- SpringBlade dict-biz/list 接口 SQL 注入漏洞
文章永久免费只为良心
oracle数据库
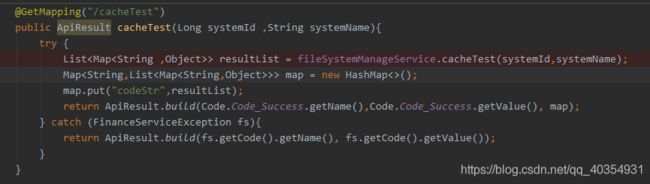
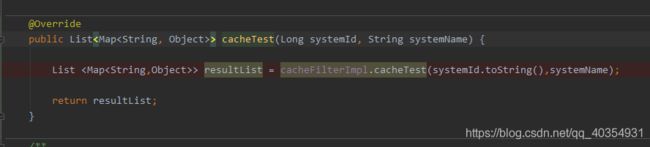
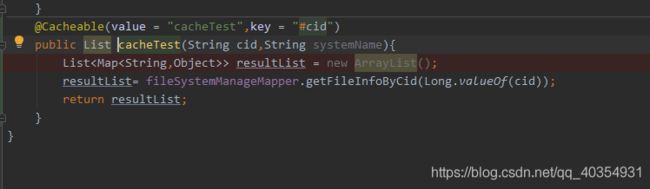
SpringBladedict-biz/list接口SQL注入漏洞POC:构造请求包查看返回包你的网址/api/blade-system/dict-biz/list?updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,md5(1),0x7e),1)=1漏洞概述在SpringBlade框架中,如果dict-biz/list接口的后台处理逻辑没有正确地对用户输入进行过滤或参数化查询(PreparedSta
- spring如何整合druid连接池?
惜.己
springspringjunit数据库javaidea后端xml
目录spring整合druid连接池1.新建maven项目2.新建mavenModule3.导入相关依赖4.配置log4j2.xml5.配置druid.xml1)xml中如何引入properties2)下面是配置文件6.准备jdbc.propertiesJDBC配置项解释7.配置druid8.测试spring整合druid连接池1.新建maven项目打开IDE(比如IntelliJIDEA,Ecl
- SpringCloudAlibaba—Sentinel(限流)
菜鸟爪哇
前言:自己在学习过程的记录,借鉴别人文章,记录自己实现的步骤。借鉴文章:https://blog.csdn.net/u014494148/article/details/105484410Sentinel介绍Sentinel诞生于阿里巴巴,其主要目标是流量控制和服务熔断。Sentinel是通过限制并发线程的数量(即信号隔离)来减少不稳定资源的影响,而不是使用线程池,省去了线程切换的性能开销。当资源
- springboot+vue项目实战一-创建SpringBoot简单项目
苹果酱0567
面试题汇总与解析springboot后端java中间件开发语言
这段时间抽空给女朋友搭建一个个人博客,想着记录一下建站的过程,就当做笔记吧。虽然复制zjblog只要一个小时就可以搞定一个网站,或者用cms系统,三四个小时就可以做出一个前后台都有的网站,而且想做成啥样也都行。但是就是要从新做,自己做的意义不一样,更何况,俺就是专门干这个的,嘿嘿嘿要做一个网站,而且从零开始,首先呢就是技术选型了,经过一番思量决定选择-SpringBoot做后端,前端使用Vue做一
- Spring MVC 全面指南:从入门到精通的详细解析
一杯梅子酱
技术栈学习springmvcjava
引言:SpringMVC,作为Spring框架的一个重要模块,为构建Web应用提供了强大的功能和灵活性。无论是初学者还是有一定经验的开发者,掌握SpringMVC都将显著提升你的Web开发技能。本文旨在为初学者提供一个全面且易于理解的学习路径,通过详细的知识点分析和实际案例,帮助你快速上手SpringMVC,让学习过程既深刻又高效。一、SpringMVC简介1.1什么是SpringMVC?Spri
- Spring Boot中实现跨域请求
BABA8891
springboot后端java
在SpringBoot中实现跨域请求(CORS,Cross-OriginResourceSharing)可以通过多种方式,以下是几种常见的方法:1.使用@CrossOrigin注解在SpringBoot中,你可以在控制器或者具体的请求处理方法上使用@CrossOrigin注解来允许跨域请求。在控制器上应用:importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.
