从挂载fuse文件系统分析mount系统调用
mount系统调用的原型如下
int mount(const char *source, const char *target,
const char *filesystemtype, unsigned long mountflags,
const void *data);
其中source为设备文件的路径名,target为挂载点路径名,filesystemtype是文件系统的类型,mountflags是挂载的一些选项,data是用户传入的私有数据,这些数据可能会被各自文件系统的mount函数解析(随后可在fuse文件系统的mount函数里看到)。
在用户态调用mount系统调用后,会陷入内核态,进而执行内核的do_mount函数
long do_mount(const char *dev_name, const char __user *dir_name,
const char *type_page, unsigned long flags, void *data_page)
user_path(dir_name, &path);
do_new_mount(&path, type_page, sb_flags, mnt_flags, dev_name, data_page);
do_mount首先调用user_path获取挂载点的path结构,path中包含struct vfsmount *mnt和struct dentry *dentry两个元素。关于user_path的实现,可以先跳过,可以认为user_path返回后,就已经获得了挂载点的mnt和dentry。然后调用do_new_mount去处理新的挂载。
static int do_new_mount(struct path *path, const char *fstype, int sb_flags,
int mnt_flags, const char *name, void *data)
struct file_system_type *type = get_fs_type(fstype);
struct vfsmount *mnt = vfs_kern_mount(type, sb_flags, name, data);
do_add_mount(real_mount(mnt), path, mnt_flags);
do_new_mount首先调用get_fs_type获得之前注册的file_system_type对象,fuse文件系统的对象定义如下,比较重要的成员就是mount,每个文件系统都有自己的mount函数
static struct file_system_type fuse_fs_type = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = "fuse",
.fs_flags = FS_HAS_SUBTYPE,
.mount = fuse_mount,
.kill_sb = fuse_kill_sb_anon,
};
然后do_new_mount会调用vfs_kern_mount做具体的挂载事项
struct vfsmount *
vfs_kern_mount(struct file_system_type *type, int flags, const char *name, void *data)
struct mount *mnt = alloc_vfsmnt(name);
struct dentry *root = mount_fs(type, flags, name, data);
root = type->mount(type, flags, name, data);
sb = root->d_sb;
sb->s_flags |= SB_BORN;
mnt->mnt.mnt_root = root;
mnt->mnt.mnt_sb = root->d_sb;
mnt->mnt_mountpoint = mnt->mnt.mnt_root;
mnt->mnt_parent = mnt;
list_add_tail(&mnt->mnt_instance, &root->d_sb->s_mounts);
return &mnt->mnt;
alloc_vfsmnt分配一个mount对象,并初始化。mount_fs会调用文件系统具体的mount函数,并返回挂载后的文件系统的根dentry。初始化mnt,并将mnt插入到sper block对应的s_mounts链表中。
如果挂载的是fuse文件系统的话,type->mount执行的就是fuse_mount函数
static struct dentry *fuse_mount(struct file_system_type *fs_type,
int flags, const char *dev_name,
void *raw_data)
return mount_nodev(fs_type, flags, raw_data, fuse_fill_super);
struct super_block *s = sget(fs_type, NULL, set_anon_super, flags, NULL);
fill_super(s, data, flags & SB_SILENT ? 1 : 0);
s->s_flags |= SB_ACTIVE;
return dget(s->s_root);
fuse_mount实际上就是调用mount_nodev,mount_nodev首先调用sget获得super_block对象,然后调用fill_super(fuse_fill_super)去填充super block。
struct super_block *sget(struct file_system_type *type,
int (*test)(struct super_block *,void *),
int (*set)(struct super_block *,void *),
int flags,
void *data)
struct user_namespace *user_ns = current_user_ns();
return sget_userns(type, test, set, flags, user_ns, data);
s = alloc_super(type, (flags & ~SB_SUBMOUNT), user_ns);
set(s, data); // set_anon_super
return get_anon_bdev(&s->s_dev);
s->s_type = type;
strlcpy(s->s_id, type->name, sizeof(s->s_id));
// 将super block插入到super_blocks链表中
list_add_tail(&s->s_list, &super_blocks);
// 将该super block插入到文件系统类型的fs_supers链表中
hlist_add_head(&s->s_instances, &type->fs_supers);
static int fuse_fill_super(struct super_block *sb, void *data, int silent)
parse_fuse_opt(data, &d, is_bdev)
sb->s_magic = FUSE_SUPER_MAGIC;
sb->s_op = &fuse_super_operations;
sb->s_xattr = fuse_xattr_handlers;
sb->s_maxbytes = MAX_LFS_FILESIZE;
sb->s_time_gran = 1;
sb->s_export_op = &fuse_export_operations;
file = fget(d.fd);
struct fuse_conn *fc = kmalloc(sizeof(*fc), GFP_KERNEL);
