查找1(符号表&二叉查找树)
文章目录
- 符号表
- 无序链表中的顺序查找
- 顺序查找(基于无序链表)
- 代码(Queue类)~1.2~
- 基于有序数组的二分查找
- 二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree BST)
- 插入操作时:put()
- 向上取整ceiling()与向下取整floor():
- 选择操作:
- 删除操作
- 范围查找
符号表
定义:符号表是一种储存键值对的数据结构,支持两种操作:插入(put),即将一组新的键值对存入表中。查找(get),即根据给定的键找到相应的值。
符号表主要的目的就是将一个键和一个值 联系起来。
无序链表中的顺序查找
符号表示用的数据结构一种简单的选择为链表,每个节点储存一个键值对。
向一个空表中插入N个不同的键需要~N2 / 2次比较。
查找某一个键的平均你叫次数为(1+2+3+···+N)/ N ~ N / 2。效率低。
顺序查找(基于无序链表)
package com.cz_lookup;
//import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
//import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
/*
IllegalArgumentException 抛出表示一种方法已经通过了非法或不正确的参数。
NoSuchElementException 被各种访问器方法抛出,表示被请求的元素不存在。
*/
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author ming
* @create 2020-02-26 15:23
*/
public class SequentialSearchST<Key, Value> {
private int n; //统计 key-val对个数
private Node first; //链表首节点,未初始化为null
//内部类
private class Node {
private Key key;
private Value val;
private Node next;
public Node(Key key, Value val, Node next) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
//空参构造器
public SequentialSearchST() {
}
//返回key-val数量
public int size() {
return n;
}
//链表为空返回true
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
//传入的key存在对应的val返回true
public boolean contains(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to contains() is null");
return get(key) != null;
}
//通过kry找val
public Value get(Key key) {
//链表为空
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to get() is null");
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (key.equals(x.key))
return x.val;
}
//未找到
return null;
}
//更新或添加key-val对
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to put() is null");
if (val == null) {//val == null; 调delete()删除此节点
delete(key);
return;
}
//将新key-val中的 key 对与链表中存在的 key 比较,相同则替换val
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (key.equals(x.key)) {
x.val = val;
return;
}
}
//将key-val加到链表中。新节点中的next指向链表中的首节点,成为新的首节点
first = new Node(key, val, first);
n++;
}
//方法重载,删除节点
public void delete(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to delete() is null");
first = delete(first, key);
}
private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) return null;//链表为空或找到链表尾并未找到 key
//从首节点开始依次与 key 比较
if (key.equals(x.key)) {//若相同,将x.next返回
n--;
return x.next;
}
//递归调用
x.next = delete(x.next, key);
return x;
}
public Queue<Key> keys() { //定义一个keys()方法来返回Iterable遍历表的键集指定的一部分,与栈中使用的方法不同
Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<>();
//将key-val对存入链表queue中,用来遍历key
//此链表实现了Iterable接口,可进行迭代
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
queue.enqueue(x.key); //见代码(Queue类)1.2
return queue;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
SequentialSearchST<String, Integer> st = new SequentialSearchST<>();
// for (int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {
// String key = StdIn.readString();
// st.put(key, i);
// }
// for (String s : st.keys())
// StdOut.println(s + " " + st.get(s));
st.put("A", 1);
st.put("C", 3);
st.put("Z", 24);
st.put("Z", 26);
st.put("E", 5);
st.put("H", 8);
st.delete("C");
int size = st.size();
int e = st.get("E");
boolean z = st.contains("Z");
System.out.println(z);//true
System.out.println(e);//5
System.out.println(size);
for (String s : st.keys()) System.out.printf("%s--%d\t", s, st.get(s));//H--8 E--5 Z--26 A--1
}
}
代码(Queue类)1.2
package com.cz_lookup;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* 链表实现先进先出队列
*
* @author ming
* @create 2020-02-27 22:04
*/
//implements Iterable- 重写 iterator();
public class Queue<Item> implements Iterable<Item> {
private Queue.Node<Item> first; // 队列开始
private Queue.Node<Item> last; // end of queue
private int n; // number of elements on queue
// 辅助链接列表类
private static class Node<Item> {
private Item item;
private Queue.Node<Item> next;
}
/**
* 构造器
*/
public Queue() {
first = null;
last = null;
n = 0;
}
/**
*
* @return 链表为空,返回true
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
/**
*
* @return 链表长度
*/
public int size() {
return n;
}
/**
*
* @return 队列头结点数据
*/
public Item peek() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow");
return first.item;
}
/**
*
* @param item 进入队列
*/
public void enqueue(Item item) {
Queue.Node<Item> oldlast = last; //保存队列尾
last = new Queue.Node<Item>(); //新建末节点
last.item = item; //数据存入新建末节点
last.next = null;
if (isEmpty()) first = last; //链表为空头结点即末节点
else oldlast.next = last; //新建末节点连接队列末
n++;
}
/**
*
* @return 出队列的数据
*/
public Item dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow");
Item item = first.item;
first = first.next;
n--;
if (isEmpty()) last = null; // to avoid loitering
return item;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
for (Item item : this) {
s.append(item);
s.append(' ');
}
return s.toString();
}
/*关于迭代
* 代码
* Stack collection = new Stack<>();
* ...
