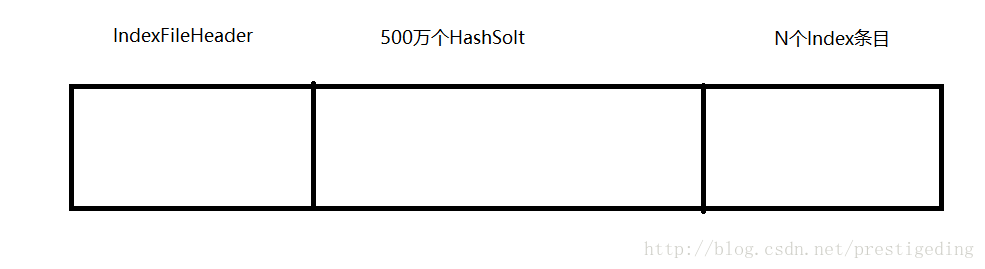源码分析RocketMQ之消费队列、Index索引文件存储结构与存储机制-上篇
RocketMQ 存储基础回顾: 源码分析RocketMQ之CommitLog消息存储机制
本文主要从源码的角度分析 Rocketmq 消费队列 ConsumeQueue 物理文件的构建与存储结构,同时分析 RocketMQ 索引文件IndexFile 文件的存储原理、存储格式以及检索方式。RocketMQ 的存储机制是所有的主题消息都存储在 CommitLog 文件中,也就是消息发送是完全的顺序 IO 操作,加上利用内存文件映射机制,极大的提供的 IO 性能。消息的全量信息存放在 commitlog 文件中,并且每条消息的长度是不一样的,消息的具体存储格式如下:
如果消费者直接基于commitlog 进行消费的话,简直就是一个恶梦,因为不同的主题的消息完全顺序的存储在 commitlog 文件中,根据主题去查询消息,不得不遍历整个 commitlog 文件,显然作为一款消息中间件这是绝不允许的。RocketMQ 的ConsumeQueue 文件就是来解决消息消费的。首先我们知道,一个主题,在 broker 上可以分成多个消费对列,默认为4个,也就是消费队列是基于主题+broker。那 ConsumeQueue 中当然不会再存储全量消息了,而是存储为定长(20字节,8字节commitlog 偏移量+4字节消息长度+8字节tag hashcode),消息消费时,首先根据 commitlog offset 去 commitlog 文件组(commitlog每个文件1G,填满了,另外创建一个文件),找到消息的起始位置,然后根据消息长度,读取整条消息。但问题又来了,如果我们需要根据消息ID,来查找消息,consumequeue 中没有存储消息ID,如果不采取其他措施,又得遍历 commitlog文件了,为了解决这个问题,rocketmq 的 index 文件又派上了用场。
接下来,本文重点关注 ConsumeQueue、Index 文件是如何基于 Commitlog 构建的,并且根据 ConsumeQueue、Index 文件如何查找消息。
根据 commitlog 文件生成 consumequeue、index 文件,主要同运作于两种情况:
1、运行中,发送端发送消息到 commitlog文件,此时如何及时传达到 consume文件、Index文件呢?
