- 项目开发日记
框架整理学习UIMgr:一、数据结构与算法1.1关键数据结构成员变量类型说明m_CtrlsList当前正在显示的所有UI页面m_CachesList已打开过、但现在不显示的页面(缓存池)1.2算法逻辑查找缓存页面:从m_Caches中倒序查找是否已有对应ePageType页面,找到则重用。页面加载:从资源管理器ResMgr加载prefab并绑定控制器/视图组件。页面关闭:从m_Ctrls移除,添加
- 2025秋招优秀项目推荐
微凉的衣柜
人工智能深度学习算法gpt
01.多个优异的数据结构与算法项目推荐良心推荐hello-algo包含多个通用的代码框架,一个框架完成多道题目,更详细请查阅labuladong02.大模型岗位面试总结:共24家,9个offer大模型岗位面试总结:共24家,9个offer03.视觉检测分割一切源码及在线DemoGrounded-Segment-Anything项目源码
- 数据结构课程设计
秋悠然
深度优先算法图论
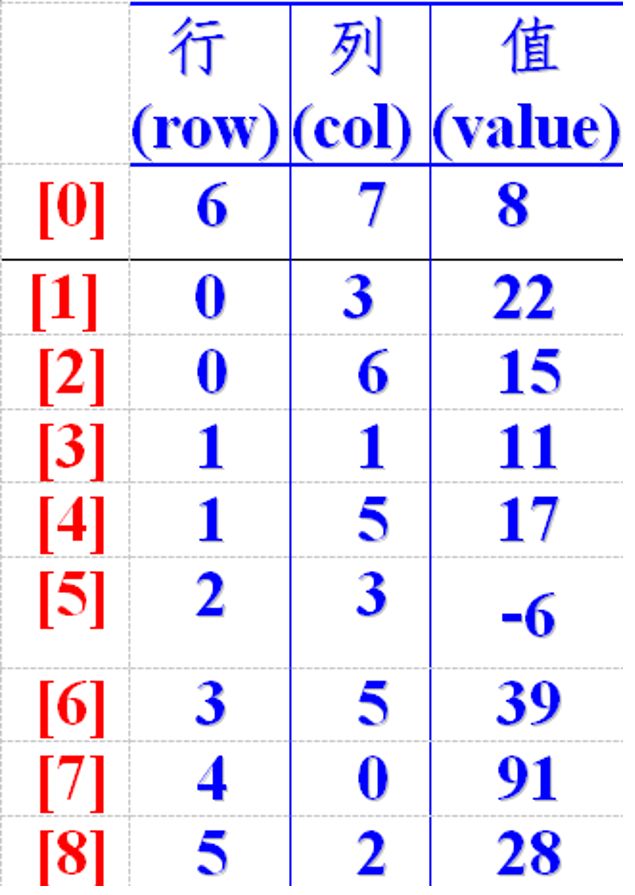
项目名称:图的遍历课程设计主要目的:1.了解并掌握数据结构与算法的设计方法。2.通过应用数据结构的基本理论和方法来解决实际问题。3.初步掌握软件开发过程中的问题分析、系统设计、程序编码、调试、数据测试等基本方法和技能。4.学习编写课程设计报告,软件开发文档。课程设计任务要求:任务:实现图的深度遍历(递归和非递归两种方法)以及实现图的广度遍历(队列)要求:1.程序能够正确运行,实现图的深度遍历和广度
- 零基础数据结构与算法——第四章:基础算法-排序(总)
qqxhb
零基础数据结构与算法算法小学生编程算法排序算法数据结构插入桶归并
排序上(冒泡/选择/插入)排序中(归并/堆排/快排)排序下(计数/基数/桶)4.1.10排序算法的比较性能比较下表总结了我们学习的排序算法的性能特点:排序算法平均时间复杂度最坏时间复杂度最好时间复杂度空间复杂度稳定性是否基于比较冒泡排序O(n²)O(n²)O(n)O(1)稳定是选择排序O(n²)O(n²)O(n²)O(1)不稳定是插入排序O(n²)O(n²)O(n)O(1)稳定是归并排序O(nlo
- 【算法专题】双指针算法之18. 四数之和(力扣)
CILMY23
算法专题算法leetcode双指针算法c++四数之和
欢迎来到CILMY23的博客本篇主题为:双指针算法之18.四数之和(力扣)个人主页:CILMY23-CSDN博客系列专栏:Python|C++|C语言|数据结构与算法|贪心算法|Linux|算法专题|代码训练营感谢观看,支持的可以给个一键三连,点赞收藏+评论。如果你觉得有帮助,还可以点点关注题目:18.四数之和-力扣(LeetCode)给你一个由n个整数组成的数组nums,和一个目标值target
- 揭秘 LeetCode 数据结构与算法的高效学习方法
数据结构与算法学习
leetcode学习方法算法ai
揭秘LeetCode数据结构与算法的高效学习方法关键词:LeetCode、数据结构、算法、高效学习、解题技巧、知识体系、面试准备摘要:本文以“如何高效通过LeetCode学习数据结构与算法”为核心,结合新手常见痛点(如刷题没方向、刷完就忘、无法举一反三),通过生活化类比、具体案例拆解和可操作的学习方法,系统讲解从“入门到精通”的全流程。无论是求职准备的程序员,还是想提升编程能力的学习者,都能从中找
- LeetCode 刷题:数据结构与算法的实战经验分享
