自编码器是一种数据压缩算法,其中数据的压缩和解压缩函数是数据相关的、从样本中训练而来的。大部分自编码器中,压缩和解压缩的函数是通过神经网络实现的。
1. 使用卷积神经网络搭建自编码器
- 导入MNIST数据集(灰度图,像素范围0~1)
 View Code
View Codeimport numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', validation_size=0)
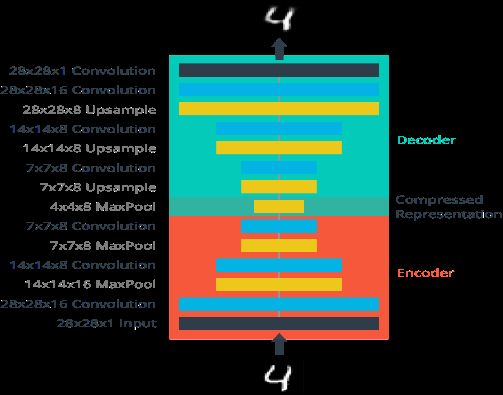
- 搭建网络
 View Code
View Codeinputs_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, 28, 28, 1), name='inputs') targets_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, 28, 28, 1), name='targets') ### Encoder conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs_, 16, (3,3), padding='same', activation=tf.nn.relu) # 28x28x16 maxpool1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv1, (2,2), (2,2), padding='same') # 14x14x16 conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(maxpool1, 8, (3,3), padding='same', activation=tf.nn.relu) # 14x14x8 maxpool2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv2, (2,2), (2,2), padding='same') # 7x7x8 conv3 = tf.layers.conv2d(maxpool2, 8, (3,3), padding='same', activation=tf.nn.relu) # 7x7x8 encoded = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv3, (2,2), (2,2), padding='same') # 4x4x8 ### Decoder upsample1 = tf.image.resize_nearest_neighbor(encoded, (7,7)) # 7x7x8 conv4 = tf.layers.conv2d(upsample1, 8, (3,3), padding='same', activation=tf.nn.relu) # 7x7x8 upsample2 = tf.image.resize_nearest_neighbor(conv4, (14,14)) # 14x14x8 conv5 = tf.layers.conv2d(upsample2, 8, (3,3), padding='same', activation=tf.nn.relu) # 14x14x8 upsample3 = tf.image.resize_nearest_neighbor(conv5, (28,28)) # 28x28x8 conv6 = tf.layers.conv2d(upsample3, 16, (3,3), padding='same', activation=tf.nn.relu) # 28x28x16 logits = tf.layers.conv2d(conv6, 1, (3,3), padding='same', activation=None) # 28x28x1 decoded = tf.nn.sigmoid(logits, name='decoded') # 28x28x1 ### Loss and Optimization: loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=targets_, logits=logits) cost = tf.reduce_mean(loss) opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cost)
模型在解码部分使用的是upsample+convolution而不是transposed convolution(参考文献)
- 训练网络
 View Code
View Codesess = tf.Session() epochs = 20 batch_size = 200 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) for e in range(epochs): for ii in range(mnist.train.num_examples//batch_size): batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) imgs = batch[0].reshape((-1, 28, 28, 1)) batch_cost, _ = sess.run([cost, opt], feed_dict={inputs_: imgs, targets_: imgs}) print("Epoch: {}/{}...".format(e+1, epochs), "Training loss: {:.4f}".format(batch_cost))
- 检验网络
 View Code
View Codefig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=10, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(20,4)) in_imgs = mnist.test.images[:10] reconstructed, compressed = sess.run([decoded, encoded], feed_dict={inputs_: in_imgs.reshape((10, 28, 28, 1))}) # plot for images, row in zip([in_imgs, reconstructed], axes): for img, ax in zip(images, row): ax.imshow(img.reshape((28, 28)), cmap='Greys_r') ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False) ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False) fig.tight_layout(pad=0.1) sess.close()
2. 使用自编码器降噪
- 搭建网络(同上但feature map的个数由16-8-8-8-8-16变为32-32-16-16-32-32)
- 训练网络
 View Code
View Codesess = tf.Session() epochs = 100 batch_size = 200 # Set's how much noise we're adding to the MNIST images noise_factor = 0.5 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) for e in range(epochs): for ii in range(mnist.train.num_examples//batch_size): batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) # Get images from the batch imgs = batch[0].reshape((-1, 28, 28, 1)) # Add random noise to the input images noisy_imgs = imgs + noise_factor * np.random.randn(*imgs.shape) # Clip the images to be between 0 and 1 noisy_imgs = np.clip(noisy_imgs, 0., 1.) # Noisy images as inputs, original images as targets batch_cost, _ = sess.run([cost, opt], feed_dict={inputs_: noisy_imgs, targets_: imgs}) print("Epoch: {}/{}...".format(e+1, epochs), "Training loss: {:.4f}".format(batch_cost))
- 检验网络
 View Code
View Codefig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=10, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(20,4)) in_imgs = mnist.test.images[:10] noisy_imgs = in_imgs + noise_factor * np.random.randn(*in_imgs.shape) noisy_imgs = np.clip(noisy_imgs, 0., 1.) reconstructed = sess.run(decoded, feed_dict={inputs_: noisy_imgs.reshape((10, 28, 28, 1))}) for images, row in zip([noisy_imgs, reconstructed], axes): for img, ax in zip(images, row): ax.imshow(img.reshape((28, 28)), cmap='Greys_r') ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False) ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False) fig.tight_layout(pad=0.1) sess.close()