SpringCloud认识五之分布式锁和分布式事务
本人讲述的是基于 Spring Cloud 的分布式架构,那么也带来了线程安全问题,比如一个商城系统,下单过程可能由不同的微服务协作完成,在高并发的情况下如果不加锁就会有问题,而传统的加锁方式只针对单一架构,对于分布式架构是不适合的,这时就需要用到分布式锁。
实现分布式锁的方式有很多,结合我的实际项目和目前的技术趋势,通过实例实现几种较为流行的分布式锁方案,最后会对不同的方案进行比较。
基于 Redis 的分布式锁
利用 SETNX 和 SETEX
基本命令主要有:
- SETNX(SET If Not Exists):当且仅当 Key 不存在时,则可以设置,否则不做任何动作。
- SETEX:可以设置超时时间
其原理为:通过 SETNX 设置 Key-Value 来获得锁,随即进入死循环,每次循环判断,如果存在 Key 则继续循环,如果不存在 Key,则跳出循环,当前任务执行完成后,删除 Key 以释放锁。
这种方式可能会导致死锁,为了避免这种情况,需要设置超时时间。
下面,请看具体的实现步骤。
1.创建一个 Maven 工程并在 pom.xml 加入以下依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.0.2.RELEASE
UTF-8
UTF-8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
2.创建启动类 Application.java:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
3.添加配置文件 application.yml:
server:
port: 8080
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
4.创建全局锁类 Lock.java:
/**
* 全局锁,包括锁的名称
*/
public class Lock {
private String name;
private String value;
public Lock(String name, String value) {
this.name = name;
this.value = value;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
}
5.创建分布式锁类 DistributedLockHandler.java:
@Component
public class DistributedLockHandler {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DistributedLockHandler.class);
private final static long LOCK_EXPIRE = 30 * 1000L;//单个业务持有锁的时间30s,防止死锁
private final static long LOCK_TRY_INTERVAL = 30L;//默认30ms尝试一次
private final static long LOCK_TRY_TIMEOUT = 20 * 1000L;//默认尝试20s
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate template;
/**
* 尝试获取全局锁
*
* @param lock 锁的名称
* @return true 获取成功,false获取失败
*/
public boolean tryLock(Lock lock) {
return getLock(lock, LOCK_TRY_TIMEOUT, LOCK_TRY_INTERVAL, LOCK_EXPIRE);
}
/**
* 尝试获取全局锁
*
* @param lock 锁的名称
* @param timeout 获取超时时间 单位ms
* @return true 获取成功,false获取失败
*/
public boolean tryLock(Lock lock, long timeout) {
return getLock(lock, timeout, LOCK_TRY_INTERVAL, LOCK_EXPIRE);
}
/**
* 尝试获取全局锁
*
* @param lock 锁的名称
* @param timeout 获取锁的超时时间
* @param tryInterval 多少毫秒尝试获取一次
* @return true 获取成功,false获取失败
*/
public boolean tryLock(Lock lock, long timeout, long tryInterval) {
return getLock(lock, timeout, tryInterval, LOCK_EXPIRE);
}
/**
* 尝试获取全局锁
*
* @param lock 锁的名称
* @param timeout 获取锁的超时时间
* @param tryInterval 多少毫秒尝试获取一次
* @param lockExpireTime 锁的过期
* @return true 获取成功,false获取失败
*/
public boolean tryLock(Lock lock, long timeout, long tryInterval, long lockExpireTime) {
return getLock(lock, timeout, tryInterval, lockExpireTime);
}
/**
* 操作redis获取全局锁
*
* @param lock 锁的名称
* @param timeout 获取的超时时间
* @param tryInterval 多少ms尝试一次
* @param lockExpireTime 获取成功后锁的过期时间
* @return true 获取成功,false获取失败
*/
public boolean getLock(Lock lock, long timeout, long tryInterval, long lockExpireTime) {
try {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(lock.getName()) || StringUtils.isEmpty(lock.getValue())) {
return false;
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
do{
if (!template.hasKey(lock.getName())) {
ValueOperations ops = template.opsForValue();
ops.set(lock.getName(), lock.getValue(), lockExpireTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return true;
} else {//存在锁
logger.debug("lock is exist!!!");
}
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime > timeout) {//尝试超过了设定值之后直接跳出循环
return false;
}
Thread.sleep(tryInterval);
}
while (template.hasKey(lock.getName())) ;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage());
return false;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 释放锁
*/
public void releaseLock(Lock lock) {
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(lock.getName())) {
template.delete(lock.getName());