- 博客网站制作教程
2401_85194651
javamaven
首先就是技术框架:后端:Java+SpringBoot数据库:MySQL前端:Vue.js数据库连接:JPA(JavaPersistenceAPI)1.项目结构blog-app/├──backend/│├──src/main/java/com/example/blogapp/││├──BlogApplication.java││├──config/│││└──DatabaseConfig.java
- RabbitMQ生产者重复机制与确认机制
java炒饭小能手
java-rabbitmqrabbitmqjava
重复机制生产者发送消息时,出现了网络故障,导致与MQ的连接中断。为了解决这个问题,SpringAMQP提供的消息发送时的重试机制。即:当RabbitTemplate与MQ连接超时后,多次重试。需要修该发送端模块的application.yaml文件,添加下面的内容:spring:rabbitmq:connection-timeout:1s#设置MQ的连接超时时间template:retry:ena
- 【Java】已解决:org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.DataSourceLookupFailureException
屿小夏
java开发语言
文章目录一、分析问题背景问题背景描述出现问题的场景二、可能出错的原因三、错误代码示例四、正确代码示例五、注意事项已解决:org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.DataSourceLookupFailureException在使用Spring框架进行开发时,数据源的配置和使用是非常关键的一环。然而,有时候我们可能会遇到org.springframewo
- SpringBoot和SpringMVC是什么关系?SpringBoot替代SpringMVC了吗?
瑞金彭于晏
springboot后端javaMVCspring数据库
SpringBoot和SpringMVC都是SpringFramework生态系统中的一部分,但它们各自扮演着不同的角色和提供不同的功能集。理解它们之间的关系,首先需要了解SpringFramework本身。SpringFrameworkSpringFramework是一个全面的、开源的应用程序开发框架,它提供了广泛的功能来支持企业应用开发的几乎所有方面。SpringFramework的核心特性之
- spring mvc @RequestBody String类型参数
zoyation
spring-mvcspringmvc
通过如下配置:text/html;charset=UTF-8application/json;charset=UTF-8在springmvc的Controller层使用@RequestBody接收Content-Type为application/json的数据时,默认支持Map方式和对象方式参数@RequestMapping(value="/{code}/saveUser",method=Requ
- Java -jar 如何在后台运行项目
vincent_hahaha
撸了今年阿里、头条和美团的面试,我有一个重要发现.......>>>说到运行jar包通常我们都会以下面的方式运行:java-jarspringboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar这样运行的话会有一个问题,就是我们一关闭当前窗口就会停止运行项目,要想解决这个问题,就需要在后台运行。nohupjava-jarbabyshark-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar >log.file 2>&
- spring security中几大组件的作用和执行顺序
阿信在这里
javaspring
springsecurity中几大组件的作用和执行顺序在SpringSecurity中,AuthenticationProvider、GroupPermissionEvaluator、PermissionEvaluator、AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter、DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler和ManageSecu