* for(String s : collection) {
* System.out.println(s);
* }
*
* 代码
* Stack collection = new Stack<>();
* ...
* Iterator i = collection.iterator();
* while(i.hasNext()) {
* String s = i.next();
* System.out.println(s);
* }
*
* 两段代码等价
* 集合数据类型必须实现iterator()方法,并返回Iterator对象;
* Iterator中包含两个方法:hasNext() (返回一个boolean值),next() (返回集合中的一个泛型元素)
*
* */
//返回:Iterator- 接口的实现类
private class LinkedIterator implements Iterator<Item> {
private Node<Item> current;
public LinkedIterator(Node<Item> first) {
current = first;
}
public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; }
//希望在迭代中避免穿插能够修改数据的操作
public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }
public Item next() {
if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException();
Item item = current.item;
current = current.next;
return item;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
基于有序数组的二分查找
这段代码为键值使用两个数组,需创建一个Key类型的Comparable的对象数组和一个Value类型的Object对象数组,并在构造函数中转化回Key[]和Value[]数组,动态调整数组大小(对于大数组来说太慢!)。
其中主要关注的方法:
get(Key key);
rank(Key key);
put(Key key, Value val);
delete(Key key);
floor(Key key);
ceiling(Key key);

package com.cz_lookup;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* 基于有序数组的二分查找
*
* @author ming
* @create 2020-02-28 15:30
*/
public class BinarySearchST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 4;
private Key[] keys;
private Value[] vals;
private int n = 0;
/**
* 初始化空符号表。默认容量为4
*/
public BinarySearchST() {
this(INIT_CAPACITY);
}
/**
* 使用指定的初始容量初始化空符号表
*
* @param capacity 最大容量
*/
public BinarySearchST(int capacity) {
keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[capacity];
vals = (Value[]) new Object[capacity];
}
// 调整基础数组的大小
private void resize(int capacity) {
assert capacity >= n;
Key[] tempk = (Key[]) new Comparable[capacity];
Value[] tempv = (Value[]) new Object[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
tempk[i] = keys[i];
tempv[i] = vals[i];
}
vals = tempv;
keys = tempk;
}
/**
* 返回此符号表中的键值对数。
*
* @return 键值对数量
*/
public int size() {
return n;
}
/**
* 如果此符号表为空,则返回true。
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/**
* 这个符号表包含给定的键吗?
*
* @param key the key
* @return {@code true} if this symbol table contains {@code key} and
* {@code false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public boolean contains(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to contains() is null");
return get(key) != null;
}
/**
* 返回与此符号表中给定键关联的值。
*
* @param key the key
* @return the value associated with the given key if the key is in the symbol table
* and {@code null} if the key is not in the symbol table
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public Value get(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to get() is null");
if (isEmpty()) return null;
int i = rank(key);
if (i < n && keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0) return vals[i];
return null;
}
/**
* Returns the number of keys in this symbol table strictly less than {@code key}.
* 返回此符号表中严格小于{@code key}的键数。
*
* @param key the key
* @return the number of keys in the symbol table strictly less than {@code key}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public int rank(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to rank() is null");
//二分查找
int lo = 0, hi = n - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; //等价与递归
int cmp = key.compareTo(keys[mid]); //通过compareTo可对key进行排序
if (cmp < 0) hi = mid - 1;
else if (cmp > 0) lo = mid + 1;
else return mid; //key在表中,返回位置索引
}
return lo; //表空,返回0;表不为空,key不在表中,返回key插入表中的位置索引(返回此符号表中严格小于key的键数)
}
/**
* 将指定的键值对插入符号表,如果符号表已包含指定的键,则用新值覆盖旧值。
* 如果指定的值为{@code null},则从该符号表中删除指定的键(及其关联的值)。
*
* @param key the key
* @param val the value
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to put() is null");
if (val == null) {
delete(key);
return;
}
int i = rank(key);
// 键已在表中,用新的键覆盖
if (i < n && keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0) {
vals[i] = val;
return;
}
// insert new key-value pair
if (n == keys.length) resize(2 * keys.length); //扩容
for (int j = n; j > i; j--) { //空出加入key的位置索引
keys[j] = keys[j - 1];
vals[j] = vals[j - 1];
}
//添加
keys[i] = key;
vals[i] = val;
n++;
assert check();
}
/**
* Removes the specified key and associated value from this symbol table
* (if the key is in the symbol table).