}
}
}
6.最后创建 HelloController 来测试分布式锁。
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private DistributedLockHandler distributedLockHandler;
@RequestMapping("index")
public String index(){
Lock lock=new Lock("lynn","min");
if(distributedLockHandler.tryLock(lock)){
try {
//为了演示锁的效果,这里睡眠5000毫秒
System.out.println("执行方法");
Thread.sleep(5000);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
distributedLockHandler.releaseLock(lock);
}
return "hello world!";
}
}
7.测试。
启动 Application.java,连续访问两次浏览器:http://localhost:8080/index,控制台可以发现先打印了一次“执行方法”,说明后面一个线程被锁住了,5秒后又再次打印了“执行方法”,说明锁被成功释放。
通过这种方式创建的分布式锁存在以下问题:
- 高并发的情况下,如果两个线程同时进入循环,可能导致加锁失败。
- SETNX 是一个耗时操作,因为它需要判断 Key 是否存在,因为会存在性能问题。
因此,Redis 官方推荐 Redlock 来实现分布式锁。
利用 Redlock
通过 Redlock 实现分布式锁比其他算法更加可靠,继续改造上一例的代码。
1.pom.xml 增加以下依赖:
org.redisson
redisson
3.7.0
2.增加以下几个类:
/**
* 获取锁后需要处理的逻辑
*/
public interface AquiredLockWorker {
T invokeAfterLockAquire() throws Exception;
}
/**
* 获取锁管理类
*/
public interface DistributedLocker {
/**
* 获取锁
* @param resourceName 锁的名称
* @param worker 获取锁后的处理类
* @param
* @return 处理完具体的业务逻辑要返回的数据
* @throws UnableToAquireLockException
* @throws Exception
*/
T lock(String resourceName, AquiredLockWorker worker) throws UnableToAquireLockException, Exception;
T lock(String resourceName, AquiredLockWorker worker, int lockTime) throws UnableToAquireLockException, Exception;
}
/**
* 异常类
*/
public class UnableToAquireLockException extends RuntimeException {
public UnableToAquireLockException() {
}
public UnableToAquireLockException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public UnableToAquireLockException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
}
/**
* 获取RedissonClient连接类
*/
@Component
public class RedissonConnector {
RedissonClient redisson;
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
redisson = Redisson.create();
}
public RedissonClient getClient(){
return redisson;
}
}
@Component
public class RedisLocker implements DistributedLocker{
private final static String LOCKER_PREFIX = "lock:";
@Autowired
RedissonConnector redissonConnector;
@Override
public T lock(String resourceName, AquiredLockWorker worker) throws InterruptedException, UnableToAquireLockException, Exception {
return lock(resourceName, worker, 100);
}
@Override
public T lock(String resourceName, AquiredLockWorker worker, int lockTime) throws UnableToAquireLockException, Exception {
RedissonClient redisson= redissonConnector.getClient();
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(LOCKER_PREFIX + resourceName);
// Wait for 100 seconds seconds and automatically unlock it after lockTime seconds
boolean success = lock.tryLock(100, lockTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (success) {
try {
return worker.invokeAfterLockAquire();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
throw new UnableToAquireLockException();
}
}
3.修改 HelloController:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private DistributedLocker distributedLocker;
@RequestMapping("index")
public String index()throws Exception{
distributedLocker.lock("test",new AquiredLockWorker4.按照上节的测试方法进行测试,我们发现分布式锁也生效了。
Redlock 是 Redis 官方推荐的一种方案,因此可靠性比较高。
基于数据库的分布式锁
基于数据库表
它的基本原理和 Redis 的 SETNX 类似,其实就是创建一个分布式锁表,加锁后,我们就在表增加一条记录,释放锁即把该数据删掉,具体实现,我这里就不再一一举出。
它同样存在一些问题:
- 没有失效时间,容易导致死锁;
- 依赖数据库的可用性,一旦数据库挂掉,锁就马上不可用;
- 这把锁只能是非阻塞的,因为数据的 insert 操作,一旦插入失败就会直接报错。没有获得锁的线程并不会进入排队队列,要想再次获得锁就要再次触发获得锁操作;
- 这把锁是非重入的,同一个线程在没有释放锁之前无法再次获得该锁。因为数据库中数据已经存在了。
乐观锁
基本原理为:乐观锁一般通过 version 来实现,也就是在数据库表创建一个 version 字段,每次更新成功,则 version+1,读取数据时,我们将 version 字段一并读出,每次更新时将会对版本号进行比较,如果一致则执行此操作,否则更新失败!