fuse_conn_init(fc);
fc->dev = sb->s_dev;
fc->sb = sb;
root = fuse_get_root_inode(sb, d.rootmode);
sb->s_d_op = &fuse_root_dentry_operations;
root_dentry = d_make_root(root);
sb->s_d_op = &fuse_dentry_operations;
list_add_tail(&fc->entry, &fuse_conn_list);
sb->s_root = root_dentry;
file->private_data = fud;
文章刚开始的时候说过,mount系统调用的最后一个参数data用于把一些配置传给文件系统,parse_fuse_opt就是解析用户传入的配置,并填充struct fuse_mount_data d对象。libfuse调用mount挂载/dev/fuse设备时,会传入“fd=%i,rootmode=%o,user_id=%u,group_id=%u”之类的配置,fd是libfuse打开/dev/fuse获得的句柄(libfuse先打开/dev/fuse,然后再挂载/dev/fuse),rootmode是文件系统根dentry的文件类型(libfuse设置为和挂载点类型相同)。然后初始化super block的一些成员,并根据/dev/fuse的句柄,从current->files找到file对象。接着初始化fuse_conn对象,fuse_conn对象用于libfuse和用户之间的通信。fuse_get_root_inode用于创建文件系统的根inode,d_make_root用于创建根inode对应的dentry。最后需要把fud赋值给file->private_data,fuse设备的open函数唯一一个功能就是把file->private_data设置为NULL。
static struct inode *fuse_get_root_inode(struct super_block *sb, unsigned mode)
{
struct fuse_attr attr;
memset(&attr, 0, sizeof(attr));
attr.mode = mode;
attr.ino = FUSE_ROOT_ID;
attr.nlink = 1;
return fuse_iget(sb, 1, 0, &attr, 0, 0);
}
struct inode *fuse_iget(struct super_block *sb, u64 nodeid,
int generation, struct fuse_attr *attr,
u64 attr_valid, u64 attr_version)
struct fuse_conn *fc = get_fuse_conn_super(sb);
struct inode *inode = iget5_locked(sb, nodeid, fuse_inode_eq, fuse_inode_set, &nodeid);
struct hlist_head *head = inode_hashtable + hash(sb, hashval);
inode = find_inode(sb, head, test, data);
inode = alloc_inode(sb);
if (sb->s_op->alloc_inode)
inode = sb->s_op->alloc_inode(sb);
inode = kmem_cache_alloc(fuse_inode_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
fi = get_fuse_inode(inode);
else
inode = kmem_cache_alloc(inode_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
return inode;
old = find_inode(sb, head, test, data);
if (!old)
// 设置inode的nodeid
set(inode, data); // fuse_inode_set
u64 nodeid = *(u64 *) _nodeidp;
get_fuse_inode(inode)->nodeid = nodeid;
inode->i_state = I_NEW;
// 将inode加入到inode_hashtable
hlist_add_head(&inode->i_hash, head);
inode_sb_list_add(inode);
list_add(&inode->i_sb_list, &inode->i_sb->s_inodes);
return inode;
inode->i_flags |= S_NOATIME;
fuse_init_inode(inode, attr);
inode->i_mode = attr->mode & S_IFMT;
if (S_ISREG(inode->i_mode)) {
fuse_init_common(inode);
fuse_init_file_inode(inode);
} else if (S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode))
fuse_init_dir(inode);
inode->i_op = &fuse_dir_inode_operations;
inode->i_fop = &fuse_dir_operations;
else if (S_ISLNK(inode->i_mode))
fuse_init_symlink(inode);
else if (S_ISCHR(inode->i_mode) || S_ISBLK(inode->i_mode) ||
S_ISFIFO(inode->i_mode) || S_ISSOCK(inode->i_mode)) {
fuse_init_common(inode);
init_special_inode(inode, inode->i_mode,
new_decode_dev(attr->rdev));
return inode;
iget5_locked首先从inode_hashtable中查找本super block中nodeid对应的inode,如果没有就会新申请一个,fuse用fuse_alloc_inode申请inode,每次从fuse_inode_cachep高速缓存分配的空间是fuse_inode大小,因为inode是fuse_inode的第一个成员,所以可以用inode指针指向fuse_inode。然后调用fuse_init_inode初始化根inode,fuse_init_inode会根据用户设置的根inode类型来初始化,比如,如果根inode是目录,就设置inode的i_op和i_fop,这些操作函数会在遍历目录,读写文件时用到。
struct dentry *d_make_root(struct inode *root_inode)
res = __d_alloc(root_inode->i_sb, NULL);
struct dentry *dentry = kmem_cache_alloc(dentry_cache, GFP_KERNEL);
dentry = kmem_cache_alloc(dentry_cache, GFP_KERNEL);
dentry->d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN-1] = 0;
if (unlikely(!name))
name = &slash_name; // “/”
dname = dentry->d_iname;
else if (name->len > DNAME_INLINE_LEN-1)
...
