二叉树三种遍历的递归和非递归版本
二叉树
-
(书上定义)定义:二叉树(Binary Tree)是包含n个节点的有限集合,该集合或者为空集(此时,二叉树称为空树),或者由一个根节点和两棵互不相交的、分别称为根节点的左子树和右子树的二叉树组成。
这二叉树就是树的一种特殊结构,特殊在一个结点最多只能有两个子结点
-
特殊二叉树
-
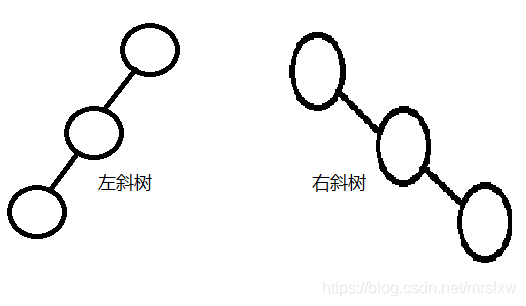
斜树
定义:所有结点都只有左子树的二叉树叫左斜树,所有结点都只有右子树的二叉树叫右斜树,这两者统称为斜树
-
满二叉树
定义:对于一棵二叉树,如果每一个非叶子节点都存在左右子树,并且二叉树中所有的叶子节点都在同一层中,这样的二叉树称为满二叉树。
-
完全二叉树
定义:对于一棵具有n个节点的二叉树按照层次编号,同时,左右子树按照先左后右编号,如果编号为i的节点与同样深度的满二叉树中编号为i的节点在二叉树中的位置完全相同,则这棵二叉树称为完全二叉树。
- 二叉树的性质
- 在二叉树中,第 i 层上至多有 2^(i-1) 个节点(i≥1)
- 深度为k的二叉树至多有 2^k−1 个节点(k≥1)
- 对一棵二叉树,如果叶子节点的个数为 n0 ,度为 2 的节点个数为 n2 ,则 n0=n2+1
- 具有n个节点的完全二叉树的深度为 (log2n)+1
二叉树的存储结构
-
顺序存储
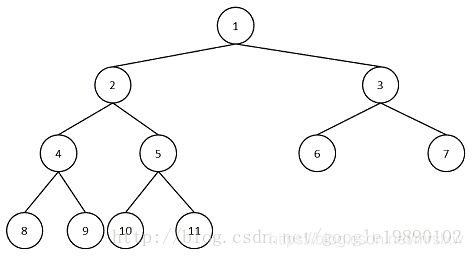
对下图的二叉树进行顺序存储
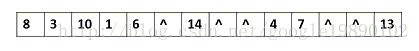
对于二叉树的是顺序存储就是将二叉树的各结点的数据存储到数组中,其数组的索引能体现结点之间的关系,且它们之间的关系是二叉树的层次关系,看看存储后的图( ^ 表示为空结点)
众所周知,顺序存储里面的数组会对内存空间造成很大的浪费
-
链式存储
直接看链式的结构定义吧
typedef struct BiTNode { ElemType data;// 数据域的值 struct BiTNode *lchild;// 左孩子 struct BiTNode *rchild;// 右孩子 }BiTNode, *BiTree;
二叉树的遍历
对于二叉树的遍历操作,主要分为:
- 前序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 层次遍历
- 这些遍历有递归遍历和非递归遍历版本,递归虽然方便,但是对空间资源上会造成很大的影响
代码:
#include
#include
#include
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct BiTNode
{
ElemType data;
struct BiTNode *lchild;
struct BiTNode *rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
typedef BiTree SElemType;
typedef struct StackNode
{
SElemType sdata;
struct StackNode *next;
}StackNode, *LinkStackNode;
typedef struct LinkStack
{
LinkStackNode top;
}LinkStack;
LinkStack S;
typedef BiTree QElemType;
typedef struct QNode
{
QElemType qdata;
struct QNode *next;
}QNode, *Queue;
typedef struct
{
Queue Front;
Queue Rear;
}LinkQueue;
LinkQueue Q;
void init_Queue(LinkQueue *Q)
{
Q->Front = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!Q->Front)
{
printf("The memory allocation failed ! Queue initialization falied! \n");
exit(0);
}
Q->Rear = Q->Front;
Q->Front->next = NULL;
}
void EnQueue(LinkQueue *Q, QElemType e)
{
Queue qNew = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!qNew)
{
printf("The memory allocation falied!Element can not enter queue!\n");
exit(0);
}
qNew->qdata = e;
qNew->next = NULL;
Q->Rear->next = qNew;
Q->Rear = qNew;
}
int size_Queue(LinkQueue Q)
{
int len = 0;
if (Q.Front == Q.Rear)
{
return 0;
}
Queue q = Q.Front->next;
while(q)
{
len++;
q = q->next;
}
return len;
}
QElemType DeQueue(LinkQueue *Q)
{
Queue q;
QElemType e;
if (Q->Front == Q->Rear)
{
printf("The queue is empty!\n");
exit(0);
}
q = Q->Front->next;
e = q->qdata;
Q->Front->next = q->next;
if (Q->Rear == q)
{
Q->Rear = Q->Front;
}
free(q);
q = NULL;
return e;
}
void init_Stack(LinkStack *S)
{
S->top = NULL;
