sql 逻辑运算符不等于_SQL不等于运算符介绍和示例
sql 逻辑运算符不等于
This article explores the SQL Not Equal comparison operator (<>) along with its usage scenarios.
本文探讨了SQL不等于比较运算符(<>)及其使用方案。
介绍 (Introduction)
We must have used comparison operators in mathematics in the early days. We use these operators to compare different values based on the conditions. For example, we might compare the performance of two authors based on a number of articles. Suppose Raj wrote 85 articles while Rajendra wrote 100 articles. We can say that-
在早期,我们必须在数学中使用比较运算符。 我们使用这些运算符根据条件比较不同的值。 例如,我们可能会根据大量文章比较两位作者的表现。 假设Raj写了85篇文章,而Rajendra写了100篇文章。 我们可以说-
The total number of articles written by Rajendra > (Greater than) the total number of articles written by Raj.
Rajendra撰写的文章总数> (大于) Rajend撰写的文章总数。
We can have the following comparison operators in SQL.
我们可以在SQL中使用以下比较运算符。
Operator |
Description |
= |
Equals to |
<> |
Not Equal |
!= |
Not Equal |
> |
Greater than |
>= |
Greater than to equals to |
< |
Less than |
<= |
Less than or equals to |
操作员 |
描述 |
= |
等于 |
<> |
不平等 |
!= |
不平等 |
> |
比...更棒 |
> = |
大于等于 |
< |
少于 |
<= |
小于或等于 |
In the table above, we can see that there are two operators for Not Equal (<> and !=) . In this article, we will explore both operators and differences in these as well.
在上表中,我们可以看到不等于(<>和!=)有两个运算符。 在本文中,我们将同时探讨运算符和它们之间的差异。
SQL不等于<>比较运算符 (SQL Not Equal <> Comparison Operator)
We use SQL Not Equal comparison operator (<>) to compare two expressions. For example, 10<>11 comparison operation uses SQL Not Equal operator (<>) between two expressions 10 and 11.
我们使用SQL不等于比较运算符(<>)比较两个表达式。 例如,10 <> 11比较操作在两个表达式10和11之间使用SQL不等于运算符(<>)。
SQL不等于运算符<>和!=之间的区别 (Difference between SQL Not Equal Operator <> and !=)
We can use both SQL Not Equal operators <> and != to do inequality test between two expressions. Both operators give the same output. The only difference is that ‘<>’ is in line with the ISO standard while ‘!=’ does not follow ISO standard. You should use <> operator as it follows the ISO standard.
我们可以同时使用SQL不等于运算符<>和!=在两个表达式之间进行不相等测试。 两个运算符给出相同的输出。 唯一的区别是'<>'符合ISO标准,而'!='不遵循ISO标准。 您应该使用<>运算符,因为它遵循ISO标准。
Let’s set up a sample table to explore SQL Not Equal operator.
让我们建立一个样本表来研究SQL不等于运算符。
CREATE TABLE dbo.Products
(ProductID INT
PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1, 1),
ProductName VARCHAR(50),
ProductLaunchDate DATETIME2
);
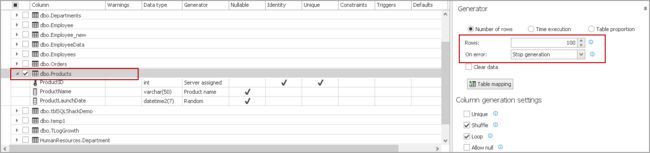
To generate the test data, I used ApexSQL Generate as shown in the following screenshot.
为了生成测试数据,我使用了ApexSQL Generate ,如以下屏幕截图所示。
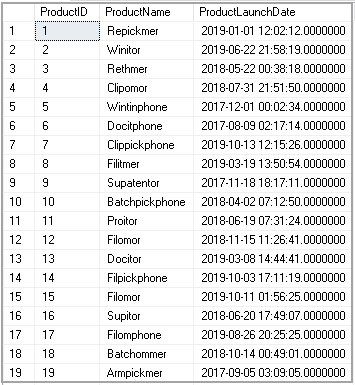
We can see sample data in the Products table.