LeetCode刷题:数据结构与算法的实战经验分享关键词:LeetCode、数据结构、算法、刷题经验、实战摘要:本文将围绕LeetCode刷题展开,深入探讨数据结构与算法在实际刷题过程中的应用。通过分享实战经验,帮助读者更好地理解和掌握数据结构与算法知识,提升解题能力。文章将从背景介绍入手,阐述刷题的目的和意义,接着详细解释核心概念,分析它们之间的关系,然后介绍核心算法原理和具体操作步骤,结合数学
- 数据结构与算法PTA 6-1【顺序表】(C语言)
页面正在加载中
数据结构与算法入门记录算法数据结构链表c语言
题目:要求根据顺序表定义和已有操作,编码完成其他的10个操作。顺序表的定义和已有操作:#defineN10typedefintElemType;typedefstruct{ElemTypedata[N];intlast;}SeqList;SeqList*InitList();voidTraverseList(SeqList*list);需要你来编写的其他操作://插入成功则返回0。如果pos非法则
- 【C语言】学习过程教训与经验杂谈:思想准备、知识回顾(五)
个人主页:艾莉丝努力练剑❄专栏传送门:《C语言》、《数据结构与算法》、C语言刷题12天IO强训、LeetCode代码强化刷题学习方向:C/C++方向⭐️人生格言:为天地立心,为生民立命,为往圣继绝学,为万世开太平前言:我们在学习过程中会碰到很多很多问题,本系列文章不会博主不会额外再创建一个新的专栏来收录,因为这一系列文章创作的初心主要是针对回顾知识点(遵循遗忘曲线并且根据自身的实际情况可以做出一些
- python进阶之数据结构与算法--入门-二叉树
小白piao
数据结构与算法python篇数据结构算法二叉树python
二叉树概念:之前已经提及了关于树的概念,要想知道之前讲了什么请关注,前边文章里都有提及。这里不做赘述。二叉树是具有以下属性的有序树:1、每个节点最多有两个孩子节点2、每个孩子节点被命名为左子节点和右子节点3、对于每个节点的孩子节点,在顺序上,左子节点优先于右子节点4、若子树的根为内部节点v的左子节点或者右子节点,则该子树相应地被称为节点v的左子树或者右子树5、若每个节点都有零个或者两个节点,则这样
- C语言数据结构与算法专栏目录
CodeAllen嵌入式
嵌入式C语言数据结构算法
后序会开一个《嵌入式数据结构专栏》主要为了学习嵌入式的同学,软件能力提升和大厂面试能力,感谢大家关注!直达专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/super828/category_11083370.html《C语言数据结构与算法》专栏已经更新完毕,共计72篇分享,后期会逐渐修改错误并添加内容0数据之间的关系有哪些?1如何度量一个算法的好坏?2常见的时间复杂度实例
- 零基础数据结构与算法—— 第三章:高级数据结构-总结
qqxhb
零基础数据结构与算法小学生编程算法数据结构算法树堆哈希表图
3.1树(上)3.1树(下)3.2堆(Heap)3.3哈希表(HashTable)3.4图(Graph)3.5高级树结构3.6本章小结在本章中,我们深入学习了几种重要的高级数据结构,这些数据结构在解决复杂问题时具有强大的能力。让我们回顾一下本章的主要内容:1.堆(Heap)堆是一种特殊的完全二叉树,具有堆序性质。我们学习了:最大堆和最小堆的概念和性质堆的基本操作(插入、删除堆顶、获取堆顶、构建堆)
- 数据结构与算法:贪心(二)
前言要加快速度啊!!一、最短无序连续子数组classSolution{public:intfindUnsortedSubarray(vector&nums){intn=nums.size();intMax=-1e9;intright=-1;//最右不符合的位置for(inti=0;inums[i])//遇到不符合递增规律的数{right=i;}Max=max(Max,nums[i]);}intMi
