lwIP TCP/IP 协议栈笔记之十六: NETCONN 接口编程
目录
1. netbuf 结构体
2. netbuf 相关函数说明
2.1 netbuf_new()
2.2 netbuf_delete()
2.3 netbuf_alloc()
2.4 netbuf_free()
2.5 netbuf_ref()
2.6 netbuf_chain()
2.7 netbuf_data()
2.8 netbuf_next()与netbuf_first()
2.9 netbuf_copy()
2.10 netbuf_take()
3. netconn 结构体
4. netconn 函数接口说明
4.1 netconn_new()
4.2 netconn_delete()
4.3 netconn_getaddr()
4.4 netconn_bind()
4.5 netconn_connect()
4.6 netconn_disconnect()
4.7 netconn_listen()
4.8 netconn_accept()
4.9 netconn_recv()
4.10 netconn_send()
4.11 netconn_sendto()
4.12 netconn_write()
5. 示例例程
5.1 TCP Client
5.2 TCP Server
5.3 UDP
1. netbuf 结构体
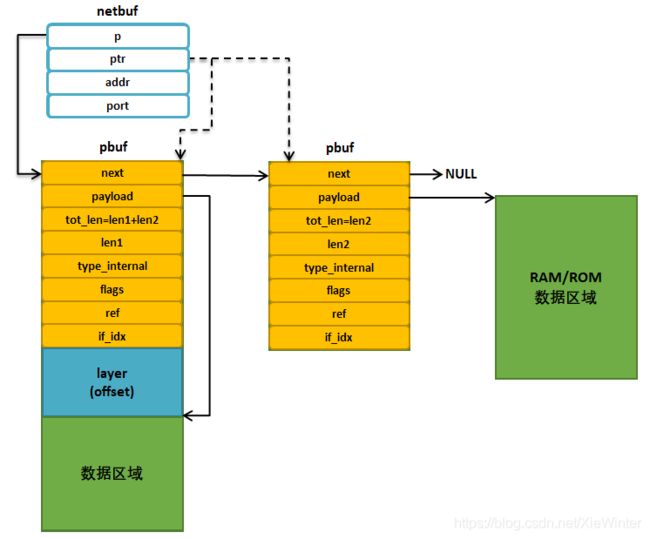
LwIP 为了更好描述应用线程发送与接收的数据,并且为了更好管理这些数据的缓冲区,LwIP 定义了一个netbuf 结构体,它是基于pbuf 上更高一层的封装,记录了主机的IP 地址与端口号,在这里再提醒一下大家,端口号对应的其实就是应用线程。在接收的时候,应用程序肯定需要知道到底是谁发数据给自己,而在发送的时候,应用程序需要将自己的端口号与IP 地址填充到netbuf 结构体对应字段中。
// netbuf.h
/** "Network buffer" - contains data and addressing info */
struct netbuf {
struct pbuf *p, *ptr;
ip_addr_t addr;
u16_t port;
#if LWIP_NETBUF_RECVINFO || LWIP_CHECKSUM_ON_COPY
u8_t flags;
u16_t toport_chksum;
#if LWIP_NETBUF_RECVINFO
ip_addr_t toaddr;
#endif /* LWIP_NETBUF_RECVINFO */
#endif /* LWIP_NETBUF_RECVINFO || LWIP_CHECKSUM_ON_COPY */
};1):netbuf 的p 字段的指针指向pbuf 链表,这是基于pbuf 上封装的结构体,因此,ptr 字段的指针也是指向pbuf,但是它与p 字段的指针有一点不一样,因为它可以指向任意的pbuf,由netbuf_next()与netbuf_first()函数来控制。
2): addr 字段记录了数据发送方的IP 地址
3):port 记录了数据发送方的端口号
netbuf 结构体指向示意图具体见图,虚线表示ptr 指针的指向位置是不固定的,它是由netbuf_next()函数与netbuf_first()函数来调整的
指向不同类型的pbuf 链表
指向相同类型pbuf 链表
2. netbuf 相关函数说明
netbuf 是LwIP 描述用户数据很重要的一个结构体,因为LwIP 是不可能让我们直接操作pbuf 的,因为分层的思想,应用数据必然是由用户操作的,因此LwIP 会提供很多函数接口让用户对netbuf 进行操作,无论是UDP 报文还是TCP 报文段,其本质都是数据,要发送出去的数据都会封装在netbuf 中,然后通过邮箱发送给内核线程(tcpip_thread 线程),然后经过内核的一系列处理,放入发送队列中,然后调用底层网卡发送函数进行发送,反之,应用线程接收到数据,也是通过netbuf 进行管理,下面一起来看看LwIP 提供给我们操作netbuf 的相关函数。
2.1 netbuf_new()
函数的功能是申请一个新的netbuf 结构体内存空间,通过memp 内存池进行申请,大小为MEMP_NETBUF,并且将netbuf 结构体全部初始化为0,并且返回一个指向netbuf结构体的指针,此时的netbuf 结构体的p 与ptr 字段不指向任何的pbuf.
struct
netbuf *netbuf_new(void)
{
struct netbuf *buf;
buf = (struct netbuf *)memp_malloc(MEMP_NETBUF);
if (buf != NULL) {
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(struct netbuf));
}
return buf;
}2.2 netbuf_delete()
与netbuf_new()函数相反,释放一个netbuf 结构体内存空间,如果netbuf 结构体的p或者ptr 字段指向的pbuf 是拥有数据的,那么对应的pbuf 也会被释放掉
void
netbuf_delete(struct netbuf *buf)
{
if (buf != NULL) {
if (buf->p != NULL) {
pbuf_free(buf->p);
buf->p = buf->ptr = NULL;
}
memp_free(MEMP_NETBUF, buf);
}
}2.3 netbuf_alloc()
为netbuf 结构体中的p 字段指向的数据区域分配指定大小的内存空间,简单来说就是申请pbuf 内存空间,由于这个函数是在应用层调用的,因此这个内存会包含链路层首部、IP 层首部与传输层首部大小,当然,这些空间是附加上去的,用户指定的是数据区域大小,当然还有很重要的一点就是,如果当前netbuf 中已经存在数据区域了,那么这个数据区域会被释放掉,然后重新申请用户指定大小的数据区域,而函数的返回是一个指向数据区域起始地址的指针(即pbuf 的payload 指针)
void *
netbuf_alloc(struct netbuf *buf, u16_t size)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_alloc: invalid buf", (buf != NULL), return NULL;);
/* Deallocate any previously allocated memory. */
if (buf->p != NULL) {
pbuf_free(buf->p);
}
buf->p = pbuf_alloc(PBUF_TRANSPORT, size, PBUF_RAM);
if (buf->p == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
LWIP_ASSERT("check that first pbuf can hold size",
(buf->p->len >= size));
buf->ptr = buf->p;
return buf->p->payload;
}2.4 netbuf_free()
直接释放netbuf 结构体指向的pbuf 内存空间,如果结构体中指向pbuf 的内容为空,则不做任何释放操作,直接将p 与ptr 字段的指针设置为NULL
void
netbuf_free(struct netbuf *buf)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_free: invalid buf", (buf != NULL), return;);
if (buf->p != NULL) {
pbuf_free(buf->p);
}
buf->p = buf->ptr = NULL;
#if LWIP_CHECKSUM_ON_COPY
buf->flags = 0;
buf->toport_chksum = 0;
#endif /* LWIP_CHECKSUM_ON_COPY */
}2.5 netbuf_ref()
函数与netbuf_alloc()函数很像,都是申请内存空间,但是,有一个很大的不同,netbuf_ref()函数只申请pbuf 首部的内存空间,包含链路层首部、IP 层首部与传输层首部,而不会申请数据区域内存空间,然后把pbuf 的payload 指针指向用户指定的数据区域起始地址dataptr,这种申请经常在发送静态数据的时候用到,因为数据保存的地址是固定的,而不用动态申请,如果netbuf 的p 或者ptr 字段已经指向了pbuf,那么这些pbuf 将被释放掉.