我们可以在“产品”表中看到示例数据。
示例1:获取除ProductID 1之外的所有产品详细信息 (Example 1: Get all product details except ProductID 1)
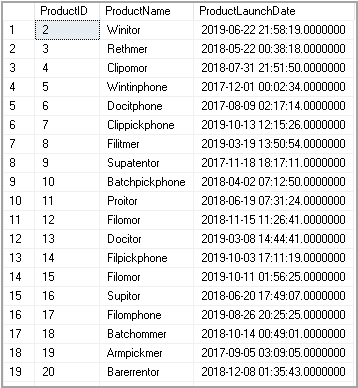
We are going to use SQL Not Equal operator <> to exclude ProductID 1 in the output.
我们将使用SQL不等于运算符<>在输出中排除ProductID 1。
Select * from dbo.products where ProductID <> 1
As stated earlier, we can use != operator as well to get the same output.
如前所述,我们也可以使用!=运算符来获得相同的输出。
Select * from dbo.products where ProductID!=1
示例2:获取2019年推出的产品以外的所有产品的列表 (Example 2: Get a list of all product except those launched in the Year 2019)
Suppose we want to get a list of products that launched except in the year 2019. We can use the following query using SQL Not Equal operator.
假设我们要获取在2019年以外发布的产品列表。我们可以使用SQL Not Equal运算符使用以下查询。
Select * from dbo.products where Year(ProductLaunchDate) <>2019
In the output, we can see all products except those launched in the Year 2019.
在输出中,我们可以看到除2019年推出的产品以外的所有产品。
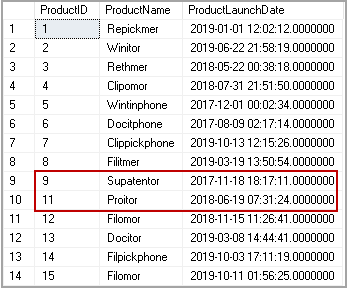
示例3:获取除特定产品之外的所有产品的列表 (Example 3: Get a list of all products excluding a specific product)
In previous examples, we used SQL Not Operator and specified a numerical value in the WHERE condition. Suppose we want to exclude a particular product from the output. We need to use string or varchar data type with a single quote in the where clause.
在前面的示例中,我们使用SQL Not运算符并在WHERE条件中指定了一个数值。 假设我们要从输出中排除特定产品。 我们需要在where子句中使用带单引号的字符串或varchar数据类型。
Select * from dbo.products where Productname<>'Batchpickphone'
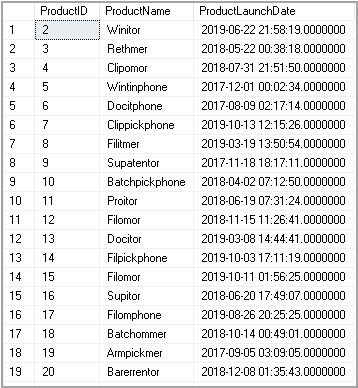
In the output, we do not have productID 10 as it gets excluded from the output.
在输出中,我们没有productID 10,因为它已从输出中排除。
If we do not specify the expression in a single quote, we get the following error message. It treats the expressions as a table column name without the single quote.
如果我们未在单引号中指定表达式,则会收到以下错误消息。 它将表达式视为没有单引号的表列名称。
Msg 207, Level 16, State 1, Line 11 Invalid column name ‘Batchpickphone’.
消息207,级别16,状态1,第11行无效的列名称“ Batchpickphone”。
示例4:使用SQL不等于运算符指定多个条件 (Example 4: Specifying multiple conditions using SQL Not Equal operator)
We can specify multiple conditions in a Where clause to exclude the corresponding rows from an output.
