目录牛客_MT1最大差值_模拟+贪心题目解析C++代码Java代码牛客_MT1最大差值_模拟+贪心最大差值_牛客题霸_牛客网描述:有一个长为n的数组A,求满足0≤a≤b&A,intn){//vectorarr(n,0x3f3f3f3f);//维护一个0到i的最小值//arr[0]=A[0];//intres=0;//for(inti=1;i
从0到1,带你快速上手Scala语言
qq_23519469
scala开发语言后端
什么是ScalaScala,读作“skah-lah”,是“ScalableLanguage”的缩写,是一门多范式编程语言。它就像是编程世界里的“变形金刚”,融合了面向对象编程(OOP)和函数式编程(FP)的特性,这意味着开发者能在同一语言中,把面向对象的设计和函数式编程的抽象结合起来使用,超级灵活!它运行在Java虚拟机(JVM)上,能与现有的Java代码无缝集成。这就好比Scala是Java的“
深入理解 Java 反射与 PropertyDescriptor 的应用
HoroMin
web基础easybbs项目疑难记录java开发语言反射
在Java编程中,反射是一项强大的功能,它允许我们在运行时动态地访问和操作类的信息,包括字段、方法和构造函数等。在处理JavaBean时,反射的灵活性尤为重要。而PropertyDescriptor类正是用于简化JavaBean属性的动态访问和操作。本文将探讨反射的基本概念,并通过具体示例展现如何使用PropertyDescriptor。什么是反射?反射是Java的一个特性,允许程序在运行时检查类
Redis客户端jedis与lettuce的区别
风雨无阻1203
RedisJava研发文档redis缓存LettuceJedis
什么是Lettuce与JedisLettuce是一个高级Redis客户端,用于线程安全的同步、异步和反应式访问。它支持高级的Redis特性,如Sentinel、集群、流水线、自动重新连接和redis数据模型等。Lettuce是完全非阻塞的,基于Netty事件驱动的通信层,其方法将返回具有可观察的类型,可在流或异步编程环境中使用。Jedis是基于Java语言的Redis的客户端,Jedis=Java
宇树科技纯技能要求总结
极梦网络无忧
杂谈科技
一、嵌入式开发与硬件设计核心技能嵌入式开发:精通C/C++,熟悉STM32、ARM开发熟悉LinuxBSP开发及驱动框架(SPI/UART/USB/FLASH/Camera/GPS/LCD)掌握主流平台(英伟达、全志、瑞芯微等)硬件设计:精通数字/模拟电路设计,熟悉PCB绘制工具(Altium等)掌握MOS驱动电路、变压器设计及EMC优化熟悉制板/贴片流程及焊接扩展技能电机控制:熟悉有感FOC算法
施磊老师c++(八)
Zhuai-行淮
施磊老师cppc++开发语言
语法是很不重要的,基本的回会了就行了cpp面经文章目录cpp面经1.程序的内存布局?--可以详看施磊老师第一节课2.堆栈区别3.函数调用参数是怎么传递的?4.为什么函数调用从右往左压栈5.函数题6.类和结构体的内存对齐----空结构体1.程序的内存布局?–可以详看施磊老师第一节课布局大概.text(代码段,放指令),.rodata(只读数据段,比如:常量字符串)—只读,不写.data(数据段:存放
施磊老师c++笔记(三)
Zhuai-行淮
施磊老师cppc++笔记
c++模板编程-学习cpp类库的编程基础文章目录c++模板编程-学习cpp类库的编程基础1.函数模板2.理解模板函数3.实现cpp的vector向量容器4.理解容器空间配置器allocator的重要性1.函数模板内容:模板的实例化,模板函数,模板类型参数,模板非类型参数,模板的实参推演,模板的特例化,模板函数模板的特例化非模板函数的重载关系区分函数模板和模板函数的概念!!!模板的意义?对类型也可以
linux网络编程(二)
Zhuai-行淮
linux网络编程linux网络服务器
