nginx(二) nginx编译安装 及 配置WEB服务
nginx(二) nginx编译安装 及 配置WEB服务
在前面《nginx详解》文章中,我们对nginx有了一个基本的认识:包括应用场景、nginx基本架构、功能特性、并发模型以及配置说明等,我们知道nginx应用比较多的场景是WEB服务器和反向代理服务器。
下面将先进行nginx编译安装,然后再进行nginx的WEB服务相关的应用配置:包括设置配置文件vim下语法高亮显示、配置虚拟主机、基于IP的访问控制、基于用户认证的访问控制、建立下载站点下载列表、URL地址重写/重定向、防盗链、提供Nginx状态页面、配置gzip压缩、日志、基于SSL提供https服务等。
1、配置环境准备
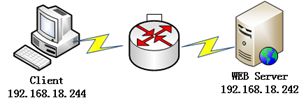
1、WEB服务器:
主机系统:CentOS 6.4 x86_64;
IP:192.168.18.242 (host name:node2.tjiyu.com);
2、Client端:
IP:192.168.18.245;
一般浏览器;
2、下载编译安装
去nginx官网上把最新稳定版本的源码包下载下来,我们这里使用nginx-1.10.2版本;然后把源码包放到我们操作的主机上,下面开始编译安装。
2-1、解压,创建软连接
[root@node2 ~]# tar xf nginx-1.10.2.tar.gz [root@node2 ~]# ln -sv nginx-1.10.2 nginx [root@node2 ~]# cd nginx [root@node2 nginx]# ll
2-2、安装编译开发工具类库
用yum安装、更新开发工具"Development Tools"和"Server Platform Deveopment",而nginx会依赖openssl-devel和pcre-devel类库,安装如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# yum groupinstall "Development Tools" "Server Platform Deveopment" [root@node2 ~]# yum install openssl-devel pcre-devel
2-3、创建用户和用户组
分别创建名为"nginx"的用户和组,用来运行nginx的worker进程,操作如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# groupadd -r nginx [root@node2 nginx]# useradd -r -g nginx nginx
2-4、编译并安装
先configure指定编译选项,如安装目录、上面创建的运行用户、需要的扩展模块(SSL、FastCGI)等,选项及参数说明:http://nginx.org/en/docs/configure.html,操作如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# ./configure \ --prefix=/usr \ --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx \ --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf \ --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \ --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \ --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid \ --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock \ --user=nginx \ --group=nginx \ --with-http_ssl_module \ --with-http_flv_module \ --with-http_stub_status_module \ --with-http_gzip_static_module \ --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/client/ \ --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/proxy/ \ --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/fcgi/ \ --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/uwsgi \ --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/scgi \ --with-pcre
Configure成功如下:
接着开始编译并安装,如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# make && make install
2-5、为nginx提供SysV init服务脚本
先创建/etc/init.d/nginx服务脚本,这基于ngInx自身提供的命令实现的,脚本内容如下:
#!/bin/sh # # nginx - this script starts and stops the nginx daemon # # chkconfig: - 85 15 # description: Nginx is an HTTP(S) server, HTTP(S) reverse \ # proxy and IMAP/POP3 proxy server # processname: nginx # config: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf # config: /etc/sysconfig/nginx # pidfile: /var/run/nginx.pid # Source function library. . /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions # Source networking configuration. . /etc/sysconfig/network # Check that networking is up. [ "$NETWORKING" = "no" ] && exit 0 nginx="/usr/sbin/nginx" prog=$(basename $nginx) NGINX_CONF_FILE="/etc/nginx/nginx.conf" [ -f /etc/sysconfig/nginx ] && . /etc/sysconfig/nginx lockfile=/var/lock/subsys/nginx make_dirs() { # make required directories user=`nginx -V 2>&1 | grep "configure arguments:" | sed 's/[^*]*--user=\([^ ]*\).*/\1/g' -` options=`$nginx -V 2>&1 | grep 'configure arguments:'` for opt in $options; do if [ `echo $opt | grep '.