2、broker 启动时,检测 commitlog 文件与 consumequeue、index 文件中信息是否一致,如果不一致,需要根据 commitlog 文件重新恢复 consumequeue 文件和 index 文件。
1、commitlog、consumequeue、index 文件同步问题
RocketMQ 采用专门的线程来根据 comitlog offset 来将 commitlog 转发给ConsumeQueue、Index。其线程为DefaultMessageStore$ReputMessageService
1.1 核心属性
- private volatile long reputFromOffset = 0
reputFromOffset ,从 commitlog 开始拉取的初始偏移量。
1.2 run方法
每处理一次 doReput 方法,休眠1毫秒,基本上是马不停蹄的在转发 commitlog 中的内容到 consumequeue、index。
接下来重点查看 doReput 方法。
private void doReput() {
for (boolean doNext = true; this.isCommitLogAvailable() && doNext; ) {
if (DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().isDuplicationEnable()
&& this.reputFromOffset >= DefaultMessageStore.this.getConfirmOffset()) {
break;
}
SelectMappedBufferResult result = DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.getData(reputFromOffset); // @1
if (result != null) {
try {
this.reputFromOffset = result.getStartOffset();
for (int readSize = 0; readSize < result.getSize() && doNext; ) {
DispatchRequest dispatchRequest =
DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.checkMessageAndReturnSize(result.getByteBuffer(), false, false); // @2
int size = dispatchRequest.getMsgSize();
if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) {
if (size > 0) {
DefaultMessageStore.this.doDispatch(dispatchRequest); // @3
if (BrokerRole.SLAVE != DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getBrokerRole()
&& DefaultMessageStore.this.brokerConfig.isLongPollingEnable()) {
DefaultMessageStore.this.messageArrivingListener.arriving(dispatchRequest.getTopic(),
dispatchRequest.getQueueId(), dispatchRequest.getConsumeQueueOffset() + 1,
dispatchRequest.getTagsCode(), dispatchRequest.getStoreTimestamp(),
dispatchRequest.getBitMap(), dispatchRequest.getPropertiesMap());
}
this.reputFromOffset += size;
readSize += size;
if (DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getBrokerRole() == BrokerRole.SLAVE) {
DefaultMessageStore.this.storeStatsService
.getSinglePutMessageTopicTimesTotal(dispatchRequest.getTopic()).incrementAndGet();
DefaultMessageStore.this.storeStatsService
.getSinglePutMessageTopicSizeTotal(dispatchRequest.getTopic())
.addAndGet(dispatchRequest.getMsgSize());
}
} else if (size == 0) {
this.reputFromOffset = DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.rollNextFile(this.reputFromOffset);
readSize = result.getSize();
}
} else if (!dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) {
if (size > 0) {
log.error("[BUG]read total count not equals msg total size. reputFromOffset={}", reputFromOffset);
this.reputFromOffset += size;
} else {
doNext = false;
if (DefaultMessageStore.this.brokerConfig.getBrokerId() == MixAll.MASTER_ID) {
log.error("[BUG]the master dispatch message to consume queue error, COMMITLOG OFFSET: {}",
this.reputFromOffset);
this.reputFromOffset += result.getSize() - readSize;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
result.release();
}
} else {
doNext = false;
}
}
}代码@1,根据 offset 从 commitlog 找到一条消息,如果找不到,退出此次循环,doReput方法跳出,此处从 commitlog 文件中取出消息的逻辑,在下文会重点分析,故在此暂时跳过。
先浏览一下 SelectMappedBufferResult
代码@2:尝试构建转发请求对象 DispatchRequest ,我大概浏览了一下 commitLog.checkMessageAndReturnSize,主要是从Nio ByteBuffer中,根据 commitlog 消息存储格式,解析出消息的核心属性:
// 消息主题
private final String topic;
// 消息队列
private final int queueId;
// commitlog中的偏移量
private final long commitLogOffset;
// 消息大小
private final int msgSize;
// tagsCode
private final long tagsCode;
// 消息存储时间
private final long storeTimestamp;
//消息在消费队列的offset
private final long consumeQueueOffset;
// 存放在消息属性中的keys: PROPERTY_KEYS = "KEYS"
private final String keys;
// 是否成功
private final boolean success;
// 消息唯一键 "UNIQ_KEY"
private final String uniqKey;
// 系统标志
private final int sysFlag;
// 事务pre消息偏移量
private final long preparedTransactionOffset;
// 属性
private final Map propertiesMap;
private byte[] bitMap; 代码@3:转发DistpachRequest。
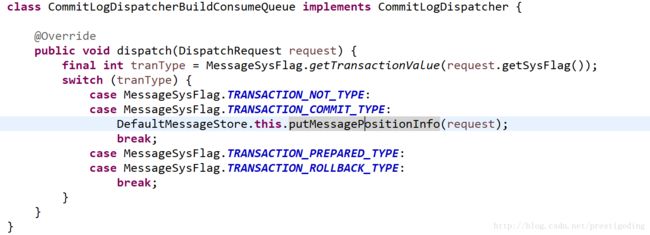
