) {
if(isDiff) {
SystemProperties.set("user.language", l.getLanguage());
SystemProperties.set("user.region", l.getCountry());
}
if(isPersist) {
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", l.getLanguage());
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", l.getCountry());
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", l.getVariant());
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(SEND_LOCALE_TO_MOUNT_DAEMON_MSG, l));
}
}
2)database:调用Settings.System.putConfiguration()方法:
if (persistent && Settings.System.hasInterestingConfigurationChanges(changes)) {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(UPDATE_CONFIGURATION_MSG);
msg.obj = new Configuration(configCopy);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
...
case UPDATE_CONFIGURATION_MSG: {
final ContentResolver resolver = mContext.getContentResolver();
Settings.System.putConfiguration(resolver, (Configuration)msg.obj);
} break;
该保存的数据保存了,但是Resource还不知道这档子事,因为Android代码和资源是分开的,Resource不知道Configuration发生了变化,Resource就不会去加载正确的资源。所以接下来此方法调用了mSystemThread.applyConfigurationToResources(configCopy)来完成这件事,mSystemThread是一个ActivityThread对象,其初始化在ActivityManagerService的构造函数中完成:
mSystemThread = ActivityThread.currentActivityThread();//此方法属于ActivityThread
public final void applyConfigurationToResources(Configuration config) {
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(config, null);
}
}
//此方法属于ResourcesManage
public final boolean applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compat) {
if (mResConfiguration == null) {
mResConfiguration = new Configuration();
}
if (!mResConfiguration.isOtherSeqNewer(config) && compat == null) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Skipping new config: curSeq="
+ mResConfiguration.seq + ", newSeq=" + config.seq);
return false;
}
int changes = mResConfiguration.updateFrom(config);
flushDisplayMetricsLocked();
DisplayMetrics defaultDisplayMetrics = getDisplayMetricsLocked(Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
if (compat != null && (mResCompatibilityInfo == null ||
!mResCompatibilityInfo.equals(compat))) {
mResCompatibilityInfo = compat;
changes |= ActivityInfo.CONFIG_SCREEN_LAYOUT
| ActivityInfo.CONFIG_SCREEN_SIZE
| ActivityInfo.CONFIG_SMALLEST_SCREEN_SIZE;
}
// set it for java, this also affects newly created Resources
if (config.locale != null) {
Locale.setDefault(config.locale);
}
Resources.updateSystemConfiguration(config, defaultDisplayMetrics, compat);
ApplicationPackageManager.configurationChanged();
//Slog.i(TAG, "Configuration changed in " + currentPackageName());
Configuration tmpConfig = null;
for (int i=mActiveResources.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ResourcesKey key = mActiveResources.keyAt(i);
Resources r = mActiveResources.valueAt(i).get();
if (r != null) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Changing resources "