day14多路IO转接:select:poll:相比select相差不多intpoll(structpollfd*fds,nfds_tnfds,inttimeout);-----fds:监听的文件描述符【数组】------structpollfd{intfd:待监听的文件描述符shortevents:待监听的文件描述符对应的监听事件取值:POLLIN、POLLOUT、POLLERR可读事件:POL
C++消息总线和数据总线,可实现代码间交互完全解耦
flower980323
C++c++开发语言架构设计模式
特性1.可以解耦所有源文件之间的交互编译依赖,作为中间者控制交互2.可使用不同枚举作为软件的模块消息或是数据标识,且编译无需依赖枚举头文件,可随意修改3.简单,只需少量代码即可实现,支持注册和触发4.消息总线支持优先级,控制消息触发顺序消息总线,可以实现函数调用的解耦#pragmaonce#include#include#include#includeclassMsgHandler{public:
Python,C++开发餐饮后厨环境远程管理APP
Geeker-2025
pythonc++
开发一款用于**餐饮后厨环境远程管理**的App,结合Python和C++的优势,可以实现高效的后端数据处理、实时的环境监控以及用户友好的前端界面。以下是一个详细的开发方案,涵盖技术选型、功能模块、开发步骤等内容。##技术选型###后端(Python)-**编程语言**:Python-**Web框架**:Django或Flask-**数据库**:PostgreSQL或MySQL-**实时通信**:
【面试问题】Java 接口与抽象类的区别
刘小炮吖i
JavaJava后端开发面试题java开发语言面试
引言在Java面向对象编程中,接口(Interface)和抽象类(AbstractClass)是两个重要的抽象工具。它们都能定义未实现的方法,但设计目标和使用场景截然不同。本文将通过语法、特性和实际案例,深入解析两者的核心区别。一、基础概念回顾抽象类(AbstractClass)定义:使用abstract关键字声明的类,包含抽象方法(无实现)和具体方法(有实现)。特点:不能被实例化,必须通过子类继
施磊老师高级c++(一)
Zhuai-行淮
施磊老师cppc++开发语言
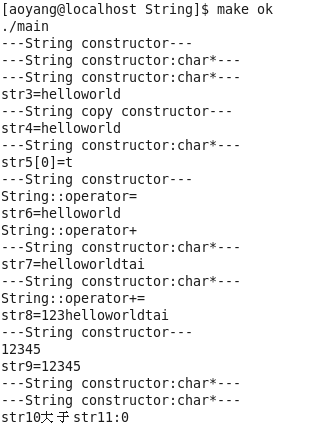
对象被优化后,才是高效的c++编程文章目录对象被优化后,才是高效的c++编程1.对象使用背后调用了哪些方法2.函数调用过程中对象背后调用方法3.总结三条对象优化的规则4.CMyString的代码问题5.添加带右值引用参数的拷贝构造和赋值函数6.String类在vector上的应用--面试题7.move移动语义和forword类型完美转发move移动语义的作用代码:**问题:**解决办法:最终代码:
目前市场上主流的机器视觉的框架有哪些?他们的特点及优劣
yuanpan
机器学习计算机视觉
目前市场上主流的机器视觉框架和工具可以分为商业软件、开源工具和深度学习框架三大类。以下是它们的总结及特点对比:1.商业软件(1)Halcon(MVTec)特点:专注于工业机器视觉,提供高精度、高效率的算法。支持复杂的工业应用,如缺陷检测、3D视觉、深度学习等。提供图形化开发工具HDevelop和多种编程接口。优势:算法优化好,适合实时工业应用。硬件兼容性强,支持多种工业相机和设备。劣势:商业软件,
go面向对象编程三大特性,封装、继承和多态
平谷一勺
Golang基础篇golang开发语言后端go封装继承多态封装多态继承
1.简介go具有面向对象编程的封装、继承和多态的特性,只是实现的方式和其它OOP语言不一样,下面看下go的三大特性是如何实现的。2.封装2.1基本介绍封装就是把抽象出的字段和对字段的操作封装在一起,数据被保护在内部,程序的其它包只能通过被授权的操作(方法),才能对字段进行操作。优点:隐藏细节。可以对数据进行验证,保证安全合理。2.2封装的实现步骤将结构体、字段(属性)的首字母小写(不能导出了,其他
代码逐行解析 | 教你在C++中使用深度学习提取特征点
3D视觉工坊
3D视觉从入门到精通c++深度学习开发语言人工智能
