阿里云【名师课堂】Java面向对象开发26 ~ 34:String类的常用方法
阿里云【名师课堂】Java面向对象开发26 ~ 34:String类的常用方法
- 26、DOC文档组成
- 使用方法
- 27、字符串与字符数组
- charAt()方法
- 字符串与字符数组的相互转换(重点)
- 28、字节与字符串
- 处理中文
- 处理英文
- 29、字符串比较
- equals()的使用
- 不区分大小写比较
- compareTo()
- 30、字符串查找
- contains()
- indexOf()
- startsWith()
- 31、字符串替换
- 32、字符串拆分
- 全部拆分
- 部分拆分
- 不能拆分
- 多次拆分
- 33、字符串截取
- 34、字符串其它操作方法
在开发中只依靠String类的基本概念无法满足需求,所以要求熟练掌握以下String类的方法。
26、DOC文档组成
Java帮助文档的使用方法,要学会使用。
只有Java6有中文版,Java8只有英文版。
- 下载链接(我下载好了,放在度盘里):https://pan.baidu.com/s/1b0mky5r50_pg-7QV7T7h8Q
提取码私信我hhhhhh
使用方法
- 类的相关定义,包括这个类的名字,有哪些父类、接口;

- 类的简介,包括属性说明、一些基本的使用;
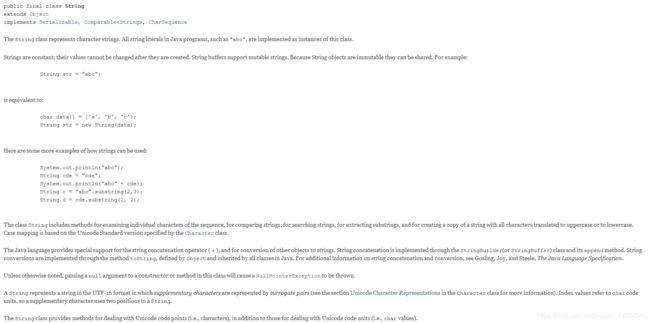
- 成员(Field)摘要:属性就是一种成员。成员摘要会列出所有的成员的信息项;

- 构造方法(Constructor Method)说明:列出该类中所有的构造方法的信息;
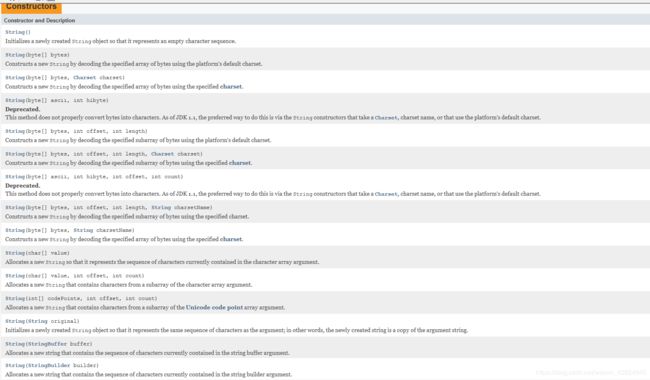
- 回顾:构造方法没有返回值;
- 如果出现Deprecated字样,表示不推荐使用,但是用也没错。
- 方法(Method)信息:所有在类中定义好的可以使用的方法。

- 左栏是返回值,右栏上是名称和参数,下是说明。
- 成员、构造方法、方法都可以通过点击名称查看详细信息。
27、字符串与字符数组
字符串就是一个字符数组,所以在String里有支持字符数组转换为字符串以及字符串转换为字符的处理方法。这些操作方法定义如下:
| 方法名称 | 类型 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
public String(char[] value) |
构造 | 将字符数组中所有内容变为字符串 |
public String(char[] value,int offset,int count) |
构造 | 将部分字符数组中内容变为字符串(offset开始,count个数) |
public char charAt(int index) |
普通 | 取得指定索引位置的字符 |
public char[] toCharArray() |
普通 | 将字符串变为字符数组返回 |
charAt()方法
范例:观察charAt()方法
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "Hello" ;
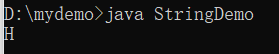
System.out.println(str1.charAt(0)) ;
// 注意范围,不要超过字符串长度,否则会有异常
}
}
字符串与字符数组的相互转换(重点)
范例:观察toCharArray()方法、构造方法String(char[] value)、String(char[] value,int offset,int count)
- 回顾:构造方法的调用:使用关键字new,注意参数匹配
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
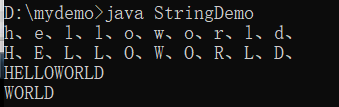
String str1 = "helloworld" ;
// 将字符串转换为字符数组 oCharArray()
char c [] = str1.toCharArray() ;
for(int x = 0; x < c.length; x++){
System.out.print(c[x] + "、") ;
}
System.out.println() ;
// 实现大小写转换(大写=小写-32)
for(int x = 0; x < c.length; x++){
c[x] -= 32 ; // c[x] = (char)(c[x] - 32) ;
System.out.print(c[x] + "、") ;
}
System.out.println() ;
// 字符数组全部转换为字符串 String(char[] value)
System.out.println(new String(c)) ;
// 字符数组部分转换为字符串 String(char[] value,int offset,int count)
System.out.println(new String(c,5,5)) ;
}
}
- 分析:因为不知道字符串长度、内容,所以可以将其变为字符数组,而后判断每个元素是否是
'0' ~ '9'之中的内容,真即为数字。
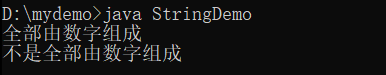
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "1123581321" ;
String str2 = "11abcdrughijklsd" ;
System.out.println(isNumber(str1) ? "全部由数字组成" : "不是全部由数字组成") ;
System.out.println(isNumber(str2) ? "全部由数字组成" : "不是全部由数字组成") ;
}
public static boolean isNumber(String str){
// 将字符串转换为字符数组 oCharArray()
char c [] = str.toCharArray() ;
for(int x = 0; x < c.length; x++){
if(c[x] < '0' || c[x] > '9'){ // 有一个不是数字就不用再继续判断