*
* @param key the key
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public void delete(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to delete() is null");
if (isEmpty()) return;
// compute rank
int i = rank(key); //如:表长为3,rank(key)可能返回 0、1、2、3
// key not in table
if (i == n || keys[i].compareTo(key) != 0) {
return;
}
for (int j = i; j < n - 1; j++) {
keys[j] = keys[j + 1];
vals[j] = vals[j + 1];
}
n--;
keys[n] = null; // 防止游离
vals[n] = null;
// resize if 1/4 full
if (n > 0 && n == keys.length / 4) resize(keys.length / 2);
assert check();
}
/**
* Removes the smallest key and associated value from this symbol table.
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty
*/
public void deleteMin() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Symbol table underflow error");
delete(min());
}
/**
* Removes the largest key and associated value from this symbol table.
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty
*/
public void deleteMax() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Symbol table underflow error");
delete(max());
}
/***************************************************************************
* Ordered symbol table methods. 有序符号表方法。
***************************************************************************/
/**
* Returns the smallest key in this symbol table.
*
* @return the smallest key in this symbol table
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this symbol table is empty
*/
public Key min() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("called min() with empty symbol table");
return keys[0];
}
/**
* Returns the largest key in this symbol table.
*
* @return the largest key in this symbol table
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this symbol table is empty
*/
public Key max() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("called max() with empty symbol table");
return keys[n - 1];
}
/**
* Return the kth smallest key in this symbol table.
*根据给定索引返回key
*
* @param k the order statistic
* @return the {@code k}th smallest key in this symbol table
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code k} is between 0 and
* n–1
*/
public Key select(int k) {
if (k < 0 || k >= size()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("called select() with invalid argument: " + k);
}
return keys[k];
}
/**
* 返回此符号表中小于或等于{@code key}的最大键。
*
* @param key the key
* @return the largest key in this symbol table less than or equal to {@code key}
* @throws NoSuchElementException if there is no such key
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public Key floor(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to floor() is null");
int i = rank(key);
if (i < n && key.compareTo(keys[i]) == 0) return keys[i];
if (i == 0) return null;
else return keys[i - 1];
}
/**
* 返回此符号表中大于或等于{@code key}的最小键。
*
* @param key the key
* @return the smallest key in this symbol table greater than or equal to {@code key}
* @throws NoSuchElementException if there is no such key
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public Key ceiling(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to ceiling() is null");
int i = rank(key);
if (i == n) return null;
else return keys[i];
}
/**
* Returns the number of keys in this symbol table in the specified range.
*返回指定索引范围key-val对数量
*
* @param lo minimum endpoint
* @param hi maximum endpoint
* @return the number of keys in this symbol table between {@code lo}
* (inclusive) and {@code hi} (inclusive)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if either {@code lo} or {@code hi}
* is {@code null}
*/
public int size(Key lo, Key hi) {
if (lo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to size() is null");
if (hi == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("second argument to size() is null");
if (lo.compareTo(hi) > 0) return 0;
if (contains(hi)) return rank(hi) - rank(lo) + 1;
else return rank(hi) - rank(lo);
}
/**
* 定义一个keys()方法来返回Iterable遍历表的键集指定的一部分,与栈中使用的方法不同
*
* 将此符号表中的所有键返回为{@code Iterable}。
* 要遍历名为{@code st}的符号表中的所有键,请使用foreach符号:{@code for(Key Key:st.keys())}。
*
* @return all keys in this symbol table
*/
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
return keys(min(), max());
}
/**
* Returns all keys in this symbol table in the given range,
* as an {@code Iterable}.
