【软件工程基础】结对项目——四则运算题目生成项目介绍及制作流程
一、项目介绍
首先附上项目的GitHub地址:
C++版本:https://github.com/Nevermore5421/PairingProjectCalculator
C#带界面版本:https://github.com/Nevermore5421/PairingProjectCalculatorWithGUI
拿到题目后,我和组队的同学经过讨论后,决定选择第二个项目——四则运算题目生成项目,在项目第三阶段中,我们选择的是第一个扩展方向,即将程序扩展为Windows电脑图形界面程序。然后我们对该项目的需求进行了分析:
第一阶段:
(1)生成一千道不重复的四则运算题目
(2)能解最多10个运算符的,带括号的四则运算表达式题目,并给出解
(3)支持真分数运算
(4)能接收用户输入,并给出答案对错的反馈
第二阶段:
支持乘方运算,以“^”和“**”两种方式都可表示乘方。
第三阶段:
(1)扩展程序,制作出Windows电脑图形界面程序
(2)增加倒计时功能,判断用户是否能在20秒内按时完成,并设置用户得分
(3)增加历史记录,把用户做题的成绩记录并展示
1.PSP表格预估时间
PSP表格实际时间将在博文结尾处写出
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(min) |
实际耗时(min) |
Planning |
计划 |
60 |
|
Estimate |
估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
2000 |
|
Development |
开发 |
1200 |
|
Analysis |
需求分析(包括学习新技术) |
480 |
|
Design Spec |
生成设计文档 |
60 |
|
Design Review |
设计复审(和同事审核设计文档) |
20 |
|
Coding Standard |
代码规范(为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
20 |
|
Design |
具体设计 |
200 |
|
Coding |
具体编码 |
400 |
|
Code Review |
代码复审 |
60 |
|
Test |
测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
200 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
30 |
|
Test Report |
测试报告 |
20 |
|
Size Measurement |
计算工作量 |
10 |
|
Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 |
60 |
|
|
合计 |
2000 |
|
2.解题思路描述
由于此项目时结对项目,我和合作的队友进行了分工,最终决定我负责生成题目部分,以及图形界面部分;队友负责解运算表达式部分。故在此篇介绍中我主要介绍生成题目部分的思路。
1)生成运算题目思路
刚开始思考这个问题时,发现生成一个四则运算题目本身不是一件特别难的事情,主要就有以下三个部分:
- 生成随机数字
- 生成加减乘除,乘方的算术符号
- 生成左右括号
但实际编写代码的过程中,会遇到很多细节上的问题,并没有想象中那么简单,例如:
- 生成表达式的长度要进行随机化和合理化,不能太简单也不能太难,更不能每道题都一样
- 某种特定运算符的运算数要进行合理化,除号后不能放0,乘方后不能放太大的数,不然正常人无法计算
- 运算符的随机生成过程同样要考虑合理化,不能出现连续多个乘方等难以计算的式子
- 括号的生成也需要合理化,例如除号后不能出现一个括号中算出是0的情况,也不能出现一个乘方符号后的数字虽然很小,但是带了括号,最终也变得很大,人类无法计算的情况出现
- 对真分数的计算,不能用正常方法计算
为解决上述问题,我针对每个问题进行了特殊处理:
- 对于表达式长度,我选择了用C11新标准中添加的random头文件中自带的正态分布来进行长度控制,使得大部分表达式长度在5左右,难度对大部分人比较合适,也会有几道比较难的和比较简单的题目,具体实现过程会在下一个部分中讲述
- 对于运算符和运算数合理化,我将乘方后的数(即幂数)控制在小于等于3,符合一般人的计算水平,同时我控制每个表达式中的乘方数量尽量少,同时不允许连续的乘方出现
- 对于括号的生成,我进行特殊判定,使得除号和乘方后不允许放左括号,这样也就不会出现上述问题了
- 对于真分数计算,我们写了一个类,把所有的数字(无论是否是真分数)都用分数表示,类中有分子,分母属性,同时将加减乘除和乘方符号重载,能直接计算这个类的对象
2)解运算题目思路
解四则运算式的方法并不难,基本思路将中缀表达式转为后缀表达式计算,即将运算符与运算数分别储存在两个栈中,按照一定的规则进栈与退栈。规则包括:
- 数字直接压入运算数栈
- 左括号直接压入运算符栈
- 右括号式运算符栈持续弹出直到弹出左括号为止
- 定义运算符优先级 +,- <*,/<^,**,当遇到运算符时,将使运算符栈持续弹出,直到栈顶运算符优先级小于当前运算符或者左括号以及栈空情况,在将运算符压入栈
- 每弹出一个运算符,弹出两个运算数,进行计算后再压入栈