+ r + " config to: " + config);
int displayId = key.mDisplayId;
boolean isDefaultDisplay = (displayId == Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
DisplayMetrics dm = defaultDisplayMetrics;
final boolean hasOverrideConfiguration = key.hasOverrideConfiguration();
if (!isDefaultDisplay || hasOverrideConfiguration) {
if (tmpConfig == null) {
tmpConfig = new Configuration();
}
tmpConfig.setTo(config);
if (!isDefaultDisplay) {
dm = getDisplayMetricsLocked(displayId);
applyNonDefaultDisplayMetricsToConfigurationLocked(dm, tmpConfig);
}
if (hasOverrideConfiguration) {
tmpConfig.updateFrom(key.mOverrideConfiguration);
}
r.updateConfiguration(tmpConfig, dm, compat);
} else {
r.updateConfiguration(config, dm, compat);
}
//Slog.i(TAG, "Updated app resources " + v.getKey()
// + " " + r + ": " + r.getConfiguration());
} else {
//Slog.i(TAG, "Removing old resources " + v.getKey());
mActiveResources.removeAt(i);
}
}
return changes != 0;
}
此方法中Resource和ApplicationPackageManager都会去更新configuration,configuration所包含的属性都会遍历到,该更新的数据更新,该清除的缓存清除。
到这里,第一件事算是做完了,就要做第二件事,让新的configuration更新到所有界面,updateConfigurationLocked()方法通过遍历保存在ProcessRecord中的进程,然后通过scheduleConfigurationChanged()方法更新它们的configuration:
for (int i=mLruProcesses.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ProcessRecord app = mLruProcesses.get(i);
try {
if (app.thread != null) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Sending to proc "
+ app.processName + " new config " + mConfiguration);
app.thread.scheduleConfigurationChanged(configCopy);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
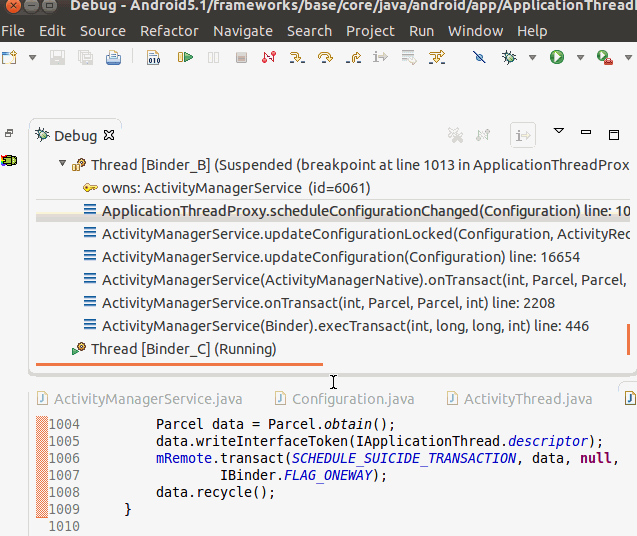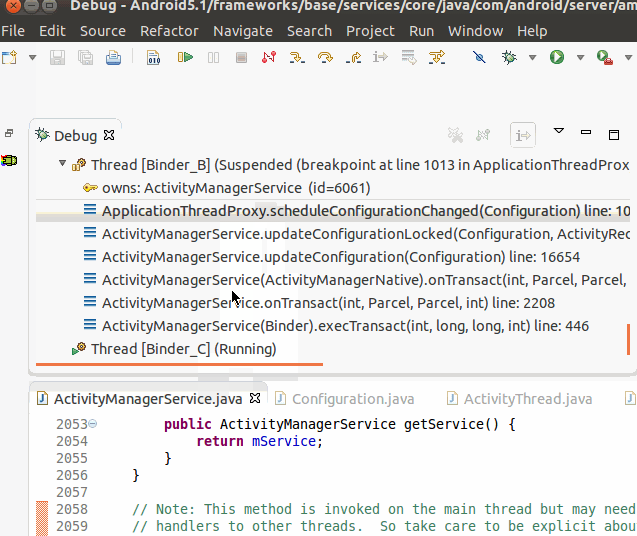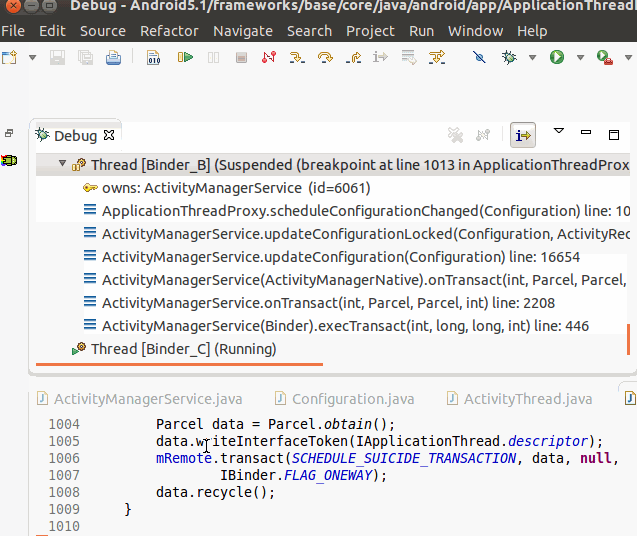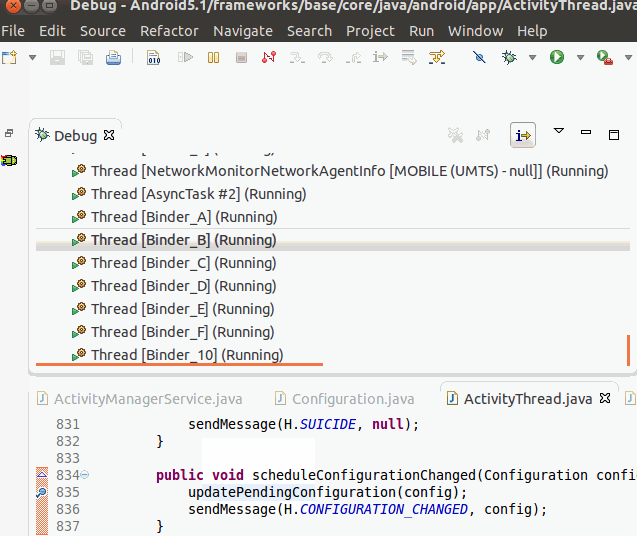
此处通过Binder机制调用ApplicationThreadNative.java中的scheduleConfigurationChanged()方法,最后调用到ActivityThread中的内部类ApplicationThread的scheduleConfigurationChanged()方法,函数调用堆栈如图:
public void scheduleConfigurationChanged(Configuration config) {
updatePendingConfiguration(config);
sendMessage(H.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED, config);
}case CONFIGURATION_CHANGED:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "configChanged");
mCurDefaultDisplayDpi = ((Configuration)msg.obj).densityDpi;
handleConfigurationChanged((Configuration)msg.obj, null);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;final void handleConfigurationChanged(Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compat) {
int configDiff = 0;
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
if (mPendingConfiguration != null) {
if (!mPendingConfiguration.isOtherSeqNewer(config)) {
config = mPendingConfiguration;
mCurDefaultDisplayDpi = config.densityDpi;
updateDefaultDensity();
}
mPendingConfiguration = null;
}
if (config == null) {
return;
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Handle configuration changed: "
