C++之链式前向星
链式前向星
- 基本定义以及实现
- 链式前向星实现
- DFS
- BFS
基本定义以及实现
(若果有一定了解,可以跳过第一部分,直接看第二部分)
我们首先来看一下什么是前向星.
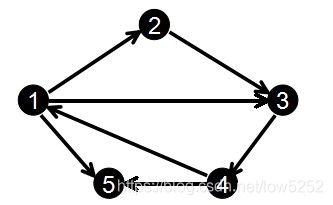
前向星是一种特殊的边集数组,我们把边集数组中的每一条边按照起点从小到大排序,如果起点相同就按照终点从小到大排序,
并记录下以某个点为起点的所有边在数组中的起始位置和存储长度,那么前向星就构造好了.
用**len[i]来记录所有以i为起点的边在数组中的存储长度.
用head[i]**记录以i为边集在数组中的第一个存储位置.
1 2
2 3
3 4
1 3
4 1
1 5
4 5
那么排完序后就得到:
编号: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
起点u: 1 1 1 2 3 4 4
终点v: 2 3 5 3 4 1 5
得到:
head[1] = 1 len[1] = 3
head[2] = 4 len[2] = 1
head[3] = 5 len[3] = 1
head[4] = 6 len[4] = 2
但是利用前向星会有排序操作,如果用快排时间至少为O(nlog(n))
如果用**链式前向星,**就可以避免排序.
我们建立边结构体为:
struct Edge
{
int next;
int to;
int w;
};
其中edge[i].to表示第i条边的终点,edge[i].next表示与第i条边同起点的下一条边的存储位置,edge[i].w为边权值.
另外还有一个数组head[],它是用来表示以i为起点的第一条边存储的位置,实际上你会发现这里的第一条边存储的位置其实
在以i为起点的所有边的最后输入的那个编号.
head[]数组一般初始化为-1,对于加边的add函数是这样的:
void add(int u,int v,int w)
{
edge[cnt].w = w;
edge[cnt].to = v;
edge[cnt].next = head[u];
head[u] = cnt++;
}
初始化cnt = 0,这样,现在我们还是按照上面的图和输入来模拟一下:
edge[0].to = 2; edge[0].next = -1; head[1] = 0;
edge[1].to = 3; edge[1].next = -1; head[2] = 1;
edge[2].to = 4; edge[2],next = -1; head[3] = 2;
edge[3].to = 3; edge[3].next = 0; head[1] = 3;
edge[4].to = 1; edge[4].next = -1; head[4] = 4;
edge[5].to = 5; edge[5].next = 3; head[1] = 5;
edge[6].to = 5; edge[6].next = 4; head[4] = 6;
很明显,head[i]保存的是以i为起点的所有边中编号最大的那个,而把这个当作顶点i的第一条起始边的位置.
这样在遍历时是倒着遍历的,也就是说与输入顺序是相反的,不过这样不影响结果的正确性.
比如以上图为例,以节点1为起点的边有3条,它们的编号分别是0,3,5 而head[1] = 5
我们在遍历以u节点为起始位置的所有边的时候是这样的:
for(int i=head[u];~i;i=edge[i].next)
那么就是说先遍历编号为5的边,也就是head[1],然后就是edge[5].next,也就是编号3的边,然后继续edge[3].next,也
就是编号0的边,可以看出是逆序的.
模板代码1:
1 #include
2 #include
3 #include
4 #include
5 using namespace std;
6 const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
7 const int M = 4444;
8 int d[M],head[M],vis[M];
9 struct nod{
10 int nex,to,w;
11 }eg[M];
12 typedef pair P;
13 int cnt=0;
14 inline void add(int u,int v,int w){
15 eg[cnt].to=v;
16 eg[cnt].w=w;
17 eg[cnt].nex=head[u];
18 head[u]=cnt++;
19 }
20 void dijkstra(int s){
21 priority_queue,greater >que;
22
23 d[s]=0;
24 que.push(P(0,s));
25 while(!que.empty()){
26 P p = que.top();
27 que.pop();
28 int v=p.second;
29 if(d[v]
模板代码2(优化):
1 #include
2 #include
3 #include
4 #include
5 #include
6 #include
7 #include
8 #include
9 using namespace std;
10 const int MAX_V = 200010;
11 const int MAX_E = 2000010;
12 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
13 int V,E,cnt;
14 int heap[MAX_V],dis[MAX_V];
15
16 struct Edge{
17 int to,next,cost;
18 }rng[MAX_E];
19 void add(int u,int v,int cost){
20 rng[cnt].to = v;
21 rng[cnt].next = heap[u];
22 rng[cnt].cost = cost;
23 heap[u] = cnt++;
24 }
25 struct Rule{
26 bool operator()(int &a,int &b)const{
27 return dis[a] > dis[b];
28 }
29 };
30 inline int read()
31 {
32 int X=0,w=1; char ch=0;
33 while(ch<'0' || ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') w=-1;ch=getchar();}
34 while(ch>='0' && ch<='9') X=(X<<3)+(X<<1)+ch-'0',ch=getchar();
35 return X*w;
36 }
37 void Dijkstra(int a_){
38 memset(dis,INF,sizeof(dis));
39 priority_queue,Rule > q;
40 dis[a_] = 0;q.push(a_);
41
42 while(!q.empty()){
43 int u = q.top();q.pop();
44 for(int k=heap[u];k != -1;k = rng[k].next){
45 int &v = rng[k].to;
46 if(dis[v] > dis[u] + rng[k].cost){
47 dis[v] = dis[u] + rng[k].cost;
48 q.push(v);
49 }
50 }
51 }
52 }
53 int main(void){
54 cnt = 0;
55 memset(heap,-1,sizeof(heap));
56 V = read(),E = read();
57 int x,y,z;
58 for(int i=1;i<=E;i++){
59 x = read(),y = read(),z = read();
60 add(x,y,z);
61 }
62 Dijkstra(1);
63 if(dis[V] == INF){
64 printf("-1\n");
65 }
66 else
67 printf("%d\n",dis[V]);
68 return 0;
69 }
链式前向星实现
DFS
图的深度优先遍历,基本思想是访问顶点,然后访问v0邻接到的未被访问的点顶点v1,在从v1出发递归地按照深度优先的方式遍历。当遇到一个所有邻接于它的顶点都被访问了的顶点u时,则回到已访问顶点的序列中最后一个拥有未被访问的相邻顶点的顶点w,从w出发继续访问。最终当任何已被访问的顶点都没有未被访问的相邻顶点时,遍历结束。也就是说深度优先遍历是沿着图的某一条分支遍历,直到末端,然后回溯,沿着另一条分支进行同样的遍历,直到所有的分支都被遍历过为止。
基于链式前向星的代码:
bool s[maxn]={0};//初始化
void dfs(int x)
{
s[x]=true;//表示被访问过
printf("%d\n",x);
int i;
for(i=head[x];x!=-1;i=edge[i].next)
{
if(s[edge[i].to])
dfs(edge[i].to);
}
}
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include BFS
图的宽度优先遍历与深度优先遍历不同之处在于:宽度优先遍历访问顶点v0然后访问v0邻接的未被访问的所有顶点,v1,v2,····vn,在依次访问v1,v2,···vn连接到的未被访问的所有顶点,如此下去,直到所有点都被访问。
代码:
bool s[maxn];
void bfs(int x)
{
int queue[maxn];
int iq=0;
queue[iq++]=x;
int i=k;
for(int i=0;i#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include 转自:http://blog.csdn.net/acdreamers/article/details/16902023
http://blog.csdn.net/henuwhr/article/details/76668590