 根据实现类,consumequeue,index 分别对应 CommitLogDispatcherBuildConsumeQueue 与 CommitlogDispatcherBuildIndex。
根据实现类,consumequeue,index 分别对应 CommitLogDispatcherBuildConsumeQueue 与 CommitlogDispatcherBuildIndex。
2.1 CommitLogDispatcherBuildConsumeQueue
核心处理方法:
public void putMessagePositionInfoWrapper(DispatchRequest request) {
final int maxRetries = 30;
boolean canWrite = this.defaultMessageStore.getRunningFlags().isCQWriteable(); // @1
for (int i = 0; i < maxRetries && canWrite; i++) {
long tagsCode = request.getTagsCode();
if (isExtWriteEnable()) {
ConsumeQueueExt.CqExtUnit cqExtUnit = new ConsumeQueueExt.CqExtUnit();
cqExtUnit.setFilterBitMap(request.getBitMap());
cqExtUnit.setMsgStoreTime(request.getStoreTimestamp());
cqExtUnit.setTagsCode(request.getTagsCode());
long extAddr = this.consumeQueueExt.put(cqExtUnit);
if (isExtAddr(extAddr)) {
tagsCode = extAddr;
} else {
log.warn("Save consume queue extend fail, So just save tagsCode! {}, topic:{}, queueId:{}, offset:{}", cqExtUnit,
topic, queueId, request.getCommitLogOffset());
}
}
boolean result = this.putMessagePositionInfo(request.getCommitLogOffset(),
request.getMsgSize(), tagsCode, request.getConsumeQueueOffset()); // @2
if (result) {
this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setLogicsMsgTimestamp(request.getStoreTimestamp()); // @3
return;
} else {
// XXX: warn and notify me
log.warn("[BUG]put commit log position info to " + topic + ":" + queueId + " " + request.getCommitLogOffset()
+ " failed, retry " + i + " times");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.warn("", e);
}
}
}
// XXX: warn and notify me
log.error("[BUG]consume queue can not write, {} {}", this.topic, this.queueId);
this.defaultMessageStore.getRunningFlags().makeLogicsQueueError();
}代码@1:判断 ConsumeQueue 是否可写。
代码@2:写入 consumequeue文件,真正的写入到 ConsumeQueue 逻辑如下。
Consumequeue#putMessagePositionInfoWrapper
Consumequeue#putMessagePositionInfoWrapper
private boolean putMessagePositionInfo(final long offset, final int size, final long tagsCode,
final long cqOffset) {
if (offset <= this.maxPhysicOffset) {
return true;
}
this.byteBufferIndex.flip();
this.byteBufferIndex.limit(CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE);
this.byteBufferIndex.putLong(offset);
this.byteBufferIndex.putInt(size);
this.byteBufferIndex.putLong(tagsCode); // 代码@1
final long expectLogicOffset = cqOffset * CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE; // @2
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile(expectLogicOffset);
if (mappedFile != null) {
if (mappedFile.isFirstCreateInQueue() && cqOffset != 0 && mappedFile.getWrotePosition() == 0) { // @3
this.minLogicOffset = expectLogicOffset;
this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(expectLogicOffset);
this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(expectLogicOffset);
this.fillPreBlank(mappedFile, expectLogicOffset);
log.info("fill pre blank space " + mappedFile.getFileName() + " " + expectLogicOffset + " "
+ mappedFile.getWrotePosition());
}
if (cqOffset != 0) {
long currentLogicOffset = mappedFile.getWrotePosition() + mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();
if (expectLogicOffset != currentLogicOffset) {
LOG_ERROR.warn(
"[BUG]logic queue order maybe wrong, expectLogicOffset: {} currentLogicOffset: {} Topic: {} QID: {} Diff: {}",
expectLogicOffset,
currentLogicOffset,
this.topic,
this.queueId,
expectLogicOffset - currentLogicOffset
);
}
}
this.maxPhysicOffset = offset;
return mappedFile.appendMessage(this.byteBufferIndex.array()); // @4
}
return false;
}首先说一下参数:
- long offset
commitlog偏移量,8字节。 - int size
消息体大小 4字节。 - long tagsCode
消息 tags 的 hashcode。 - long cqOffset
写入 consumequeue 的偏移量。
代码@1:首先将一条 ConsueQueue 条目总共20个字节,写入到 ByteBuffer 中。
代码@2:计算期望插入 ConsumeQueue 的 consumequeue 文件位置。
代码@3:如果文件是新建的,需要先填充空格。
代码@4:写入到 ConsumeQueue 文件中,整个过程都是基于 MappedFile 来操作的。
我们现在已经知道 ConsumeQueue 每一个条目都是 20个字节(8个字节commitlog偏移量+4字节消息长度+8字节tag的hashcode
那 consumqu e文件的路径,默认大小是多少呢?
