android N拨打电话流程
本文主要分析从拨号盘拨号发出Intent开始,最终到RIL.java中执行拨号操作的过程。
(1)首先拨号盘应用发送了action为android.intent.action.CALL的Intent,被UserCallActivity接收处理,UserCallActivity调用UserCallIntentProcessor来处理:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle bundle) {
super.onCreate(bundle);
Log.startSession("UCA.oC");
try {
Intent intent = getIntent();
verifyCallAction(intent);
final UserManager userManager = (UserManager) getSystemService(Context.USER_SERVICE);
final UserHandle userHandle = new UserHandle(userManager.getUserHandle());
new UserCallIntentProcessor(this, userHandle).processIntent(getIntent(),
getCallingPackage(), true /* hasCallAppOp*/);
} finally {
Log.endSession();
}
finish();
(2)UserCallIntentProcessor通过processOutgoingCallIntent(),sendBroadcastToReceiver()调用PrimaryCallReceiver来处理:
private boolean sendBroadcastToReceiver(Intent intent) {
intent.putExtra(CallIntentProcessor.KEY_IS_INCOMING_CALL, false);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
intent.setClass(mContext, PrimaryCallReceiver.class);
Log.d(this, "Sending broadcast as user to CallReceiver");
mContext.sendBroadcastAsUser(intent, UserHandle.SYSTEM);
return true;
}(3)PrimaryCallReceiver中处理:
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Log.startSession("PCR.oR");
synchronized (getTelecomSystem().getLock()) {
getTelecomSystem().getCallIntentProcessor().processIntent(intent);
}
Log.endSession();
}(3)CallIntentProcessor中处理:
public void processIntent(Intent intent) {
final boolean isUnknownCall = intent.getBooleanExtra(KEY_IS_UNKNOWN_CALL, false);
Log.i(this, "onReceive - isUnknownCall: %s", isUnknownCall);
Trace.beginSection("processNewCallCallIntent");
if (isUnknownCall) {
processUnknownCallIntent(mCallsManager, intent);
} else {
processOutgoingCallIntent(mContext, mCallsManager, intent);
}
Trace.endSection();
}在processOutgoingCallIntent中主要的跳转逻辑
Call call = callsManager
.startOutgoingCall(handle, phoneAccountHandle, clientExtras, initiatingUser);
if (call != null) {
NewOutgoingCallIntentBroadcaster broadcaster = new NewOutgoingCallIntentBroadcaster(
context, callsManager, call, intent, callsManager.getPhoneNumberUtilsAdapter(),
isPrivilegedDialer);
final int result = broadcaster.processIntent();
final boolean success = result == DisconnectCause.NOT_DISCONNECTED;
if (!success && call != null) {
callsManager.clearPendingMOEmergencyCall();
disconnectCallAndShowErrorDialog(context, call, result);
}
}其中重点通过CallManager的startOutgoingCall方法构造了一个Call对象,其中重点会为该Call设置PhoneAccountHandle
Call startOutgoingCall(Uri handle, PhoneAccountHandle phoneAccountHandle, Bundle extras,
UserHandle initiatingUser) {
boolean isReusedCall = true;
Call call = reuseOutgoingCall(handle);
// Create a call with original handle. The handle may be changed when the call is attached
// to a connection service, but in most cases will remain the same.
if (call == null) {
call = new Call(getNextCallId(), mContext,
this,
mLock,
mConnectionServiceRepository,
mContactsAsyncHelper,
mCallerInfoAsyncQueryFactory,
mPhoneNumberUtilsAdapter,
handle,
null /* gatewayInfo */,
null /* connectionManagerPhoneAccount */,
null /* phoneAccountHandle */,
Call.CALL_DIRECTION_OUTGOING /* callDirection */,
false /* forceAttachToExistingConnection */,
false /* isConference */
);
if ((extras != null) &&
extras.getBoolean(TelephonyProperties.EXTRA_DIAL_CONFERENCE_URI, false)) {
//Reset PostDialDigits with empty string for ConfURI call.
call.setPostDialDigits("");
}
call.initAnalytics();
call.setInitiatingUser(initiatingUser);
isReusedCall = false;
}
...