- 数据结构与算法:贪心算法的优化案例展示
数据结构与算法:贪心算法的优化案例展示关键词:贪心算法、局部最优、全局最优、活动选择问题、霍夫曼编码、硬币找零、算法优化摘要:贪心算法是计算机科学中最“接地气”的算法思想之一——它像极了我们日常生活中“走一步看一步,每次选当前最好”的决策方式。但这种“短视”的策略为何能在某些问题中得到全局最优解?它的优化边界在哪里?本文将通过5个经典案例,从生活场景到代码实现,一步步拆解贪心算法的核心逻辑与优化技
- C++ 智能指针
随意023
C++重构c++开发语言
STL和智能指针关系1.STL是标准库的子集:专注于数据结构与算法。2.智能指针属于“通用工具库”:与std::thread、std::future等工具同属一类,不隶属于STL的核心组件。1.智能指针智能指针是一个类模板,通过RAII(资源获取即初始化)技术封装原始指针,自动管理对象生命周期。1.核心功能避免内存泄漏:无需手动调用delete。2.RAII(资源获取即初始化)RAII(Resou
- 数据结构与算法中外部排序的详细剖析
数据结构与算法学习
网络ai
数据结构与算法中外部排序的详细剖析关键词:外部排序、归并排序、多路归并、置换选择排序、败者树、磁盘I/O优化、大数据处理摘要:本文将深入探讨外部排序技术,这是处理大规模数据时不可或缺的算法。我们将从基本概念出发,逐步解析多路归并、置换选择排序等核心技术,并通过实际代码示例展示如何实现高效的外部排序。文章还将分析外部排序在现代大数据处理中的应用场景和优化策略。背景介绍目的和范围本文旨在全面介绍外部排
- 数据结构与算法领域线性探测的性能分析
数据结构与算法学习
哈希算法散列表数据结构ai
数据结构与算法领域线性探测的性能分析关键词:哈希表、线性探测、冲突解决、时间复杂度、负载因子、性能分析、散列函数摘要:本文深入探讨哈希表中线性探测冲突解决方法的性能特点。我们将从基本概念出发,通过生活化的比喻解释线性探测的工作原理,分析其在不同场景下的时间复杂度表现,并通过Python代码实现和实验数据展示其实际性能。文章还将讨论线性探测的优缺点、适用场景以及优化策略,帮助读者全面理解这一经典算法
- 【C++】拷贝复制:拷贝构造函数的使用
CILMY23
C++c++开发语言类和对象拷贝构造函数自定义类型内置类型深拷贝
欢迎来到CILMY23的博客本篇主题为:拷贝复制:拷贝构造函数的使用博客主页:CILMY23-CSDN博客个人专栏:Python|C++|C语言|数据结构与算法感谢观看,支持的可以给个一键三连,点赞关注+收藏。写在前头:构造函数是函数名和类名相同,而析构函数是在前面加个~,我们也总结了最好是全缺省的构造函数更实用,以及构造函数和析构函数的调用顺序(链接),并且默认成员函数和默认构造函数也存在区别:
- Python数据结构之 Big O
ぃ曦晔°
数据结构算法BigO复杂度
学习课程:【Udemy高分付费课程】Python数据结构与算法-终极Python编码面试和计算机科学训练营在Python中,BigO表示法用于描述算法的时间复杂度,即算法运行时间与输入大小之间的关系;或空间复杂度,即算法运行时所占用的内存。在处理时间复杂度和空间复杂度是有3个希腊字母:Ω--最佳速度θ--平均速度O--最坏情况我们在讨论BigO时,总是在谈论最坏情况(WorstCase)Pytho
- 数据结构与算法 第一章 绪论