- 当算式处理完,使运算符栈不断弹出,直至栈为空,则运算数栈栈顶即为结果
但单纯处理只能处理浮点数范围情况,由于需要支持分数情况,我们重新设计一个类,勒种包括分子,分母等分数的特征,每一数字x在一开始就化为分数x/1的情况,再将分数的特征量,记录下来,并重载+,-,*,/,^运算符,使其按照分数的规则计算。
设计完这个类后只需按照上述规则进行正常计算即可。
同时处于实际情况的考虑,我们对于运算式的生成做了一定限制,始终的数字只会在一定范围内,为了方便处理,我们将分析并切割运算式与实际计算进行了分割。我们先将运算式按照一定规则映射到一个整形数组中,其中运算符均为超出范围的整数,在处理这个整形数组得到预算结果。
3.设计实现过程
在这个项目中,我们逐渐由c语言过渡到c++,用了num类将所有数字都用分数表示,简化真分数计算。
1)类设计
上述中num类的设计如下:
class num {
private:
int numerator; //分子
int denominator; //分母
int mygcd; //公约数
void gcd(int x, int y)
{
if (y == 0)
mygcd = x;
else
gcd(y, x%y);
}
public:
num();
num(int x);
num(int x, int y);
void print();
friend num operator +(num a, num b);
friend num operator -(num a, num b);
friend num operator *(num a, num b);
friend num operator /(num a, num b);
friend num operator ^(num a, num b);
};
num::num()
{
numerator = 0;
denominator = 1;
}
num::num(int x)
{
numerator = x;
denominator = 1;
}
num::num(int x, int y)
{
numerator = x;
denominator = y;
}
void num::print()
{
gcd(numerator, denominator);
cout << numerator / mygcd;
if(denominator / mygcd!=1)
cout<<"/"<类中有分子,分母属性,以及分子分母公约数判断,以判断某个数输出时应输出分数形式还是小数形式。
类中还有五个运算符的重载,以及输出数字的成员函数
2)随机化设计
default_random_engine generator(time(NULL));
normal_distribution lendis(5, 3);
normal_distribution numdis(5, 2);
auto lendice = bind(lendis, generator);
auto numdice = bind(numdis, generator); 这段代码是C11中新增的Random头文件设计随机化的核心。
第一行代码是建立一个随机引擎,作用类似于srand()函数生成随机种子的功能,可以在系统时间的控制下生成真随机数。
2,3行代码是建立一个正态分布,其中参数第一个是期望,第二个是方差。
4,5行代码是建立一个分布和随机引擎的连接,用这个lendice和numdice变量就可以类似于rand()函数一样生成随机数了。
3)生成题目函数设计
void BuildExp(int buildnum,int mode)
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < buildnum; i++)
{
//memset(IsUseNumber, 0, sizeof(IsUseNumber));
int lastbracket = 0;
bool HavePow = false;
int expnum = RandExpLen();
int p = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= expnum; j++)
{
if (j == expnum )//最后一个数字的判断
{
Expression[i][p++] = RandExpNum(10);
if (Expression[i][p - 2] == 104 && Expression[i][p - 1] == 0)//判断分母0
Expression[i][p - 1] = 1;
if (lastbracket != 0)//若有未匹配左括号,则最后一位强制添加右括号
Expression[i][p++] = 107;
break;
}
else
{
Expression[i][p++] = RandExpNum(10);//生成随机数
if (Expression[i][p - 2] == 105)
Expression[i][p - 1] = PownumEasy();
if (Expression[i][p - 2] == 104 && Expression[i][p - 1] == 0)//判断分母0
Expression[i][p - 1] = 1;
if (RandSymbol(4) && lastbracket > 2)//右括号
{