List accounts =
constructPossiblePhoneAccounts(handle, initiatingUser, scheme);
if (phoneAccountHandle != null) {
if (!accounts.contains(phoneAccountHandle)) {
phoneAccountHandle = null;
}
}
if (phoneAccountHandle == null && accounts.size() > 0) {
if(accounts.size() > 1) {
PhoneAccountHandle defaultPhoneAccountHandle =
mPhoneAccountRegistrar.getOutgoingPhoneAccountForScheme(scheme,
initiatingUser);
if (defaultPhoneAccountHandle != null &&
accounts.contains(defaultPhoneAccountHandle)) {
phoneAccountHandle = defaultPhoneAccountHandle;
}
} else {
phoneAccountHandle = accounts.get(0);
}
}
call.setTargetPhoneAccount(phoneAccountHandle);
...
boolean needsAccountSelection = phoneAccountHandle == null && accounts.size() > 1 &&
!call.isEmergencyCall();
if (needsAccountSelection) {
call.setState(CallState.SELECT_PHONE_ACCOUNT, "needs account selection");
// Create our own instance to modify (since extras may be Bundle.EMPTY)
extras = new Bundle(extras);
extras.putParcelableList(android.telecom.Call.AVAILABLE_PHONE_ACCOUNTS, accounts);
} else {
call.setState(
CallState.CONNECTING,
phoneAccountHandle == null ? "no-handle" : phoneAccountHandle.toString());
}
...
return call;
} (3)NewOutgoingCallIntentBroadcaster中主要逻辑:
if (callImmediately) {
String scheme = isUriNumber ? PhoneAccount.SCHEME_SIP : PhoneAccount.SCHEME_TEL;
boolean speakerphoneOn = mIntent.getBooleanExtra(
TelecomManager.EXTRA_START_CALL_WITH_SPEAKERPHONE, false);
int videoState = mIntent.getIntExtra(
TelecomManager.EXTRA_START_CALL_WITH_VIDEO_STATE,
VideoProfile.STATE_AUDIO_ONLY);
mCall.setNewOutgoingCallIntentBroadcastIsDone();
mCallsManager.placeOutgoingCall(mCall, Uri.fromParts(scheme, number, null), null,
speakerphoneOn, videoState);
}重点调用CallsManager的placeOutgoingCal()方法
在placeOutgoingCal中核心调用了call.startCreateConnection(mPhoneAccountRegistrar);
if (call.getTargetPhoneAccount() != null || call.isEmergencyCall()) {
if (!call.isEmergencyCall()) {
updateLchStatus(call.getTargetPhoneAccount().getId());
}
if (mPendingMOEmerCall == null) {
call.startCreateConnection(mPhoneAccountRegistrar);
}
} else if (mPhoneAccountRegistrar.getCallCapablePhoneAccounts(
requireCallCapableAccountByHandle ? call.getHandle().getScheme() : null, false,
call.getInitiatingUser()).isEmpty()) {
markCallAsDisconnected(call, new DisconnectCause(DisconnectCause.CANCELED,
"No registered PhoneAccounts"));
markCallAsRemoved(call);
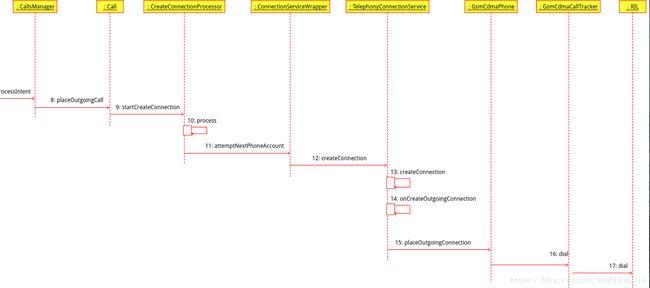
}(4)startCreateConnection中处理:
void startCreateConnection(PhoneAccountRegistrar phoneAccountRegistrar) {
if (mCreateConnectionProcessor != null) {
Log.w(this, "mCreateConnectionProcessor in startCreateConnection is not null. This is" +
" due to a race between NewOutgoingCallIntentBroadcaster and " +
"phoneAccountSelected, but is harmlessly resolved by ignoring the second " +
"invocation.");
return;
}
mCreateConnectionProcessor = new CreateConnectionProcessor(this, mRepository, this,
phoneAccountRegistrar, mContext);
mCreateConnectionProcessor.process();
} public void process() {
Log.v(this, "process");
clearTimeout();
mAttemptRecords = new ArrayList<>();
if (mCall.getTargetPhoneAccount() != null) {
mAttemptRecords.add(new CallAttemptRecord(
mCall.getTargetPhoneAccount(), mCall.getTargetPhoneAccount()));
}
adjustAttemptsForConnectionManager();
adjustAttemptsForEmergency(mCall.getTargetPhoneAccount());
mAttemptRecordIterator = mAttemptRecords.iterator();
attemptNextPhoneAccount();
}其中重点逻辑在attemptNextPhoneAccount();