注意:在使用该函数的时候用户需要传递有效的静态数据区域起始地址,比如某个静态字符串的起始地址。
err_t
netbuf_ref(struct netbuf *buf, const void *dataptr, u16_t size)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_ref: invalid buf", (buf != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
if (buf->p != NULL) {
pbuf_free(buf->p);
}
buf->p = pbuf_alloc(PBUF_TRANSPORT, 0, PBUF_REF);
if (buf->p == NULL) {
buf->ptr = NULL;
return ERR_MEM;
}
((struct pbuf_rom *)buf->p)->payload = dataptr;
buf->p->len = buf->p->tot_len = size;
buf->ptr = buf->p;
return ERR_OK;
}2.6 netbuf_chain()
netbuf_chain()函数是将tail 中的pbuf 数据连接到head 中的pbuf 后面,形成一个pbuf链表,在调用此函数之后,会将tail 结构删除
void
netbuf_chain(struct netbuf *head, struct netbuf *tail)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_chain: invalid head", (head != NULL), return;);
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_chain: invalid tail", (tail != NULL), return;);
pbuf_cat(head->p, tail->p);
head->ptr = head->p;
memp_free(MEMP_NETBUF, tail);
}2.7 netbuf_data()
获取netbuf中的数据指针和数据长度。
err_t
netbuf_data(struct netbuf *buf, void **dataptr, u16_t *len)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_data: invalid buf", (buf != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_data: invalid dataptr", (dataptr != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_data: invalid len", (len != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
if (buf->ptr == NULL) {
return ERR_BUF;
}
*dataptr = buf->ptr->payload;
*len = buf->ptr->len;
return ERR_OK;
}2.8 netbuf_next()与netbuf_first()
netbuf_next()用于移动netbuf 的ptr 数据指针,使ptr 指针指向pbuf 链表的下一个pbuf。同样的netbuf_first()函数可以将ptr 指针指向pbuf 链表的第一个pbuf。这两个函数是很有用的,比如netbuf 中p 字段的指针指向一个pbuf 链表,并且pbuf 链表中拥有多个pbuf,那么需要配合netbuf_data()函数将链表中的所有的pbuf 读取并且处理;如果netbuf_next()函数的返回值为0,表示调整成功,而如果返回值小于0 时,则表示调整失败
s8_t
netbuf_next(struct netbuf *buf)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_next: invalid buf", (buf != NULL), return -1;);
if (buf->ptr->next == NULL) {
return -1;
}
buf->ptr = buf->ptr->next;
if (buf->ptr->next == NULL) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void
netbuf_first(struct netbuf *buf)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_first: invalid buf", (buf != NULL), return;);
buf->ptr = buf->p;
}2.9 netbuf_copy()
这个函数用于将netbuf 结构体数据区域pbuf 中的所有数据拷贝到dataptr 指针指向的存储区,即使pbuf(链表)中的数据被保存在多个pbuf 中,它也会完全拷贝出来,len 参数指定要拷贝数据的最大长度,如果netbuf 的数据区域空间小于len 指定的大小,那么内核只会拷贝netbuf 数据区域大小的数据,此外,该函数本质是一个宏定义,真正实现的函数在pbuf.c
#define netbuf_copy_partial(buf, dataptr, len, offset) \
pbuf_copy_partial((buf)->p, (dataptr), (len), (offset))
#define netbuf_copy(buf,dataptr,len) netbuf_copy_partial(buf, dataptr, len, 0)2.10 netbuf_take()
函数用于将用户指定区域的数据dataptr 拷贝到netbuf 结构体数据区域pbuf 中,可能用户数据太多,一个pbuf 存储不下用户的数据,那么内核将对数据进行切割处理,使用多个pbuf 存储,len 参数指定要拷贝数据的长度
#define netbuf_take(buf, dataptr, len) pbuf_take((buf)->p, dataptr, len)
/**
* @ingroup pbuf
* Copy application supplied data into a pbuf.
* This function can only be used to copy the equivalent of buf->tot_len data.
*
* @param buf pbuf to fill with data
* @param dataptr application supplied data buffer
* @param len length of the application supplied data buffer
*
* @return ERR_OK if successful, ERR_MEM if the pbuf is not big enough
*/
err_t
pbuf_take(struct pbuf *buf, const void *dataptr, u16_t len);#define netbuf_len(buf) ((buf)->p->tot_len)
#define netbuf_fromaddr(buf) (&((buf)->addr))
#define netbuf_set_fromaddr(buf, fromaddr) ip_addr_set(&((buf)->addr), fromaddr)
#define netbuf_fromport(buf) ((buf)->port)3. netconn 结构体
在LwIP 中,如TCP 连接,UDP 通信,都是需要提供一个编程接口给用户使用的,那么为了描述这样子的一个接口,LwIP 抽象出来一个nettonn 结构体,它能描述一个连接,供应用程序使用,同时内核的NETCONN API 接口也对各种连接操作函数进行了统一的封装,这样子,用户程序可以很方便使netconn 和编程函数,我们暂且将netconn 称之为连接结构体。
一个连接结构体中包含的成员变量很多,如描述连接的类型,连接的状态(主要是在TCP 连接中使用),对应的控制块(如UDP 控制块、TCP 控制块等等),还有对应线程的消息邮箱以及一些记录的信息.