悲观锁(排他锁)
实现步骤见下面说明。
1.创建一张数据库表:
CREATE TABLE `methodLock` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`method_name` varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '锁定的方法名',
`desc` varchar(1024) NOT NULL DEFAULT '备注信息',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '保存数据时间,自动生成',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `uidx_method_name` (`method_name `) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='锁定中的方法';
2.通过数据库的排他锁来实现分布式锁。
基于 MySQL 的 InnoDB 引擎,可以使用以下方法来实现加锁操作:
public boolean lock(){
connection.setAutoCommit(false)
while(true){
try{
result = select * from methodLock where method_name=xxx for update;
if(result==null){
return true;
}
}catch(Exception e){
}
sleep(1000);
}
return false;
}
3.我们可以认为获得排它锁的线程即可获得分布式锁,当获取到锁之后,可以执行方法的业务逻辑,执行完方法之后,再通过以下方法解锁:
public void unlock(){
connection.commit();
}
基于 Zookeeper 的分布式锁
ZooKeeper 简介
ZooKeeper 是一个分布式的,开放源码的分布式应用程序协调服务,是 Google Chubby 的一个开源实现,是 Hadoop 和 Hbase 的重要组件。它是一个为分布式应用提供一致性服务的软件,提供的功能包括:配置维护、域名服务、分布式同步、组服务等。
分布式锁实现原理
实现原理为:
- 建立一个节点,假如名为 lock 。节点类型为持久节点(Persistent)
- 每当进程需要访问共享资源时,会调用分布式锁的 lock() 或 tryLock() 方法获得锁,这个时候会在第一步创建的 lock 节点下建立相应的顺序子节点,节点类型为临时顺序节点(
EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL),通过组成特定的名字 name+lock+顺序号。 - 在建立子节点后,对 lock 下面的所有以 name 开头的子节点进行排序,判断刚刚建立的子节点顺序号是否是最小的节点,假如是最小节点,则获得该锁对资源进行访问。
- 假如不是该节点,就获得该节点的上一顺序节点,并监测该节点是否存在注册监听事件。同时在这里阻塞。等待监听事件的发生,获得锁控制权。
- 当调用完共享资源后,调用 unlock() 方法,关闭 ZooKeeper,进而可以引发监听事件,释放该锁。
实现的分布式锁是严格的按照顺序访问的并发锁。
代码实现
我们继续改造本文的工程。
1.创建 DistributedLock 类:
public class DistributedLock implements Lock, Watcher{
private ZooKeeper zk;
private String root = "/locks";//根
private String lockName;//竞争资源的标志
private String waitNode;//等待前一个锁
private String myZnode;//当前锁
private CountDownLatch latch;//计数器
private CountDownLatch connectedSignal=new CountDownLatch(1);
private int sessionTimeout = 30000;
/**
* 创建分布式锁,使用前请确认config配置的zookeeper服务可用
* @param config localhost:2181
* @param lockName 竞争资源标志,lockName中不能包含单词_lock_
*/
public DistributedLock(String config, String lockName){
this.lockName = lockName;
// 创建一个与服务器的连接
try {
zk = new ZooKeeper(config, sessionTimeout, this);
connectedSignal.await();
Stat stat = zk.exists(root, false);//此去不执行 Watcher
if(stat == null){
// 创建根节点
zk.create(root, new byte[0], ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
} catch (KeeperException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
}
}
/**
* zookeeper节点的监视器
*/
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
//建立连接用
if(event.getState()== Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected){
connectedSignal.countDown();
return;
}
//其他线程放弃锁的标志
if(this.latch != null) {
this.latch.countDown();
}
}
public void lock() {
try {
if(this.tryLock()){
System.out.println("Thread " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + " " +myZnode + " get lock true");
return;
}
else{
waitForLock(waitNode, sessionTimeout);//等待锁
}
} catch (KeeperException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
}
}
public boolean tryLock() {
try {
String splitStr = "_lock_";
if(lockName.contains(splitStr))
throw new LockException("lockName can not contains \\u000B");
//创建临时子节点
myZnode = zk.create(root + "/" + lockName + splitStr, new byte[0], ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL);
System.out.println(myZnode + " is created ");
//取出所有子节点
List subNodes = zk.getChildren(root, false);
//取出所有lockName的锁
List lockObjNodes = new ArrayList();
for (String node : subNodes) {
String _node = node.split(splitStr)[0];
if(_node.equals(lockName)){
lockObjNodes.add(node);
}
}
Collections.sort(lockObjNodes);
if(myZnode.equals(root+"/"+lockObjNodes.get(0))){
//如果是最小的节点,则表示取得锁
System.out.println(myZnode + "==" + lockObjNodes.get(0));
return true;
}
//如果不是最小的节点,找到比自己小1的节点
String subMyZnode = myZnode.substring(myZnode.lastIndexOf("/") + 1);
waitNode = lockObjNodes.get(Collections.binarySearch(lockObjNodes, subMyZnode) - 1);//找到前一个子节点
} catch (KeeperException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new LockException(e);
}
return false;
}
public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) {
try {
if(this.tryLock()){
return true;
}
return waitForLock(waitNode,time);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
private boolean waitForLock(String lower, long waitTime) throws InterruptedException, KeeperException {
Stat stat = zk.exists(root + "/" + lower,true);//同时注册监听。
//判断比自己小一个数的节点是否存在,如果不存在则无需等待锁,同时注册监听
if(stat != null){
System.out.println("Thread " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + " waiting for " + root + "/" + lower);
this.latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
this.latch.await(waitTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);//等待,这里应该一直等待其他线程释放锁
this.latch = null;
}
return true;
}
public void unlock() {
try {
System.out.println("unlock " + myZnode);
zk.delete(myZnode,-1);
myZnode = null;
zk.close();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (KeeperException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
this.lock();
}
public Condition newCondition() {
return null;
}
public class LockException extends RuntimeException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public LockException(String e){
super(e);
}
public LockException(Exception e){
super(e);
}
}
}
2.改造 HelloController.java:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("index")
public String index()throws Exception{
DistributedLock lock = new DistributedLock("localhost:2181","lock");
lock.lock();
//共享资源
if(lock != null){
System.out.println("执行方法");
Thread.sleep(5000);
lock.unlock();
}
return "hello world!";
}
}
3.按照本文 Redis 分布式锁的方法测试,我们发现同样成功加锁了。
总结
通过以上的实例可以得出以下结论:
- 通过数据库实现分布式锁是最不可靠的一种方式,对数据库依赖较大,性能较低,不利于处理高并发的场景。
- 通过 Redis 的 Redlock 和 ZooKeeper 来加锁,性能有了比较大的提升。
- 针对 Redlock,曾经有位大神对其实现的分布式锁提出了质疑,但是 Redis 官方却不认可其说法,所谓公说公有理婆说婆有理,对于分布式锁的解决方案,没有最好,只有最适合的,根据不同的项目采取不同方案才是最合理的。
首先我们应知道,事务是为了保证数据的一致性而产生的。那么分布式事务,顾名思义,就是我们要保证分布在不同数据库、不同服务器、不同应用之间的数据一致性。
为什么需要分布式事务?
