Linux下使用fuse编写自己的文件系统
一、前言
近几天调研了一下fuse编写文件系统的方法,先尝试拿fuse写一套类似tmpfs的简易文件系统,文件信息都保留在内存中。文件系统需要一个数据结构来管理文件节点 inode,正好《c语言实现map-使用内核红黑树》一文将rbtree结构拿出来了可以用上。
目标:支持文件读写操作:echo、cat;支持目录操作ls、mkdir、cd。
二、知识准备
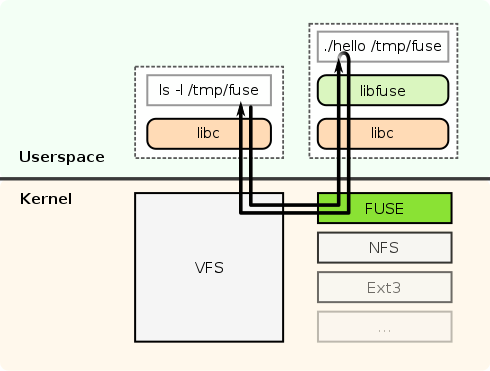
FUSE(Filesystem in Userspace)为Linux下用户态的文件系统接口,通常情况文件系统的操作在内核态处理,存在调试不方便,开发效率低的情况,使用FUSE可以在用户空间进行方便地开发、调试。
如图所示,用户层的 list 操作,通过内核VFS\FUSE中转,在用户层通过libfuse到自定义程序hello中进行处理、返回。这种操作是非常灵活的,即list操作的结果是由你的应用来决定的,也就是说你能实现list展示你的自定义列表、自定义数据项等信息。当然,灵活性所需要付出的代价:用户态实现的操作系统会引入“内核态/用户态切换”额外的开销,进而影响性能。
fuse安装比较简单:
1、内核需要开启fuse的支持(默认带)
2、准备安装包 fuse-2.9.7.tar.gz
3、源码安装./configure --prefix=/usr && make -j4 && make install(编译过程提示我缺库,util-linux-ng-2.17.1.tar.gz)
三、实现
编译过程中需要指定库文件:-lfuse -pthread
首先需要定义文件系统支持的操作函数,填在结构体 struct fuse_operations 中,其他的可以详见[附录]:
static struct fuse_operations memfs_oper = {
.getattr = memfs_getattr,
.access = memfs_access,
.readdir = memfs_readdir,
.open = memfs_open,
.read = memfs_read,
.write = memfs_write,
.release = memfs_release,
.mknod = memfs_mknod,
.unlink = memfs_unlink,
.mkdir = memfs_mkdir,
.rmdir = memfs_rmdir,
.statfs = memfs_statfs,
};主要包含了一些基础操作:
1、新建目录:mkdir、getattr;删除目录:rmdir;遍历目录:readdir;进入目录:access;
2、新建文件:getattr、mknod、open、write、read、release;删除文件:unlink;
3、状态查看:statfs;
然后看下数据结构,memfs为全局变量(多个终端操作为多线程访问该变量),并定义、初始化了statvfs结构来维护系统状态信息,定义了文件块BlockSize大小为4096,块上限MaxBlocks为1048576个,文件数MaxInode为1048576个:
struct memfs {
struct rb_root root;
struct statvfs statvfs;
pthread_mutex_t lock;
pthread_mutex_t lock_write;
};
#define FUSE_SUPER_MAGIC 0x65735546
#define BLOCKSIZE (1024UL * 4)
#define MAX_NAME 255
#define MAX_INODE (1024UL * 1024)
#define MAX_BLOCKS (1024UL * 1024)
/* Set global instance */
static struct memfs memfs = {
.root = RB_ROOT,
.statvfs = {
.f_bsize = BLOCKSIZE, /* Filesystem block size */
.f_frsize = BLOCKSIZE, /* Fragment size */
.f_blocks = MAX_BLOCKS, /* Size of fs in f_frsize units */
.f_bfree = MAX_BLOCKS, /* Number of free blocks */
.f_bavail = MAX_BLOCKS, /* Number of free blocks for unprivileged users */
.f_files = MAX_INODE, /* Number of inodes */
.f_ffree = MAX_INODE, /* Number of free inodes */
.f_favail = MAX_INODE, /* Number of free inodes for unprivileged users */
.f_fsid = 0x0123456701234567, /* Filesystem ID */
// .f_flags = 0, /* Mount flags */
.f_namemax = MAX_NAME, /* Maximum filename length */
},
.lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER,
.lock_write = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER,
};
/* File inodes store in rbtree */
struct memfs_file {
char *path; /* File path */
void *data; /* File content */
u8 free_on_delete;
struct stat vstat; /* File stat */
pthread_mutex_t lock;
struct rb_node node;
};所以外部执行df,df -i的时候,将调用.statfs进行状态查询:
static int memfs_statfs(const char *path, struct statvfs *stbuf)
{
printf("%s: %s\n", __FUNCTION__, path);
*stbuf = memfs.statvfs;
return 0;
}
文件、目录节点均使用红黑树进行维护,相关的操作请看《c语言实现map-使用内核红黑树》;
由于数据结构将被多线程使用,所以使用mutex互斥锁对其进行保护;
getattr为非常常用的方法,用于查询节点是否存在、查询节点属性等动作:
static int memfs_getattr(const char *path, struct stat *stbuf)
{
int res = 0;
printf("%s: %s\n", __FUNCTION__, path);
memset(stbuf, 0, sizeof(struct stat));