noruta
408#数据结构与算法数据结构
1.1.数据结构的基本概念数据:对计算机来说,能被计算机程序识别和处理的符号的集合。(比如二进制0和1)数据元素:数据的基本单位,通常作为一个整体进行考虑和处理。(比如一个学生的信息是一个数据元素)数据项:构成数据元素的最小单位。(学生的学号,姓名,班级构成一个学生信息)要根据实际的业务需求来确定什么是数据元素、什么是数据项。数据结构:相互之间存在一种或多种特定关系的数据元素的集合。比如汉字有左右
- 电子词典开源项目源代码完全解析
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:电子词典作为数字化学习工具,已由传统硬件发展为可定制的开源软件应用。本源代码提供深入理解其工作机制的机会,包括用户界面设计、词典数据库、查询引擎、翻译算法等。源代码通常由主流编程语言编写,涉及到数据结构与算法、UI设计、数据库管理、自然语言处理、本地化与多语言支持、版本控制、软件工程、API接口以及开源社区的协作和交流。1.电子词典工作原理和定制功能电子词典工
- 【数据结构与算法】单向链表(添加节点、顺序添加节点、更新节点、删除节点、反转链表、获取链表长度、获取倒数第几个节点、打印链表、反转打印链表)
目录1.单向链表的介绍2.带head头的单向链表实现1.单向链表的介绍单向链表是有序的列表。以节点的方式来存储,是链式存储,每个节点包含data域和next域(指向下一个节点),所以单向链表在内存中的储存是无序的单向链表分带头节点的单向链表,和没有头节点的单向链表2.带head头的单向链表实现实现对单向链表的增、删、改、查等操作单向链表各节点说明:head节点:不储存数据,next指向下一个节点最
- 数据结构与算法:深度优先的实战指南
数据结构与算法:深度优先的实战指南关键词:深度优先搜索(DFS)、递归、栈、图遍历、路径查找、迷宫寻路、算法实战摘要:深度优先搜索(DFS)是计算机科学中最经典的算法之一,被广泛应用于路径查找、游戏AI、社交网络分析等场景。本文将用“迷宫探险”的故事串联核心概念,结合生活案例、代码实战和LeetCode经典题,带您从0到1掌握DFS的底层逻辑与实战技巧。即使你是算法新手,也能通过通俗易懂的讲解,真
- 数据结构与算法中单调栈的常见误区
数据结构与算法学习
服务器运维ai
数据结构与算法中单调栈的常见误区关键词:单调栈、数据结构、算法、误区、栈、时间复杂度、应用场景摘要:单调栈是一种特殊的数据结构,它在解决某些特定问题时非常高效。然而,许多初学者在使用单调栈时容易陷入一些常见的误区。本文将详细介绍单调栈的概念、原理和应用,重点分析使用单调栈时的常见误区,并通过实际代码示例展示如何正确使用单调栈解决问题。背景介绍目的和范围本文旨在帮助读者深入理解单调栈的概念和工作原理
- Golang数据结构与算法:实现经典算法的Go版本
Golang编程笔记
golang算法开发语言ai
Golang数据结构与算法:实现经典算法的Go版本关键词:Golang、数据结构、算法、经典算法、Go实现摘要:本文将带领大家深入探索在Golang中实现经典算法。我们会先介绍一些基础的数据结构和算法概念,然后用生动的故事和例子来解释这些概念,接着给出核心概念之间的关系。通过详细的代码示例,展示如何在Go语言里实现这些经典算法,还会介绍它们的实际应用场景、相关工具和资源,探讨未来的发展趋势与挑战。
- C#推箱子游戏源代码解析与实践指南
Boa波雅