最传统的架构是单一架构,数据是存放在一个数据库上的,采用数据库的事务就能满足我们的要求。随着业务的不断扩张,数据的不断增加,单一数据库已经到达了一个瓶颈,因此我们需要对数据库进行分库分表。为了保证数据的一致性,可能需要不同的数据库之间的数据要么同时成功,要么同时失败,否则可能导致产生一些脏数据,也可能滋生 Bug。
在这种情况下,分布式事务思想应运而生。
应用场景
分布式事务的应用场景很广,我也无法一一举例,我列举出比较常见的场景,以便于读者在实际项目中,在用到了一些场景时即可考虑分布式事务。
支付
最经典的场景就是支付了,一笔支付,是对买家账户进行扣款,同时对卖家账户进行加钱,这些操作必须在一个事务里执行,要么全部成功,要么全部失败。而对于买家账户属于买家中心,对应的是买家数据库,而卖家账户属于卖家中心,对应的是卖家数据库,对不同数据库的操作必然需要引入分布式事务。
在线下单
买家在电商平台下单,往往会涉及到两个动作,一个是扣库存,第二个是更新订单状态,库存和订单一般属于不同的数据库,需要使用分布式事务保证数据一致性。
银行转账
账户 A 转账到账户 B,实际操作是账户 A 减去相应金额,账户 B 增加相应金额,在分库分表的前提下,账户 A 和账户 B 可能分别存储在不同的数据库中,这时需要使用分布式事务保证数据库一致性。否则可能导致的后果是 A 扣了钱 B 却没有增加钱,或者 B 增加了钱 A 却没有扣钱。
SpringBoot 集成 Atomikos 实现分布式事务
Atomikos 简介
Atomikos 是一个为 Java 平台提供增值服务的开源类事务管理器。
以下是包括在这个开源版本中的一些功能:
- 全面崩溃 / 重启恢复;
- 兼容标准的 SUN 公司 JTA API;
- 嵌套事务;
- 为 XA 和非 XA 提供内置的 JDBC 适配器。
注释:XA 协议由 Tuxedo 首先提出的,并交给 X/Open 组织,作为资源管理器(数据库)与事务管理器的接口标准。目前,Oracle、Informix、DB2 和 Sybase 等各大数据库厂家都提供对 XA 的支持。XA 协议采用两阶段提交方式来管理分布式事务。XA 接口提供资源管理器与事务管理器之间进行通信的标准接口。XA 协议包括两套函数,以
xa_开头的及以ax_开头的。
具体实现
1.在本地创建两个数据库:test01,test02,并且创建相同的数据库表:
2.改造上篇的工程,在 pom.xml 增加以下依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
1.1.1
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.40
3.修改配置文件 application.yml 如下:
server:
port: 8080
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
mysql:
datasource:
test1:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test01?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: 1qaz2wsx
minPoolSize: 3
maxPoolSize: 25
maxLifetime: 20000
borrowConnectionTimeout: 30
loginTimeout: 30
maintenanceInterval: 60
maxIdleTime: 60
testQuery: select 1
test2:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test02?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: 1qaz2wsx
minPoolSize: 3
maxPoolSize: 25
maxLifetime: 20000
borrowConnectionTimeout: 30
loginTimeout: 30
maintenanceInterval: 60
maxIdleTime: 60
testQuery: select 1
4.创建以下类:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mysql.datasource.test1")
@SpringBootConfiguration
public class DBConfig1 {
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
private int minPoolSize;
private int maxPoolSize;
private int maxLifetime;
private int borrowConnectionTimeout;
private int loginTimeout;
private int maintenanceInterval;
private int maxIdleTime;
private String testQuery;
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public int getMinPoolSize() {
return minPoolSize;
}
public void setMinPoolSize(int minPoolSize) {
this.minPoolSize = minPoolSize;
}
public int getMaxPoolSize() {
return maxPoolSize;
}
public void setMaxPoolSize(int maxPoolSize) {
this.maxPoolSize = maxPoolSize;
}
public int getMaxLifetime() {
return maxLifetime;
}
public void setMaxLifetime(int maxLifetime) {
this.maxLifetime = maxLifetime;
}
public int getBorrowConnectionTimeout() {
return borrowConnectionTimeout;
}
public void setBorrowConnectionTimeout(int borrowConnectionTimeout) {
this.borrowConnectionTimeout = borrowConnectionTimeout;
}
public int getLoginTimeout() {
return loginTimeout;
}
public void setLoginTimeout(int loginTimeout) {
this.loginTimeout = loginTimeout;
}
public int getMaintenanceInterval() {
return maintenanceInterval;
}
