要求从1到9 所有满足下列条件的表达式;“abc + def =ghi ”,其中每个字母代表不同的数字,如124+659=783
《1到9满足abc + def =ghi样式的算法》
方法一——利用itertools 中的permutations函数
1.基本思路.(核心思想是排序)
- (1).求出从1到9的所有排列方式
- (2).用函数permutations求出的所有排列方式列表化后添加到一个新的列表中形成一个双重列表result
- (3).通过循环读取result中每一个小列表,并使用判断条件输出
2.代码
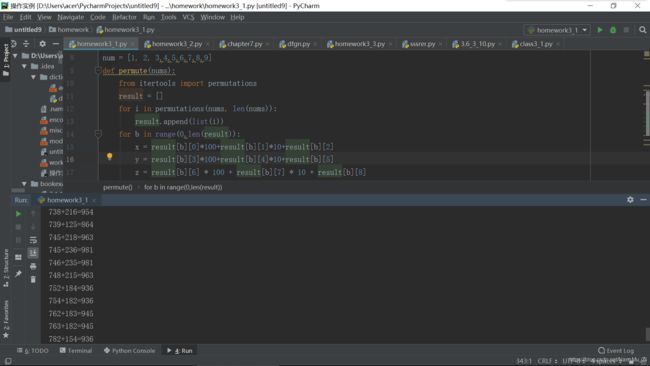
num = [1, 2, 3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
def permute(nums):
from itertools import permutations
result = []
for i in permutations(nums, len(nums)):
result.append(list(i))
for b in range(0,len(result)):
x = result[b][0]*100+result[b][1]*10+result[b][2]
y = result[b][3]*100+result[b][4]*10+result[b][5]
z = result[b][6] * 100 + result[b][7] * 10 + result[b][8]
if x + y ==z:
print("{}+{}={}".format(x,y,z))
print('\n')
print(permute(num))
方法二——利用reduce和lambda
1.基本思路.(核心思想是排序)
思路等等同第一种方法差不多
2.代码
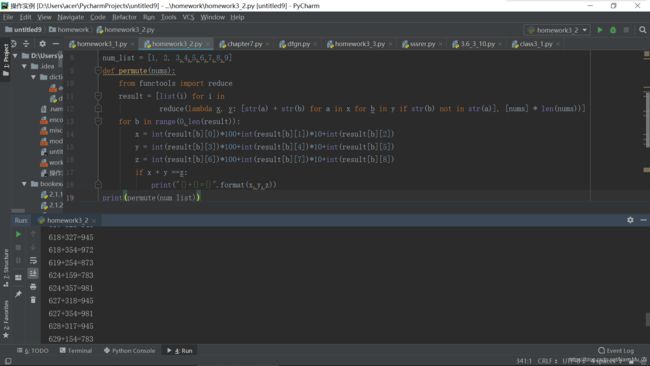
num_list = [1, 2, 3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
def permute(nums):
from functools import reduce
result = [list(i) for i in
reduce(lambda x, y: [str(a) + str(b) for a in x for b in y if str(b) not in str(a)], [nums] * len(nums))]
for b in range(0,len(result)):
x = int(result[b][0])*100+int(result[b][1])*10+int(result[b][2])
y = int(result[b][3])*100+int(result[b][4])*10+int(result[b][5])
z = int(result[b][6])*100+int(result[b][7])*10+int(result[b][8])
if x + y ==z:
print("{}+{}={}".format(x,y,z))
print(permute(num_list))
- 1 . lambda表达式,通常是在需要一个函数,但是又不想费神去命名一个函数的场合下使用,也就是指匿名函数
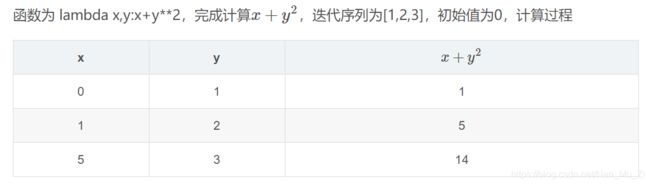
- 2.reduce()结合使用 其实是一种积累运算。函数将一个数据集合如集合或元组等传给 reduce 中的匿名函数lambda先对集合中的第前面俩 个元素进行操作,得到的结果再与第三个数据用匿名 函数运算,最后得到一个结果。具体例子可以如下
图片以及下述代码引用自:https://blog.csdn.net/yangfanswt/article/details/82016430
from functools import reduce
a=reduce(lambda x,y:x+y**2,[1,2,3],0)
print(a)
- 3.借助reduce累计运算功能将数字转换成字符串拼接到一起,如果新取出来的数和之前的不重复就继续拼接;也就是执行[str(a)+str(b) for a in x for b in y if str(b) not in str(a) ],生成的是列表
关于reduce和lambda可以参考https://blog.csdn.net/yangfanswt/article/details/82016430
方法三——“笨”方法
- 仅仅利用for循环以及条件表达式
list = [1, 2, 3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
for a in range(1,10):
for b in range(1,10):
for c in range(1,10):
for d in range(1, 10):
for e in range(1, 10):
for f in range(1, 10):
for g in range(1,10):
for h in range(1,10):
for i in range(1,10):
if a!=b and a!=c and a!= d and a!=e and a!=f and a!=g and a!=h and a!=i:
if b!=c and b!= d and b!=e and b!=f and b!=g and b!=h and b!=i:
if c!= d and c!=e and c!=f and c!=g and c!=h and c!=i:
if d!=e and d!=f and d!=g and d!=h and d!=i:
if e!=f and e!=g and e!=h and e!=i:
if f!=g and f!=h and f!=i:
if g!=h and g!=i:
if h!=i:
if (a*100+b*10+c) + (d*100+e*10+f) == (g*100+h*10+i):
x = a*100+b*10+c
y = d*100+e*10+f
z = g*100+h*10+i
print("{}+{}={}".format(x,y,z))