UI之测量原理
上一篇文章UI之Activity启动流程介绍了Activity从启动到屏幕可见的流程,Activity是通过发送Handle消息反射创建除了Activity,并调用Activity的各个生命周期,在onCreate中加载了系统原始View-decorView,并解析了自己布局的xml保存至LayoutParams中,在handleResumeActivity中就开始了具体的UI绘制流程,最终将我们DecorView以及LayoutParams传递给了ViewRootImpl,在该类中依次调用View自己的测量Measure、布局Layout、绘制Draw,至此我们的界面展现在屏幕上。
本篇文章主要是了解我们的绘制流程Measure,为以后的自定义UI打下基础。
首先我看performTraversal#ViewRootImpl.java中调用测量的代码
if (!mStopped || mReportNextDraw) {
boolean focusChangedDueToTouchMode = ensureTouchModeLocally(
(relayoutResult&WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_RES_IN_TOUCH_MODE) != 0);
if (focusChangedDueToTouchMode || mWidth != host.getMeasuredWidth()
|| mHeight != host.getMeasuredHeight() || contentInsetsChanged ||
updatedConfiguration) {
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(mTag, "Ooops, something changed! mWidth="
+ mWidth + " measuredWidth=" + host.getMeasuredWidth()
+ " mHeight=" + mHeight
+ " measuredHeight=" + host.getMeasuredHeight()
+ " coveredInsetsChanged=" + contentInsetsChanged);
// Ask host how big it wants to be
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
// Implementation of weights from WindowManager.LayoutParams
// We just grow the dimensions as needed and re-measure if
// needs be
int width = host.getMeasuredWidth();
int height = host.getMeasuredHeight();在performMeasure方法中传入了childWidthMeasureSpec和childHeightMeasureSpec
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
//调用了DecorView的测量方法
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}可以看出在这个方法中它直接调用decorView的测量方法,在进入该测量方法之前我们先来看一下childWidthMeasureSpec和childHeightMeasureSpec是什么值
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);从应为的翻译上我们不难看出他们的意思是宽高测量规格,那么这个规格具体是指什么,怎么来的,我们继续进入getRootMeasureSpec方法中。
/**
* Figures out the measure spec for the root view in a window based on it's
* layout params.
* 根据Layout Params计算出根View的测量规格
*
* @param windowSize
* 窗口可用的宽高
*
* @param rootDimension
* 宽高的Layout params模式是什么(MATCH_PARENT,WRAP_CONTENT,具体的数值)
*
* @return The measure spec to use to measure the root view.
*/
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
在该方法主要作用是根据我们窗口的可用大小以及根View的layoutParams模式,通过MeasureSpec类计算出我们的根View的测量规格
MeasureSpec.java源码如下
public static class MeasureSpec {
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
/** @hide */
@IntDef({UNSPECIFIED, EXACTLY, AT_MOST})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface MeasureSpecMode {}
/**
* 父控件不对子控件做任何的限制,它需要多大给多大
*
*/
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* 父控件有一个确定的值限制其子控件的大小
*
*/
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
*子控件可以想要它需要的任何值
*
*/
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
*
* 将size和mode生成一个32位数值,前两位代表mode,其他位代表size
*
*/
public static int makeMeasureSpec(@IntRange(from = 0, to = (1 << MeasureSpec.MODE_SHIFT) - 1) int size,
@MeasureSpecMode int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
}
public static int makeSafeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
if (sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec && mode == UNSPECIFIED) {
return 0;
}
return makeMeasureSpec(size, mode);
}
/**
* 从宽高规格中返回模式
*/
@MeasureSpecMode
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
//noinspection ResourceType
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
/**
*
*从宽高规格中返回数值大小
*/
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
}
通过对MeasureSpec的源码分析配合上getRootMeasureSpec方法中的case判断我们可以得到MeasureSpec三种模式的对应关系如下:
EXACTLY-----》match_parent以及确定数值的情况
AT_MOST----》wrap_content
UNSPECIFIED---》源码内部使用,如ScrollView,ListView
且其在计算测量规格的时候将这三种模式对应的值0,1,2左位移30位。
接着往下看源码中一共有三个重要的方法:
makeMeasureSpec---》Size和Mode打包
getMode---》获取Mode
getSize---》获取Size
第一个方法makeMeasureSpec:
public static int makeMeasureSpec(@IntRange(from = 0, to = (1 << MeasureSpec.MODE_SHIFT) - 1) int size,@MeasureSpecMode int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
}在生成这个32位数值的时候进行了如下运算“(size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK)”,
将size通过MODE_MASK操作后,将size转换成32位后放入后30位并组合Mode,然后返回其值,其运算方式如下图:
第二个方法 getMode
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
//noinspection ResourceType
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
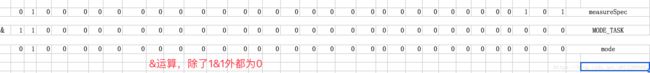
}运算规则是通过measureSpec与MODE_MASK进行与运算,取出Mode,其运算方式如下
第三个方法getSize
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}运算规则是先将MODE_MASK取反,再与measureSpec进行运算,其运算过程如下:
由上可知传给我们的measureSpec是一个mode+size的组合值,在测量的过程不停往下传递,其他view在使用的时候通过getMode()和getSize()进行使用。
到目前为止我们已经得到一个DecorView的MeasureSpec,在接下来的绘制流程,各个子View拿着这个MeasureSpec开始自己的测量,现在我们继续接着上面的performMeasure往下看看系统还做了什么。
performMeasure#ViewRootImpl.java
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}由上可见它拿着跟视图的测量规格,开始了从DecorView的测量。
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int oWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int oHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(widthMeasureSpec, optical ? -oWidth : oWidth);
heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(heightMeasureSpec, optical ? -oHeight : oHeight);
}
// Suppress sign extension for the low bytes
long key = (long) widthMeasureSpec << 32 | (long) heightMeasureSpec & 0xffffffffL;
if (mMeasureCache == null) mMeasureCache = new LongSparseLongArray(2);
final boolean forceLayout = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
// Optimize layout by avoiding an extra EXACTLY pass when the view is
// already measured as the correct size. In API 23 and below, this
// extra pass is required to make LinearLayout re-distribute weight.