private void attemptNextPhoneAccount() {
CallAttemptRecord attempt = null;
if (mAttemptRecordIterator.hasNext()) {
attempt = mAttemptRecordIterator.next();
if (!mPhoneAccountRegistrar.phoneAccountRequiresBindPermission(
attempt.connectionManagerPhoneAccount)) {
attemptNextPhoneAccount();
return;
}
if (!attempt.connectionManagerPhoneAccount.equals(attempt.targetPhoneAccount) &&
!mPhoneAccountRegistrar.phoneAccountRequiresBindPermission(
attempt.targetPhoneAccount)) {
attemptNextPhoneAccount();
return;
}
}
if (mCallResponse != null && attempt != null) {
PhoneAccountHandle phoneAccount = attempt.connectionManagerPhoneAccount;
mService = mRepository.getService(phoneAccount.getComponentName(),
phoneAccount.getUserHandle());
if (mService == null) {
Log.i(this, "Found no connection service for attempt %s", attempt);
attemptNextPhoneAccount();
} else {
mConnectionAttempt++;
mCall.setConnectionManagerPhoneAccount(attempt.connectionManagerPhoneAccount);
mCall.setTargetPhoneAccount(attempt.targetPhoneAccount);
mCall.setConnectionService(mService);
setTimeoutIfNeeded(mService, attempt);
mService.createConnection(mCall, this);
}
} else {
DisconnectCause disconnectCause = mLastErrorDisconnectCause != null ?
mLastErrorDisconnectCause : new DisconnectCause(DisconnectCause.ERROR);
notifyCallConnectionFailure(disconnectCause);
}
其中主要逻辑是找到一个正确的PhoneAccount然后通过调用mService.createConnection(mCall, this),其中mService为ConnectionServiceWrapper类型的对象。
(6)ConnectionServiceWrapper中处理:
public void createConnection(final Call call, final CreateConnectionResponse response) {
BindCallback callback = new BindCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
String callId = mCallIdMapper.getCallId(call);
mPendingResponses.put(callId, response);
GatewayInfo gatewayInfo = call.getGatewayInfo();
Bundle extras = call.getIntentExtras();
if (gatewayInfo != null && gatewayInfo.getGatewayProviderPackageName() != null &&
gatewayInfo.getOriginalAddress() != null) {
extras = (Bundle) extras.clone();
extras.putString(
TelecomManager.GATEWAY_PROVIDER_PACKAGE,
gatewayInfo.getGatewayProviderPackageName());
extras.putParcelable(
TelecomManager.GATEWAY_ORIGINAL_ADDRESS,
gatewayInfo.getOriginalAddress());
}
try {
mServiceInterface.createConnection(
call.getConnectionManagerPhoneAccount(),
callId,
new ConnectionRequest(
call.getTargetPhoneAccount(),
call.getHandle(),
extras,
call.getVideoState(),
callId),
call.shouldAttachToExistingConnection(),
call.isUnknown());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(this, e, "Failure to createConnection -- %s", getComponentName());
mPendingResponses.remove(callId).handleCreateConnectionFailure(
new DisconnectCause(DisconnectCause.ERROR, e.toString()));
}
}
};
mBinder.bind(callback, call);
}其中最主要的一步还是下面的代码
mServiceInterface.createConnection(
call.getConnectionManagerPhoneAccount(),
callId,
new ConnectionRequest(
call.getTargetPhoneAccount(),
call.getHandle(),
extras,
call.getVideoState(),
callId),
call.shouldAttachToExistingConnection(),
call.isUnknown());那么问题来了mServiceInterface到底是什么东西,上面所有的分析都是在Telecomm中发生的,众所周知,android中的phone是运行在自己单独的进程中的,到此为止,以后的流程都是发生在phone进程中的,马上分析一下mServiceInterface是一个什么东西。
可以看出上面的代码是在调用mBinder.bind(callback, call)后回调函数中调用的(mBinder是ConnectionServiceWrapper的父类ServiceBinder中的一个内部类),所以才可应该是bind操作后对mServiceInterface进行了赋值。
void bind(BindCallback callback, Call call) {
Log.d(ServiceBinder.this, "bind()");
// Reset any abort request if we're asked to bind again.