默认路径为:rockemt_home/store/consume/ {topic} / {queryId},默认大小为,30W条记录,也就是30W * 20字节。
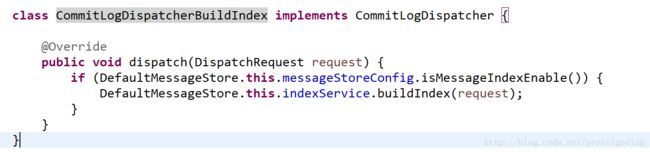
2.2 CommitLogDispatcherBuildIndex
其核心实现类 IndexService#buildIndex,存放 Index 文件的封装类为:IndexFile。
2.2.1 IndexFile 详解
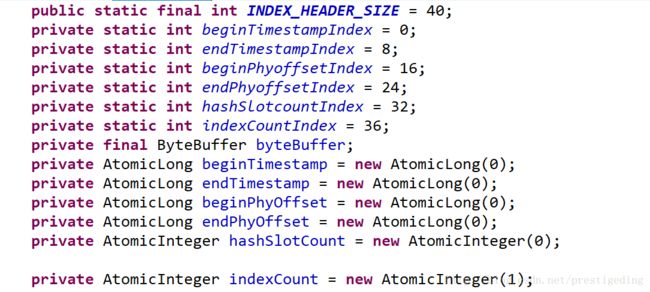
2.2.1.1 核心属性
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggerName.STORE_LOGGER_NAME);
// 每个 hash 槽所占的字节数
private static int hashSlotSize = 4;
// 每条indexFile条目占用字节数
private static int indexSize = 20;
// 用来验证是否是一个有效的索引。
private static int invalidIndex = 0;
// index 文件中 hash 槽的总个数
private final int hashSlotNum;
// indexFile中包含的条目数
private final int indexNum;
// 对应的映射文件
private final MappedFile mappedFile;
// 对应的文件通道
private final FileChannel fileChannel;
// 对应 PageCache
private final MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer;
// IndexHeader,每一个indexfile的头部信息
private final IndexHeader indexHeader; IndexHeader 详解:
index存储路径:/rocket_home/store/index/年月日时分秒。
目前了解到这来,目光继续投向IndexService。
2.2.2 IndexService
2.2.2.1 核心属性与构造方法
private final DefaultMessageStore defaultMessageStore;
private final int hashSlotNum;
private final int indexNum;
private final String storePath;
private final ArrayList indexFileList = new ArrayList();
private final ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
public IndexService(final DefaultMessageStore store) {
this.defaultMessageStore = store;
this.hashSlotNum = store.getMessageStoreConfig().getMaxHashSlotNum();
this.indexNum = store.getMessageStoreConfig().getMaxIndexNum();
this.storePath =
StorePathConfigHelper.getStorePathIndex(store.getMessageStoreConfig().getStorePathRootDir());
} - hashSlotNum
hash槽数量,默认5百万个。 - indexNum
index条目个数,默认为 2千万个。 - storePath
index存储路径,默认为:/rocket_home/store/index。
2.2.2.2 buildIndex
public void buildIndex(DispatchRequest req) {
IndexFile indexFile = retryGetAndCreateIndexFile(); // @1
if (indexFile != null) {
long endPhyOffset = indexFile.getEndPhyOffset();
DispatchRequest msg = req;
String topic = msg.getTopic();
String keys = msg.getKeys();
if (msg.getCommitLogOffset() < endPhyOffset) { // @2
return;
}
final int tranType = MessageSysFlag.getTransactionValue(msg.getSysFlag());
switch (tranType) {
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_NOT_TYPE:
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_PREPARED_TYPE:
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_COMMIT_TYPE:
break;
case MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_ROLLBACK_TYPE:
return;
}
if (req.getUniqKey() != null) { // @3
indexFile = putKey(indexFile, msg, buildKey(topic, req.getUniqKey()));
if (indexFile == null) {
log.error("putKey error commitlog {} uniqkey {}", req.getCommitLogOffset(), req.getUniqKey());
return;
}
}
if (keys != null && keys.length() > 0) { // @4
String[] keyset = keys.split(MessageConst.KEY_SEPARATOR);