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:C#推箱子游戏是一个经典的益智游戏,适合编程初学者学习C#语言和游戏开发的基础知识。本篇文章将深入探讨使用C#语言开发推箱子游戏的源代码,涉及面向对象编程、图形用户界面(GUI)、事件驱动编程、数据结构与算法、状态管理、错误检查与边界条件、游戏逻辑以及调试技巧。通过学习本课程,初学者将能够掌握C#编程的基础和游戏逻辑的实现,并能够创建用户友好的界面。1.面向对
- 数据结构与算法--Python栈 栈实现综合计算器和逆波兰计算器 前缀表达式 中缀表达式 后缀表达式 逆波兰表达式
storyfull
数据结构与算法算法python栈逆波兰表达式逆波兰计算器
阅读目录栈实现综合计算器思路及Python实现思路Python实现模拟逆波兰计算器思路及Python实现思路Python实现正则表达式实现计算器栈实现综合计算器思路及Python实现思路先建立一个“数栈”用来压入数字,还有一个“符号栈”用来压入运算符,规定:减法从栈底向栈顶方法运算,乘除法优先级高于加减法具体操作过程:以“3+26-2”为例(1)数栈和符号栈皆为空,指针从左向右扫描表达式,数栈入栈
- c++面试八股文(大公司通用)
挨踢小明
IT生涯开发语言c++
在C++面试中,常见的问题通常会围绕C++的基础知识、数据结构与算法、系统设计、编程技巧、以及实际应用中的场景。以下是华为C++面试中常见的“八股文”问题及其简要回答思路。1.C++语言基础C++中const的用法有哪些?回答:常量变量:constinta=10;指针常量:constint*p;(指向常量的指针),int*constp;(指针本身是常量)成员函数常量:voidfunc()const
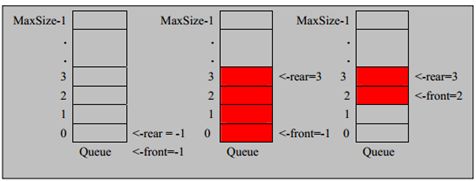
- 零基础数据结构与算法——第二章:基本数据结构-队列&总结
2.1数组(Array)2.2链表(LinkedList)2.3栈(Stack)2.4队列(Queue)2.4.1队列的定义与特点想象一下排队买票的场景,先到的人先买票,后到的人排在队伍末尾,这就是队列的基本概念。队列是一种遵循先进先出(FIFO,First-In-First-Out)原则的线性数据结构。队列的主要特点包括:两端操作:在一端(队尾)添加元素,在另一端(队头)移除元素,就像人们在队伍
- 《解锁Vcpkg国内镜像源:C++开发者的速度秘籍》
空云风语
QT人工智能c++开发语言
一、Vcpkg初相识在C++开发的广袤世界里,Vcpkg犹如一把神奇的钥匙,为开发者们打开了便捷之门,尤其是在依赖管理方面,发挥着举足轻重的作用。包管理工具对于C++开发而言,是至关重要的存在。C++作为一门强大且广泛应用的编程语言,在开发过程中常常需要依赖众多的第三方库。这些库涵盖了各种功能领域,比如网络通信、图形处理、数据结构与算法等。以网络通信为例,开发网络应用程序时,可能会用到像Boost
- Spring4.1新特性——Spring MVC增强
jinnianshilongnian
spring 4.1
目录
Spring4.1新特性——综述
Spring4.1新特性——Spring核心部分及其他
Spring4.1新特性——Spring缓存框架增强
Spring4.1新特性——异步调用和事件机制的异常处理
Spring4.1新特性——数据库集成测试脚本初始化
Spring4.1新特性——Spring MVC增强
Spring4.1新特性——页面自动化测试框架Spring MVC T
- mysql 性能查询优化
annan211
javasql优化mysql应用服务器
1 时间到底花在哪了?