public void setMaintenanceInterval(int maintenanceInterval) {
this.maintenanceInterval = maintenanceInterval;
}
public int getMaxIdleTime() {
return maxIdleTime;
}
public void setMaxIdleTime(int maxIdleTime) {
this.maxIdleTime = maxIdleTime;
}
public String getTestQuery() {
return testQuery;
}
public void setTestQuery(String testQuery) {
this.testQuery = testQuery;
}
}
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mysql.datasource.test2")
@SpringBootConfiguration
public class DBConfig2 {
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
private int minPoolSize;
private int maxPoolSize;
private int maxLifetime;
private int borrowConnectionTimeout;
private int loginTimeout;
private int maintenanceInterval;
private int maxIdleTime;
private String testQuery;
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public int getMinPoolSize() {
return minPoolSize;
}
public void setMinPoolSize(int minPoolSize) {
this.minPoolSize = minPoolSize;
}
public int getMaxPoolSize() {
return maxPoolSize;
}
public void setMaxPoolSize(int maxPoolSize) {
this.maxPoolSize = maxPoolSize;
}
public int getMaxLifetime() {
return maxLifetime;
}
public void setMaxLifetime(int maxLifetime) {
this.maxLifetime = maxLifetime;
}
public int getBorrowConnectionTimeout() {
return borrowConnectionTimeout;
}
public void setBorrowConnectionTimeout(int borrowConnectionTimeout) {
this.borrowConnectionTimeout = borrowConnectionTimeout;
}
public int getLoginTimeout() {
return loginTimeout;
}
public void setLoginTimeout(int loginTimeout) {
this.loginTimeout = loginTimeout;
}
public int getMaintenanceInterval() {
return maintenanceInterval;
}
public void setMaintenanceInterval(int maintenanceInterval) {
this.maintenanceInterval = maintenanceInterval;
}
public int getMaxIdleTime() {
return maxIdleTime;
}
public void setMaxIdleTime(int maxIdleTime) {
this.maxIdleTime = maxIdleTime;
}
public String getTestQuery() {
return testQuery;
}
public void setTestQuery(String testQuery) {
this.testQuery = testQuery;
}
}
@SpringBootConfiguration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.lynn.demo.test01", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "sqlSessionTemplate")
public class MyBatisConfig1 {
// 配置数据源
@Primary
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
public DataSource dataSource(DBConfig1 config) throws SQLException {
MysqlXADataSource mysqlXaDataSource = new MysqlXADataSource();
mysqlXaDataSource.setUrl(config.getUrl());
mysqlXaDataSource.setPinGlobalTxToPhysicalConnection(true);
mysqlXaDataSource.setPassword(config.getPassword());
mysqlXaDataSource.setUser(config.getUsername());
mysqlXaDataSource.setPinGlobalTxToPhysicalConnection(true);
AtomikosDataSourceBean xaDataSource = new AtomikosDataSourceBean();
xaDataSource.setXaDataSource(mysqlXaDataSource);
xaDataSource.setUniqueResourceName("dataSource");
xaDataSource.setMinPoolSize(config.getMinPoolSize());
xaDataSource.setMaxPoolSize(config.getMaxPoolSize());
xaDataSource.setMaxLifetime(config.getMaxLifetime());
xaDataSource.setBorrowConnectionTimeout(config.getBorrowConnectionTimeout());
xaDataSource.setLoginTimeout(config.getLoginTimeout());