final boolean specChanged = widthMeasureSpec != mOldWidthMeasureSpec
|| heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec;
final boolean isSpecExactly = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY
&& MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
final boolean matchesSpecSize = getMeasuredWidth() == MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)
&& getMeasuredHeight() == MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
final boolean needsLayout = specChanged
&& (sAlwaysRemeasureExactly || !isSpecExactly || !matchesSpecSize);
if (forceLayout || needsLayout) {
// first clears the measured dimension flag
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
resolveRtlPropertiesIfNeeded();
int cacheIndex = forceLayout ? -1 : mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key);
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
//进入View自己实现的测量方法中
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
// Casting a long to int drops the high 32 bits, no mask needed
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
// flag not set, setMeasuredDimension() was not invoked, we raise
// an exception to warn the developer
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) {
throw new IllegalStateException("View with id " + getId() + ": "
+ getClass().getName() + "#onMeasure() did not set the"
+ " measured dimension by calling"
+ " setMeasuredDimension()");
}
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;
mMeasureCache.put(key, ((long) mMeasuredWidth) << 32 |
(long) mMeasuredHeight & 0xffffffffL); // suppress sign extension
}
源码看到这里,我们发现它最终的测量进入了view自己实现的onMeasure方法中,以上就是我们布局测量的核心,不同的view的测量方式不同,由于我们的顶层view是FreamLayout,为了更好地掌握测量的使用方法,我们进入FreamLayout的源码看一看。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//获取当前子View的个数
int count = getChildCount();
//判断当前的View的mode是不是match_parent或者一个准确值,如果不是则将
//measureMatchParentChildren设为true
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {//遍历子view
final View child = getChildAt(i);
//显示的view进行一下操作
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
//测量子view
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//找到子view中宽高最大的,因为当FrameLayout的模式是warp_content,
//则它的宽高是由它宽高最大的view决定的
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
//如果FrameLayout的模式warp_content为,那么需要记录模式为MATCH_PARENT的子
//view,因为他们的宽高受父控件影响
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// Account for padding too
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// Check against our minimum height and width
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// Check against our foreground's minimum height and width
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
//确定了最终的测量结果,进行保存,在自定义view中一定要设置这一步
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
//处理view中模式为match_parent
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
/**
如果子View的模式是match_parent,那么确定了FrameLayout的宽高后,
那么需要重新确定子View的宽高规格,
子控件能够占领的宽度为=父控件的宽度-padding-margin,模式为EXACTLY
如果子View的模式是warp_content,那么子控件的宽度为自己的宽度+padding+margin
*/
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
//同上的高度处理
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}以上是FrameLayout的测量过程,从最底层的View一层一层的测量上来,找到view中宽高最大的值,已确定自己的值,最后通过setMeasuredDimension确定自己的宽高,而当父控件是warp_content模式,而子view是Match_parent模式,那么这个时候需要重新确定子view的宽高规格。
下面我们看下保存测量宽高的方法setMeasuredDimension,这个方法接收的是resolveSizeAndState的值,
resolveSizeAndState#View.java
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) {
final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
final int result;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (specSize < size) {
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
default:
result = size;
}
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}该方法的实现思路是,当测量模式为EXACTLY的时候,直接返回specSize 的值,如果模式是AT_MOST则返回specSize和宽高规格的自小值。
总结:自此我们查看了一下view的测量的大致流程:首先根据window的大小和decorView的模式生成根view的测量规格(size+LayoutParams),然后用这个宽高规格逐层测量view的宽度,最后根据子View的宽高自己的layoutParams确定自己的宽高,为以后的layout的draw做准备.