api.h
/** A netconn descriptor */
struct netconn {
/** 类型netconn (TCP, UDP or RAW) */
enum netconn_type type;
/** 当前状态 the netconn */
enum netconn_state state;
/** the lwIP internal protocol control block */
union {
struct ip_pcb *ip;
struct tcp_pcb *tcp;
struct udp_pcb *udp;
struct raw_pcb *raw;
} pcb;
/** 这个netconn 最后一个异步未报告的错误 */
err_t pending_err;
#if !LWIP_NETCONN_SEM_PER_THREAD
/** 信号量 that is used to synchronously execute functions in the core context */
sys_sem_t op_completed;
#endif
/** 消息邮箱 where received packets are stored until they are fetched
by the netconn application thread (can grow quite big) */
sys_mbox_t recvmbox;
#if LWIP_TCP
/** mbox where new connections are stored until processed
by the application thread */
sys_mbox_t acceptmbox;
#endif /* LWIP_TCP */
#if LWIP_NETCONN_FULLDUPLEX
/** number of threads waiting on an mbox. This is required to unblock
all threads when closing while threads are waiting. */
int mbox_threads_waiting;
#endif
/** only used for socket layer */
#if LWIP_SOCKET
int socket;
#endif /* LWIP_SOCKET */
#if LWIP_SO_SNDTIMEO
/** timeout to wait for sending data (which means enqueueing data for sending
in internal buffers) in milliseconds */
s32_t send_timeout;
#endif /* LWIP_SO_RCVTIMEO */
#if LWIP_SO_RCVTIMEO
/** timeout in milliseconds to wait for new data to be received
(or connections to arrive for listening netconns) */
u32_t recv_timeout;
#endif /* LWIP_SO_RCVTIMEO */
#if LWIP_SO_RCVBUF
/** maximum amount of bytes queued in recvmbox
not used for TCP: adjust TCP_WND instead! */
int recv_bufsize;
/** number of bytes currently in recvmbox to be received,
tested against recv_bufsize to limit bytes on recvmbox
for UDP and RAW, used for FIONREAD */
int recv_avail;
#endif /* LWIP_SO_RCVBUF */
#if LWIP_SO_LINGER
/** values <0 mean linger is disabled, values > 0 are seconds to linger */
s16_t linger;
#endif /* LWIP_SO_LINGER */
/** flags holding more netconn-internal state, see NETCONN_FLAG_* defines */
u8_t flags;
#if LWIP_TCP
/** TCP: when data passed to netconn_write doesn't fit into the send buffer,
this temporarily stores the message.
Also used during connect and close. */
struct api_msg *current_msg;
#endif /* LWIP_TCP */
/** A callback function that is informed about events for this netconn */
netconn_callback callback;
};enum netconn_type {
NETCONN_INVALID = 0,
/** TCP IPv4 */
NETCONN_TCP = 0x10,
#if LWIP_IPV6
/** TCP IPv6 */
NETCONN_TCP_IPV6 = NETCONN_TCP | NETCONN_TYPE_IPV6 /* 0x18 */,
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 */
/** UDP IPv4 */
NETCONN_UDP = 0x20,
/** UDP IPv4 lite */
NETCONN_UDPLITE = 0x21,
/** UDP IPv4 no checksum */
NETCONN_UDPNOCHKSUM = 0x22,
#if LWIP_IPV6
/** UDP IPv6 (dual-stack by default, unless you call @ref netconn_set_ipv6only) */
NETCONN_UDP_IPV6 = NETCONN_UDP | NETCONN_TYPE_IPV6 /* 0x28 */,
/** UDP IPv6 lite (dual-stack by default, unless you call @ref netconn_set_ipv6only) */
NETCONN_UDPLITE_IPV6 = NETCONN_UDPLITE | NETCONN_TYPE_IPV6 /* 0x29 */,
/** UDP IPv6 no checksum (dual-stack by default, unless you call @ref netconn_set_ipv6only) */
NETCONN_UDPNOCHKSUM_IPV6 = NETCONN_UDPNOCHKSUM | NETCONN_TYPE_IPV6 /* 0x2a */,
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 */
/** Raw connection IPv4 */
NETCONN_RAW = 0x40
#if LWIP_IPV6
/** Raw connection IPv6 (dual-stack by default, unless you call @ref netconn_set_ipv6only) */
, NETCONN_RAW_IPV6 = NETCONN_RAW | NETCONN_TYPE_IPV6 /* 0x48 */
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 */
};/** Current state of the netconn. Non-TCP netconns are always
* in state NETCONN_NONE! */
enum netconn_state {
NETCONN_NONE,
NETCONN_WRITE,
NETCONN_LISTEN,
NETCONN_CONNECT,
NETCONN_CLOSE
};4. netconn 函数接口说明
下面这些函数都在api_lib.c 文件中实现,在api.h 头文件中声明.
4.1 netconn_new()
函数 netconn_new ()本质上是一个宏定义,它用来创建一个新的连接结构,连接结构的类型可以选择为 TCP 或 UDP 等,参数 type 描述了连接的类型,可以为 NETCONN_TCP或NETCONN_UDP 等,在这个函数被调用时,会初始化相关的字段,而并不会创建连接.
#define netconn_new(t) netconn_new_with_proto_and_callback(t, 0, NULL)
/**
* Create a new netconn (of a specific type) that has a callback function.
* The corresponding pcb is also created.
*
* @param t the type of 'connection' to create (@see enum netconn_type)
* @param proto the IP protocol for RAW IP pcbs
* @param callback a function to call on status changes (RX available, TX'ed)
* @return a newly allocated struct netconn or
* NULL on memory error
*/
struct netconn *
netconn_new_with_proto_and_callback(enum netconn_type t, u8_t proto, netconn_callback callback)
{
struct netconn *conn;
API_MSG_VAR_DECLARE(msg);
API_MSG_VAR_ALLOC_RETURN_NULL(msg);
conn = netconn_alloc(t, callback);
if (conn != NULL) {
err_t err;
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.n.proto = proto;
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).conn = conn;
err = netconn_apimsg(lwip_netconn_do_newconn, &API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg));
if (err != ERR_OK) {
LWIP_ASSERT("freeing conn without freeing pcb", conn->pcb.tcp == NULL);
LWIP_ASSERT("conn has no recvmbox", sys_mbox_valid(&conn->recvmbox));
#if LWIP_TCP
LWIP_ASSERT("conn->acceptmbox shouldn't exist", !sys_mbox_valid(&conn->acceptmbox));
#endif /* LWIP_TCP */
#if !LWIP_NETCONN_SEM_PER_THREAD
LWIP_ASSERT("conn has no op_completed", sys_sem_valid(&conn->op_completed));
sys_sem_free(&conn->op_completed);
#endif /* !LWIP_NETCONN_SEM_PER_THREAD */
sys_mbox_free(&conn->recvmbox);
memp_free(MEMP_NETCONN, conn);
API_MSG_VAR_FREE(msg);
return NULL;
}
}
API_MSG_VAR_FREE(msg);
return conn;
}4.2 netconn_delete()
个函数的功能与netconn_new()函数刚好是相反的,它用于删除一个netconn 连接结构,对于TCP 连接,如果此时是处于连接状态的,在调用该函数后,将请求内核执行终止连接操作,此时应用线程是无需理会到底是怎么运作的,因为LwIP 内核将会完成所有的挥手过程,需要注意的是此时的TCP 控制块还是不会立即被删除的,因为需要完成真正的断开挥手操作,这些状态可以参考TCP 协议状态转移图。而对于UDP 协议,UDP 控制块将被删除,终止通信.