pthread_mutex_lock(&memfs.lock);
struct memfs_file *pf = __search(&memfs.root, path);
if (!pf) {
res = -ENOENT;
}
else {
*stbuf = pf->vstat;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&memfs.lock);
return res;
}进入目录、创建目录、删除目录:
static int memfs_access(const char *path, int mask)
{
int res = 0;
printf("%s: %s\n", __FUNCTION__, path);
pthread_mutex_lock(&memfs.lock);
struct memfs_file *pf = __search(&memfs.root, path);
if (!pf) {
res = -ENOENT;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&memfs.lock);
return res;
}
static int memfs_mkdir(const char *path, mode_t mode)
{
int res = 0;
struct memfs_file *pf = NULL;
printf("%s: %s\n", __FUNCTION__, path);
pf = __new(path, S_IFDIR | mode);
if (!pf) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&memfs.lock);
res = __insert(&memfs.root, pf);
if (res != SUCCESS) {
__free(pf);
res = -EEXIST;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&memfs.lock);
__do_update_times(pf, U_ALL);
return res;
}
static int memfs_rmdir(const char *path)
{
int res = 0;
printf("%s: %s\n", __FUNCTION__, path);
pthread_mutex_lock(&memfs.lock);
if (__delete(&memfs.root, path) < 0) {
res = -ENOENT;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&memfs.lock);
return res;
}
试验1:cd /mnt/fuse && mkdir 1 2 3 && rmdir 1 2 3
memfs_getattr: /
memfs_access: /
memfs_getattr: /1
memfs_mkdir: /1
memfs_getattr: /1
memfs_getattr: /2
memfs_mkdir: /2
memfs_getattr: /2
memfs_getattr: /3
memfs_mkdir: /3
memfs_getattr: /3
memfs_getattr: /
memfs_getattr: /1
memfs_rmdir: /1
memfs_getattr: /2
memfs_rmdir: /2
memfs_getattr: /3
memfs_rmdir: /3
文件操作:创建文件mknod、打开文件open、关闭文件release、删除文件unlink;
注意mknod、unlink的时候需要更新statvfs中的inode计数器。
static int memfs_mknod(const char *path, mode_t mode, dev_t rdev)
{
int res = 0;
struct memfs_file *pf = NULL;
printf("%s: %s\n", __FUNCTION__, path);
pf = __new(path, mode);
if (!pf) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&memfs.lock);
res = __insert(&memfs.root, pf);
if (res != SUCCESS) {
__free(pf);
res = -EEXIST;
}
memfs.statvfs.f_favail = --memfs.statvfs.f_ffree;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&memfs.lock);
return res;
}
static int memfs_open(const char *path, struct fuse_file_info *fi)
{
int res = 0;
struct memfs_file *pf = NULL;
printf("%s: %s\n", __FUNCTION__, path);
pthread_mutex_lock(&memfs.lock);
pf = __search(&memfs.root, path);
if (!pf) {
if ((fi->flags & O_ACCMODE) == O_RDONLY ||
!(fi->flags & O_CREAT)) {
res = -ENOENT;
goto unlock;
}
pf = __new(path, S_IFREG | 0755);
__insert(&memfs.root, pf);
}
else {
if (S_ISDIR(pf->vstat.st_mode)) {
res = -EISDIR;
goto unlock;
}
}
fi->fh = (unsigned long)pf;
unlock:
pthread_mutex_unlock(&memfs.lock);
return res;
}
static int memfs_release(const char *path, struct fuse_file_info *fi)
{
printf("%s: %s\n", __FUNCTION__, path);
return 0;
}
static int memfs_unlink(const char *path)
{
int res = 0, blocks = 0;
printf("%s: %s\n", __FUNCTION__, path);
pthread_mutex_lock(&memfs.lock);
blocks = __delete(&memfs.root, path);
if (blocks < 0) {
res = -ENOENT;
goto unlock;
}
memfs.statvfs.f_bfree = memfs.statvfs.f_bavail += blocks;