}
void push_Stack(LinkStack *S, SElemType e)
{
LinkStackNode sNew = (LinkStackNode)malloc(sizeof(StackNode));
sNew->sdata = e;
sNew->next = S->top;
S->top = sNew;
}
void pop_Stack(LinkStack *S, SElemType &e)
{
LinkStackNode p = S->top;
if (p == NULL)
{
return;
}
e = p->sdata;
S->top = p->next;
free(p);
p = NULL;
}
SElemType get_Top(LinkStack S)
{
if (S.top != NULL)
{
return S.top->sdata;
}
else
{
return NULL;
}
}
bool isEmpty(LinkStack S)
{
if (S.top == NULL)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void creat_Tree(BiTree &T)
{
init_Stack(&S);
ElemType node[100] = {};
scanf("%s", node);
int len = strlen(node);
BiTree pd1, pd2;
bool flag;
if (node[0] != '#')
{
pd1 = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
pd1->data = node[0];
pd1->lchild = pd1;
pd1->rchild = pd1;
T = pd1;
int k = 0;
push_Stack(&S, pd1);
while(!isEmpty(S) && k != len -1)
{
flag = false;
if (node[++k] != '#')
{
pd2 = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
pd2->data = node[k];
pd2->lchild = pd2;
pd2->rchild = pd2;
flag = true;
}
else
{
pd2 = NULL;
}
pd1 = get_Top(S);
// char a = pd1->data;
while (pd1->lchild != pd1 && pd1->rchild != pd1)
{
pop_Stack(&S, pd1);
pd1 = get_Top(S);
}
if (pd1->lchild == pd1)
{
pd1->lchild = pd2;
}
else
{
pd1->rchild = pd2;
}
// a = pd1->data;
if (flag)
{
push_Stack(&S, pd2);
}
}
}
else
{
T = NULL;
printf("The tree is empty! The tree can`t created!\n");
}
}
void pre_Re_Traverse(BiTree T)
{
if (T)
{
printf("%c ", T->data);
pre_Re_Traverse(T->lchild);
pre_Re_Traverse(T->rchild);
}
}
void pre_nre_Traverse(BiTree T)
{
init_Stack(&S);
BiTree tree = T;
if (tree == NULL)
{
printf("The tree is empty! \n");
}
else
{
while (!isEmpty(S) || tree)
{
while(tree)
{
printf("%c ", tree->data);
push_Stack(&S, tree);
tree = tree->lchild;
}
pop_Stack(&S, tree);
tree = tree->rchild;
}
}
}
void in_Re_Traverse(BiTree T)
{
if (T)
{
in_Re_Traverse(T->lchild);
printf("%c ", T->data);
in_Re_Traverse(T->rchild);
}
}
void in_NRe_Traverse(BiTree T)
{
init_Stack(&S);
BiTree tree = T;
if (tree == NULL)
{
printf("The tree is empty!\n");
}
else
{
while (!isEmpty(S) || tree)
{
while(tree)
{
push_Stack(&S, tree);
tree = tree->lchild;
}
pop_Stack(&S, tree);
printf("%c ", tree->data);
tree = tree->rchild;
}
}
}
void pos_Re_Traverse(BiTree T)
{
if (T)
{
pos_Re_Traverse(T->lchild);
pos_Re_Traverse(T->rchild);
printf("%c ", T->data);
}
}
void pos_NRe_Traverse(BiTree T)
{
init_Stack(&S);
BiTree tree = T;
if (tree == NULL)
{
printf("The tree is empty!\n");
}
else
{
BiTree cur = NULL;
BiTree pre = NULL;
push_Stack(&S, tree);
while (!isEmpty(S))
{
cur = get_Top(S);