/**
* @ingroup netconn_common
* Close a netconn 'connection' and free its resources.
* UDP and RAW connection are completely closed, TCP pcbs might still be in a waitstate
* after this returns.
*
* @param conn the netconn to delete
* @return ERR_OK if the connection was deleted
*/
err_t
netconn_delete(struct netconn *conn)
{
err_t err;
/* No ASSERT here because possible to get a (conn == NULL) if we got an accept error */
if (conn == NULL) {
return ERR_OK;
}
#if LWIP_NETCONN_FULLDUPLEX
if (conn->flags & NETCONN_FLAG_MBOXINVALID) {
/* Already called netconn_prepare_delete() before */
err = ERR_OK;
} else
#endif /* LWIP_NETCONN_FULLDUPLEX */
{
err = netconn_prepare_delete(conn);
}
if (err == ERR_OK) {
netconn_free(conn);
}
return err;
}真正处理的函数是netconn_prepare_delete(),它同样是调用netconn_apimsg()函数先构造一个API 消息,然后投递到系统邮箱,请求LwIP 内核线程去执行lwip_netconn_do_delconn()函数,这个函数会将对应的netconn 连接结构删除,在执行完毕之后,通过信号量进行同步,应用线程得以继续执行.
4.3 netconn_getaddr()
获取一个netconn 连接结构的源IP 地址、端口号与目标IP 地址、端口号等信息,并且IP 地址保存在addr 中,端口号保存在port 中,而local 指定需要获取的信息是本地IP 地址(源IP 地址)还是远端IP 地址(目标IP 地址),如果是1 则表示获取本地IP 地址与端口号,如果为0 表示远端IP 地址与端口号。同样的,该函数会调用netconn_apimsg()函数构造一个API 消息,并且请求内核执行lwip_netconn_do_getaddr()函数,然后通过netconn 连接结构的信号量进行同步.
/**
* Get the local or remote IP address and port of a netconn.
* For RAW netconns, this returns the protocol instead of a port!
*
* @param conn the netconn to query
* @param addr a pointer to which to save the IP address
* @param port a pointer to which to save the port (or protocol for RAW)
* @param local 1 to get the local IP address, 0 to get the remote one
* @return ERR_CONN for invalid connections
* ERR_OK if the information was retrieved
*/
err_t
netconn_getaddr(struct netconn *conn, ip_addr_t *addr, u16_t *port, u8_t local)
{
API_MSG_VAR_DECLARE(msg);
err_t err;
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_getaddr: invalid conn", (conn != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_getaddr: invalid addr", (addr != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_getaddr: invalid port", (port != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
API_MSG_VAR_ALLOC(msg);
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).conn = conn;
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.ad.local = local;
#if LWIP_MPU_COMPATIBLE
err = netconn_apimsg(lwip_netconn_do_getaddr, &API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg));
*addr = msg->msg.ad.ipaddr;
*port = msg->msg.ad.port;
#else /* LWIP_MPU_COMPATIBLE */
msg.msg.ad.ipaddr = addr;
msg.msg.ad.port = port;
err = netconn_apimsg(lwip_netconn_do_getaddr, &msg);
#endif /* LWIP_MPU_COMPATIBLE */
API_MSG_VAR_FREE(msg);
return err;
}4.4 netconn_bind()
将一个 IP 地址及端口号与netconn 连接结构进行绑定,如果作为服务器端,这一步操作是必然需要的,同样的,该函数会调用netconn_apimsg()函数构造一个API 消息,并且请求内核执行lwip_netconn_do_bind()函数,然后通过netconn 连接结构的信号量进行同步,事实上内核线程的处理也是通过函数调用xxx_bind(xxx_bind 可以是udp_bind、tcp_bind、raw_bind,具体是哪个函数内核是根据netconn 的类型决定的)完成相应控制块的绑定工作.
/**
* @ingroup netconn_common
* Bind a netconn to a specific local IP address and port.
* Binding one netconn twice might not always be checked correctly!
*
* @param conn the netconn to bind
* @param addr the local IP address to bind the netconn to
* (use IP4_ADDR_ANY/IP6_ADDR_ANY to bind to all addresses)
* @param port the local port to bind the netconn to (not used for RAW)
* @return ERR_OK if bound, any other err_t on failure
*/
err_t
netconn_bind(struct netconn *conn, const ip_addr_t *addr, u16_t port)
{
API_MSG_VAR_DECLARE(msg);
err_t err;
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_bind: invalid conn", (conn != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
#if LWIP_IPV4
/* Don't propagate NULL pointer (IP_ADDR_ANY alias) to subsequent functions */
if (addr == NULL) {
addr = IP4_ADDR_ANY;
}
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 */
#if LWIP_IPV4 && LWIP_IPV6
/* "Socket API like" dual-stack support: If IP to bind to is IP6_ADDR_ANY,
* and NETCONN_FLAG_IPV6_V6ONLY is 0, use IP_ANY_TYPE to bind
*/
if ((netconn_get_ipv6only(conn) == 0) &&
ip_addr_cmp(addr, IP6_ADDR_ANY)) {
addr = IP_ANY_TYPE;
}
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 && LWIP_IPV6 */
API_MSG_VAR_ALLOC(msg);
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).conn = conn;
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.bc.ipaddr = API_MSG_VAR_REF(addr);
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.bc.port = port;
err = netconn_apimsg(lwip_netconn_do_bind, &API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg));
API_MSG_VAR_FREE(msg);
return err;
}4.5 netconn_connect()
netconn_connect()函数是一个主动建立连接的函数,它一般在客户端中调用,将服务器端的 IP 地址和端口号与本地的netconn 连接结构绑定,当TCP 协议使用该函数的时候就是进行握手的过程,调用的应用线程将阻塞至握手完成;而对于UDP 协议来说,调用该函数只是设置UDP 控制块的目标IP 地址与目标端口号,其实这个函数也是通过调用netconn_apimsg()函数构造一个API 消息,并且请求内核执行lwip_netconn_do_connect()函数,然后通过netconn 连接结构的信号量进行同步,lwip_netconn_do_connect()函数中,根据netconn 的类型不同,调用对应的xxx_connect()函数进行对应的处理,如果是TCP 连接,将调用tcp_connect();如果是UDP 协议,将调用udp_connect();如果是RAW,将调用raw_connect()函数处理.
/**
* @ingroup netconn_common
* Connect a netconn to a specific remote IP address and port.