memfs.statvfs.f_favail = ++memfs.statvfs.f_ffree;
unlock:
pthread_mutex_unlock(&memfs.lock);
return res;
}文件读写操作:read、write;
注意write过程中需要对statvfs的blocks计数器进行更新,并调用__do_update_times对文件时间戳更新;
思路是open获取文件节点后,将节点挂在struct fuse_file_info结构的fh成员内,文件内容写在了memfs_file::data中;
该例子仅对单次写入进行加锁保护,但并没有加入文件级别的锁,没解决同时多人打开文件写的问题。
#define U_ATIME (1 << 0)
#define U_CTIME (1 << 1)
#define U_MTIME (1 << 2)
#define U_ALL (U_ATIME | U_CTIME | U_MTIME)
static inline void __do_update_times(struct memfs_file *pf, int which)
{
time_t now = time(0);
if (which & U_ATIME) {
pf->vstat.st_atime = now;
}
if (which & U_CTIME) {
pf->vstat.st_ctime = now;
}
if (which & U_MTIME) {
pf->vstat.st_mtime = now;
}
}
static int memfs_write(const char *path,
const char *buf, size_t size, off_t offset,
struct fuse_file_info *fi)
{
struct memfs_file *pf = (struct memfs_file *)fi->fh;
printf("%s: %s, size: %zd\n", __FUNCTION__, path, size);
// TODO Check whether the file was opened for reading
blkcnt_t req_blocks = (offset + size + BLOCKSIZE - 1) / BLOCKSIZE;
pthread_mutex_lock(&pf->lock);
if (pf->vstat.st_blocks < req_blocks) {
void *newdata = realloc(pf->data, req_blocks * BLOCKSIZE);
if (!newdata) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
memfs.statvfs.f_bfree = memfs.statvfs.f_bavail -= req_blocks - pf->vstat.st_blocks;
pf->data = newdata;
pf->vstat.st_blocks = req_blocks;
}
memcpy(pf->data + offset, buf, size);
// Update file size if necessary
off_t minsize = offset + size;
if (minsize > pf->vstat.st_size) {
pf->vstat.st_size = minsize;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pf->lock);
__do_update_times(pf, U_ALL);
return size;
}
static int memfs_read(const char *path,
char *buf, size_t size, off_t offset,
struct fuse_file_info *fi)
{
struct memfs_file *pf = (struct memfs_file *)fi->fh;
printf("%s: %s\n", __FUNCTION__, path);
// TODO Check whether the file was opened for reading
off_t filesize = pf->vstat.st_size;
if (offset > filesize) {
return 0;
}
size_t avail = filesize - offset;
size_t rsize = (size < avail) ? size : avail;
memcpy(buf, pf->data + offset, rsize);
__do_update_times(pf, U_ATIME);
return rsize;
}试验2:cd /mnt/fuse && echo "Helloworld" >test.txt && cat test.txt && rm -rf test.txt
memfs_getattr: /
memfs_access: /
memfs_getattr: /test.txt
memfs_mknod: /test.txt
memfs_getattr: /test.txt
memfs_open: /test.txt
memfs_write: /test.txt, size: 11
memfs_release: /test.txt
memfs_getattr: /
memfs_getattr: /test.txt
memfs_open: /test.txt
memfs_read: /test.txt
memfs_getattr: /test.txt
memfs_release: /test.txt
memfs_getattr: /test.txt
memfs_unlink: /test.txt最后是遍历目录readdir的实现,basename、dirname字符串处理麻烦一点点,基本思路是先找到父目录节点,然后后序遍历直到离开父目录(rbtree能够实现范围查找,hashmap则不行)。
文件名处理也可以用#include
filler函数中填写的文件名为basename,不能带'/';
/*
* @parent - "/tmp"
* @path - "/tmp/1.txt"
*/
static inline const char *__is_parent(const char *parent, const char *path)
{
const char delim = '/';
if (parent[1] == '\0' && parent[0] == '/' && path[0] == '/') {
return path;
}
while (*parent != '\0' && *path != '\0' && *parent == *path) {
++parent, ++path;
}
return (*parent == '\0' && *path == delim) ? path : NULL;
}
static int __do_readdir(const char *dirname, void *buf, fuse_fill_dir_t filler)