for (int i = 0; i < keyset.length; i++) {
String key = keyset[i];
if (key.length() > 0) {
indexFile = putKey(indexFile, msg, buildKey(topic, key));
if (indexFile == null) {
log.error("putKey error commitlog {} uniqkey {}", req.getCommitLogOffset(), req.getUniqKey());
return;
}
}
}
}
} else {
log.error("build index error, stop building index");
}
}代码@1:创建或获取当前写入的IndexFile.
代码@2:如果 indexfile 中的最大偏移量大于该消息的 commitlog offset,忽略本次构建。
代码@3,@4:将消息中的 keys,uniq_keys 写入 index 文件中。重点看一下putKey方法。
这是首先看一下,到底什么是消息的 keys 和 uniq_keys。
由此可以看出,keys,uniqKey存放在消息的propertiesmap中。
keys:用户在发送消息时候,可以指定,多个 key 用英文逗号隔开,对应代码:
uniqKey:消息唯一键,与消息ID不一样,为什么呢?因为消息ID在 commitlog 文件中并不是唯一的,消息消费重试时,发送的消息的消息ID与原先的一样。
uniqKey具体算法:(代码见 MessageClientIDSetter)
接下来重点进入IndexService#putKey方法:
private IndexFile putKey(IndexFile indexFile, DispatchRequest msg, String idxKey) {
for (boolean ok = indexFile.putKey(idxKey, msg.getCommitLogOffset(), msg.getStoreTimestamp()); !ok; ) {
log.warn("Index file [" + indexFile.getFileName() + "] is full, trying to create another one");
indexFile = retryGetAndCreateIndexFile();
if (null == indexFile) {
return null;
}
ok = indexFile.putKey(idxKey, msg.getCommitLogOffset(), msg.getStoreTimestamp());
}
return indexFile;
}
IndexFile#putKey
public boolean putKey(final String key, final long phyOffset, final long storeTimestamp) { // @1
if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() < this.indexNum) { // @2
int keyHash = indexKeyHashMethod(key);
int slotPos = keyHash % this.hashSlotNum; // @3
int absSlotPos = IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + slotPos * hashSlotSize; // @4
FileLock fileLock = null;
try {
// fileLock = this.fileChannel.lock(absSlotPos, hashSlotSize,
// false);
int slotValue = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absSlotPos); // @5
if (slotValue <= invalidIndex || slotValue > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()) {
slotValue = invalidIndex;
}
long timeDiff = storeTimestamp - this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp();
timeDiff = timeDiff / 1000;
if (this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp() <= 0) {
timeDiff = 0;
} else if (timeDiff > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
timeDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
} else if (timeDiff < 0) {
timeDiff = 0;
} // @6
int absIndexPos =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize
+ this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() * indexSize; // @7
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos, keyHash); // @8
this.mappedByteBuffer.putLong(absIndexPos + 4, phyOffset);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8, (int) timeDiff);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4, slotValue);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absSlotPos, this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()); // @9