clearAbort();
if (!mCallbacks.isEmpty()) {
// Binding already in progress, append to the list of callbacks and bail out.
mCallbacks.add(callback);
return;
}
mCallbacks.add(callback);
if (mServiceConnection == null) {
Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(mServiceAction).setComponent(mComponentName);
ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceBinderConnection(call);
Log.event(call, Log.Events.BIND_CS, mComponentName);
final int bindingFlags = Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE | Context.BIND_FOREGROUND_SERVICE;
final boolean isBound;
if (mUserHandle != null) {
isBound = mContext.bindServiceAsUser(serviceIntent, connection, bindingFlags,
mUserHandle);
} else {
isBound = mContext.bindService(serviceIntent, connection, bindingFlags);
}
if (!isBound) {
handleFailedConnection();
return;
}
} else {
Log.d(ServiceBinder.this, "Service is already bound.");
Preconditions.checkNotNull(mBinder);
handleSuccessfulConnection();
}
} 可以看出果然去bind了service,然后绑定成功后,应该会回调ServiceBinderConnection的onServiceConnected:
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder binder) {
try {
synchronized (mLock) {
mCall = null;
if (mIsBindingAborted) {
clearAbort();
logServiceDisconnected("onServiceConnected");
mContext.unbindService(this);
handleFailedConnection();
return;
}
mServiceConnection = this;
setBinder(binder);
handleSuccessfulConnection();
}
} finally {
Log.endSession();
}
}可以看出在绑定成功后回调用setBinder(binder)来保存获取到的远程Binder对象,看看setBinder的实现:
private void setBinder(IBinder binder) {
if (mBinder != binder) {
if (binder == null) {
removeServiceInterface();
mBinder = null;
for (Listener l : mListeners) {
l.onUnbind(this);
}
} else {
mBinder = binder;
setServiceInterface(binder);
}
}
}可以看出如果绑定成功的话会调用setServiceInterface方法,该方法是ServiceBinder的一个抽象函数,看看ServiceBinder的子类ConnectionServiceWrapper的实现:
@Override
protected void setServiceInterface(IBinder binder) {
mServiceInterface = IConnectionService.Stub.asInterface(binder);
Log.v(this, "Adding Connection Service Adapter.");
addConnectionServiceAdapter(mAdapter);
}真相大白,原来mServiceInterface就是mBinder.bind(callback, call)中绑定服务返回的远程Binder对象,下面分析到底bind了那个服务,在bind函数中明确指定了Intent的ComponentName。
Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(mServiceAction).setComponent(mComponentName);
ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceBinderConnection(call);mComponentName是从哪里来的?
public class ConnectionServiceWrapper extends ServiceBinder{
ConnectionServiceWrapper(
ComponentName componentName,
ConnectionServiceRepository connectionServiceRepository,
PhoneAccountRegistrar phoneAccountRegistrar,
CallsManager callsManager,
Context context,
TelecomSystem.SyncRoot lock,
UserHandle userHandle) {
super(ConnectionService.SERVICE_INTERFACE, componentName, context, lock, userHandle);
mConnectionServiceRepository = connectionServiceRepository;
phoneAccountRegistrar.addListener(new PhoneAccountRegistrar.Listener() {
});
mPhoneAccountRegistrar = phoneAccountRegistrar;
mCallsManager = callsManager;
mAppOpsManager = (AppOpsManager) context.getSystemService(Context.APP_OPS_SERVICE);
}
} protected ServiceBinder(String serviceAction, ComponentName componentName, Context context,
TelecomSystem.SyncRoot lock, UserHandle userHandle) {
Preconditions.checkState(!TextUtils.isEmpty(serviceAction));
Preconditions.checkNotNull(componentName);
mContext = context;
mLock = lock;
mServiceAction = serviceAction;
mComponentName = componentName;
mUserHandle = userHandle;
}可以看出mComponentName是在构造ConnectionServiceWrapper对象时候传入的。回到attemptNextPhoneAccount方法中:
private ConnectionServiceWrapper mService;
mService = mRepository.getService(phoneAccount.getComponentName(),