*
* @param conn the netconn to connect
* @param addr the remote IP address to connect to
* @param port the remote port to connect to (no used for RAW)
* @return ERR_OK if connected, return value of tcp_/udp_/raw_connect otherwise
*/
err_t
netconn_connect(struct netconn *conn, const ip_addr_t *addr, u16_t port)
{
API_MSG_VAR_DECLARE(msg);
err_t err;
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_connect: invalid conn", (conn != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
#if LWIP_IPV4
/* Don't propagate NULL pointer (IP_ADDR_ANY alias) to subsequent functions */
if (addr == NULL) {
addr = IP4_ADDR_ANY;
}
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 */
API_MSG_VAR_ALLOC(msg);
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).conn = conn;
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.bc.ipaddr = API_MSG_VAR_REF(addr);
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.bc.port = port;
err = netconn_apimsg(lwip_netconn_do_connect, &API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg));
API_MSG_VAR_FREE(msg);
return err;
}4.6 netconn_disconnect()
该函数是用于终止一个UDP 协议的通信,注意,是UDP 协议,而不是TCP 协议,因为这个函数只能用于UDP 协议,简单来说就是将UDP 控制块的目标IP 地址与目标端口号清除,不过麻雀虽小,但五脏俱全,同样的该函数也是构造API 消息请求内核执行lwip_netconn_do_disconnect()函数
/**
* @ingroup netconn_udp
* Disconnect a netconn from its current peer (only valid for UDP netconns).
*
* @param conn the netconn to disconnect
* @return See @ref err_t
*/
err_t
netconn_disconnect(struct netconn *conn)
{
API_MSG_VAR_DECLARE(msg);
err_t err;
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_disconnect: invalid conn", (conn != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
API_MSG_VAR_ALLOC(msg);
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).conn = conn;
err = netconn_apimsg(lwip_netconn_do_disconnect, &API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg));
API_MSG_VAR_FREE(msg);
return err;
}4.7 netconn_listen()
netconn_listen()函数的本质是一个带参宏,其真正调用的函数是netconn_listen_with_backlog(),只适用于TCP 服务器中调用,它的作用是让netconn 连接结构处于监听状态,同时让TCP 控制块的状态处于LISTEN 状态,以便客户端连接,同样的,它通过netconn_apimsg()函数请求内核执行lwip_netconn_do_listen(),这个函数才是真正处理TCP 连接的监听状态,并且在这个函数中会创建一个连接邮箱——acceptmbox 邮箱在netconn 连接结构中,然后在TCP 控制块中注册连接回调函数——accept_function(),当有客户端连接的时候,这个回调函数被执行,并且向acceptmbox 邮箱发送一个消息,通知应用程序有一个新的客户端连接,以便用户去处理这个连接。当然,在lwip_netconn_do_listen()函数处理完成的时候会释放一个信号量,以进行线程间的同步.
/** @ingroup netconn_tcp */
#define netconn_listen(conn) netconn_listen_with_backlog(conn, TCP_DEFAULT_LISTEN_BACKLOG)
/**
* @ingroup netconn_tcp
* Set a TCP netconn into listen mode
*
* @param conn the tcp netconn to set to listen mode
* @param backlog the listen backlog, only used if TCP_LISTEN_BACKLOG==1
* @return ERR_OK if the netconn was set to listen (UDP and RAW netconns
* don't return any error (yet?))
*/
err_t
netconn_listen_with_backlog(struct netconn *conn, u8_t backlog)
{
#if LWIP_TCP
API_MSG_VAR_DECLARE(msg);
err_t err;
/* This does no harm. If TCP_LISTEN_BACKLOG is off, backlog is unused. */
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(backlog);
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_listen: invalid conn", (conn != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
API_MSG_VAR_ALLOC(msg);
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).conn = conn;
#if TCP_LISTEN_BACKLOG
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.lb.backlog = backlog;
#endif /* TCP_LISTEN_BACKLOG */
err = netconn_apimsg(lwip_netconn_do_listen, &API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg));
API_MSG_VAR_FREE(msg);
return err;
#else /* LWIP_TCP */
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(conn);
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(backlog);
return ERR_ARG;
#endif /* LWIP_TCP */
}4.8 netconn_accept()
函数用于TCP 服务器中,接受远端主机的连接,内核会在acceptmbox 邮箱中获取一个连接请求,如果邮箱中没有连接请求,将阻塞应用程序,直到接收到从远端主机发出的连接请求。调用这个函数的应用程序必须处于监听(LISTEN)状态,因此在调用netconn_accept()函数之前必须调用netconn_listen()函数进入监听状态,在与远程主机的连接建立后,函数返回一个连接结构netconn;该函数在并不会构造一个API 消息,而是直接获取acceptmbox 邮箱中的连接请求,如果没有连接请求,将一直阻塞,当接收到远端主机的连接请求后,它会触发一个连接事件的回调函数(netconn 结构体中的回调函数字段),连接的信息由accept_function()函数完成。可能没发现这个回调函数啊,其实在LwIP 在将TCP 服务器进入监听状态的时候就已经注册了这个回调函数,在有连接的时候,就直接进行连接。在lwip_netconn_do_listen() 函数中调用 tcp_accept()函数进行注册连接时候的回调函数.
/**
* @ingroup netconn_tcp
* Accept a new connection on a TCP listening netconn.
*
* @param conn the TCP listen netconn
* @param new_conn pointer where the new connection is stored
* @return ERR_OK if a new connection has been received or an error
* code otherwise
*/
err_t
netconn_accept(struct netconn *conn, struct netconn **new_conn)
{
#if LWIP_TCP
err_t err;
void *accept_ptr;
struct netconn *newconn;
#if TCP_LISTEN_BACKLOG
API_MSG_VAR_DECLARE(msg);
#endif /* TCP_LISTEN_BACKLOG */
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_accept: invalid pointer", (new_conn != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
*new_conn = NULL;
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_accept: invalid conn", (conn != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
/* NOTE: Although the opengroup spec says a pending error shall be returned to