- 探索Zebra4J:构建高效企业级Web应用的微服务框架
叶准鑫Natalie
探索Zebra4J:构建高效企业级Web应用的微服务框架ZebraZebra4J/Zebra4Js基于SpringBoot的JavaWeb/Nodejs框架项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/zebra/Zebra项目介绍在当今快速发展的技术环境中,构建高效、可扩展的企业级Web应用是每个开发团队的追求。Zebra4J作为一款基于SpringBoot的全新微服务
- 基于JavaWeb开发的Java+SpringMvc+vue+element实现上海汽车博物馆平台
网顺技术团队
成品程序项目javavue.js汽车课程设计springboot
基于JavaWeb开发的Java+SpringMvc+vue+element实现上海汽车博物馆平台作者主页网顺技术团队欢迎点赞收藏⭐留言文末获取源码联系方式查看下方微信号获取联系方式承接各种定制系统精彩系列推荐精彩专栏推荐订阅不然下次找不到哟Java毕设项目精品实战案例《1000套》感兴趣的可以先收藏起来,还有大家在毕设选题,项目以及论文编写等相关问题都可以给我留言咨询,希望帮助更多的人文章目录基
- 分布式锁和spring事务管理
暴躁的鱼
锁及事务分布式springjava
最近开发一个小程序遇到一个需求需要实现分布式事务管理业务需求用户在使用小程序的过程中可以查看景点,对景点地区或者城市标记是否想去,那么需要统计一个地点被标记的人数,以及记录某个用户对某个地点是否标记为想去,用两个表存储数据,一个地点表记录改地点被标记的次数,一个用户意向表记录某个用户对某个地点是否标记为想去。由于可能有多个用户同时标记一个地点,每个用户在前端点击想去按钮之后,后台接收到请求,从数据
- Java面试笔记记录6
今天背八股了吗
java面试笔记
1.Spring是什么?特性?有哪些模块?Spring是一个轻量级、非入侵式的控制反转Ioc和面向切面AOP的框架。特性:1.Ioc和DISpring的核心就是一个大的工厂容器,可以维护所有对象的创建和依赖关系,Spring工厂用于生成Bean,并且管理Bean的生命周期,实现高内聚低耦合的设计理念。2.AOP编程Spring提供面向切面编程,可以方便实现对程序进行权限拦截、运行监控等切面功能。3
- Sentinel
眼泪落在琴弦
springcloudjavajava
Sentinel(服务熔断降级限流)1.引入spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel2.下载sentinel服务器3.配置application地址信息4.在控制台调整参数【默认所以流控设置保存在内存中,重启失效】5.想实时监控需每个微服务导入actuator,并配置application暴露所有端口6.自定义sentinel流控返回数据7.配置sentinel类
- Spring @Async 深度解读:默认线程池执行器的配置与优化
小码快撩
springjava前端
在Spring中,@Async注解用于异步执行方法。默认情况下,@Async注解的任务是由一个线程池执行的。然而,这个默认的线程池是如何初始化的呢?本文将深入探讨这一过程,帮助你理解Spring异步任务背后的线程池执行器的初始化原理。1.@Async的基本使用首先,让我们快速回顾一下@Async的基本用法。@Async通常用于标注在需要异步执行的方法上,比如:@Servicepublicclass
- Sentinel实时监控不展示问题
朱杰jjj
sentinelsentinel
问题官方插件Endpoint支持,可以实时统计出SpringBoot的健康状况和请求的调用信息在使用Endpoint特性之前需要在Maven中添加spring-boot-starter-actuator依赖,并在配置中允许Endpoints的访问。SpringBoot1.x中添加配置management.security.enabled=false。暴露的endpoint路径为/sentinelS
- 36. MyBatis如何支持多数据库操作?如何配置不同的数据源?