Expression[i][p++] = 107;
lastbracket = 0;
}
Expression[i][p++] = RandSymbol(mode);//生成随机符号
{//检查乘方个数
if (Expression[i][p - 1] == 105 && HavePow)
Expression[i][p - 1] = RandSymbol(1);
else if (Expression[i][p - 1] == 105)
HavePow = true;
}
if (RandSymbol(4)&&j代码的主要功能都有相应注释进行解释,这是生成题目的主循环,对上述提到的多个问题进行了特殊处理和解决。
4)运算式映射设计
void changeintomaped(char * formula, int * maped)
{
int temp = -1, pos = 0, flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; formula[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
if (formula[i] == ' ') //跳过空格
continue;
if (formula[i] >= '0'&&formula[i] <= '9')
{
if (temp == -1) //数字可能为0,为碰到数字时将计数置为-1,碰到数字后开始
temp = 0;
temp *= 10;
temp += formula[i] - '0';
}
else
{
if (temp != -1) //在数字后遇到第一个非数字符号,将之前累加的数字置入
{
maped[pos++] = temp;
temp = -1;
}
if (formula[i] == '+')
maped[pos++] = 101;
else if (formula[i] == '-')
maped[pos++] = 102;
else if (formula[i] == '*') //称号后若第一个非空格字符为乘号则为乘方,否则为乘号
{
int j;
for (j = i + 1; formula[j] == ' '; j++);
if (formula[j] == '*')
{
maped[pos++] = 105;
i = j;
}
else
maped[pos++] = 103;
}
else if (formula[i] == '/')
maped[pos++] = 104;
else if (formula[i] == '^')
maped[pos++] = 105;
else if (formula[i] == '(')
maped[pos++] = 106;
else if (formula[i] == ')')
maped[pos++] = 107;
}
}
if (temp != -1)
{
maped[pos++] = temp;
temp = -1;
}
}
设定的运算数的范围为0-100,将+,-,*,/,^,(),映射到101-107,其中^与**功能相同均为105.
5)解运算式设计
num calculate(num num1, num num2, int opera)
{
if (opera == 101)
return num1 + num2;
else if (opera == 102)
return num1 - num2;
else if (opera == 103)
return num1*num2;
else if (opera == 104)
return num1 / num2;
else if (opera == 105)
return num1^num2;
}
num getans(int * operation)
{
/*将四则运算映射到一串十进制数,0-100为运算数,
101-104分别代表+,-,*,/,105为乘方,106为左括号,107为右括号*/
stack operators; //运算符栈
stack operand; //运算数栈
for (int i = 0; i= 0 && operation[i] <= 100)
{
num temp(operation[i]);
operand.push(temp);
}
else if (operation[i] == 105 || operation[i] == 106) //左括号与乘方必定入栈
operators.push(operation[i]);
else if (operation[i] == 103 || operation[i] == 104) //乘除会弹出乘方与乘除
{
while (!operators.empty() && (operators.top() == 103||operators.top() == 104|| operators.top() == 105))
{
int opera = operators.top();
operators.pop();
num num1 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
num num2 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
operand.push(calculate(num2, num1, opera));
