JSON之三:获取JSON文本并解释(以google的天气API为例)
google提供了天气的api,以广州天气为例,地址为:
http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q=guangzhou
返回的结果为:
{
"coord": {
"lon": 113.25,
"lat": 23.12
},
"sys": {
"message": 0.2088,
"country": "CN",
"sunrise": 1400017567,
"sunset": 1400065233
},
"weather": [
{
"id": 501,
"main": "Rain",
"description": "moderate rain",
"icon": "10d"
}
],
"base": "cmc stations",
"main": {
"temp": 299.818,
"temp_min": 299.818,
"temp_max": 299.818,
"pressure": 1004.54,
"sea_level": 1014.72,
"grnd_level": 1004.54,
"humidity": 97
},
"wind": {
"speed": 4.42,
"deg": 201.501
},
"rain": {
"3h": 6
},
"clouds": {
"all": 44
},
"dt": 1400055192,
"id": 1809858,
"name": "Guangzhou",
"cod": 200
}
因此,在本范例中,写一个天气查询的DEMO,用于输入地点,并查询天气情况。
项目更新请见:https://code.csdn.net/jediael_lu/googleweatherparse/tree/master
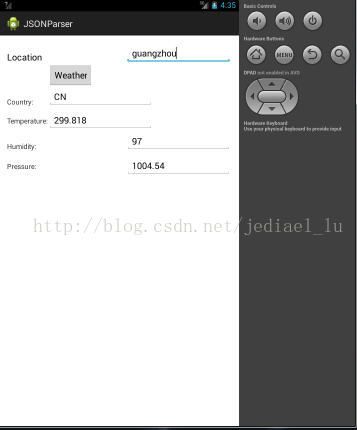
效果如下:
详细步骤如下:
1、主界面布局文件
2、定义String.xml
JSONParser
Settings
Hello world!
Location
Country:
Temperature:
Humidity:
Pressure:
Weather
3、在AndroidManifest.xml中添加internet访问权限。
4、创建一个bean,用于保存天气信息。
package com.example.jsonparser.model;
public class WeatherBean {
private String country;
private int Temperature;
private int humidity;
private int pressure;
public String getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public int getTemperature() {
return Temperature;
}
public void setTemperature(int temperature) {
Temperature = temperature;
}
public int getHumidity() {
return humidity;
}
public void setHumidity(int humidity) {
this.humidity = humidity;
}
public int getPressure() {
return pressure;
}
public void setPressure(int pressure) {
this.pressure = pressure;
}
}
5、创建用于访问网络的类,并返回JSON文本。
package com.example.jsonparser;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class JSONFetcher {
private String jsonText = "";
//本方法通过指定url访问网络数据,并返回JSON格式的string。
public String getJSONText(final URL url){
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
InputStream is =null;
BufferedReader in = null;
try {
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setReadTimeout(10000 /* milliseconds */);
conn.setConnectTimeout(15000 /* milliseconds */);
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setDoInput(true);
conn.connect();
is = conn.getInputStream();
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String line = "";
while((line = in.readLine()) != null){
jsonText += line;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
in.close();
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
thread.start();
//等待上述线程完成执行后再返回jsonText。
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return jsonText;
}
}
6、创建用于处理JSON文本的类,返回一个WeatherBean对象。
package com.example.jsonparser;
import java.net.URL;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import com.example.jsonparser.model.WeatherBean;
public class JSONUtil {
public static WeatherBean getWeatherBean(URL url){
String jsonText = new JSONFetcher().getJSONText(url);
System.out.println(jsonText);
WeatherBean weather = new WeatherBean();
try {
JSONObject weatherJSONObject = new JSONObject(jsonText);
JSONObject sysJSONObject = weatherJSONObject.getJSONObject("sys");
String country = sysJSONObject.getString("country");
JSONObject mainJSONObject = weatherJSONObject.getJSONObject("main");
int temperature = mainJSONObject.getInt("temp");
int pressure = mainJSONObject.getInt("pressure");
int humidity = mainJSONObject.getInt("humidity");
weather.setCountry(country);
weather.setTemperature(temperature);
weather.setHumidity(humidity);
weather.setPressure(pressure);
} catch (JSONException e) {
System.out.println("test");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return weather;
}
}
7、主布局文件,将WeatherBean中的内容在手机中展现。
package com.example.jsonparser;
import java.net.URL;
import com.example.jsonparser.model.WeatherBean;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private String url1 = "http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q=";
private EditText location, country, temperature, humidity, pressure;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
location = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText1);
country = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText2);
temperature = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText3);
humidity = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText4);
pressure = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText5);
}
public void open(View view) {
try {
URL url = new URL(url1 + location.getText().toString());
System.out.println(url);
WeatherBean weatherBean = JSONUtil.getWeatherBean(url);
country.setText(weatherBean.getCountry());
humidity.setText(weatherBean.getHumidity() + "");
pressure.setText(weatherBean.getPressure() + "");
temperature.setText(weatherBean.getTemperature() + "");
System.out.println("test2");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}