mysql在执行查询的时候需要执行一系列的子任务,这些子任务包含了整个查询周期最重要的阶段,这其中包含了大量为了
检索数据列到存储引擎的调用以及调用后的数据处理,包括排序、分组等。在完成这些任务的时候,查询需要在不同的地方
花费时间,包括网络、cpu计算、生成统计信息和执行计划、锁等待等。尤其是向底层存储引擎检索数据的调用操作。这些调用需要在内存操
- windows系统配置
cherishLC
windows
删除Hiberfil.sys :使用命令powercfg -h off 关闭休眠功能即可:
http://jingyan.baidu.com/article/f3ad7d0fc0992e09c2345b51.html
类似的还有pagefile.sys
msconfig 配置启动项
shutdown 定时关机
ipconfig 查看网络配置
ipconfig /flushdns
- 人体的排毒时间
Array_06
工作
========================
|| 人体的排毒时间是什么时候?||
========================
转载于:
http://zhidao.baidu.com/link?url=ibaGlicVslAQhVdWWVevU4TMjhiKaNBWCpZ1NS6igCQ78EkNJZFsEjCjl3T5EdXU9SaPg04bh8MbY1bR
- ZooKeeper
cugfy
zookeeper
Zookeeper是一个高性能,分布式的,开源分布式应用协调服务。它提供了简单原始的功能,分布式应用可以基于它实现更高级的服务,比如同步, 配置管理,集群管理,名空间。它被设计为易于编程,使用文件系统目录树作为数据模型。服务端跑在java上,提供java和C的客户端API。 Zookeeper是Google的Chubby一个开源的实现,是高有效和可靠的协同工作系统,Zookeeper能够用来lea
- 网络爬虫的乱码处理
随意而生
爬虫网络
下边简单总结下关于网络爬虫的乱码处理。注意,这里不仅是中文乱码,还包括一些如日文、韩文 、俄文、藏文之类的乱码处理,因为他们的解决方式 是一致的,故在此统一说明。 网络爬虫,有两种选择,一是选择nutch、hetriex,二是自写爬虫,两者在处理乱码时,原理是一致的,但前者处理乱码时,要看懂源码后进行修改才可以,所以要废劲一些;而后者更自由方便,可以在编码处理
- Xcode常用快捷键
张亚雄
xcode
一、总结的常用命令:
隐藏xcode command+h
退出xcode command+q
关闭窗口 command+w
关闭所有窗口 command+option+w
关闭当前
- mongoDB索引操作
adminjun
mongodb索引
一、索引基础: MongoDB的索引几乎与传统的关系型数据库一模一样,这其中也包括一些基本的优化技巧。下面是创建索引的命令: > db.test.ensureIndex({"username":1}) 可以通过下面的名称查看索引是否已经成功建立: &nbs
- 成都软件园实习那些话
aijuans
成都 软件园 实习
无聊之中,翻了一下日志,发现上一篇经历是很久以前的事了,悔过~~
断断续续离开了学校快一年了,习惯了那里一天天的幼稚、成长的环境,到这里有点与世隔绝的感觉。不过还好,那是刚到这里时的想法,现在感觉在这挺好,不管怎么样,最要感谢的还是老师能给这么好的一次催化成长的机会,在这里确实看到了好多好多能想到或想不到的东西。
都说在外面和学校相比最明显的差距就是与人相处比较困难,因为在外面每个人都
- Linux下FTP服务器安装及配置
ayaoxinchao
linuxFTP服务器vsftp
检测是否安装了FTP
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -q vsftpd
如果未安装:package vsftpd is not installed 安装了则显示:vsftpd-2.0.5-28.el5累死的版本信息
安装FTP
运行yum install vsftpd命令,如[root@localhost ~]# yum install vsf
- 使用mongo-java-driver获取文档id和查找文档
BigBird2012
driver
注:本文所有代码都使用的mongo-java-driver实现。
在MongoDB中,一个集合(collection)在概念上就类似我们SQL数据库中的表(Table),这个集合包含了一系列文档(document)。一个DBObject对象表示我们想添加到集合(collection)中的一个文档(document),MongoDB会自动为我们创建的每个文档添加一个id,这个id在