+ config);
mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(config, compat);
if (mConfiguration == null) {
mConfiguration = new Configuration();
}
if (!mConfiguration.isOtherSeqNewer(config) && compat == null) {
return;
}
configDiff = mConfiguration.diff(config);
mConfiguration.updateFrom(config);
config = applyCompatConfiguration(mCurDefaultDisplayDpi);
}
ArrayList callbacks = collectComponentCallbacks(false, config);
freeTextLayoutCachesIfNeeded(configDiff);
if (callbacks != null) {
final int N = callbacks.size();
for (int i=0; i
到这里设置语言以后,代码跑的流程就基本结束了,需要一提的是performConfigurationChanged()方法。为什么要提它呢?因为有时候写应用的时候activity需要关注一些configChanged,如:android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden|screenSize",然后重写onConfigurationChanged()方法。然而触发这个方法回调的触发点在哪里呢?这里就以设置语言为例,设置语言触发了configuration的改变。先来看下performConfigurationChanged()方法:
private static void performConfigurationChanged(ComponentCallbacks2 cb, Configuration config) {
// Only for Activity objects, check that they actually call up to their
// superclass implementation. ComponentCallbacks2 is an interface, so
// we check the runtime type and act accordingly.
Activity activity = (cb instanceof Activity) ? (Activity) cb : null;
if (activity != null) {
activity.mCalled = false;
}
boolean shouldChangeConfig = false;
if ((activity == null) || (activity.mCurrentConfig == null)) {
shouldChangeConfig = true;
} else {
// If the new config is the same as the config this Activity
// is already running with then don't bother calling
// onConfigurationChanged
int diff = activity.mCurrentConfig.diff(config);
if (diff != 0) {
// If this activity doesn't handle any of the config changes
// then don't bother calling onConfigurationChanged as we're
// going to destroy it.
if ((~activity.mActivityInfo.getRealConfigChanged() & diff) == 0) {
shouldChangeConfig = true;
}
}
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Config callback " + cb
+ ": shouldChangeConfig=" + shouldChangeConfig);
if (shouldChangeConfig) {
cb.onConfigurationChanged(config);
if (activity != null) {
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + activity.getLocalClassName() +
" did not call through to super.onConfigurationChanged()");
}
activity.mConfigChangeFlags = 0;
activity.mCurrentConfig = new Configuration(config);
}
}
}
如果configuration确实改变了,那么此方法中就会调用cb.onConfigurationChanged(config)。cb代表ComponentCallbacks2,而ComponentCallbacks2 又继承于ComponentCallbacks,所以onConfigurationChanged()方法属于ComponentCallbacks,同样Activity类也实现了ComponentCallbacks2这个接口,如此一来这个回调的过程就连接上了。也充分说明了为什么在configuration改变以后,activity关注的config会回调其父类的onConfigurationChanged()方法。
最后就是广播configuration改变了,updateConfigurationLocked()广播了ACTION_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED和ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED,使用的方法是broadcastIntentLocked(),此方法广播成功返回BROADCAST_SUCCESS。具体就不多说了。