{
struct rb_node *node = NULL;
struct memfs_file *pentry = __search(&memfs.root, dirname);
if (!pentry) {
return -ENOENT;
}
else if (!S_ISDIR(pentry->vstat.st_mode)) {
return -ENOTDIR;
}
for (node = rb_next(&pentry->node); node; node = rb_next(node)) {
const struct memfs_file *pf = rb_entry(node, struct memfs_file, node);
const char *basename = __is_parent(dirname, pf->path);
if (!basename) {
break;
}
else if (strchr(basename + 1, '/')) {
continue;
}
filler(buf, basename + 1, &pf->vstat, 0);
printf(" readdir: %10s, path: %10s\n", basename, pf->path);
}
return 0;
}
static int memfs_readdir(const char *path, void *buf, fuse_fill_dir_t filler,
off_t offset, struct fuse_file_info *fi)
{
int res = 0;
printf("%s: %s\n", __FUNCTION__, path);
filler(buf, ".", NULL, 0);
if (strcmp(path, "/") != 0) {
filler(buf, "..", NULL, 0);
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&memfs.lock);
res = __do_readdir(path, buf, filler);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&memfs.lock);
return res;
}试验3:cd /mnt/fuse && mkdir 1 2 3 4 && ls -l
memfs_getattr: /
memfs_access: /
memfs_getattr: /1
memfs_mkdir: /1
memfs_getattr: /1
memfs_getattr: /2
memfs_mkdir: /2
memfs_getattr: /2
memfs_getattr: /3
memfs_mkdir: /3
memfs_getattr: /3
memfs_getattr: /4
memfs_mkdir: /4
memfs_getattr: /4
memfs_getattr: /
memfs_readdir: /
readdir: /1, path: /1
readdir: /2, path: /2
readdir: /3, path: /3
readdir: /4, path: /4
四、结论
本文对fuse开发文件系统进行了探索,并简单实现了基于内存的文件系统,开发、调试过程是比较方便,遇到不会写的函数就参考一下fuse/example底下的案例,或者看下sshfs的源码。另外线程安全的问题也是需要在应用中重点考虑的部分。
然后尝试大批小文件写入发现速度达到10000ops,对比了一下tmpfs居然有40000ops的速度,果然多了两层内核态/用户态的切换性能影响还是挺大的。所以对于重扩展不重性能的应用,可以考虑fuse去实现(网络文件协议挂载到本地),但对于性能型应用还是考虑调用api比较合适。
附录:
/* from fuse.h */
struct fuse_operations
{
/** Get file attributes. */
int (*getattr) (const char *, struct stat *);
/** Read the target of a symbolic link */
int (*readlink) (const char *, char *, size_t);
/** Create a file node */
int (*mknod) (const char *, mode_t, dev_t);
/** Create a directory */
int (*mkdir) (const char *, mode_t);
/** Remove a file */
int (*unlink) (const char *);
/** Remove a directory */
int (*rmdir) (const char *);
/** Create a symbolic link */
int (*symlink) (const char *, const char *);
/** Rename a file */
int (*rename) (const char *, const char *);
/** Create a hard link to a file */
int (*link) (const char *, const char *);
/** Change the permission bits of a file */
int (*chmod) (const char *, mode_t);
/** Change the owner and group of a file */
int (*chown) (const char *, uid_t, gid_t);
/** Change the size of a file */
int (*truncate) (const char *, off_t);
/** Change the access and/or modification times of a file */
int (*utime) (const char *, struct utimbuf *);
/** File open operation */
int (*open) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Read data from an open file */
int (*read) (const char *, char *, size_t, off_t,
struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Write data to an open file */
int (*write) (const char *, const char *, size_t, off_t,
struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Get file system statistics */