点击下方卡片,关注「3D视觉工坊」公众号选择星标,干货第一时间送达扫描下方二维码,加入3D视觉技术星球,星球内汇集了众多3D视觉实战问题,以及各个模块的学习资料:最新顶会论文、书籍、源码、视频(近20门系统课程[星球成员可免费学习])等。想要入门3D视觉、做项目、搞科研,就加入我们吧。作者:泡椒味的口香糖|来源:3DCV添加微信:dddvision
Ada语言的数据结构与算法
尤宸翎
包罗万象golang开发语言后端
Ada语言的数据结构与算法引言在计算机科学的领域里,数据结构与算法是核心的组成部分,围绕着如何高效地存储和处理数据。这些概念不仅是程序设计的重要基础,也是提高程序性能的关键。Ada是一种强类型、结构化的编程语言,早在20世纪80年代就被设计用于军用和实时系统。由于其高可靠性和可维护性,Ada逐渐在航空航天、军事和其他需要高安全性的领域获得了广泛应用。本文将探讨Ada语言中的数据结构和算法,包括常见
Julia语言的饼图
尤宸翎
包罗万象golang开发语言后端
Julia语言的饼图:全面剖析与实战指南引言在数据可视化的领域中,饼图作为一种经典的可视化工具,广泛用于展示各个分类在总体中的占比关系。尽管饼图在一些数据分析师中被视为相对简单和直观的图形,但它在实际运用中依然扮演着重要角色。本文将重点探讨如何使用Julia语言实现饼图的绘制,分析其背后的逻辑,并通过实例帮助读者掌握这一基本技能。Julia语言简介Julia是一种高性能、高级别的编程语言,适用于数
Java 并发包之线程池和原子计数
lijingyao8206
Java计数ThreadPool并发包java线程池
对于大数据量关联的业务处理逻辑,比较直接的想法就是用JDK提供的并发包去解决多线程情况下的业务数据处理。线程池可以提供很好的管理线程的方式,并且可以提高线程利用率,并发包中的原子计数在多线程的情况下可以让我们避免去写一些同步代码。
这里就先把jdk并发包中的线程池处理器ThreadPoolExecutor 以原子计数类AomicInteger 和倒数计时锁C
java编程思想 抽象类和接口
百合不是茶
java抽象类接口
接口c++对接口和内部类只有简介的支持,但在java中有队这些类的直接支持
1 ,抽象类 : 如果一个类包含一个或多个抽象方法,该类必须限定为抽象类(否者编译器报错)
抽象方法 : 在方法中仅有声明而没有方法体
package com.wj.Interface;
[房地产与大数据]房地产数据挖掘系统
comsci
数据挖掘
随着一个关键核心技术的突破,我们已经是独立自主的开发某些先进模块,但是要完全实现,还需要一定的时间...
所以,除了代码工作以外,我们还需要关心一下非技术领域的事件..比如说房地产
&nb
数组队列总结
沐刃青蛟
数组队列
数组队列是一种大小可以改变,类型没有定死的类似数组的工具。不过与数组相比,它更具有灵活性。因为它不但不用担心越界问题,而且因为泛型(类似c++中模板的东西)的存在而支持各种类型。
以下是数组队列的功能实现代码:
import List.Student;
public class
Oracle存储过程无法编译的解决方法
IT独行者
oracle存储过程
今天同事修改Oracle存储过程又导致2个过程无法被编译,流程规范上的东西,Dave 这里不多说,看看怎么解决问题。
1. 查看无效对象
XEZF@xezf(qs-xezf-db1)> select object_name,object_type,status from all_objects where status='IN
重装系统之后oracle恢复
文强chu
oracle
前几天正在使用电脑,没有暂停oracle的各种服务。
突然win8.1系统奔溃,无法修复,开机时系统 提示正在搜集错误信息,然后再开机,再提示的无限循环中。
无耐我拿出系统u盘 准备重装系统,没想到竟然无法从u盘引导成功。
晚上到外面早了一家修电脑店,让人家给装了个系统,并且那哥们在我没反应过来的时候,
直接把我的c盘给格式化了 并且清理了注册表,再装系统。
然后的结果就是我的oracl
python学习二( 一些基础语法)
小桔子
pthon基础语法
紧接着把!昨天没看继续看django 官方教程,学了下python的基本语法 与c类语言还是有些小差别:
1.ptyhon的源文件以UTF-8编码格式
2.