}
operators.push(operation[i]);
}
else if (operation[i] == 101 || operation[i] == 102) //加减可能弹出乘除与乘方
{
while (!operators.empty() && (operators.top() != 106 && operators.top() != 107))
{
int opera = operators.top();
operators.pop();
num num1 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
num num2 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
operand.push(calculate(num2, num1, opera));
}
operators.push(operation[i]);
}
else if (operation[i] == 107) //右括号会一直弹出直至左括号
{
while (operators.top() != 106)
{
int opera = operators.top();
operators.pop();
num num1 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
num num2 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
operand.push(calculate(num2, num1, opera));
}
operators.pop();
}
}
while (!operators.empty())
{
int opera = operators.top();
operators.pop();
num num1 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
num num2 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
operand.push(calculate(num2, num1, opera));
}
return operand.top(); //最终运算数栈顶为结果
}
按照运算规则进行计算,即可得到结果。
4.扩展功能实现——C#Winform界面
要实现C++的界面,现在主流的方法是mfc和qt,但是经过几天的学习,我们发现在我们的程序中,有部分代码使用mfc会非常困难,要修改很多内容,导致一直调不好bug,所以考虑更换思路。
由于我们两人都有C#的基础,所以我们考虑把C++的代码进行彻底地封装,改成C#来实现,再使用C#中比较方便简洁的界面——Winform来进行实现。
1)将C++代码转化为C#代码
在从C++代码修改为C#代码的过程中,除了语法上的不同,我们还发现在原先C++的代码中,有一些功能需要更进一步的整合和封装。由于C#中每一个文件就是一个类,所以原先c++头文件中可能把很多不同功能的函数放到了一起,在C#中我们就需把所有相同功能封装到一个类中。
例如以下代码是解题代码C++部分和C#部分的对比:
C++代码:
num getans(int * operation)
{
/*将四则运算映射到一串十进制数,0-100为运算数,
101-104分别代表+,-,*,/,105为乘方,106为左括号,107为右括号*/
stack operators;
stack operand;
for (int i = 0; i= 0 && operation[i] <= 100)
{
num temp(operation[i]);
operand.push(temp);
}
else if (operation[i] == 105 || operation[i] == 106) //左括号与乘方必定入栈
operators.push(operation[i]);
else if (operation[i] == 103 || operation[i] == 104) //乘除会弹出乘方与乘除
{
while (!operators.empty() && (operators.top() == 103||operators.top() == 104|| operators.top() == 105))
{
int opera = operators.top();
operators.pop();
num num1 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
num num2 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
operand.push(calculate(num2, num1, opera));
}
operators.push(operation[i]);
}
else if (operation[i] == 101 || operation[i] == 102) //加减可能弹出乘除与乘方
{
while (!operators.empty() && (operators.top() != 106 && operators.top() != 107))