* 返回此符号表中给定范围内的所有键,作为{@code Iterable}。
*
* @param lo minimum endpoint
* @param hi maximum endpoint
* @return all keys in this symbol table between {@code lo}
* (inclusive) and {@code hi} (inclusive)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if either {@code lo} or {@code hi}
* is {@code null}
*/
public Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) {
if (lo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to keys() is null");
if (hi == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("second argument to keys() is null");
Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>(); //见代码(Queue类)1.2
if (lo.compareTo(hi) > 0) return queue;
for (int i = rank(lo); i < rank(hi); i++)
queue.enqueue(keys[i]);
if (contains(hi)) queue.enqueue(keys[rank(hi)]);
return queue;
}
/***************************************************************************
* Check internal invariants.检查内部不变量。
***************************************************************************/
private boolean check() {
return isSorted() && rankCheck();
}
// 数组中的项是否按升序排列?
private boolean isSorted() {
for (int i = 1; i < size(); i++)
if (keys[i].compareTo(keys[i - 1]) < 0) return false;
return true;
}
// 表中数组索引与键或值是否匹配
private boolean rankCheck() {
for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++)
if (i != rank(select(i))) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++)
if (keys[i].compareTo(select(rank(keys[i]))) != 0) return false;
return true;
}
/**
*测试
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchST<String, Integer> st = new BinarySearchST<>();
st.put("b", 2);
st.put("a", 1);
st.put("d", 4);
st.put("c", 3);
st.put("w", 3);
st.put("z", 4);
st.delete("c");
System.out.println(st.size());//5
st.deleteMax();
for (String key : st.keys()) {
System.out.printf("key-%s,val-%d\t\t", key, st.get(key));
//key-a,val-1 key-b,val-2 key-d,val-4 key-w,val-3
}
}
}
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree BST)
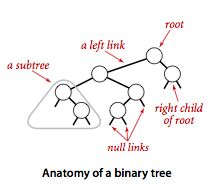
能够将链表插入的灵活性和有序数组查找的高效性结合起来的符号表,具体来说就是使用每个节点含有两个链接(链表中每个节点只含有一个链接)的二叉查找树来高效的实现符号表。
定义: 一棵二叉查找树是一棵二叉树,其中每个节点都含一个Comparable的键(以及相关联的值),且每一个节点的键都大于其左子树中任意节点的键,而小于右子树中任意节点的键。
查找get()操作几乎与二分查找一样
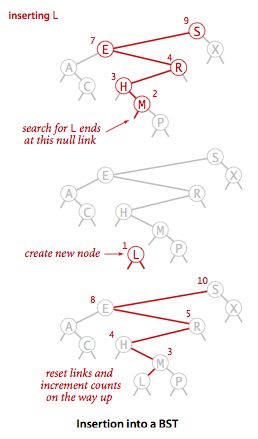
插入操作时:put()
意味着重置搜索路径上的每个父结点指向子节点的链接,并增加路径上每个节点中计数器的值。在一棵简单的二叉查找树中,唯一的新结点就是在最底层指向新结点的链接,重置更上层的链接,可以通过比较语句来避免,同样我们只需要将路径上每个节点中的计数器的值增加1,当我们使用了更通用的代码,使之等于节点的所有子节点(2、1、0个)的计数器之和加1。
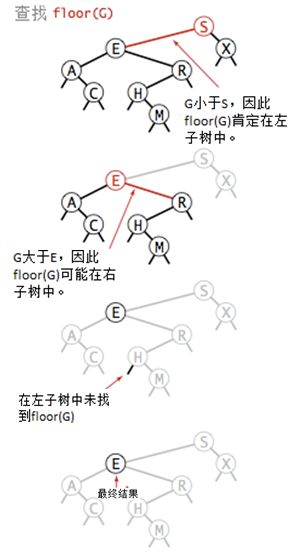
向上取整ceiling()与向下取整floor():
如果给定键key小于二叉查找树的根节点,则小于等于key的最大键floor(key)一定在跟节点的左子树中;如果给定键key大于二叉查找树的根节点,则小于等于key的最大键floor(key)可能在跟节点的右子树中;ceiling()的算法类似。
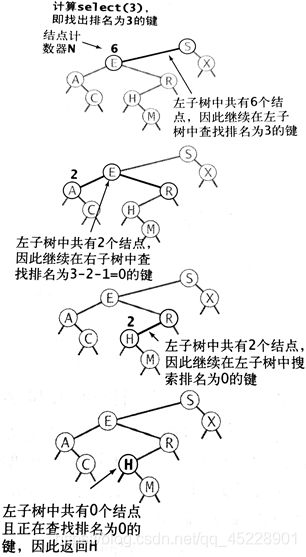
选择操作:
select(int k) rink(Key key) deleteMax();deleteMin();delete() 对于delete() 在删除节点x后,用它的后继节点填补它的位置,因为x有一个右子节点,因此,它的后继节点就是其右子节点中的最小节点,这样替换仍然能够保证树的有序性,因为x.key和它的后继结点的键之间不存在其他键,我们能用四个简单的步骤完成任务: 此方法对于一般情况的的效率不错,对于大规模应用可能会有一点问题。 能过返回给定范围內键的keys()方法,我们需要便利二叉查找树的方法—中序遍历,先遍历左子树,在遍历根节点,最后遍历右子树。 代码实现
* 如果根节点的左链接为空,则最小值为根节点,如果左节点为非空,那么树中最小键就是
* 左子树中的最小键,则通过递归找到最小键
*
* @return the smallest key in the symbol table
*/ 持续未完⏩
假设我们想找到排名为k的键(k从0开始计),正好有k个小于它的键,如果左子树中的结点数t>k,那么我们继续(递归的)在左子树中查找排名为k的键,如果t=k,我们就返回根节点中的键,如果t
是select(int k)的逆方法,它会返回给定键的排名。删除操作
跟put()一样,我们递归方法接受一个节点,并返回一个节点,这样能方便的改变树的结构。
对于deleteMin()方法来说,我们不断深入根节点的左子树,直到遇到一个空链接,然后将指向该节点的链接,改为指向该节点的右子树,(如图)。并更新路径上所有节点的计数器值。deleteMax()方法完全类似。
范围查找
package com.cz_lookup;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* @author ming
