C++string类模拟实现与深浅拷贝
文章目录
- 1.深浅拷贝
- 1)深浅拷贝的引入
- 2)浅拷贝
- 3)深拷贝
- a.传统写法
- b.现代写法
- 4)写时拷贝
- 2.string的模拟实现
- String.h
- String.cc
1.深浅拷贝
1)深浅拷贝的引入
观察下面的代码:
class String
{
public:
String(const char* str = "")
{
// 构造string类对象时,如果传递nullptr指针,认为程序非法,此处断言下
if(nullptr == str)
{
assert(false);
return;
}
_str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
~String()
{
if(_str)
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
}
private:
char* _str;
};
// 测试
void TestString()
{
String s1("hello bit!!!");
String s2(s1);
}
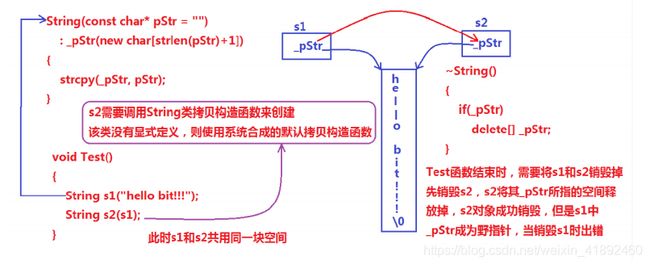
上述String类没有显式定义其拷贝构造函数与赋值运算符重载,此时编译器会合成默认的,当用s1构造s2时,编译器会调用默认的拷贝构造。最终导致的问题是s1、s2共用同一块内存空间,在释放时同一块空间被释放多次而引起程序崩溃,这种拷贝方式,称为浅拷贝。
2)浅拷贝
浅拷贝:也称位拷贝,编译器只是将对象中的值拷贝过来。如果对象中管理资源,最后就会导致多个对象共
享同一份资源,当一个对象销毁时就会将该资源释放掉,而此时另一些对象不知道该资源已经被释放,以为
还有效,所以 当继续对资源进项操作时,就会发生发生了访问违规。
3)深拷贝
如果一个类中涉及到资源的管理,其拷贝构造函数、赋值运算符重载以及析构函数必须要显式给出。一般情
况都是按照深拷贝方式提供。

a.传统写法
class String
{
public:
String(const char* str = "")
{
// 构造string类对象时,如果传递nullptr指针,认为程序非法,此处断言下
if(nullptr == str)
{
assert(false);
return;
}
_str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
String(const String& s)
: _str(new char[strlen(s._str)+1])
{
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}
String& operator=(const String& s)
{
if(this != &s)
{
char* pStr = new char[strlen(s._str) + 1];
strcpy(pStr, s._str);
delete[] _str;
_str = pStr;
}
return *this;
}
~String()
{
if(_str)
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
}
private:
char* _str;
};
b.现代写法
class String
{
public:
String(const char* str = "")
{
if(nullptr == str)
str = "";
_str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
String(const String& s)
: _str(nullptr)
{
String strTmp(s._str);
swap(_str, strTmp);
}
// 对比下和上面的赋值那个实现比较好?
String& operator=(String s)
{
swap(_str, s._str);
return *this;
}
/*
String& operator=(const String& s)
{
if(this != &s)
{
String strTmp(s);
swap(_str, strTmp._str);
}
return *this;
}
*/
~String()
{
if(_str)
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
}
private:
char* _str;
};
4)写时拷贝
写时拷贝就是一种拖延症,是在浅拷贝的基础之上增加了引用计数的方式来实现的。
引用计数:用来记录资源使用者的个数。在构造时,将资源的计数给成1,每增加一个对象使用该资源,就给计数增加1,当某个对象被销毁时,先给该计数减1,然后再检查是否需要释放资源,如果计数为1,说明该对象时资源的最后一个使用者,将该资源释放;否则就不能释放,因为还有其他对象在使用该资源。
2.string的模拟实现
String.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 0
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
namespace TJ
{
class String
{
public:
//类里面实现的函数默认为inline
String(const char*str = " ")
{
_size = strlen(str);
_capacity = _size > 20 ? _size : 20;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
~String()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
void Swap(String& s)
{
swap(_str, s._str);
swap(_size, s._size);
swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
String(const String& s)
:_str(nullptr)
, _size(0)
, _capacity(0)
{
String tmp(s._str);
swap(_str, tmp._str);
}
String& operator=(String s)
{
this->Swap(s);
return *this;
}
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
const char& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
size_t Size()const
{
return _size;
}
size_t Capacity()const
{
return _capacity;
}
const char* c_str()
{
return _str;
}
void Reserve(size_t n);
void Resize(size_t n, char ch = '\0');
void PushBack(char ch);
void Append(const char* str);
String& operator+=(char ch);
String& operator+=(const char* str);
size_t Find(char ch, size_t pos = 0);
size_t RFind(char ch, size_t pos = npos);
size_t Find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0);
void Insert(size_t pos, char ch);
void Insert(size_t pos, const char* str);
void Erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos);
String Substr(size_t pos, size_t len = npos);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const String& s);
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
public:
static const size_t npos ;
};
const size_t String::npos = -1;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const String& s);
}
String.cc
#include"String.h"
