USB共享网络:android手机通过USB与Ubuntu进行socket网络通信
测试平台:三星S4,内核3.4.5
Ubuntu版本:14.04
===========================
1. 打开手机移动热点中USB网络共享,并将手机通过USB连接到PC
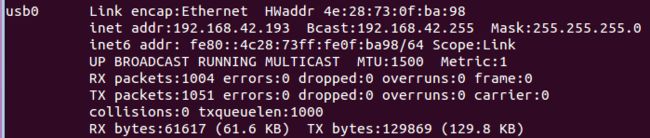
2. Ubuntu下使用命令ifconfig
2.1 inet addr:192.168.42.193就是我们客户端程序connect使用的地址:
address.sin_family = AF_INET;
address.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("192.168.42.193");
address.sin_port = htons(9734);
len = sizeof(address);
result = connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&address, len);
2.2 服务器端也是使用192.168.42.193这个ip地址进行bind,调用bind()函数之后,为socket()函数创建的套接字关联一个相应地址,发送到这个地址的数据可以通过该套接字读取与使用。
server_address.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_address.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("192.168.42.193");
server_address.sin_port = htons(9734);
server_len = sizeof(server_address);
bind(server_sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&server_address, server_len);
或者使用: server_address.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); 意味着可以接收本系统所安装的任何一个网卡的数据包。
3. 编写代码并编译
arm-client3.c
/* Make the necessary includes and set up the variables. */
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
int sockfd;
int len;
struct sockaddr_in address;
int result;
char ch = 'A';
/* Create a socket for the client. */
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
/* Name the socket, as agreed with the server. */
address.sin_family = AF_INET;
address.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("192.168.42.138");
address.sin_port = htons(9734);
len = sizeof(address);
/* Now connect our socket to the server's socket. */
result = connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&address, len);
if(result == -1) {
perror("oops: client3");
exit(1);
}
/* We can now read/write via sockfd. */
write(sockfd, &ch, 1);
read(sockfd, &ch, 1);
printf("char from server = %c\n", ch);
close(sockfd);
exit(0);
}
server3.c
/* Make the necessary includes and set up the variables. */
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
int server_sockfd, client_sockfd;
int server_len, client_len;
struct sockaddr_in server_address;
struct sockaddr_in client_address;
/* Remove any old socket and create an unnamed socket for the server. */
server_sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
/* Name the socket. */
server_address.sin_family = AF_INET;
// server_address.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
server_address.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("192.168.42.193");
server_address.sin_port = htons(9734);
server_len = sizeof(server_address);
bind(server_sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&server_address, server_len);
/* Create a connection queue and wait for clients. */
listen(server_sockfd, 5);
while(1) {
char ch;
printf("server waiting\n");
/* Accept a connection. */
client_len = sizeof(client_address);
client_sockfd = accept(server_sockfd,
(struct sockaddr *)&client_address, &client_len);
/* We can now read/write to client on client_sockfd. */
read(client_sockfd, &ch, 1);
ch++;
write(client_sockfd, &ch, 1);
close(client_sockfd);
}
}
服务器编译:gcc -o server3 server3.c
客户端编译:arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc -static -o arm-client3 arm-client3.c
4. 运行
先将arm-client3 push到手机:adb push ./arm-client3 /sdcard/
Ubuntu下: ./server3
adb shell下: ./arm-client3