if ((cur->lchild == NULL && cur->rchild == NULL) || (pre != NULL && (pre == cur->rchild || pre == cur->lchild)))
{
printf("%c ", cur->data);
pop_Stack(&S, pre);
}
else
{
if (cur->rchild != NULL)
{
push_Stack(&S, cur->rchild);
}
if (cur->lchild != NULL)
{
push_Stack(&S, cur->lchild);
}
}
}
}
}
void layer_Traversal(BiTree T)
{
init_Queue(&Q);
BiTree tree = T;
if (!tree)
{
printf("The tree is empty!\n");
return;
}
EnQueue(&Q, tree);
while (Q.Front != Q.Rear)
{
tree = DeQueue(&Q);
printf("%c ", tree->data);
if (tree->lchild)
{
EnQueue(&Q, tree->lchild);
}
if (tree->rchild)
{
EnQueue(&Q, tree->rchild);
}
}
}
int treeDepth(BiTree T) //Recursive -- 递归计算深度
{
if (T == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int deleft = treeDepth(T->lchild);
int deright = treeDepth(T->rchild);
return (deleft > deright) ? (deleft + 1) : (deright + 1);
}
int UNre_treeDepth(BiTree T) //UN—Recursive -- 非递归计算深度
{
BiTree tree = T;
if (!tree)
{
return 0;
}
init_Queue(&Q);
EnQueue(&Q, tree);
int curLevel_num; //Number of node in the current level in the tree --- 当前层的节点数
int levels = 0; //Number of levels -- -- 层数
while (size_Queue(Q))
{
curLevel_num = size_Queue(Q);
while (curLevel_num-- > 0)
{
tree = DeQueue(&Q);
if (tree->lchild)
{
EnQueue(&Q, tree->lchild);
}
if (tree->rchild)
{
EnQueue(&Q, tree->rchild);
}
}
levels++;
}
return levels;
}
int main()
{
BiTree T;
//以先序遍历来创建二叉树
printf("Creat binary tree in the form of preorder traversal : ");
creat_Tree(T);
int option = 0;
printf("\n\t 1. Recursive traversal (递归遍历) \n\t 2. UN-Recursive traversal(非递归遍历) \n");
printf("Please enter your option: ");
scanf("%d", &option);
if (option == 1) //Start to recursive traversal -----开始递归遍历
{
printf("Recursive preorder traversal : ");
pre_Re_Traverse(T); //Recursive preorder traversal ------ 先序遍历
printf("\n");
printf("Recursive in-order traversal : ");
in_Re_Traverse(T); //Recursive in-order traversal ------ 中序遍历
printf("\n");
printf("Recursive post-order traversal : ");
pos_Re_Traverse(T); //Recursive post-order traversal ------ 后序遍历
printf("\n\n");
}
else if (option == 2) //Start to UN-Recursive traversal -----开始非递归遍历
{
printf("UN-Recursive preorder traversal : "); //先序遍历
pre_nre_Traverse(T);
printf("\n");
printf("UN-Recursive in-order traversal : "); //中序遍历
in_NRe_Traverse(T);
printf("\n");
printf("UN-Recursive post-order traversal : "); //后序遍历
pos_NRe_Traverse(T);
printf("\n");
printf("Traversal by layer : "); //按层遍历
layer_Traversal(T);
printf("\n\n");
}
//Calculate the depth of tree ---计算树的深度
printf("The tree`s height is %d \n", treeDepth(T));
printf("The tree`s height is %d \n", UNre_treeDepth(T));
return 0;
}
//ABDH#K###E##CFI###G#J##