if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() <= 1) { // @10
this.indexHeader.setBeginPhyOffset(phyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setBeginTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
this.indexHeader.incHashSlotCount();
this.indexHeader.incIndexCount();
this.indexHeader.setEndPhyOffset(phyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setEndTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("putKey exception, Key: " + key + " KeyHashCode: " + key.hashCode(), e);
} finally {
if (fileLock != null) {
try {
fileLock.release();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Failed to release the lock", e);
}
}
}
} else {
log.warn("Over index file capacity: index count = " + this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()
+ "; index max num = " + this.indexNum);
}
return false;
}从这个方法我们也能得知 IndexFile 的存储协议。
代码@1:参数详解:
- phyOffset
消息存储在commitlog的偏移量。 - storeTimestamp
消息存入commitlog的时间戳。
代码@2:如果目前 index file 存储的条目数小于允许的条目数,则存入当前文件中,如果超出,则返回 false, 表示存入失败,IndexService 中有重试机制,默认重试3次。
从代码@3开始,主要是根据 IndexFile 的文件格式进行存储。
代码@3:先获取 key 的 hashcode,然后用 hashcode 和 hashSlotNum 取模,得到该 key 所在的 hashslot 下标,hashSlotNum默认500万个。
代码@4:根据 key 所算出来的 hashslot 的下标计算出绝对位置,从这里可以看出端倪:IndexFile的文件布局:文件头(IndexFileHeader 40个字节) + (hashSlotNum * 4)。
代码@5:读取 key 所在 hashslot 下标处的值(4个字节),如果小于0或超过当前包含的 indexCount,则设置为0。
代码@6:计算消息的存储时间与当前 IndexFile 存放的最小时间差额(单位为秒)。
代码@7:计算该 key 存放的条目的起始位置,等于=文件头(IndexFileHeader 40个字节) + (hashSlotNum * 4) + IndexSize(一个条目20个字节) * 当前存放的条目数量。
代码@8:填充 IndexFile 条目,4字节(hashcode) + 8字节(commitlog offset) + 4字节(commitlog存储时间与indexfile第一个条目的时间差,单位秒) + 4字节(同hashcode的上一个的位置,0表示没有上一个)。
代码@9:将当前先添加的条目的位置,存入到 key hashcode 对应的 hash槽,也就是该字段里面存放的是该 hashcode 最新的条目(如果产生hash冲突,不同的key,hashcode相同。
代码@10:更新IndexFile头部相关字段,比如最小时间,当前最大时间等。
这个方法,可以得出IndexFile的存储格式:
HashSolt 每个槽4个字节,存放的是对应 hashcode 最新的index条目的位置。
indexFIleItem:index条目,每个20个字节,4字节(hashcode) + 8字节(commitlog offset) + 4字节(commitlog存储时间与indexfile第一个条目的时间差,单位秒) + 4字节(同hashcode的上一个的位置,0表示没有上一个)。
上述设计,可以支持 hashcode 冲突,,多个不同的key,相同的 hashcode,index 条目其实是一个逻辑链表的概念,因为每个index 条目的最后4个字节存放的就是上一个的位置。知道存了储结构,要检索 index文件就变的简单起来来,其实就根据 key 得到 hashcode,然后从最新的条目开始找,匹配时间戳是否有效,得到消息的物理地址(存放在commitlog文件中),然后就可以根据 commitlog 偏移量找到具体的消息,从而得到最终的key-value。
我们在顺便看一下IndexFile#selectPhyOffset。
public void selectPhyOffset(final List phyOffsets, final String key, final int maxNum,
final long begin, final long end, boolean lock) { // @1
if (this.mappedFile.hold()) {
int keyHash = indexKeyHashMethod(key);
int slotPos = keyHash % this.hashSlotNum;
int absSlotPos = IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + slotPos * hashSlotSize; // @2
FileLock fileLock = null;
try {
if (lock) {
// fileLock = this.fileChannel.lock(absSlotPos,