我们可以在Where子句中指定多个条件,以从输出中排除相应的行。
For example, we want to exclude ProductID 1 and ProductName Winitor (having ProductID 2). Execute the following code to satisfy the condition.
例如,我们要排除ProductID 1和ProductName Winitor(具有ProductID 2)。 执行以下代码以满足条件。
Select * from dbo.products where ProductID<>1 and ProductName<>'Winitor''
In the output, we do not have ProductID 1 and ProductID 2.
在输出中,我们没有ProductID 1和ProductID 2。
示例5:SQL不等于运算符和SQL Group By子句 (Example 5: SQL Not Equal operator and SQL Group By clause)
We can use SQL Not Equal operator in combination with the SQL Group By clause. In the following query, we use SQL Group by on ProductLaunchDate column to get a count of products excluding the year 2019.
我们可以将SQL不等于运算符与SQL Group By子句结合使用。 在以下查询中,我们在ProductLaunchDate列上使用SQL Group by来获取不包括2019年的产品数量。
Select Count(ProductLaunchDate)
from dbo.Products
group by ProductLaunchDate
having Year(ProductLaunchDate) <>2019
SQL不等于运算符的性能考虑
(Performance consideration of SQL Not Equal operator
)
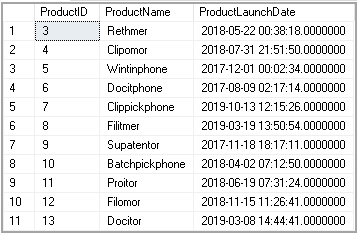
In this part, we will explore the performance consideration of SQL Not Equal operator. For this part, let’s keep only 10 records in the products table. It helps to demonstrate the situation quickly.
在这一部分中,我们将探讨SQL不等于运算符的性能注意事项。 对于这一部分,让我们在产品表中仅保留10条记录。 它有助于快速显示情况。
Execute the following query to delete products having ProductID>10.
执行以下查询,删除ProductID> 10的产品。
Delete from products where ProductID>10
We have the following records in the Products table.
我们在产品表中有以下记录。
Let’s execute the following query with the following tasks.
让我们通过以下任务执行以下查询。
- We use SET STATISTICS IO ON to show statistics of IO activity during query execution 我们使用SET STATISTICS IO ON来显示查询执行期间IO活动的统计信息
- We use SET STATISTICS TIME to display the time for parse, compile and execute each statement in a query batch 我们使用SET STATISTICS TIME来显示分析,编译和执行查询批处理中的每个语句的时间
- Enable the Actual Execution plan to show the execution plan used to retrieve results for this query by the query optimizer 启用实际执行计划以显示执行计划,以用于查询优化器检索此查询的结果
Set Statistics IO ON
Set Statistics Time On
Select * from dbo.products where ProductID<>1 and Year(ProductLaunchDate)<>2018 and ProductName<>'Winitor'
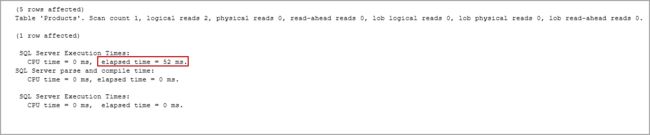
In the message tab, we can see the elapsed time for this query is 52 ms.