- JSONObject以及json串
bijian1013
jsonJSONObject
一.JAR包简介
要使程序可以运行必须引入JSON-lib包,JSON-lib包同时依赖于以下的JAR包:
1.commons-lang-2.0.jar
2.commons-beanutils-1.7.0.jar
3.commons-collections-3.1.jar
&n
- [Zookeeper学习笔记之三]Zookeeper实例创建和会话建立的异步特性
bit1129
zookeeper
为了说明问题,看个简单的代码,
import org.apache.zookeeper.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocal
- 【Scala十二】Scala核心六:Trait
bit1129
scala
Traits are a fundamental unit of code reuse in Scala. A trait encapsulates method and field definitions, which can then be reused by mixing them into classes. Unlike class inheritance, in which each c
- weblogic version 10.3破解
ronin47
weblogic
版本:WebLogic Server 10.3
说明:%DOMAIN_HOME%:指WebLogic Server 域(Domain)目录
例如我的做测试的域的根目录 DOMAIN_HOME=D:/Weblogic/Middleware/user_projects/domains/base_domain
1.为了保证操作安全,备份%DOMAIN_HOME%/security/Defa
- 求第n个斐波那契数
BrokenDreams
今天看到群友发的一个问题:写一个小程序打印第n个斐波那契数。
自己试了下,搞了好久。。。基础要加强了。
&nbs
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-访问者模式-Visitor
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
interface IVisitor {
//第二次分派,Visitor调用Element
void visitConcret
- MatConvNet的excise 3改为网络配置文件形式
cherishLC
matlab
MatConvNet为vlFeat作者写的matlab下的卷积神经网络工具包,可以使用GPU。
主页:
http://www.vlfeat.org/matconvnet/
教程:
http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/practicals/cnn/index.html
注意:需要下载新版的MatConvNet替换掉教程中工具包中的matconvnet:
http
- ZK Timeout再讨论
chenchao051
zookeepertimeouthbase
http://crazyjvm.iteye.com/blog/1693757 文中提到相关超时问题,但是又出现了一个问题,我把min和max都设置成了180000,但是仍然出现了以下的异常信息:
Client session timed out, have not heard from server in 154339ms for sessionid 0x13a3f7732340003
- CASE WHEN 用法介绍
daizj
sqlgroup bycase when
CASE WHEN 用法介绍
1. CASE WHEN 表达式有两种形式
--简单Case函数
CASE sex
WHEN '1' THEN '男'
WHEN '2' THEN '女'
ELSE '其他' END
--Case搜索函数
CASE
WHEN sex = '1' THEN
- PHP技巧汇总:提高PHP性能的53个技巧
dcj3sjt126com
PHP
PHP技巧汇总:提高PHP性能的53个技巧 用单引号代替双引号来包含字符串,这样做会更快一些。因为PHP会在双引号包围的字符串中搜寻变量, 单引号则不会,注意:只有echo能这么做,它是一种可以把多个字符串当作参数的函数译注: PHP手册中说echo是语言结构,不是真正的函数,故把函数加上了双引号)。 1、如果能将类的方法定义成static,就尽量定义成static,它的速度会提升将近4倍