/ 除 结果浮点型
// 除 结果整形
% 除 取余数
* 乘
** 乘方 eg 5**2 结果是5的2次方25
_&
svn 常用命令
aichenglong
SVN版本回退
1 svn回退版本
1)在window中选择log,根据想要回退的内容,选择revert this version或revert chanages from this version
两者的区别:
revert this version:表示回退到当前版本(该版本后的版本全部作废)
revert chanages from this versio
某小公司面试归来
alafqq
面试
先填单子,还要写笔试题,我以时间为急,拒绝了它。。时间宝贵。
老拿这些对付毕业生的东东来吓唬我。。
面试官很刁难,问了几个问题,记录下;
1,包的范围。。。public,private,protect. --悲剧了
2,hashcode方法和equals方法的区别。谁覆盖谁.结果,他说我说反了。
3,最恶心的一道题,抽象类继承抽象类吗?(察,一般它都是被继承的啊)
4,stru
动态数组的存储速度比较 集合框架
百合不是茶
集合框架
集合框架:
自定义数据结构(增删改查等)
package 数组;
/**
* 创建动态数组
* @author 百合
*
*/
public class ArrayDemo{
//定义一个数组来存放数据
String[] src = new String[0];
/**
* 增加元素加入容器
* @param s要加入容器
用JS实现一个JS对象,对象里有两个属性一个方法
bijian1013
js对象
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
用js代码实现一个js对象,对象里有两个属性,一个方法
</body>
<script>
var obj={a:'1234567',b:'bbbbbbbbbb',c:function(x){
探索JUnit4扩展:使用Rule
bijian1013
java单元测试JUnitRule
在上一篇文章中,讨论了使用Runner扩展JUnit4的方式,即直接修改Test Runner的实现(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner)。但这种方法显然不便于灵活地添加或删除扩展功能。下面将使用JUnit4.7才开始引入的扩展方式——Rule来实现相同的扩展功能。
1. Rule
&n
[Gson一]非泛型POJO对象的反序列化
bit1129
POJO
当要将JSON数据串反序列化自身为非泛型的POJO时,使用Gson.fromJson(String, Class)方法。自身为非泛型的POJO的包括两种:
1. POJO对象不包含任何泛型的字段
2. POJO对象包含泛型字段,例如泛型集合或者泛型类
Data类 a.不是泛型类, b.Data中的集合List和Map都是泛型的 c.Data中不包含其它的POJO
【Kakfa五】Kafka Producer和Consumer基本使用
bit1129
kafka
0.Kafka服务器的配置
一个Broker,
一个Topic
Topic中只有一个Partition() 1. Producer:
package kafka.examples.producers;
import kafka.producer.KeyedMessage;
import kafka.javaapi.producer.Producer;
impor
lsyncd实时同步搭建指南——取代rsync+inotify
ronin47
1. 几大实时同步工具比较 1.1 inotify + rsync
最近一直在寻求生产服务服务器上的同步替代方案,原先使用的是 inotify + rsync,但随着文件数量的增大到100W+,目录下的文件列表就达20M,在网络状况不佳或者限速的情况下,变更的文件可能10来个才几M,却因此要发送的文件列表就达20M,严重减低的带宽的使用效率以及同步效率;更为要紧的是,加入inotify
java-9. 判断整数序列是不是二元查找树的后序遍历结果
bylijinnan
java
public class IsBinTreePostTraverse{
static boolean isBSTPostOrder(int[] a){
if(a==null){
return false;
}
/*1.只有一个结点时,肯定是查找树
*2.只有两个结点时,肯定是查找树。例如{5,6}对应的BST是 6 {6,5}对应的BST是
MySQL的sum函数返回的类型
bylijinnan
javaspringsqlmysqljdbc
今天项目切换数据库时,出错
访问数据库的代码大概是这样:
String sql = "select sum(number) as sumNumberOfOneDay from tableName";
List<Map> rows = getJdbcTemplate().queryForList(sql);
for (Map row : rows
java设计模式之单例模式
chicony
java设计模式
在阎宏博士的《JAVA与模式》一书中开头是这样描述单例模式的:
作为对象的创建模式,单例模式确保某一个类只有一个实例,而且自行实例化并向整个系统提供这个实例。这个类称为单例类。 单例模式的结构
单例模式的特点:
单例类只能有一个实例。
单例类必须自己创建自己的唯一实例。
单例类必须给所有其他对象提供这一实例。
饿汉式单例类
publ
javascript取当月最后一天
ctrain
JavaScript
<!--javascript取当月最后一天-->
<script language=javascript>
var current = new Date();