void TJ::String::Reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* newstr = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(newstr, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = newstr;
_capacity = n;
}
}
void TJ::String::Resize(size_t n, char ch)
{
if (n <= _size)
{
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
else
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
Reserve(n);
}
size_t pos = _size;
while (pos < n)
{
_str[pos] = ch;
++pos;
}
_size = n;
_str[n] = '\0';
}
}
void TJ::String::PushBack(char ch)
{
if(_size == _capacity )
{
Reserve(_capacity = 0 ? 2 : _capacity*2);
}
_str[_size] = ch;
_size++;
_str[_size] = '\0';
/*Insert(_size, ch);*/
}
void TJ::String::Append(const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
Reserve(_size + len);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;
/*Insert(_size, str);*/
}
TJ::String& TJ::String::operator+=(char ch)
{
this->PushBack(ch);
return *this;
}
TJ::String& TJ::String::operator+=(const char* str)
{
this->Append(str);
return *this;
}
size_t TJ::String::Find(char ch, size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
while (pos < _size)
{
if (_str[pos] == ch)
{
return pos;
}
++pos;
}
return String::npos;
}
TJ::String TJ::String::Substr(size_t pos, size_t len)
{
if (_size - pos < len)
{
len = _size - pos;
}
TJ::String sub;
sub.Reserve(len);
for (size_t i = pos; i < pos + len; ++i)
{
sub += _str[i];
}
return sub;
}
size_t TJ::String::RFind(char ch, size_t pos)
{
int end = _size - 1;
if (pos != String::npos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
end = pos;
}
while (end > 0)
{
if (_str[end] == ch)
{
return end;
}
end--;
}
return String::npos;
}
size_t TJ::String::Find(const char* str, size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
char* substr = strstr(_str + pos, str);
if (substr == nullptr)
{
return npos;
}
else
{
return substr - _str;
}
}
void TJ::String::Insert(size_t pos, char ch)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
//增容
if ((_size + 1) > _capacity)
{
Reserve(_capacity * 2);
}
int i = _size;
for (; i >= (int)pos; i--)
{
_str[i + 1] = _str[i];
}
_str[pos] = ch;
_size++;
}
void TJ::String::Insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
assert(pos < _size);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
Reserve(_size + len);
}
int end = _size;
while (end >= (int)pos)
{
_str[end + len] = _str[end];
--end;
}
while (*str)
{
_str[pos++] = *str++;
}
_size += len;
}
void TJ::String::Erase(size_t pos, size_t len)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
_str[pos] = _str[pos + len];
pos++;
}
_size -= len;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
}
ostream& TJ::operator<<(ostream& _cout, const String& s)
{
_cout << s._str;
return _cout;
}
void TestBitString1()
{
TJ::String s1;
TJ::String s2("hello bit");
TJ::String s3(s2);
s1 = s3;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.Size() << endl;
cout << s1.Capacity() << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
}
void TestBitString2()
{
TJ::String s1("hello");
/*s1.PushBack(' ');
s1.PushBack('b');*/
s1.Append("jj");
//s1 += 't';
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.Size() << endl;
cout << s1.Capacity() << endl;
//利用迭代器打印string中的元素
auto it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it++;
}
cout << endl;
TJ::String s2("hello world!!!");
s1.Swap(s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
}
void TestBitString3()
{
TJ::String s("hellhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhho");
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.Size() << endl;
cout << s.Capacity() << endl;
s.Resize(10);
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.Size() << endl;
cout << s.Capacity() << endl;
s.Resize(15);
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.Size() << endl;
cout << s.Capacity() << endl;
s.Resize(20,'a');
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.Size() << endl;
cout << s.Capacity() << endl;
s.Reserve(50);
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.Size() << endl;
cout << s.Capacity() << endl;
}
int main()
{
TestBitString2();
system("pause");
}