dentry->d_name.len = name->len;
dentry->d_name.hash = name->hash;
memcpy(dname, name->name, name->len);
dname[name->len] = 0;
dentry->d_name.name = dname;
dentry->d_parent = dentry;
dentry->d_sb = sb;
d_set_d_op(dentry, dentry->d_sb->s_d_op);
dentry->d_op = op;
d_instantiate(res, root_inode);
d_make_root首先申请dentry空间,然后初始化dentry,因为是根dentry,所以d_name.name设置为“/”。
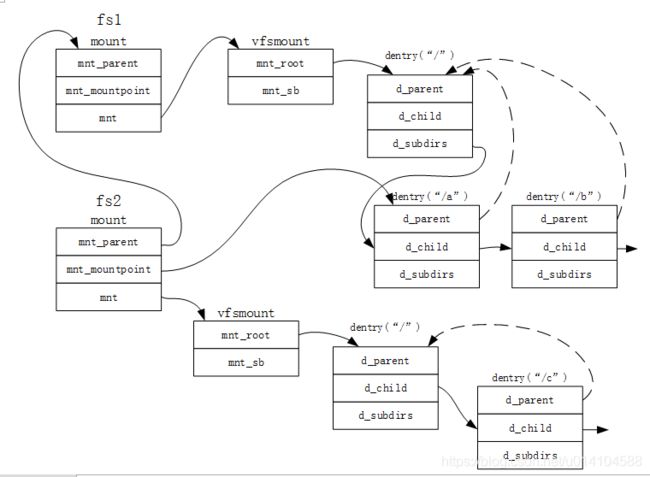
到这里,vfs_kern_mount就已经分析结束,已经获得了文件系统的vfsmount对象,mount对象,super_block对象,根inode和根dentry。紧接着就会调用do_add_mount将该文件系统和父文件系统关联起来。
static int do_add_mount(struct mount *newmnt, struct path *path, int mnt_flags)
struct mountpoint *mp = lock_mount(path);
struct mountpoint *mp = get_mountpoint(dentry);
new = kmalloc(sizeof(struct mountpoint), GFP_KERNEL);
new->m_dentry = dentry;
new->m_count = 1;
hlist_add_head(&new->m_hash, mp_hash(dentry));
mp = new;
return mp;
return mp;
parent = real_mount(path->mnt);
newmnt->mnt.mnt_flags = mnt_flags;
graft_tree(newmnt, parent, mp);
return attach_recursive_mnt(mnt, p, mp, NULL);
struct mountpoint *smp = get_mountpoint(source_mnt->mnt.mnt_root);
detach_mnt(source_mnt, parent_path);
attach_mnt(source_mnt, dest_mnt, dest_mp);
mnt_set_mountpoint(parent, mp, mnt);
// void mnt_set_mountpoint(struct mount *mnt, struct mountpoint *mp, struct mount *child_mnt)
child_mnt->mnt_mountpoint = dget(mp->m_dentry);
child_mnt->mnt_parent = mnt;
child_mnt->mnt_mp = mp;
hlist_add_head(&child_mnt->mnt_mp_list, &mp->m_list);
__attach_mnt(mnt, parent);
// static void __attach_mnt(struct mount *mnt, struct mount *parent)
hlist_add_head_rcu(&mnt->mnt_hash, m_hash(&parent->mnt, mnt->mnt_mountpoint));
list_add_tail(&mnt->mnt_child, &parent->mnt_mounts);
最终挂载文件系统后,子文件系统和父文件系统的关系如下图所示,假设fs1文件系统下有a和b两个子目录,fs2文件系统挂载到a目录下,并有一个c子目录。