这孩子叫逆
Mybatis笔记mybatis数据库
在许多企业级应用中,可能需要访问多个数据库。MyBatis可以通过配置多个数据源和动态切换数据源来支持多数据库操作。下面介绍如何在MyBatis中配置和使用多个数据源。1.多数据源的基本配置1.1配置多个数据源要支持多个数据源,首先需要在Spring或SpringBoot中配置不同的数据源。假设我们要连接两个数据库db1和db2,可以通过以下步骤进行配置。SpringBoot示例:applicat
- SpringBoot整合ES搜索引擎 实现网站热搜词及热度计算
码踏云端
springbootElasticsearchspringbootelasticsearch后端热搜词热度计算java
博主简介:历代文学网(PC端可以访问:https://literature.sinhy.com/#/literature?__c=1000,移动端可微信小程序搜索“历代文学”)总架构师,15年工作经验,精通Java编程,高并发设计,Springboot和微服务,熟悉Linux,ESXI虚拟化以及云原生Docker和K8s,热衷于探索科技的边界,并将理论知识转化为实际应用。保持对新技术的好奇心,乐于
- Spring Security静态资源过滤(11)
小黑屋说YYDS
spring
在一个实际项目中,并非所有的请求都需要经过SpringSecurity过滤器,有一些特殊的请求,例如静态资源等,一般来说并不需要经过SpringSecurity过滤器链,用户如果访问这些静态资源,直接返回对应的资源即可。回顾关于WebSecurity的讲解,提到它里边维护了一个ignoredRequests变量,该变量,记录的就是所有需要被忽略的请求,这些被忽略的请求将不再经过SpringSecu
- Spring Security定义多个过滤器链(10)
小黑屋说YYDS
spring
在SpringSecurity中可以同时存在多个过滤器链,一个WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的实例就可以配置一条过滤器链。我们来看如下一个案例:@ConfigurationpublicclassSecurityConfig{@BeanUserDetailsServiceus(){InMemoryUserDetailsManagerusers=newInMemoryUser
- java 技术 架构 相关文档
圣心
java架构开发语言
在Java中,有许多不同的技术和架构,这里我将列举一些常见的Java技术和架构,并提供一些相关的文档资源。SpringFrameworkSpring是一个开源的Java/JavaEE全功能框架,以Apache许可证形式发布,提供了一种实现企业级应用的方法。官方文档:SpringFrameworkSpringBootSpringBoot是Spring的一个子项目,旨在简化创建生产级的Spring应用
- SpringSecurity初学总结
weixin_66442229
spring
springSecurity安全框架基于Java的安全框架主要有:SpringSecurity和Shiro介绍基础概念安全框架是对用户访问权限的控制,保证应用的安全性。其主要的工作是用户认证和用户授权|鉴权主要应用于Spring的企业应用系统,提供声明式的安全访问控制解决方案。它提供了一组可以在Spring应用上下文中配置的Bean能很好的结合Spring的DI依赖注入和AOP面向切面编程功能应用
- java获取applicationcontext,SpringBoot获取ApplicationContext的3种方式
花儿街参考
ApplicationContext是什么?简单来说就是Spring中的容器,可以用来获取容器中的各种bean组件,注册监听事件,加载资源文件等功能。ApplicationContext获取的几种方式1直接使用Autowired注入@ComponentpublicclassBook1{@AutowiredprivateApplicationContextapplicationContext;pub
- SpringBoot 设置传入参数非必要
loveLifeLoveCoding
springbootspringbootjavaspring
查看RequestParam源码packageorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation;importjava.lang.annotation.Documented;importjava.lang.annotation.ElementType;importjava.lang.annotation.Retention;importjava.lang.annotat
- SpringBoot 获取 ApplicationContext
loveLifeLoveCoding
springbootspringbootjavaspring
1.概念ApplicationContext是什么?简单来说就是Spring中的容器,可以用来获取容器中的各种bean组件,注册监听事件,加载资源文件等功能2.获取ApplicationContext的方式2.1.创建工具类通过此工具类,可以方便的获取bean组件,获取配置信息等importorg.springframework.beans.BeansException;importorg.spr
- java打印标签(机型TOSHIBA条码打印机B-EX4T)
嘘
JAVAjava
java打印标签实现方式标签效果代码获取更多相关资料实现rfid写入功能实现方式打印机设置网络ipjava获取socket连接,调用TPCL指令标签效果代码packageorg.jeecg.modules.invinfo.util;importorg.jeecg.modules.invinfo.vo.BatKcInventoryDetailVo;importorg.springframework.