send/recv/getsockopt(SO_ERROR) only, we return it for listening
connections also, to handle embedded-system errors */
err = netconn_err(conn);
if (err != ERR_OK) {
/* return pending error */
return err;
}
if (!NETCONN_ACCEPTMBOX_WAITABLE(conn)) {
/* don't accept if closed: this might block the application task
waiting on acceptmbox forever! */
return ERR_CLSD;
}
API_MSG_VAR_ALLOC_ACCEPT(msg);
NETCONN_MBOX_WAITING_INC(conn);
if (netconn_is_nonblocking(conn)) {
if (sys_arch_mbox_tryfetch(&conn->acceptmbox, &accept_ptr) == SYS_ARCH_TIMEOUT) {
API_MSG_VAR_FREE_ACCEPT(msg);
NETCONN_MBOX_WAITING_DEC(conn);
return ERR_WOULDBLOCK;
}
} else {
#if LWIP_SO_RCVTIMEO
if (sys_arch_mbox_fetch(&conn->acceptmbox, &accept_ptr, conn->recv_timeout) == SYS_ARCH_TIMEOUT) {
API_MSG_VAR_FREE_ACCEPT(msg);
NETCONN_MBOX_WAITING_DEC(conn);
return ERR_TIMEOUT;
}
#else
sys_arch_mbox_fetch(&conn->acceptmbox, &accept_ptr, 0);
#endif /* LWIP_SO_RCVTIMEO*/
}
NETCONN_MBOX_WAITING_DEC(conn);
#if LWIP_NETCONN_FULLDUPLEX
if (conn->flags & NETCONN_FLAG_MBOXINVALID) {
if (lwip_netconn_is_deallocated_msg(accept_ptr)) {
/* the netconn has been closed from another thread */
API_MSG_VAR_FREE_ACCEPT(msg);
return ERR_CONN;
}
}
#endif
/* Register event with callback */
API_EVENT(conn, NETCONN_EVT_RCVMINUS, 0);
if (lwip_netconn_is_err_msg(accept_ptr, &err)) {
/* a connection has been aborted: e.g. out of pcbs or out of netconns during accept */
API_MSG_VAR_FREE_ACCEPT(msg);
return err;
}
if (accept_ptr == NULL) {
/* connection has been aborted */
API_MSG_VAR_FREE_ACCEPT(msg);
return ERR_CLSD;
}
newconn = (struct netconn *)accept_ptr;
#if TCP_LISTEN_BACKLOG
/* Let the stack know that we have accepted the connection. */
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).conn = newconn;
/* don't care for the return value of lwip_netconn_do_recv */
netconn_apimsg(lwip_netconn_do_accepted, &API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg));
API_MSG_VAR_FREE(msg);
#endif /* TCP_LISTEN_BACKLOG */
*new_conn = newconn;
/* don't set conn->last_err: it's only ERR_OK, anyway */
return ERR_OK;
#else /* LWIP_TCP */
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(conn);
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(new_conn);
return ERR_ARG;
#endif /* LWIP_TCP */
}4.9 netconn_recv()
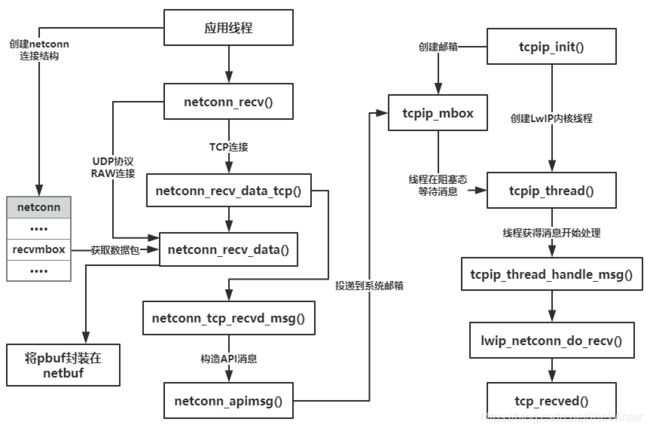
这个函数可能是我们在写代码中遇到最多的函数了,它可以接收一个UDP 或者TCP的数据包,从recvmbox 邮箱中获取数据包,如果该邮箱中没有数据包,那么线程调用这个函数将会进入阻塞状态以等待消息的到来,如果在等待TCP 连接上的数据时,远端主机终止连接,将返回一个终止连接的错误代码(ERR_CLSD),应用程序可以根据错误的类型进行不一样的处理。
对应TCP 连接,netconn_recv()函数将调用netconn_recv_data_tcp()函数去获取TCP 连接上的数据,在获取数据的过程中,调用netconn_recv_data()函数从recvmbox 邮箱获取pbuf,然后通过netconn_tcp_recvd_msg()->netconn_apimsg()函数构造一个API 消息投递给系统邮箱,请求内核执行lwip_netconn_do_recv()函数,该函数将调用tcp_recved()函数去更新TCP 接收窗口,同时netconn_recv()函数将完成pbuf 数据包封装在netbuf 中,返回个应用程序;而对于UDP 协议、RAW连接,将简单多了,将直接调用netconn_recv_data()函数获取数据,完成pbuf 封装在netbuf 中,返回给应用程序.
/**
* @ingroup netconn_common
* Receive data (in form of a netbuf containing a packet buffer) from a netconn
*
* @param conn the netconn from which to receive data
* @param new_buf pointer where a new netbuf is stored when received data
* @return ERR_OK if data has been received, an error code otherwise (timeout,
* memory error or another error)
*/
err_t
netconn_recv(struct netconn *conn, struct netbuf **new_buf)
{
#if LWIP_TCP
struct netbuf *buf = NULL;
err_t err;
#endif /* LWIP_TCP */
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_recv: invalid pointer", (new_buf != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
*new_buf = NULL;
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_recv: invalid conn", (conn != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
#if LWIP_TCP
#if (LWIP_UDP || LWIP_RAW)
if (NETCONNTYPE_GROUP(conn->type) == NETCONN_TCP)
#endif /* (LWIP_UDP || LWIP_RAW) */
{
struct pbuf *p = NULL;
/* This is not a listening netconn, since recvmbox is set */
buf = (struct netbuf *)memp_malloc(MEMP_NETBUF);
if (buf == NULL) {
return ERR_MEM;
}
err = netconn_recv_data_tcp(conn, &p, 0);
if (err != ERR_OK) {
memp_free(MEMP_NETBUF, buf);
return err;
}
LWIP_ASSERT("p != NULL", p != NULL);
buf->p = p;
buf->ptr = p;
buf->port = 0;
ip_addr_set_zero(&buf->addr);
*new_buf = buf;
/* don't set conn->last_err: it's only ERR_OK, anyway */
return ERR_OK;
}
#endif /* LWIP_TCP */
#if LWIP_TCP && (LWIP_UDP || LWIP_RAW)
else
#endif /* LWIP_TCP && (LWIP_UDP || LWIP_RAW) */
{
#if (LWIP_UDP || LWIP_RAW)
return netconn_recv_data(conn, (void **)new_buf, 0);
#endif /* (LWIP_UDP || LWIP_RAW) */
}
}接收数据运作的示意图
4.10 netconn_send()
整个数据发送函数我们在实际中使用的也是非常多的,它用于UDP 协议、RAW连接发送数据,通过参数conn 选择指定的UDP 或者RAW控制块发送参数buf 中的数据,UDP/RAW 控制块中已经记录了目标IP 地址与目标端口号了。这些数据被封装在netbuf 中,如果没有使用IP 数据报分片功能,那么这些数据不能太大,数据长度不能大于网卡最大传输单元MTU,因为这个API 目前还没有提供直接获取底层网卡最大传输单元MTU 数值的函数,这就需要采用其它的途径来避免超过MTU 值,所以规定了一个上限,即netbuf 中包含的数据不能大于1000 个字节,这就需要我们自己在发送数据的时候要注意,当然,使用了IP 数据报分片功能的话,就不用管这些限制了。该函数会调用netconn_apimsg()函数构造一个API 消息,并且请求内核执行lwip_netconn_do_send()函数,这个函数会通过消息得到目标IP 地址与端口号以及pbuf 数据报等信息,然后调用raw_send()/udp_send()等函数发送数据,最后通过netconn 连接结构的信号量进行同步
/**
* @ingroup netconn_udp
* Send data over a UDP or RAW netconn (that is already connected).