xaDataSource.setMaintenanceInterval(config.getMaintenanceInterval());
xaDataSource.setMaxIdleTime(config.getMaxIdleTime());
xaDataSource.setTestQuery(config.getTestQuery());
return xaDataSource;
}
@Primary
@Bean(name = "sqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("dataSource") DataSource dataSource)
throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return bean.getObject();
}
@Primary
@Bean(name = "sqlSessionTemplate")
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(
@Qualifier("sqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
@SpringBootConfiguration
//basePackages 最好分开配置 如果放在同一个文件夹可能会报错
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.lynn.demo.test02", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "sqlSessionTemplate2")
public class MyBatisConfig2 {
// 配置数据源
@Bean(name = "dataSource2")
public DataSource dataSource(DBConfig2 config) throws SQLException {
MysqlXADataSource mysqlXaDataSource = new MysqlXADataSource();
mysqlXaDataSource.setUrl(config.getUrl());
mysqlXaDataSource.setPinGlobalTxToPhysicalConnection(true);
mysqlXaDataSource.setPassword(config.getPassword());
mysqlXaDataSource.setUser(config.getUsername());
mysqlXaDataSource.setPinGlobalTxToPhysicalConnection(true);
AtomikosDataSourceBean xaDataSource = new AtomikosDataSourceBean();
xaDataSource.setXaDataSource(mysqlXaDataSource);
xaDataSource.setUniqueResourceName("dataSource2");
xaDataSource.setMinPoolSize(config.getMinPoolSize());
xaDataSource.setMaxPoolSize(config.getMaxPoolSize());
xaDataSource.setMaxLifetime(config.getMaxLifetime());
xaDataSource.setBorrowConnectionTimeout(config.getBorrowConnectionTimeout());
xaDataSource.setLoginTimeout(config.getLoginTimeout());
xaDataSource.setMaintenanceInterval(config.getMaintenanceInterval());
xaDataSource.setMaxIdleTime(config.getMaxIdleTime());
xaDataSource.setTestQuery(config.getTestQuery());
return xaDataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "sqlSessionFactory2")
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("dataSource2") DataSource dataSource)
throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean(name = "sqlSessionTemplate2")
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(
@Qualifier("sqlSessionFactory2") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
在 com.lynn.demo.test01 和 com.lynn.demo.test02 中分别创建以下 mapper:
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper1 {
@Insert("insert into test_user(name,age) values(#{name},#{age})")
void addUser(@Param("name")String name,@Param("age") int age);
}
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper2 {
@Insert("insert into test_user(name,age) values(#{name},#{age})")
void addUser(@Param("name") String name,@Param("age") int age);
}
创建 service 类:
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper1 userMapper1;
@Autowired
private UserMapper2 userMapper2;
@Transactional
public void addUser(User user)throws Exception{
userMapper1.addUser(user.getName(),user.getAge());
userMapper2.addUser(user.getName(),user.getAge());
}
}
5.创建单元测试类进行测试:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class)