在消息选项卡中,我们可以看到此查询的经过时间为52毫秒。
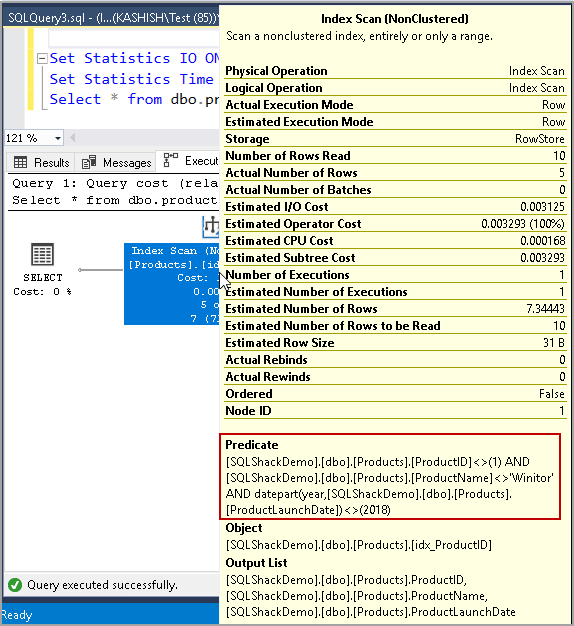
In the actual execution plan of this query, we can see SQL Not Equal predicates along with a Non-clustered index scan operator.
在该查询的实际执行计划中,我们可以看到SQL不等于谓词以及非聚集索引扫描运算符。
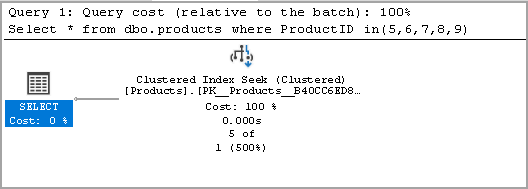
Let’s rewrite this query using IN operator. We get the same number of rows in this as well in comparison with a previous query using SQL Not Equal operator.
让我们使用IN运算符重写此查询。 与使用SQL Not Equal运算符的先前查询相比,在此方法中得到的行数也相同。
Set Statistics IO ON
Set Statistics Time On
Select * from dbo.products where ProductID in(5,6,7,8,9)
This time query took less time to return the same number of rows. It took only 1 ms while query with SQL Not Equal took 52 ms.
这次查询花费更少的时间返回相同数量的行。 使用SQL不等于查询仅花费了1毫秒,而花费了52毫秒。
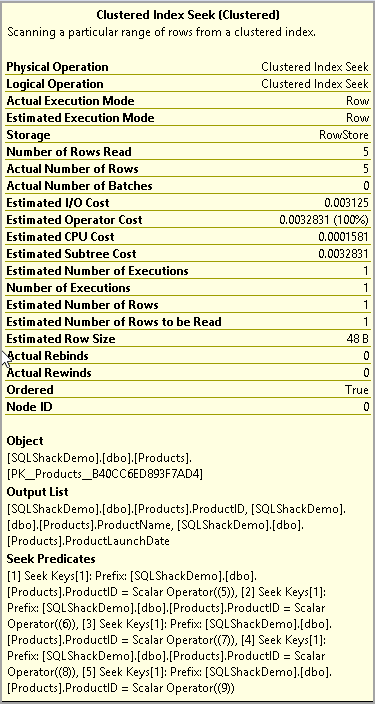
In the Actual Execution plan, it used Clustered Index Seek while SQL Not Equal used
在实际执行计划中,它使用聚簇索引查找,而使用SQL不等于
In the property for the Clustered Index Seek, it uses an equality operator to produce a similar result set.
在“聚簇索引查找”的属性中,它使用相等运算符生成相似的结果集。
- Caution: We should use the Equality operator to get a better performance in comparison with the SQL Not Equal operator.注意:与SQL Not Equal运算符相比,我们应该使用Equality运算符获得更好的性能。
结论 (Conclusion)
In this article, we explored SQL Not Operator along with examples. We also considered its performance implications in comparison with the Equality operators. You should try to use the Equality operator for better query performance. If you have any comments or questions, feel free to leave them in the comments below.
在本文中,我们与示例一起探讨了SQL Not Operator。 与Equality运算符相比,我们还考虑了其性能影响。 您应该尝试使用Equality运算符以获得更好的查询性能。 如果您有任何意见或疑问,请随时将其留在下面的评论中。
翻译自: https://www.sqlshack.com/sql-not-equal-operator/
sql 逻辑运算符不等于