*
* @param conn the UDP or RAW netconn over which to send data
* @param buf a netbuf containing the data to send
* @return ERR_OK if data was sent, any other err_t on error
*/
err_t
netconn_send(struct netconn *conn, struct netbuf *buf)
{
API_MSG_VAR_DECLARE(msg);
err_t err;
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_send: invalid conn", (conn != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
LWIP_DEBUGF(API_LIB_DEBUG, ("netconn_send: sending %"U16_F" bytes\n", buf->p->tot_len));
API_MSG_VAR_ALLOC(msg);
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).conn = conn;
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.b = buf;
err = netconn_apimsg(lwip_netconn_do_send, &API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg));
API_MSG_VAR_FREE(msg);
return err;
}4.11 netconn_sendto()
函数与netconn_send()函数是一样的功能,只不过参数中直接指出目标IP 地址与目标端口号,并且填写在pbuf 中.
/**
* @ingroup netconn_udp
* Send data (in form of a netbuf) to a specific remote IP address and port.
* Only to be used for UDP and RAW netconns (not TCP).
*
* @param conn the netconn over which to send data
* @param buf a netbuf containing the data to send
* @param addr the remote IP address to which to send the data
* @param port the remote port to which to send the data
* @return ERR_OK if data was sent, any other err_t on error
*/
err_t
netconn_sendto(struct netconn *conn, struct netbuf *buf, const ip_addr_t *addr, u16_t port)
{
if (buf != NULL) {
ip_addr_set(&buf->addr, addr);
buf->port = port;
return netconn_send(conn, buf);
}
return ERR_VAL;
}4.12 netconn_write()
etconn_write()函数的本质是一个宏,用于处于稳定连接状态的TCP 协议发送数据,我们也知道,TCP 协议的数据是以流的方式传输的,只需要指出发送数据的起始地址与长度即可,LwIP 内核会帮我们直接处理这些数据,将这些数据按字节流进行编号,让它们按照TCP 协议的方式进行传输,这样子就无需我们理会怎么传输了,对于数据的长度也没限制,内核会直接处理,使得它们变成最适的方式发送出去。
/** @ingroup netconn_tcp */
#define netconn_write(conn, dataptr, size, apiflags) \
netconn_write_partly(conn, dataptr, size, apiflags, NULL)/**
* @ingroup netconn_tcp
* Send data over a TCP netconn.
*
* @param conn the TCP netconn over which to send data
* @param dataptr pointer to the application buffer that contains the data to send
* @param size size of the application data to send
* @param apiflags combination of following flags :
* - NETCONN_COPY: data will be copied into memory belonging to the stack
* - NETCONN_MORE: for TCP connection, PSH flag will be set on last segment sent
* - NETCONN_DONTBLOCK: only write the data if all data can be written at once
* @param bytes_written pointer to a location that receives the number of written bytes
* @return ERR_OK if data was sent, any other err_t on error
*/
err_t
netconn_write_partly(struct netconn *conn, const void *dataptr, size_t size,
u8_t apiflags, size_t *bytes_written)
{
struct netvector vector;
vector.ptr = dataptr;
vector.len = size;
return netconn_write_vectors_partly(conn, &vector, 1, apiflags, bytes_written);
}
/**
* Send vectorized data atomically over a TCP netconn.
*
* @param conn the TCP netconn over which to send data
* @param vectors array of vectors containing data to send
* @param vectorcnt number of vectors in the array
* @param apiflags combination of following flags :
* - NETCONN_COPY: data will be copied into memory belonging to the stack
* - NETCONN_MORE: for TCP connection, PSH flag will be set on last segment sent
* - NETCONN_DONTBLOCK: only write the data if all data can be written at once
* @param bytes_written pointer to a location that receives the number of written bytes
* @return ERR_OK if data was sent, any other err_t on error
*/
err_t
netconn_write_vectors_partly(struct netconn *conn, struct netvector *vectors, u16_t vectorcnt,
u8_t apiflags, size_t *bytes_written)
{
API_MSG_VAR_DECLARE(msg);
err_t err;
u8_t dontblock;
size_t size;
int i;
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_write: invalid conn", (conn != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
LWIP_ERROR("netconn_write: invalid conn->type", (NETCONNTYPE_GROUP(conn->type) == NETCONN_TCP), return ERR_VAL;);
dontblock = netconn_is_nonblocking(conn) || (apiflags & NETCONN_DONTBLOCK);
#if LWIP_SO_SNDTIMEO
if (conn->send_timeout != 0) {
dontblock = 1;
}
#endif /* LWIP_SO_SNDTIMEO */
if (dontblock && !bytes_written) {
/* This implies netconn_write() cannot be used for non-blocking send, since
it has no way to return the number of bytes written. */
return ERR_VAL;
}
/* sum up the total size */
size = 0;
for (i = 0; i < vectorcnt; i++) {
size += vectors[i].len;
if (size < vectors[i].len) {
/* overflow */
return ERR_VAL;
}
}
if (size == 0) {
return ERR_OK;
} else if (size > SSIZE_MAX) {
ssize_t limited;
/* this is required by the socket layer (cannot send full size_t range) */
if (!bytes_written) {
return ERR_VAL;
}
/* limit the amount of data to send */
limited = SSIZE_MAX;
size = (size_t)limited;
}
API_MSG_VAR_ALLOC(msg);
/* non-blocking write sends as much */
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).conn = conn;
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.w.vector = vectors;
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.w.vector_cnt = vectorcnt;
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.w.vector_off = 0;
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.w.apiflags = apiflags;
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.w.len = size;
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.w.offset = 0;
#if LWIP_SO_SNDTIMEO
if (conn->send_timeout != 0) {
/* get the time we started, which is later compared to
sys_now() + conn->send_timeout */
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.w.time_started = sys_now();
} else {
API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.w.time_started = 0;
}
#endif /* LWIP_SO_SNDTIMEO */
/* For locking the core: this _can_ be delayed on low memory/low send buffer,
but if it is, this is done inside api_msg.c:do_write(), so we can use the