- Yii框架中CGridView的使用方法以及详细示例
dcj3sjt126com
yii
CGridView显示一个数据项的列表中的一个表。
表中的每一行代表一个数据项的数据,和一个列通常代表一个属性的物品(一些列可能对应于复杂的表达式的属性或静态文本)。 CGridView既支持排序和分页的数据项。排序和分页可以在AJAX模式或正常的页面请求。使用CGridView的一个好处是,当用户浏览器禁用JavaScript,排序和分页自动退化普通页面请求和仍然正常运行。
实例代码如下:
- Maven项目打包成可执行Jar文件
dyy_gusi
assembly
Maven项目打包成可执行Jar文件
在使用Maven完成项目以后,如果是需要打包成可执行的Jar文件,我们通过eclipse的导出很麻烦,还得指定入口文件的位置,还得说明依赖的jar包,既然都使用Maven了,很重要的一个目的就是让这些繁琐的操作简单。我们可以通过插件完成这项工作,使用assembly插件。具体使用方式如下:
1、在项目中加入插件的依赖:
<plugin>
- php常见错误
geeksun
PHP
1. kevent() reported that connect() failed (61: Connection refused) while connecting to upstream, client: 127.0.0.1, server: localhost, request: "GET / HTTP/1.1", upstream: "fastc
- 修改linux的用户名
hongtoushizi
linuxchange password
Change Linux Username
更改Linux用户名,需要修改4个系统的文件:
/etc/passwd
/etc/shadow
/etc/group
/etc/gshadow
古老/传统的方法是使用vi去直接修改,但是这有安全隐患(具体可自己搜一下),所以后来改成使用这些命令去代替:
vipw
vipw -s
vigr
vigr -s
具体的操作顺
- 第五章 常用Lua开发库1-redis、mysql、http客户端
jinnianshilongnian
nginxlua
对于开发来说需要有好的生态开发库来辅助我们快速开发,而Lua中也有大多数我们需要的第三方开发库如Redis、Memcached、Mysql、Http客户端、JSON、模板引擎等。
一些常见的Lua库可以在github上搜索,https://github.com/search?utf8=%E2%9C%93&q=lua+resty。
Redis客户端
lua-resty-r
- zkClient 监控机制实现
liyonghui160com
zkClient 监控机制实现
直接使用zk的api实现业务功能比较繁琐。因为要处理session loss,session expire等异常,在发生这些异常后进行重连。又因为ZK的watcher是一次性的,如果要基于wather实现发布/订阅模式,还要自己包装一下,将一次性订阅包装成持久订阅。另外如果要使用抽象级别更高的功能,比如分布式锁,leader选举
- 在Mysql 众多表中查找一个表名或者字段名的 SQL 语句
pda158
mysql
在Mysql 众多表中查找一个表名或者字段名的 SQL 语句:
方法一:SELECT table_name, column_name from information_schema.columns WHERE column_name LIKE 'Name';
方法二:SELECT column_name from information_schema.colum
- 程序员对英语的依赖
Smile.zeng
英语程序猿
1、程序员最基本的技能,至少要能写得出代码,当我们还在为建立类的时候思考用什么单词发牢骚的时候,英语与别人的差距就直接表现出来咯。
2、程序员最起码能认识开发工具里的英语单词,不然怎么知道使用这些开发工具。
3、进阶一点,就是能读懂别人的代码,有利于我们学习人家的思路和技术。
4、写的程序至少能有一定的可读性,至少要人别人能懂吧...
以上一些问题,充分说明了英语对程序猿的重要性。骚年
- Oracle学习笔记(8) 使用PLSQL编写触发器
vipbooks
oraclesql编程活动Access
时间过得真快啊,转眼就到了Oracle学习笔记的最后个章节了,通过前面七章的学习大家应该对Oracle编程有了一定了了解了吧,这东东如果一段时间不用很快就会忘记了,所以我会把自己学习过的东西做好详细的笔记,用到的时候可以随时查找,马上上手!希望这些笔记能对大家有些帮助!
这是第八章的学习笔记,学习完第七章的子程序和包之后