int (*statfs) (const char *, struct statvfs *);
/** Possibly flush cached data */
int (*flush) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Release an open file */
int (*release) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Synchronize file contents */
int (*fsync) (const char *, int, struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Set extended attributes */
int (*setxattr) (const char *, const char *, const char *, size_t, int);
/** Get extended attributes */
int (*getxattr) (const char *, const char *, char *, size_t);
/** List extended attributes */
int (*listxattr) (const char *, char *, size_t);
/** Remove extended attributes */
int (*removexattr) (const char *, const char *);
/** Open directory */
int (*opendir) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Read directory */
int (*readdir) (const char *, void *, fuse_fill_dir_t, off_t,
struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Release directory */
int (*releasedir) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Synchronize directory contents */
int (*fsyncdir) (const char *, int, struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Initialize filesystem */
void *(*init) (struct fuse_conn_info *conn);
/** Clean up filesystem */
void (*destroy) (void *);
/** Check file access permissions */
int (*access) (const char *, int);
/** Create and open a file */
int (*create) (const char *, mode_t, struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Change the size of an open file */
int (*ftruncate) (const char *, off_t, struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Get attributes from an open file */
int (*fgetattr) (const char *, struct stat *, struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Perform POSIX file locking operation */
int (*lock) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *, int cmd,
struct flock *);
/**
* Change the access and modification times of a file with
* nanosecond resolution
*/
int (*utimens) (const char *, const struct timespec tv[2]);
/** Map block index within file to block index within device */
int (*bmap) (const char *, size_t blocksize, uint64_t *idx);
/** Ioctl */
int (*ioctl) (const char *, int cmd, void *arg,
struct fuse_file_info *, unsigned int flags, void *data);
/** Poll for IO readiness events */
int (*poll) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *,
struct fuse_pollhandle *ph, unsigned *reventsp);
/** Write contents of buffer to an open file */
int (*write_buf) (const char *, struct fuse_bufvec *buf, off_t off,
struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Store data from an open file in a buffer */
int (*read_buf) (const char *, struct fuse_bufvec **bufp,
size_t size, off_t off, struct fuse_file_info *);
/** Perform BSD file locking operation */
int (*flock) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *, int op);
/** Allocates space for an open file */
int (*fallocate) (const char *, int, off_t, off_t,
struct fuse_file_info *);
};参考文章:
[1] https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-hans/FUSE
[2] http://libfuse.github.io/doxygen/index.html