public class TestDB {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void test(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("lynn");
user.setAge(10);
try {
userService.addUser(user);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
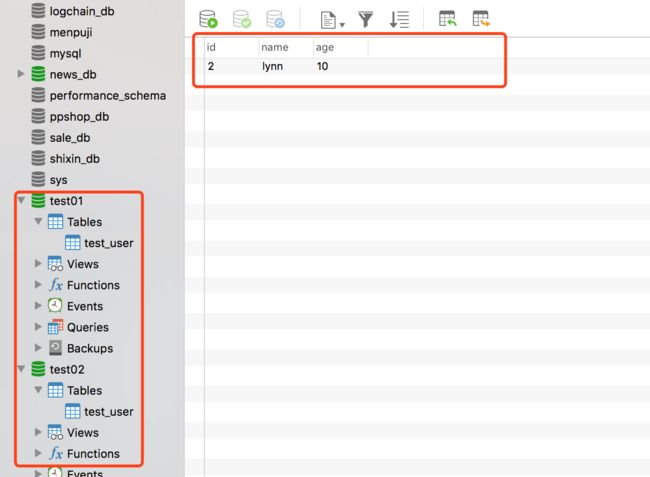
经过测试,如果没有报错,则数据被分别添加到两个数据库表中,如果有报错,则数据不会增加。
通过前面基础组件的学习,我们已经可以利用这些组件搭建一个比较完整的微服务架构,为了巩固我们前面学习的知识,从本文开始,将以一个实际的案例带领大家构建一个完整的微服务架构。
需求分析
我要实现的一个产品是新闻门户网站,首先我们需要对其进行需求分析,本新闻门户网站包括的功能大概有以下几个:
- 注册登录
- 新闻列表
- 用户评论
产品设计
根据需求分析,就可以进行产品设计,主要是原型设计,我们先看看大致的原型设计图。
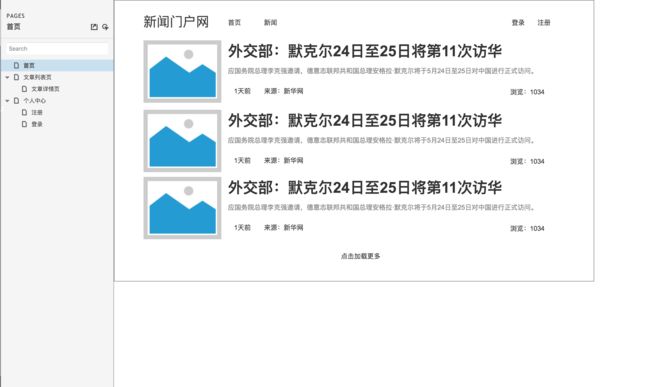
首页原型设计图
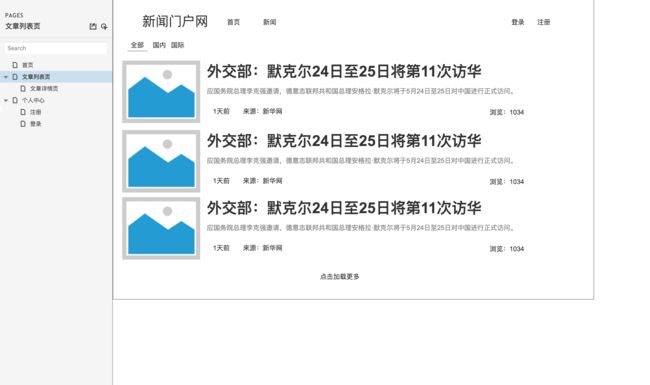
文章列表页原型设计图
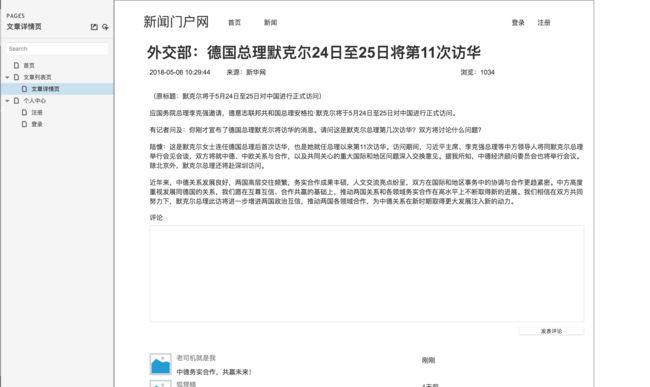
文章详情页原型设计图
个人中心页原型设计图
用户注册页原型设计图
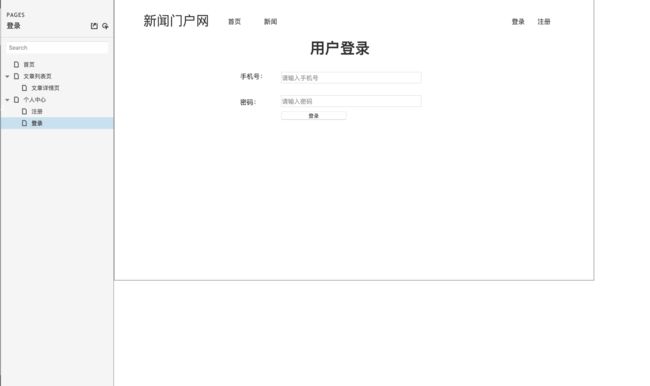
用户登录页原型设计图
数据库设计
根据原型设计图,我们可以分析出数据结构,从而设计数据库:
/*
Navicat Premium Data Transfer
Source Server : 本地
Source Server Type : MySQL
Source Server Version : 50709
Source Host : localhost:3306
Source Schema : news_db
Target Server Type : MySQL
Target Server Version : 50709
File Encoding : 65001
Date: 07/06/2018 21:15:58
*/
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for news_article
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `news_article`;
CREATE TABLE `news_article` (
`id` bigint(16) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增ID',
`gmt_create` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
`gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '修改时间',
`title` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '标题',
`summary` varchar(256) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '摘要',
`pic_url` varchar(256) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '图片',
`view_count` int(8) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '浏览数',
`source` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '来源',
`content` text COMMENT '文章内容',
`category_id` bigint(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '分类ID',
`is_recommend` tinyint(1) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '是否推荐',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for news_captcha
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `news_captcha`;
CREATE TABLE `news_captcha` (
`id` bigint(16) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增ID',
`gmt_create` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '修改时间',
`mobile` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '手机号',
`code` varchar(8) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '验证码',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for news_category
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `news_category`;
CREATE TABLE `news_category` (
`id` bigint(16) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增ID',
`gmt_create` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '修改时间',
`name` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '分类名',
`parent_id` bigint(16) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '上级分类ID(0为顶级分类)',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for news_comment
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `news_comment`;
CREATE TABLE `news_comment` (
`id` bigint(16) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增ID',