- java封装继承多态等
麦田的设计者
javaeclipsejvmcencapsulatopn
最近一段时间看了很多的视频却忘记总结了,现在只能想到什么写什么了,希望能起到一个回忆巩固的作用。
1、final关键字
译为:最终的
&
- F5与集群的区别
bijian1013
weblogic集群F5
http请求配置不是通过集群,而是F5;集群是weblogic容器的,如果是ejb接口是通过集群。
F5同集群的差别,主要还是会话复制的问题,F5一把是分发http请求用的,因为http都是无状态的服务,无需关注会话问题,类似
- LeetCode[Math] - #7 Reverse Integer
Cwind
java题解MathLeetCodeAlgorithm
原题链接:#7 Reverse Integer
要求:
按位反转输入的数字
例1: 输入 x = 123, 返回 321
例2: 输入 x = -123, 返回 -321
难度:简单
分析:
对于一般情况,首先保存输入数字的符号,然后每次取输入的末位(x%10)作为输出的高位(result = result*10 + x%10)即可。但
- BufferedOutputStream
周凡杨
首先说一下这个大批量,是指有上千万的数据量。
例子:
有一张短信历史表,其数据有上千万条数据,要进行数据备份到文本文件,就是执行如下SQL然后将结果集写入到文件中!
select t.msisd
- linux下模拟按键输入和鼠标
被触发
linux
查看/dev/input/eventX是什么类型的事件, cat /proc/bus/input/devices
设备有着自己特殊的按键键码,我需要将一些标准的按键,比如0-9,X-Z等模拟成标准按键,比如KEY_0,KEY-Z等,所以需要用到按键 模拟,具体方法就是操作/dev/input/event1文件,向它写入个input_event结构体就可以模拟按键的输入了。
linux/in
- ContentProvider初体验
肆无忌惮_
ContentProvider
ContentProvider在安卓开发中非常重要。与Activity,Service,BroadcastReceiver并称安卓组件四大天王。
在android中的作用是用来对外共享数据。因为安卓程序的数据库文件存放在data/data/packagename里面,这里面的文件默认都是私有的,别的程序无法访问。
如果QQ游戏想访问手机QQ的帐号信息一键登录,那么就需要使用内容提供者COnte
- 关于Spring MVC项目(maven)中通过fileupload上传文件
843977358
mybatisspring mvc修改头像上传文件upload
Spring MVC 中通过fileupload上传文件,其中项目使用maven管理。
1.上传文件首先需要的是导入相关支持jar包:commons-fileupload.jar,commons-io.jar
因为我是用的maven管理项目,所以要在pom文件中配置(每个人的jar包位置根据实际情况定)
<!-- 文件上传 start by zhangyd-c --&g
- 使用svnkit api,纯java操作svn,实现svn提交,更新等操作
aigo
svnkit
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/hardwin/article/details/7963318
import java.io.File;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.tmatesoft.svn.core.SVNCommitInfo;
import org.tmateso
- 对比浏览器,casperjs,httpclient的Header信息
alleni123
爬虫crawlerheader
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException
{
String type=req.getParameter("type");
Enumeration es=re
- java.io操作 DataInputStream和DataOutputStream基本数据流
百合不是茶
java流
1,java中如果不保存整个对象,只保存类中的属性,那么我们可以使用本篇文章中的方法,如果要保存整个对象 先将类实例化 后面的文章将详细写到