non-blocking version here. */
err = netconn_apimsg(lwip_netconn_do_write, &API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg));
if (err == ERR_OK) {
if (bytes_written != NULL) {
*bytes_written = API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.w.offset;
}
/* for blocking, check all requested bytes were written, NOTE: send_timeout is
treated as dontblock (see dontblock assignment above) */
if (!dontblock) {
LWIP_ASSERT("do_write failed to write all bytes", API_MSG_VAR_REF(msg).msg.w.offset == size);
}
}
API_MSG_VAR_FREE(msg);
return err;
}apiflags 参数
/* Flags for netconn_write (u8_t) */
// 没有标志位(默认标志位)
#define NETCONN_NOFLAG 0x00
// 不拷贝数据到内核线程
#define NETCONN_NOCOPY 0x00 /* Only for source code compatibility */
// 拷贝数据到内核线程
#define NETCONN_COPY 0x01
// 尽快递交给上层应用
#define NETCONN_MORE 0x02
// 当内核缓冲区满时,不会被阻塞,而是直接返回
#define NETCONN_DONTBLOCK 0x04
// 不自动更新接收窗口,需要调用netconn_tcp_recvd()函数完成
#define NETCONN_NOAUTORCVD 0x08 /* prevent netconn_recv_data_tcp() from updating the tcp window - must be done manually via netconn_tcp_recvd() */
// 上层已经收到数据,将FIN 保留在队列中直到再次调用
#define NETCONN_NOFIN 0x10 /* upper layer already received data, leave FIN in queue until called again */
当apiflags 的值为NETCONN_COPY 时, dataptr 指针指向的数据将会被拷贝到为这些数据分配的内部缓冲区,这样的话,在调用本函数之后可以直接对这些数据进行修改而不会影响数据,但是拷贝的过程是需要消耗系统资源的,CPU 需要参与数据的拷贝,而且还会占用新的内存空间。
如果apiflags 值为NETCONN_NOCOPY,数据不会被拷贝而是直接使用dataptr 指针来引用。但是这些数据在函数调用后不能立即被修改,因为这些数据可能会被放在当前TCP连接的重传队列中,以防对方未收到数据进行重传,而这段时间是不确定的。但是如果用户需要发送的数据在ROM 中(静态数据),这样子就无需拷贝数据,直接引用数据即可。
如果apiflags 值为NETCONN_MORE,那么接收端在组装这些TCP 报文段的时候,会将报文段首部的PSH 标志置一,这样子,这些数据完成组装的时候,将会被立即递交给上层应用。
如果apiflags 值为NETCONN_DONTBLOCK,表示在内核发送缓冲区满的时候,再调用netconn_write()函数将不会被阻塞,而是会直接返回一个错误代码ERR_VAL 告诉应用程序发送数据失败,应用程序可以自行处理这些数据,在适当的时候进行重传操作。
如果apiflags 值为NETCONN_NOAUTORCVD,表示在TCP 协议接收到数据的时候,调用netconn_recv_data_tcp()函数的时候不会去更新接收窗口,只能由用户自己调用netconn_tcp_recvd()函数完成接收窗口的更新操作
5. 示例例程
5.1 TCP Client
#include "client.h"
#include "lwip/opt.h"
#include "lwip/sys.h"
#include "lwip/api.h"
static void client(void *thread_param)
{
struct netconn *conn;
int ret;
ip4_addr_t ipaddr;
uint8_t send_buf[]= "This is a TCP Client test...\n";
while(1)
{
conn = netconn_new(NETCONN_TCP);
if (conn == NULL)
{
printf("create conn failed!\n");
vTaskDelay(10);
continue;
}
IP4_ADDR(&ipaddr,192,168,0,181);
ret = netconn_connect(conn,&ipaddr,5001);
if (ret == -1)
{
printf("Connect failed!\n");
netconn_delete(conn);
vTaskDelay(10);
continue;
}
printf("Connect to iperf server successful!\n");
while (1)
{
ret = netconn_write(conn,send_buf,sizeof(send_buf),0);
vTaskDelay(1000);
}
}
}
void
client_init(void)
{
sys_thread_new("client", client, NULL, 512, 4);
}5.2 TCP Server
#include "tcpecho.h"
#include "lwip/opt.h"
#if LWIP_NETCONN
#include "lwip/sys.h"
#include "lwip/api.h"
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
static void
tcpecho_thread(void *arg)
{
struct netconn *conn, *newconn;
err_t err;
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(arg);
/* Create a new connection identifier. */
/* Bind connection to well known port number 7. */
#if LWIP_IPV6
conn = netconn_new(NETCONN_TCP_IPV6);
netconn_bind(conn, IP6_ADDR_ANY, 5001);
#else /* LWIP_IPV6 */
conn = netconn_new(NETCONN_TCP);
netconn_bind(conn, IP_ADDR_ANY, 5001);
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 */
LWIP_ERROR("tcpecho: invalid conn", (conn != NULL), return;);
/* Tell connection to go into listening mode. */
netconn_listen(conn);
while (1) {
/* Grab new connection. */
err = netconn_accept(conn, &newconn);
/*printf("accepted new connection %p\n", newconn);*/
/* Process the new connection. */
if (err == ERR_OK) {
struct netbuf *buf;
void *data;
u16_t len;
while ((err = netconn_recv(newconn, &buf)) == ERR_OK) {
/*printf("Recved\n");*/
// 接收newconn 客户端发来的数据
do {
netbuf_data(buf, &data, &len);
err = netconn_write(newconn, data, len, NETCONN_COPY);
#if 0
if (err != ERR_OK) {
printf("tcpecho: netconn_write: error \"%s\"\n", lwip_strerr(err));
}
#endif
/* 可能客户端发送的数据很多,可能netbuf 中还有数据,那就调用netbuf_next()函数移动ptr 指针,指向下一个pbuf。*/
} while (netbuf_next(buf) >= 0);
netbuf_delete(buf); // 释放这些数据区域空间
}
/*printf("Got EOF, looping\n");*/
/* Close connection and discard connection identifier. */
netconn_close(newconn); // 主动关闭与客户端的连接
netconn_delete(newconn); // 释放newconn 的空间
}
}
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void
tcpecho_init(void)
{
sys_thread_new("tcpecho_thread", tcpecho_thread, NULL, 512, 4);
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#endif /* LWIP_NETCONN */5.3 UDP
#include "udpecho.h"
#include "lwip/opt.h"
#if LWIP_NETCONN
#include "lwip/api.h"
#include "lwip/sys.h"
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
static void
udpecho_thread(void *arg)
{
struct netconn *conn;
struct netbuf *buf;
char buffer[4096];
err_t err;
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(arg);
#if LWIP_IPV6
conn = netconn_new(NETCONN_UDP_IPV6);
netconn_bind(conn, IP6_ADDR_ANY, 5001);
#else /* LWIP_IPV6 */
conn = netconn_new(NETCONN_UDP);
netconn_bind(conn, IP_ADDR_ANY, 5001);
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 */
LWIP_ERROR("udpecho: invalid conn", (conn != NULL), return;);
while (1) {
err = netconn_recv(conn, &buf);
if (err == ERR_OK) {
/* no need netconn_connect here, since the netbuf contains the address */
if(netbuf_copy(buf, buffer, sizeof(buffer)) != buf->p->tot_len) {
LWIP_DEBUGF(LWIP_DBG_ON, ("netbuf_copy failed\n"));
} else {
buffer[buf->p->tot_len] = '\0';
err = netconn_send(conn, buf);
if(err != ERR_OK) {
LWIP_DEBUGF(LWIP_DBG_ON, ("netconn_send failed: %d\n", (int)err));
} else {
LWIP_DEBUGF(LWIP_DBG_ON, ("got %s\n", buffer));
}
}
netbuf_delete(buf);
}
}
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void
udpecho_init(void)
{
sys_thread_new("udpecho_thread", udpecho_thread, NULL, 2048, 4);
}
#endif /* LWIP_NETCONN */