* @create 2020-03-03 13:30
*/
public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
private Node root; // root of BST 根节点
private class Node {
private Key key; // sorted by key
private Value val; // associated data
private Node left, right; // left and right subtrees
private int size; // 子树中的节点数
public Node(Key key, Value val, int size) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.size = size;
}
}
public BST() {
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table.
*
* @return 符号表中键值对数
*/
public int size() {
return size(root);
}
// 返回以x为根的BST中的键值对数
private int size(Node x) { //rank()和select()方法需要知道每个节点代表的子树中的总节点数,
if (x == null) return 0; //若不实现rank()和select()方法方法,直接用变量保存总节点数简化。
else return x.size;
}
/**
* key是否存在
*/
public boolean contains(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to contains() is null");
return get(key) != null;
}
/**
* Returns the value associated with the given key.
* 返回与给定键关联的值。
*/
public Value get(Key key) {
return get(root, key);
}
//以x为根节点的子树中找并返回key对应的值,这里使用递归,但基本的二叉查找树实现常常是非递归的(包括下面的put方法)
private Value get(Node x, Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("calls get() with a null key");
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) return get(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0) return get(x.right, key);
else return x.val;
}
/**
* 将指定的键值对插入符号表,如果符号表已包含指定的键,则用新值覆盖旧值。
* 如果指定的值是{@code null},则从该符号表中删除指定的键(及其关联值)。
*
* @param key the key
* @param val the value
*/
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("calls put() with a null key");
if (val == null) {
delete(key);
return;
}
root = put(root, key, val);
}
private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value val) {
if (x == null) return new Node(key, val, 1); //以x为根的树为空直接插入
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) x.left = put(x.left, key, val);
else if (cmp > 0) x.right = put(x.right, key, val);
else x.val = val;
x.size = 1 + size(x.left) + size(x.right); //更新路径上节点中计数器
return x;
}
/**
* Removes the smallest key and associated value from the symbol table.
*/
public void deleteMin() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Symbol table underflow");
root = deleteMin(root);
}
//返回删除最小节点后的头结点
private Node deleteMin(Node x) {
if (x.left == null) return x.right;
x.left = deleteMin(x.left);
x.size = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
/**
* Removes the largest key and associated value from the symbol table.
*/
public void deleteMax() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Symbol table underflow");
root = deleteMax(root);
}
//返回删除节点后的头结点
private Node deleteMax(Node x) {
if (x.right == null) return x.left;
x.right = deleteMax(x.right);
x.size = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
/**
* 从符号表中删除指定的键及其关联值(如果键在此符号表中)
*
* @param key the key
*/
public void delete(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("calls delete() with a null key");
root = delete(root, key);
}
private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
if (key == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) x.left = delete(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0) x.right = delete(x.right, key);
else {
if (x.right == null) return x.left;
if (x.left == null) return x.right;
Node t = x; //1
x = min(t.right); //2
x.right = deleteMin(t.right); //3
x.left = t.left; //4
}
x.size = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
/**
* 返回符号表中的最小键
*