2,DataInputStream 是java.io包中一个数据输入流允许应用程序以与机器无关方式从底层输入流中读取基本 Java 数据类型。应用程序可以使用数据输出流写入稍后由数据输入流读取的数据。
- 车辆保险理赔案例
bijian1013
车险
理赔案例:
一货运车,运输公司为车辆购买了机动车商业险和交强险,也买了安全生产责任险,运输一车烟花爆竹,在行驶途中发生爆炸,出现车毁、货损、司机亡、炸死一路人、炸毁一间民宅等惨剧,针对这几种情况,该如何赔付。
赔付建议和方案:
客户所买交强险在这里不起作用,因为交强险的赔付前提是:“机动车发生道路交通意外事故”;
如果是交通意外事故引发的爆炸,则优先适用交强险条款进行赔付,不足的部分由商业
- 学习Spring必学的Java基础知识(5)—注解
bijian1013
javaspring
文章来源:http://www.iteye.com/topic/1123823,整理在我的博客有两个目的:一个是原文确实很不错,通俗易懂,督促自已将博主的这一系列关于Spring文章都学完;另一个原因是为免原文被博主删除,在此记录,方便以后查找阅读。
有必要对
- 【Struts2一】Struts2 Hello World
bit1129
Hello world
Struts2 Hello World应用的基本步骤
创建Struts2的Hello World应用,包括如下几步:
1.配置web.xml
2.创建Action
3.创建struts.xml,配置Action
4.启动web server,通过浏览器访问
配置web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="
- 【Avro二】Avro RPC框架
bit1129
rpc
1. Avro RPC简介 1.1. RPC
RPC逻辑上分为二层,一是传输层,负责网络通信;二是协议层,将数据按照一定协议格式打包和解包
从序列化方式来看,Apache Thrift 和Google的Protocol Buffers和Avro应该是属于同一个级别的框架,都能跨语言,性能优秀,数据精简,但是Avro的动态模式(不用生成代码,而且性能很好)这个特点让人非常喜欢,比较适合R
- lua set get cookie
ronin47
lua cookie
lua:
local access_token = ngx.var.cookie_SGAccessToken
if access_token then
ngx.header["Set-Cookie"] = "SGAccessToken="..access_token.."; path=/;Max-Age=3000"
end
- java-打印不大于N的质数
bylijinnan
java
public class PrimeNumber {
/**
* 寻找不大于N的质数
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=100;
PrimeNumber pn=new PrimeNumber();
pn.printPrimeNumber(n);
System.out.print
- Spring源码学习-PropertyPlaceholderHelper
bylijinnan
javaspring
今天在看Spring 3.0.0.RELEASE的源码,发现PropertyPlaceholderHelper的一个bug
当时觉得奇怪,上网一搜,果然是个bug,不过早就有人发现了,且已经修复:
详见:
http://forum.spring.io/forum/spring-projects/container/88107-propertyplaceholderhelper-bug
- [逻辑与拓扑]布尔逻辑与拓扑结构的结合会产生什么?
comsci
拓扑
如果我们已经在一个工作流的节点中嵌入了可以进行逻辑推理的代码,那么成百上千个这样的节点如果组成一个拓扑网络,而这个网络是可以自动遍历的,非线性的拓扑计算模型和节点内部的布尔逻辑处理的结合,会产生什么样的结果呢?
是否可以形成一种新的模糊语言识别和处理模型呢? 大家有兴趣可以试试,用软件搞这些有个好处,就是花钱比较少,就算不成
- ITEYE 都换百度推广了
cuisuqiang
GoogleAdSense百度推广广告外快
以前ITEYE的广告都是谷歌的Google AdSense,现在都换成百度推广了。
为什么个人博客设置里面还是Google AdSense呢?