return false ;
}
}
return true ;
}
}
28、字节与字符串
字节的使用场景:数据传输、编码转换,在String类里提供有对字节操作的支持。
| 方法名称 | 类型 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
public String(byte[] bytes) |
构造 | 将字节数组中所有内容变为字符串 |
public String(byte[] bytes,int offset,int length) |
构造 | 将部分字节数组中内容变为字符串(offset开始,length个数) |
public byte[] getBytes() |
普通 | 将字符串以字节数组的形式返回 |
public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName) throws UnsupportedEncodingException |
普通 | 将字符串转码(编码转换处理) |
处理中文
范例:实现字符串与字符数组的转换处理
public class StringDemo {
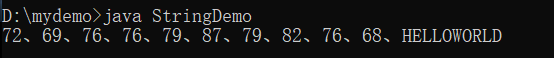
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "你好世界" ;
byte bit [] = str1.getBytes() ;
for(int x = 0; x < bit.length; x++){
System.out.print(bit[x] + "、") ;
}
}
}

可以看到数字溢出,byte型范围-128 ~127,不难发现:字节不能用来处理中文。
处理英文
范例:实现字符串与字符数组的转换处理
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "helloworld" ;
byte bit [] = str1.getBytes() ;
for(int x = 0; x < bit.length; x++){
bit[x] -= 32 ;
System.out.print(bit[x] + "、") ;
}
System.out.println(new String(bit)) ;
}
}
29、字符串比较
之前学习了equals()方法,下面总结几个比较方法:
| 方法名称 | 类型 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
public boolean equals(String anObject) |
普通 | 比较字符串内容(区分大小写) |
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) |
普通 | 比较字符串内容(不区分大小写) |
public int compareTo(String anotherString) |
普通 | 比较字符串内容大小关系(大多少、小多少) |
equals()的使用
请回顾《阿里云【名师课堂】Java面向对象开发21 ~ 25:String类的基本特点》的22、23部分。
不区分大小写比较
- 范例
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println("helloWORLD".equals(str1)) ; // 区分
System.out.println("helloWORLD".equalsIgnoreCase(str1)) ; / /不区分
}
}
compareTo()
compareTo()是重点内容,这里先简单讲解。
从public int compareTo(String anotherString)看出,该方法返回值是一个整型int,该数据根据前字符串与后字符串大小关系有三种答案:
- 相等:返回0
- 小于:返回的内容小于0
- 大于:返回的内容大于0
范例:观察compareTo()
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
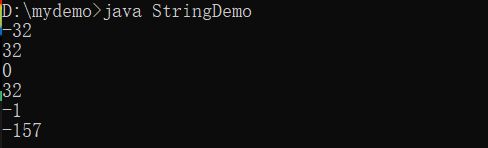
System.out.println("A".compareTo("a")) ; // -32,A比a小32
System.out.println("a".compareTo("A")) ; // 32,a比A大23
System.out.println("a".compareTo("a")) ; // 0
// 按顺序一个一个比较,只比较第一次遇到的不同字符
System.out.println("ab".compareTo("Ac")) ; // 32,a比A大23
System.out.println("ab".compareTo("ac")) ; // -1,b比c小1
// 还可以比较中文
System.out.println("山".compareTo("崎")) ; // -157,山比崎小157
}
}
30、字符串查找
查找方法有很多:
| 方法名称 | 类型 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
public boolean contains(CharSequence s) |
普通 | 判断一个子字符串是否存在 |
public int indexOf(String str) |
普通 | 从字符串头开始查找指定字符串的位置,查到了返回位置的开始索引值(子字符串头),查不到返回-1 |
public int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex) |
普通 | (上个方法的重载)从字符串指定位置开始查找指定字符串的位置 |
public int lastIndexOf(String str) |
普通 | 由后向前查找指定字符串的位置 |
public int lastIndexOf(String str,int fromIndex) |
普通 | (上个方法的重载)从字符串指定位置开始由后向前查找指定字符串的位置 |