`gmt_create` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '修改时间',
`article_id` bigint(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '文章ID',
`content` varchar(256) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '评论内容',
`parent_id` bigint(16) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '上级评论ID(0为顶级评论)',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for news_user
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `news_user`;
CREATE TABLE `news_user` (
`id` bigint(16) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增ID',
`gmt_create` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '修改时间',
`mobile` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '手机号',
`password` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '密码(SHA1加密)',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
架构图设计
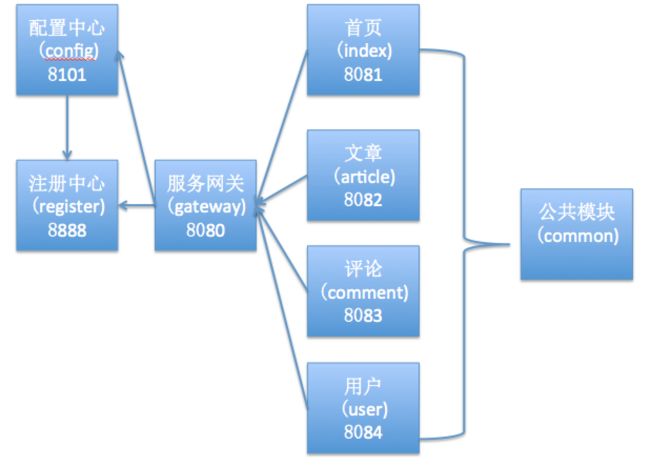
对于现代微服务架构来说,我们在搭建项目之前最好先设计架构图,因为微服务工程较多,关系比较复杂,有了架构图,更有利于我们进行架构设计,下面请看本实例的架构图:
框架搭建
根据架构图,我们就可以开始搭建框架,首先要进行技术选型,也就是需要集成什么技术,本实例,我们将能够看到注册中心、配置中心、服务网关、Redis、MySQL、API 鉴权等技术,下面请看具体代码。
架构图截图:
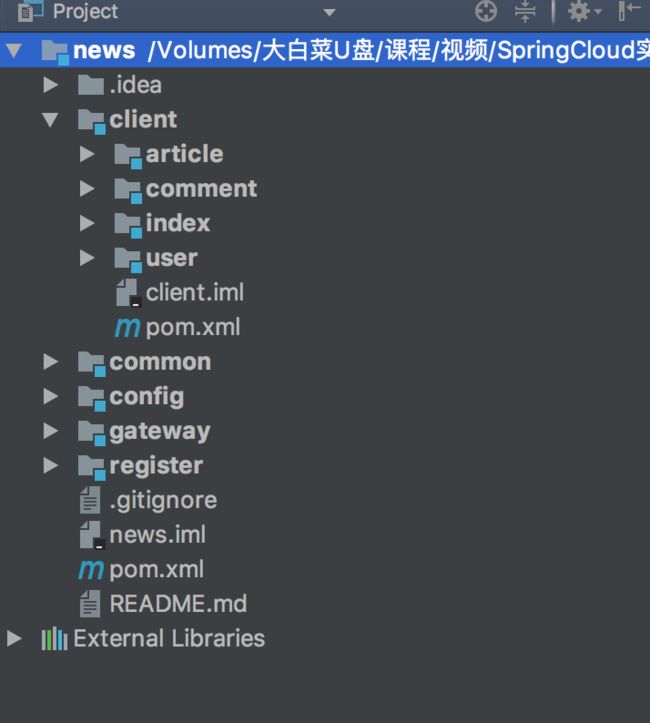
我们知道,微服务架构其实是由多个工程组成的,根据架构图,我们就可以先把所有工程创建好:
其中,common 不是一个项目工程,而是公共类库,所有项目都依赖它,我们可以把公共代码放在 common 下,比如字符串的处理、日期处理、Redis 处理、JSON 处理等。
client 包括客户端工程,config 为配置中心,gateway 为服务网关,register 为注册中心。
本文我们先来搭建注册中心、配置中心和服务网关。
1.注册中心
首先创建启动类:
package com.lynn.register;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@EnableEurekaServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
然后创建 YAML 配置文件:
server:
port: 8888
spring:
application:
name: register
profiles:
active: dev
eureka:
server:
#开启自我保护
enable-self-preservation: true
instance:
#以IP地址注册
preferIpAddress: true
hostname: ${spring.cloud.client.ipAddress}
instanceId: ${spring.cloud.client.ipAddress}:${server.port}
client:
registerWithEureka: false
fetchRegistry: false
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
2.配置中心
创建启动类:
package com.lynn.config;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@EnableConfigServer
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
创建 YAML 配置文件:
server:
port: 8101
spring:
application:
name: config
profiles:
active: dev
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/springcloudlynn/springcloudinactivity #配置git仓库地址
searchPaths: repo #配置仓库路径
username: springcloudlynn #访问git仓库的用户名
password: ly123456 #访问git仓库的用户密码
label: master #配置仓库的分支
eureka:
instance:
hostname: ${spring.cloud.client.ipAddress}
instanceId: ${spring.cloud.client.ipAddress}:${server.port}
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8888/eureka/
3.服务网关
我们继续编写服务网关。
首先是启动类:
package com.lynn.gateway;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.EnableZuulProxy;
@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableZuulProxy
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
服务网关的配置可以通过配置中心拉下来,下面是配置文件代码,此时配置文件名字为 bootstrap.yml:
spring:
application:
name: gateway
profiles:
active: dev
cloud:
config:
name: gateway,eureka,key
label: master
discovery:
enabled: true
serviceId: config
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8888/eureka/
基础框架就搭建到这里,后面将继续搭建基础框架,谢谢继续关注。