都知道Google AdSense不好申请,这在ITEYE上也不是讨论了一两天了,强烈建议ITEYE换掉Google AdSense。至少,用一个好申请的吧。
什么时候能从ITEYE上来点外快,哪怕少点
- 新浪微博技术架构分析
dalan_123
新浪微博架构
新浪微博在短短一年时间内从零发展到五千万用户,我们的基层架构也发展了几个版本。第一版就是是非常快的,我们可以非常快的实现我们的模块。我们看一下技术特点,微博这个产品从架构上来分析,它需要解决的是发表和订阅的问题。我们第一版采用的是推的消息模式,假如说我们一个明星用户他有10万个粉丝,那就是说用户发表一条微博的时候,我们把这个微博消息攒成10万份,这样就是很简单了,第一版的架构实际上就是这两行字。第
- 玩转ARP攻击
dcj3sjt126com
r
我写这片文章只是想让你明白深刻理解某一协议的好处。高手免看。如果有人利用这片文章所做的一切事情,盖不负责。 网上关于ARP的资料已经很多了,就不用我都说了。 用某一位高手的话来说,“我们能做的事情很多,唯一受限制的是我们的创造力和想象力”。 ARP也是如此。 以下讨论的机子有 一个要攻击的机子:10.5.4.178 硬件地址:52:54:4C:98
- PHP编码规范
dcj3sjt126com
编码规范
一、文件格式
1. 对于只含有 php 代码的文件,我们将在文件结尾处忽略掉 "?>" 。这是为了防止多余的空格或者其它字符影响到代码。例如:<?php$foo = 'foo';2. 缩进应该能够反映出代码的逻辑结果,尽量使用四个空格,禁止使用制表符TAB,因为这样能够保证有跨客户端编程器软件的灵活性。例
- linux 脱机管理(nohup)
eksliang
linux nohupnohup
脱机管理 nohup
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2166699
nohup可以让你在脱机或者注销系统后,还能够让工作继续进行。他的语法如下
nohup [命令与参数] --在终端机前台工作
nohup [命令与参数] & --在终端机后台工作
但是这个命令需要注意的是,nohup并不支持bash的内置命令,所
- BusinessObjects Enterprise Java SDK
greemranqq
javaBOSAPCrystal Reports
最近项目用到oracle_ADF 从SAP/BO 上调用 水晶报表,资料比较少,我做一个简单的分享,给和我一样的新手 提供更多的便利。
首先,我是尝试用JAVA JSP 去访问的。
官方API:http://devlibrary.businessobjects.com/BusinessObjectsxi/en/en/BOE_SDK/boesdk_ja
- 系统负载剧变下的管控策略
iamzhongyong
高并发
假如目前的系统有100台机器,能够支撑每天1亿的点击量(这个就简单比喻一下),然后系统流量剧变了要,我如何应对,系统有那些策略可以处理,这里总结了一下之前的一些做法。
1、水平扩展
这个最容易理解,加机器,这样的话对于系统刚刚开始的伸缩性设计要求比较高,能够非常灵活的添加机器,来应对流量的变化。
2、系统分组
假如系统服务的业务不同,有优先级高的,有优先级低的,那就让不同的业务调用提前分组
- BitTorrent DHT 协议中文翻译
justjavac
bit
前言
做了一个磁力链接和BT种子的搜索引擎 {Magnet & Torrent},因此把 DHT 协议重新看了一遍。
BEP: 5Title: DHT ProtocolVersion: 3dec52cb3ae103ce22358e3894b31cad47a6f22bLast-Modified: Tue Apr 2 16:51:45 2013 -070
- Ubuntu下Java环境的搭建
macroli
java工作ubuntu
配置命令:
$sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras
再运行如下命令:
$sudo apt-get install sun-java6-jdk
待安装完毕后选择默认Java.
$sudo update- alternatives --config java
安装过程提示选择,输入“2”即可,然后按回车键确定。
- js字符串转日期(兼容IE所有版本)
qiaolevip
TODateStringIE
/**
* 字符串转时间(yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss)
* result (分钟)
*/
stringToDate : function(fDate){
var fullDate = fDate.split(" ")[0].split("-");
var fullTime = fDate.split("
- 【数据挖掘学习】关联规则算法Apriori的学习与SQL简单实现购物篮分析
superlxw1234
sql数据挖掘关联规则
关联规则挖掘用于寻找给定数据集中项之间的有趣的关联或相关关系。
关联规则揭示了数据项间的未知的依赖关系,根据所挖掘的关联关系,可以从一个数据对象的信息来推断另一个数据对象的信息。
例如购物篮分析。牛奶 ⇒ 面包 [支持度:3%,置信度:40%] 支持度3%:意味3%顾客同时购买牛奶和面包。 置信度40%:意味购买牛奶的顾客40%也购买面包。 规则的支持度和置信度是两个规则兴
- Spring 5.0 的系统需求,期待你的反馈
wiselyman
spring
Spring 5.0将在2016年发布。Spring5.0将支持JDK 9。
Spring 5.0的特性计划还在工作中,请保持关注,所以作者希望从使用者得到关于Spring 5.0系统需求方面的反馈。