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) |
普通 | 从头开始判断是否以指定字符串开头 |
public boolean startsWith(String prefix,int toffset) |
普通 | (上个方法的重载)从指定位置开始判断是否以指定字符串开头 |
public boolean endsWith(String suffix) |
普通 | 判断是否以指定字符串结尾 |
contains()
范例:字符串查找,最方便的是contains(),因为它直接返回boolean类型。
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str1.contains("wor")) ;
}
}
indexOf()
查到了返回位置的开始索引值(子字符串头),查不到返回-1。如果字符串有重复内容,会对查找产生影响。
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("wor")) ; // 5,即w开始的索引
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("java")) ; // -1,找不到
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("l")) ; // 2,第一个l出现的索引
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("l",5)) ; // 8,从w开始找,第一个l出现的索引
System.out.println(str1.lastIndexOf("l")) ; // 8,从后往前找,第一个l出现的索引
}
}
startsWith()
范例:判断开头或结尾
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "**@@helloworld&&" ;
System.out.println(str1.startsWith("**")) ;
System.out.println(str1.startsWith("@@",2)) ;
System.out.println(str1.endsWith("&&")) ;
}
}
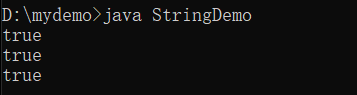
当一些参数利用一些标记做特殊的处理时,需要用到startsWith()或endsWith()。
31、字符串替换
初步了解,后期学习正则时会详细说明。
使用一个新的字符串替换掉已有的字符串数据,有如下方法:
| 方法名称 | 类型 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
public String replaceAll(String regex,String replacement) |
普通 | 替换所有的指定内容 |
public String replaceFirst(String regex,String replacement) |
普通 | 替换首个内容 |
范例:实现字符串的替换处理
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "helloworld" ;
//替换之后返回的类型还是字符串,因此可以直接输出
System.out.println(str1.replaceAll("l","L")) ;
System.out.println(str1.replaceFirst("o","O")) ;
}
}
32、字符串拆分
将一个完整的字符串按照指定的分割符划分为若干个子字符串。
| 方法名称 | 类型 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
public String[] split(String regex) |
普通 | 将字符串全部拆分 |
public String[] split(String regex,int limit) |
普通 | 将字符串部分拆分,拆成limit个。即:返回的字符串数组元素个数是limit。 |
全部拆分
范例:实现字符串全部拆分
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
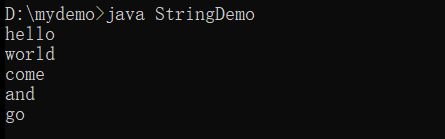
String str1 = "hello world come and go" ;
//拆分之后返回字符串数组
String result [] = str1.split(" ") ;
for(int x = 0; x < result.length; x++){
System.out.println(result[x]) ;
}
}
}
部分拆分
范例:实现字符串部分拆分
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "hello world come and go" ;
//拆分之后返回字符串数组
String result [] = str1.split(" ",2) ;
for(int x = 0; x < result.length; x++){
System.out.println(result[x]) ;
}
}
}
不能拆分
如果字符串中没有split()中设定的分割符,不会拆分。
如果发现有些内容无法拆分(比如IP地址120.0.0.1无法用.拆开),需要使用转义字符\\。
范例:拆分IP地址
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
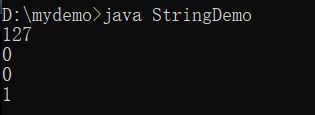
String str1 = "127.0.0.1" ;
//拆分之后返回字符串数组
String result [] = str1.split("\\.") ;
for(int x = 0; x < result.length; x++){
System.out.println(result[x]) ;
}
}
}
多次拆分