{
int opera = operators.top();
operators.pop();
num num1 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
num num2 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
operand.push(calculate(num2, num1, opera));
}
operators.push(operation[i]);
}
else if (operation[i] == 107) //右括号会一直弹出直至左括号
{
while (operators.top() != 106)
{
int opera = operators.top();
operators.pop();
num num1 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
num num2 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
operand.push(calculate(num2, num1, opera));
}
operators.pop();
}
}
while (!operators.empty())
{
int opera = operators.top();
operators.pop();
num num1 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
num num2 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
operand.push(calculate(num2, num1, opera));
}
return operand.top();
}
C#代码:
class Ans
{
/*要求用户输入答案并与结果比较*/
public int GetResult(MyNumber res,string yourans)
{
int formflag = CheckYourAnswer(yourans); //判断答案格式是否正确
if (formflag == 1)
{
//sign代表答案符号,ansnum[0]为分子,[1]为分母
int[] ansnum = new int[] { 0, 1 };
int sign = TurnToNumber(yourans, ansnum);
if (ansnum[1] != 0) //判断分母是否为0
{
MyNumber yourres = new MyNumber(ansnum[0], ansnum[1], sign);
if (yourres == res)
{
return 1;
}
//cout << "Right" << endl;
else
{
return 0;
}
//cout << "Wrong" << endl;
}
else
return 0;
}
else
return 3;
}
/*判断答案格式*/
int CheckYourAnswer(string yourans)
{
int[] flag =new int[50];
int pos = 0;
for (int i = 0; i<50; i++)
flag[i] = 0;
for (int i = 0; yourans[i] == ' '; i++) //去除前置空格
flag[i] = 1;
while (pos= 0 && yourans[i] == ' '; i--) //去除后置空格
flag[i] = 1;
string tempans="";
for (int i = 0; i= '0' && yourans[i] <= '9')
continue;
else if (yourans[i] == '/' && divisioncnt < 1)
{
divisioncnt++;
continue;
}
else if (yourans[i] == '-' && (i == 0 || yourans[i - 1] == '/' || yourans[i - 1] == '-'))
continue;
else
{
formflag = 0;
break;
}
}
return formflag;
}
/*将答案字符串转为数字*/
int TurnToNumber(string yourans, int[] ansnum)
{
int pos = 0, sign = 1;
for (int i = 0; i= '0' && yourans[i] <= '9')
ansnum[pos] = ansnum[pos] * 10 + yourans[i] - '0';
else if (yourans[i] == '/')
{
pos++;
ansnum[pos] = 0;
}
}
return sign;
}
} 2)用Winform实现界面
由于这个项目中所需的界面并不复杂,所以我们把界面中需要实现的功能集成在了一个框体中。
接下来我们将对每个功能分别进行解说:
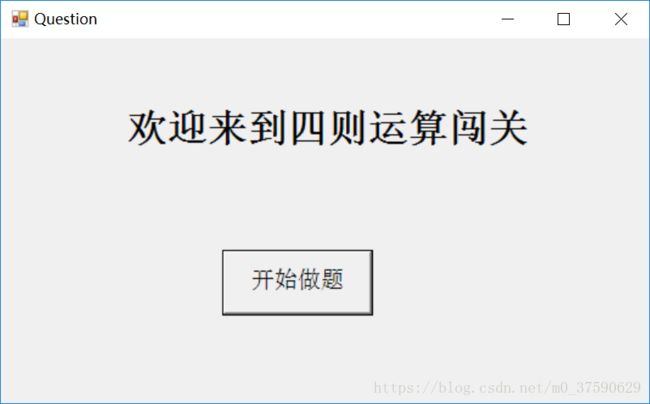
①目录界面
这个界面是程序开始时的初始界面,点击开始做题就会开始第一题。
