PCL_PCA-最小包围盒(画出最小包围盒顶点)
1.包围盒简介
包围盒也叫外接最小矩形,是一种求解离散点集最优包围空间的算法,基本思想是用体积稍大且特性简单的几何体(称为包围盒)来近似地代替复杂的几何对象。
常见的包围盒算法有AABB包围盒、包围球、方向包围盒OBB以及固定方向凸包FDH。碰撞检测问题在虚拟现实、计算机辅助设计与制造、游戏及机器人等领域有着广泛的应用,甚至成为关键技术。而包围盒算法是进行碰撞干涉初步检测的重要方法之一。

在此借助于PCL点云库寻找点云的最小包围盒,代码参考网上代码,因为工程需要包围盒的顶点坐标或偏转角度,网上代码都只画出了最小包围盒没有求出顶点坐标,所以自己折腾了很久终于把顶点坐标求出,下面将代码放出来供大家参考.
2.原理简述
最小包围盒的计算过程大致如下:
1.利用PCA主元分析法获得点云的三个主方向,获取质心,计算协方差,获得协方差矩阵,求取协方差矩阵的特征值和特长向量,特征向量即为主方向。
2.利用1中获得的主方向和质心,将输入点云转换至原点,且主方向与坐标系方向重回,建立变换到原点的点云的包围盒。
3.给输入点云设置主方向和包围盒,通过输入点云到原点点云变换的逆变换实现。
最小包围盒顶点计算的过程大致如下:
1.输入点云转换至远点后,求得变换后点云的最大最小x,y,z轴的坐标,此时(max.x,max.y,max.z),(max.x,min.y,max.z),(max.x,max.y,min.z),(min.x,max.y,max.z),(min.x,max.y,min.z),(min.x,min.y,max.z),(min.x,min.y,max.z),(min.x,min.y,min.z)
即为变换后点云的包围盒,也是原始输入点云包围盒顶点坐标经过变化后的坐标.
2.将上述求得的8个包围盒坐标逆变换回输入点云的坐标系,即得到原始输入点云的包围盒顶点坐标.
3.详细代码
#include 4.代码编译
在此使用的是CMake编译,因此需要添加CMakeLists.txt文件后才可以进行编译
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
5.运行
运行时记得在后面加上点云文件的名字,代码里面支持’.pcd’格式和’.txt’格式,其它格式需要自己编写读取代码.’.txt’格式的文件中点云格式如下,一行代表一个点的坐标,横轴、纵轴、竖轴坐标之间加空格隔开:
point1.x point1.y point1.z
point2.x point2.y point2.z
...
pointN.x pointN.y pointN.z
运行命令如下
./rectangular_bounding_box ../milk.pcd
6.效果图
2维点云包围盒效果图

3维点云包围盒效果图
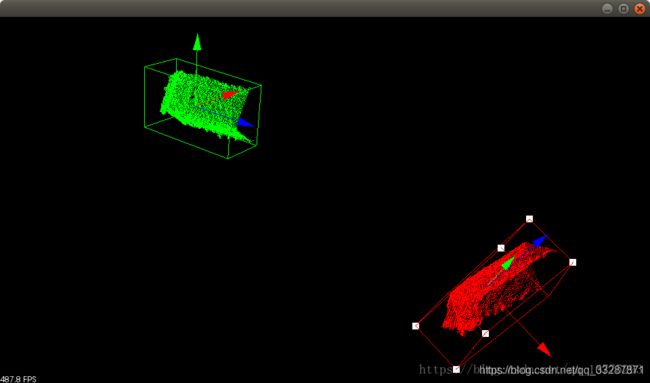
3维点云包围盒运行时间图

7.完整代码下载
如果不想自己写“CMakeLists.txt”的朋友可以下完整的代码,点击这里下载,包括“.cpp”文件,“CMakeLists.txt”文件。