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "Dexter:20|Tsukishima Kei:17|Toono Takaki:14" ;
// 第一次拆|:通过"\\|"
String result0 [] = str1.split("\\|") ;
for(int x = 0; x < result0.length; x++){
// 第二次拆:
// result0数组有三个元素:Dexter:20、Tsukishima Kei:17、Toono Takaki:14
// result数组有两个元素:姓名年龄
String result [] = result0[x].split(":") ;
System.out.println(result[0] + ":" + result[1]) ; // 可以用for循环输出,但是因为只有两个元素,就偷个懒直接输出
}
}
}
33、字符串截取
从字符串中截取一定长度的字符串。
| 方法名称 | 类型 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
public String substring(int beginIndex) |
普通 | 从指定索引截取到最后 |
public String substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex) |
截取部分内容:从指定索引截取到指定索引 |
- 回顾:索引从零开始到长度-1结束,没有负数,注意索引不要越界。
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str1.substring(4)) ;
System.out.println(str1.substring(4,7)) ;
}
}
34、字符串其它操作方法
一些小方法:
| 方法名称 | 类型 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
public String trim() |
普通 | 去掉字符串中的左右空格,保留中间空格 |
public String toUpperCase() |
普通 | 字符串转大写 |
public String toLowerCase() |
普通 | 字符串转小写 |
public String intern() |
普通 | 字符串入对象池,详见https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43624945/article/details/106622718 |
public String concat(String str) |
普通 | 字符串连接(等同于+) |
public int length() |
普通 | 取得字符串长度 |
public boolean isEmpty() |
普通 | 判断是否为空字符串 |
一些小问题:
- 通过
concat()方法不能入对象池,要用intern()方法入池; - 注意
length()是一个方法,调用时必须有实例化的对象,不要忘记()。对比记忆:数组中的length使用时没有(); - 注意
isEmpty()方法判断的是字符串长度是否为0,而不是字符串是否为null。
范例:观察上述方法
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
// 去掉左右空格
String str1 = " hello world " ;
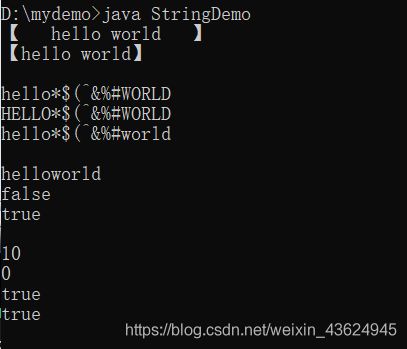
System.out.println("【" + str1 + "】") ;
System.out.println("【" + str1.trim() + "】") ;
System.out.println() ;
// 大小写转换,不是字母不转换
String str2 = "hello*$(^&%#WORLD" ;
System.out.println(str2) ;
System.out.println(str2.toUpperCase()) ;
System.out.println(str2.toLowerCase()) ;
System.out.println() ;
// concat()连接字符串,intern()入池
String str3 = "hello".concat("world") ;
System.out.println(str3) ;
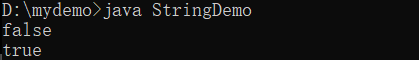
System.out.println(str == str3) ;
System.out.println(str == str3.intern()) ;
System.out.println() ;
// length()查看字符串长度,isEmpty()查看是否内容为空
System.out.println(str.length()) ;
System.out.println("".length()) ;
System.out.println("".isEmpty()) ;
System.out.println(new String().isEmpty()) ;
}
}
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(fstLetterCap(str)) ;
System.out.println(fstLetterCap("")) ;
}
public static String fstLetterCap(String str){
if(str == null || "".equals(str)){ // "".equals(str)与str.inEmpty()作用相同
return "Wrong *Input!!" ;
} else if(str.length() > 1){
return str.substring(0,1).toUpperCase() + str.substring(1); // 字符串部分截取
} else
return str.toUpperCase() ;
}
}