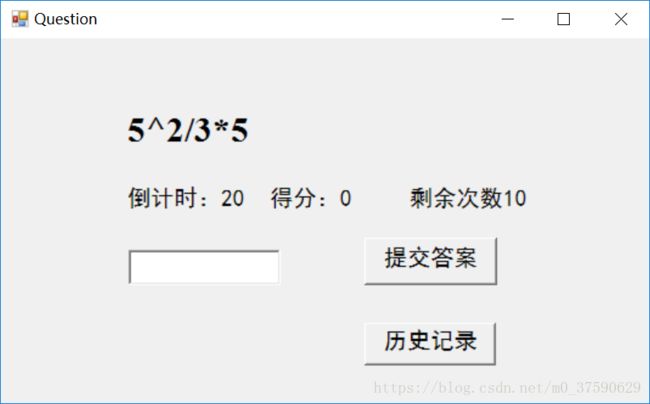
②主要做题界面
下面三张图是最主要向用户呈现的界面,可见在界面上方是用加粗字体显示的题目,题目下方有倒计时,得分和剩余次数。
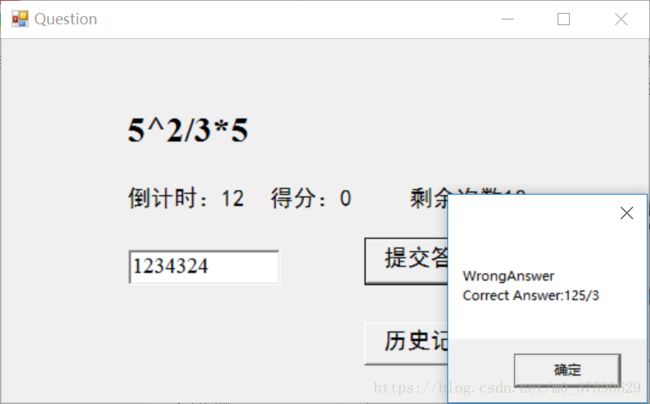
每道题都会有20秒的倒计时,20秒时间到未作答或作答错误都会减少一次剩余次数,剩余次数减为0时,退出程序;作答错误还会在弹出的框体中显示正确答案;
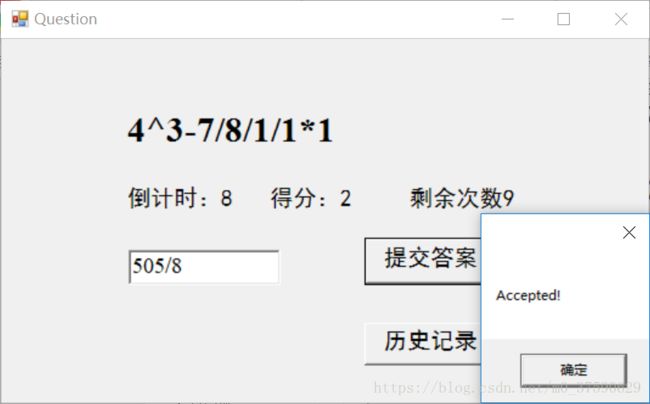
而作答正确,则会得分加一分。
输入中支持分数,且可以不进行约分。不支持小数(为了避免无法除尽的情况)。如果出现除了数字和分号的其他字符,则会报格式错误,并且让用户进行重新输入。
③历史记录功能
点击框体中的历史记录按钮,会显示出当次运行程序中碰到的所有题目,会显示题目的正确答案,用户可以检查自己计算错误在哪里。
点击返回即继续做点击历史记录前的题目。
下面是提交答案按钮(也是最主要的按钮)的代码实现:
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (ansText.Text == "")
{
ansText.Focus();
return;
}
Ans ans = new Ans();
MyNumber correctAnswer = calculate.GetAns(save, build.p);
int ansflag = ans.GetResult(correctAnswer, this.ansText.Text);
string correctAnswerStr = correctAnswer.M_ToString();
if (ansflag == 1)
{
timer1.Stop();
MessageBox.Show("Accepted!\n");
timer1.Start();
score++;
scoreText.Text = "得分:" + score.ToString();
button1_Click(null, null);
this.ansText.Text = "";
totalTime = 20;
}
else if (ansflag == 0)
{
timer1.Stop();
MessageBox.Show("WrongAnswer\n"+ "Correct Answer:" + correctAnswerStr);
timer1.Start();
chance=chance-1;
if (chance <= 0)
{
MessageBox.Show("错误次数过多!");
Application.Exit();
}
hp.Text = "剩余次数" + chance.ToString();
button1_Click(null, null);
this.ansText.Text = "";
totalTime = 20;
}
else
{
timer1.Stop();
MessageBox.Show("输入格式有误!");
timer1.Start();
this.ansText.Text = "";
this.ansText.Focus();
}
record.Text += build.M_ToString() + "="+correctAnswerStr+"\r\n";
}5.PSP表格实际时间
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(min) |
实际耗时(min) |
Planning |
计划 |
60 |
80 |
Estimate |
估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
2000 |
2500 |
Development |
开发 |
1200 |
1500 |
Analysis |
需求分析(包括学习新技术) |
480 |
300 |
Design Spec |
生成设计文档 |
60 |
60 |
Design Review |
设计复审(和同事审核设计文档) |
20 |
30 |
Coding Standard |
代码规范(为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
20 |
30 |
Design |
具体设计 |
200 |
300 |
Coding |
具体编码 |
400 |
500 |
Code Review |
代码复审 |
60 | 50 |
Test |
测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
200 |
120 |
Reporting |
报告 |
30 |
40 |
Test Report |
测试报告 |
20 |
30 |
Size Measurement |
计算工作量 |
10 |
10 |
Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 |
60 |
60 |
|
合计 |
2000 |
2500 |
总结:
通过这个项目的学习和制作,我学习到了如何在多人项目中和队友进行合作,交流,使我们俩的代码结合到一起有1+1>2的效果,同时我学习了很多软件制作过程中的基本技巧学会了开发前进行计划,安排和设计。