phoneAccount.getUserHandle());
public ConnectionServiceWrapper getService(ComponentName componentName, UserHandle userHandle) {
Pair cacheKey = Pair.create(componentName, userHandle);
ConnectionServiceWrapper service = mServiceCache.get(cacheKey);
if (service == null) {
service = new ConnectionServiceWrapper(
componentName,
this,
mPhoneAccountRegistrar,
mCallsManager,
mContext,
mLock,
userHandle);
service.addListener(mUnbindListener);
mServiceCache.put(cacheKey, service);
}
return service;
} 可以看出mComponentName来源于phoneAccount.getComponentName()(PhoneAccount为PhoneAccountHandle类型变量,PhoneAccount类中有个成员变量PhoneAccountHandle,android有时候起得变量名容易让人混淆,PhoneAccountHandle主要是保存了创建链接的服务的包名类名信息,PhoneAccount中包含了PhoneAccountHandle,还有最关键的该Account的Capabilities,支持不支持语音通话等),现在问题又来了phoneAccount是怎么来的。对于PhoneAccount我理解就是可以安卓为了打电话功能可以扩展新加的东西,现在我们手机大部分情况通过SIM卡打电话,走的是运营商网络,但是还有其他电话类型比如VOIP,具体我也不了解,所以系统可能也可以有很多的PhoneAccount。当然现在我们还是走的标准的打电话流程,我们去看看SIM卡的PhoneAccount是在哪里创建的。
在TelecomAccountRegistry中注册了PhoneAccount
private PhoneAccount registerPstnPhoneAccount(boolean isEmergency, boolean isDummyAccount) {
String dummyPrefix = isDummyAccount ? "Dummy " : "";
PhoneAccountHandle phoneAccountHandle =
PhoneUtils.makePstnPhoneAccountHandleWithPrefix(
mPhone, dummyPrefix, isEmergency);
PhoneAccount account = PhoneAccount.builder(phoneAccountHandle, label)
.setAddress(Uri.fromParts(PhoneAccount.SCHEME_TEL, line1Number, null))
.setSubscriptionAddress(
Uri.fromParts(PhoneAccount.SCHEME_TEL, subNumber, null))
.setCapabilities(capabilities)
.setIcon(icon)
.setHighlightColor(color)
.setShortDescription(description)
.setSupportedUriSchemes(Arrays.asList(
PhoneAccount.SCHEME_TEL, PhoneAccount.SCHEME_VOICEMAIL))
.setExtras(instantLetteringExtras)
.setGroupId(groupId)
.build();
mTelecomManager.registerPhoneAccount(account);
return account;
}此时我们关心的mComponentName就是在下面代码中创建的:
PhoneAccountHandle phoneAccountHandle =
PhoneUtils.makePstnPhoneAccountHandleWithPrefix(
mPhone, dummyPrefix, isEmergency);在PhoneUtils中:
private static final ComponentName PSTN_CONNECTION_SERVICE_COMPONENT =
new ComponentName("com.android.phone",
"com.android.services.telephony.TelephonyConnectionService");可以看出是在phone进程中的一个服务,所以回到最上面的代码mServiceInterface.createConnection(),其实调用的是TelephonyConnectionService的createConnection方法,好,继续往下走(注意,此时后已经进入phone进程了,上面的所有操作都不是在phone进程中的),发现TelephonyConnectionService没有实现该方法,用的父类ConnectionService的方法。该类代码路径为frameworks/base/telecomm/java/android/telecom/ConnectionService.java.给我们一个启示,我们想扩展电话功能需要继承实现该类,并注册我们自己的PhoneAccount。
private void createConnection(
final PhoneAccountHandle callManagerAccount,
final String callId,
final ConnectionRequest request,
boolean isIncoming,
boolean isUnknown) {
Connection connection = isUnknown ? onCreateUnknownConnection(callManagerAccount, request)
: isIncoming ? onCreateIncomingConnection(callManagerAccount, request)
: onCreateOutgoingConnection(callManagerAccount, request);
}我们现在是呼出,所以调用的是onCreateOutgoingConnection,该方法在ConnectionService中是空的实现,所以又回到了TelephonyConnectionService中,在onCreateOutgoingConnection中,代码很长我就不贴了,主要是创建了一个链接:
Connection resultConnection = getTelephonyConnection(request, numberToDial,
isEmergencyNumber, handle, phone);然后处理该链接
placeOutgoingConnection((TelephonyConnection) resultConnection, phone, request);重点就在该方法
private void placeOutgoingConnection(
TelephonyConnection connection, Phone phone, int videoState, Bundle extras,
ConnectionRequest request) {
com.android.internal.telephony.Connection originalConnection = null;
try {
if (phone != null) {
if (isAddParticipant) {
phone.addParticipant(number);
return;
} else {
originalConnection = phone.dial(number, null, request.getVideoState(), bundle);
}
}
}
}