var year = current.getYear();
var month = current.getMonth();
showMonthLastDay(year, mont
linux tune2fs命令详解
daizj
linuxtune2fs查看系统文件块信息
一.简介:
tune2fs是调整和查看ext2/ext3文件系统的文件系统参数,Windows下面如果出现意外断电死机情况,下次开机一般都会出现系统自检。Linux系统下面也有文件系统自检,而且是可以通过tune2fs命令,自行定义自检周期及方式。
二.用法:
Usage: tune2fs [-c max_mounts_count] [-e errors_behavior] [-g grou
做有中国特色的程序员
dcj3sjt126com
程序员
从出版业说起 网络作品排到靠前的,都不会太难看,一般人不爱看某部作品也是因为不喜欢这个类型,而此人也不会全不喜欢这些网络作品。究其原因,是因为网络作品都是让人先白看的,看的好了才出了头。而纸质作品就不一定了,排行榜靠前的,有好作品,也有垃圾。 许多大牛都是写了博客,后来出了书。这些书也都不次,可能有人让为不好,是因为技术书不像小说,小说在读故事,技术书是在学知识或温习知识,有
Android:TextView属性大全
dcj3sjt126com
textview
android:autoLink 设置是否当文本为URL链接/email/电话号码/map时,文本显示为可点击的链接。可选值(none/web/email/phone/map/all) android:autoText 如果设置,将自动执行输入值的拼写纠正。此处无效果,在显示输入法并输
tomcat虚拟目录安装及其配置
eksliang
tomcat配置说明tomca部署web应用tomcat虚拟目录安装
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2097184
1.-------------------------------------------tomcat 目录结构
config:存放tomcat的配置文件
temp :存放tomcat跑起来后存放临时文件用的
work : 当第一次访问应用中的jsp
浅谈:APP有哪些常被黑客利用的安全漏洞
gg163
APP
首先,说到APP的安全漏洞,身为程序猿的大家应该不陌生;如果抛开安卓自身开源的问题的话,其主要产生的原因就是开发过程中疏忽或者代码不严谨引起的。但这些责任也不能怪在程序猿头上,有时会因为BOSS时间催得紧等很多可观原因。由国内移动应用安全检测团队爱内测(ineice.com)的CTO给我们浅谈关于Android 系统的开源设计以及生态环境。
1. 应用反编译漏洞:APK 包非常容易被反编译成可读
C#根据网址生成静态页面
hvt
Web.netC#asp.nethovertree
HoverTree开源项目中HoverTreeWeb.HVTPanel的Index.aspx文件是后台管理的首页。包含生成留言板首页,以及显示用户名,退出等功能。根据网址生成页面的方法:
bool CreateHtmlFile(string url, string path)
{
//http://keleyi.com/a/bjae/3d10wfax.htm
stri
SVG 教程 (一)
天梯梦
svg
SVG 简介
SVG 是使用 XML 来描述二维图形和绘图程序的语言。 学习之前应具备的基础知识:
继续学习之前,你应该对以下内容有基本的了解:
HTML
XML 基础
如果希望首先学习这些内容,请在本站的首页选择相应的教程。 什么是SVG?
SVG 指可伸缩矢量图形 (Scalable Vector Graphics)
SVG 用来定义用于网络的基于矢量
一个简单的java栈
luyulong
java数据结构栈
public class MyStack {
private long[] arr;
private int top;
public MyStack() {
arr = new long[10];
top = -1;
}
public MyStack(int maxsize) {
arr = new long[maxsize];
top
基础数据结构和算法八:Binary search
sunwinner
AlgorithmBinary search
Binary search needs an ordered array so that it can use array indexing to dramatically reduce the number of compares required for each search, using the classic and venerable binary search algori
12个C语言面试题,涉及指针、进程、运算、结构体、函数、内存,看看你能做出几个!
刘星宇
c面试
12个C语言面试题,涉及指针、进程、运算、结构体、函数、内存,看看你能做出几个!
1.gets()函数
问:请找出下面代码里的问题:
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char buff[10];
memset(buff,0,sizeof(buff));
ITeye 7月技术图书有奖试读获奖名单公布
ITeye管理员
活动ITeye试读
ITeye携手人民邮电出版社图灵教育共同举办的7月技术图书有奖试读活动已圆满结束,非常感谢广大用户对本次活动的关注与参与。
7月试读活动回顾:
http://webmaster.iteye.com/blog/2092746
本次技术图书试读活动的优秀奖获奖名单及相应作品如下(优秀文章有很多,但名额有限,没获奖并不代表不优秀):
《Java性能优化权威指南》