// hashSlotSize, true);
}
int slotValue = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absSlotPos);
// if (fileLock != null) {
// fileLock.release();
// fileLock = null;
// }
if (slotValue <= invalidIndex || slotValue > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()
|| this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() <= 1) { // @3
} else {
for (int nextIndexToRead = slotValue; ; ) { // @4 开始循环找(相同hashcode的index条目是不连续的单向链表,最新的指向上一个。
if (phyOffsets.size() >= maxNum) {
break;
}
int absIndexPos =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize
+ nextIndexToRead * indexSize;
int keyHashRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos);
long phyOffsetRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getLong(absIndexPos + 4);
long timeDiff = (long) this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8); // 找到对应的条目
int prevIndexRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4);
if (timeDiff < 0) { // 如果时间非法,则表示无效
break;
}
timeDiff *= 1000L;
long timeRead = this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp() + timeDiff;
boolean timeMatched = (timeRead >= begin) && (timeRead <= end);
if (keyHash == keyHashRead && timeMatched) { // @5
phyOffsets.add(phyOffsetRead);
}
if (prevIndexRead <= invalidIndex
|| prevIndexRead > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()
|| prevIndexRead == nextIndexToRead || timeRead < begin) {
break;
}
nextIndexToRead = prevIndexRead;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("selectPhyOffset exception ", e);
} finally {
if (fileLock != null) {
try {
fileLock.release();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Failed to release the lock", e);
}
}
this.mappedFile.release();
}
}
} 代码@1:方法参数详解:
- phyOffsets
符合查找条件的物理偏移量(commitlog文件中的偏移量) - key
索引键值,待查找的key。 - start
开始时间戳(毫秒)。 - end
结束时间戳(毫秒)。
代码@2:根据 key 算出 hashcode,然后定位到 hash槽的位置。
代码@3:如果该位置存储的值小于0,或者大于当前indexCount的值,则视为无效,也就是该hashcode值并没有对应的index条码存储,如果等于0或小于当前条目的大小,则表示至少存储了一个。
代码@4@5:找到条目内容,然后与查询条件进行匹配,如果符合,则将物理偏移量加入到phyOffsets中,否则,继续寻找。
行文至此,已经解答了如下问题:
1、运行过程中,消息发送到commitlog文件后,会同步将消息转发到消息队列(ConsumeQueue)、index文件(IndexFile),此时保存到内存映射文件中,并没有执行刷盘操作。
2、ConsuemeQueue的文件存储格式
3、索引文件存储格式及其查找
找到comitlog的偏移量,就能很快定位到文件,我们继续重点看一下根据offset,如何从commitlog文件中查找消息。
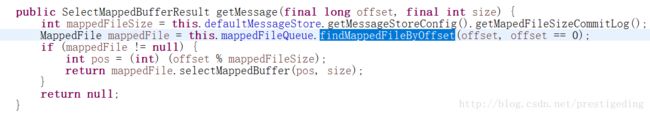
主要根据偏移量,找到所在的commitlog文件,commitlog文件封装成MappedFile(内存映射文件),然后直接从偏移量开始,读取指定的字节(消息的长度),要是事先不知道消息的长度,只知道offset呢?其实也简单,先找到MapFile,然后从offset处先读取4个字节,就能获取该消息的总长度。
本节就先到这里了,,主要讲解了RocketMQ在运行期间ConsumeQueue,IndexFile文件的构造过程。下篇重要讲解RocketMQ在启动时,如果根据commitlog里的内容重新构建正确的consumeque、index文件。
备注:本文是《RocketMQ技术内幕》的前期素材记录,建议关注笔者的书籍:《RocketMQ技术内幕》。
欢迎加笔者微信号(dingwpmz),加群探讨,笔者优质专栏目录:
1、源码分析RocketMQ专栏(40篇+)
2、源码分析Sentinel专栏(12篇+)
3、源码分析Dubbo专栏(28篇+)
4、源码分析Mybatis专栏
5、源码分析Netty专栏(18篇+)
6、源码分析JUC专栏
7、源码分析Elasticjob专栏
8、Elasticsearch专栏
9、源码分析Mycat专栏