*-temp-path'` ]; then value=`echo $opt | cut -d "=" -f 2` if [ ! -d "$value" ]; then # echo "creating" $value mkdir -p $value && chown -R $user $value fi fi done } start() { [ -x $nginx ] || exit 5 [ -f $NGINX_CONF_FILE ] || exit 6 make_dirs echo -n $"Starting $prog: " daemon $nginx -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE retval=$? echo [ $retval -eq 0 ] && touch $lockfile return $retval } stop() { echo -n $"Stopping $prog: " killproc $prog -QUIT retval=$? echo [ $retval -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile return $retval } restart() { configtest || return $? stop sleep 1 start } reload() { configtest || return $? echo -n $"Reloading $prog: " killproc $nginx -HUP RETVAL=$? echo } force_reload() { restart } configtest() { $nginx -t -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE } rh_status() { status $prog } rh_status_q() { rh_status >/dev/null 2>&1 } case "$1" in start) rh_status_q && exit 0 $1 ;; stop) rh_status_q || exit 0 $1 ;; restart|configtest) $1 ;; reload) rh_status_q || exit 7 $1 ;; force-reload) force_reload ;; status) rh_status ;; condrestart|try-restart) rh_status_q || exit 0 ;; *) echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|try-restart|reload|force-reload|configtest}" exit 2 esac
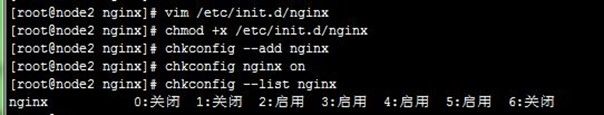
并为此脚本赋予执行权限,然后添加到系统服务管理列表,并让其开机自动启动,操作如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# vim /etc/init.d/nginx [root@node2 nginx]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginx [root@node2 nginx]# chkconfig --add nginx [root@node2 nginx]# chkconfig nginx on [root@node2 nginx]# chkconfig --list nginx
2-6、启动并访问测试
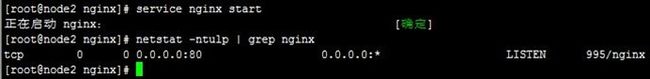
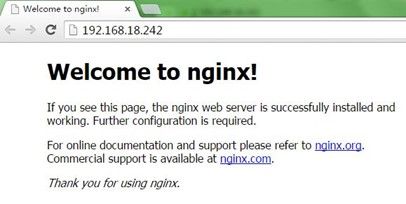
启动nginx,我们看到因为httpd占用80端口而失败,关闭httpd后再启动nginx正常;查看网络状态,可以看到nginx正在监听80端口;用测试主机访问nginx主机的IP,可以看到nginx的欢迎页面,过程如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# service nginx start [root@node2 nginx]# netstat -ntulp | grep nginx
3、配置Nginx
前面编译nginx的时候,我们用选项--conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf(默认也是这个目录),指定的了配置文件及所在目录,所以我们到/etc/nginx/下可以看到nginx.conf配置文件,而.default结尾的是nginx默认编译选项的配置文件,已经没有意义了。
前面《nginx详解》我们已经详细分析说明nginx配置文件的几个配置区域块和大部分的配置选项,下面就不一一说明了,只说明一些用到的配置选项。
3-1、设置配置文件vim下语法高亮显示
linux系统下vim或者vi编辑器默认是没有对nginx配置的语法高亮设置。但是我们可以到http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=1886下载nginx.vim,然后根据它上面的说明,进行简单的配置,如下:
[root@node2 ~]# mkdir .vim/syntax -pv [root@node2 ~]# cd .vim/syntax/ [root@node2 syntax]# mv ~/nginx.vim ./ [root@node2 syntax]# ls nginx.vim [root@node2 syntax]# cd .. [root@node2 .vim]# vim filetype.vim [root@node2 .vim]# cat filetype.vim au BufRead,BufNewFile /etc/nginx/*,/usr/local/nginx/conf/* if &ft == '' | setfiletype nginx | endif [root@node2 .vim]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
3-2、配置虚拟主机
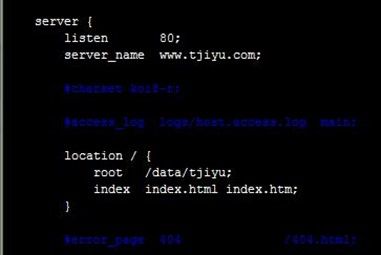
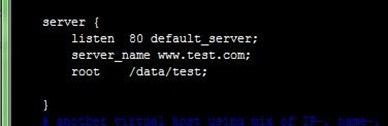
编辑nginx.conf,配置两个虚拟主机www.tjiyu.com和www.test.com,资源文件目录分别/data/tjiyu和/data/test,可以看到最简单的配置只需要三行,操作如下:
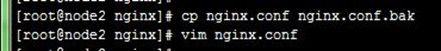
[root@node2 nginx]# cp nginx.conf nginx.conf.bak [root@node2 nginx]# vim nginx.confserver { listen 80; server_name www.tjiyu.com; location / { root /data/tjiyu; index index.html index.htm; } } server { listen 80 default_server; #配置默认虚拟主机 server_name www.test.com; root /data/test; }
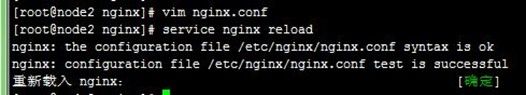
然后分别创建资源目录,提供index.html测试页面,然后使nginx重新加载配置,操作如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# mkdir /data [root@node2 nginx]# mkdir /data/tjiyu [root@node2 nginx]# echo "www.tjiyu.com
" > /data/tjiyu/index.html [root@node2 nginx]# mkdir /data/test [root@node2 nginx]# echo "www.test.com
" > [root@node2 nginx]# service nginx reload
在我们的测试主机上配置hosts,让访问虚拟主机名可以指向主机IP,win7 x86_64上C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\HOSTS添加如下两行记录,如上:
192.168.18.242 www.tjiyu.com 192.168.18.242 www.test.com
然后访问两个访问虚拟主机,可以看到提供的测试页面;因为我们在www.test.com的listen选项配置了default_server,所以直接访问主机IP是返回的是该虚拟主机的页面,如下:
3-3、基于IP的访问控制
基于IP的访问控制是ngx_http_access_module模块的功能,只有允许选项allow和禁止选项deny。
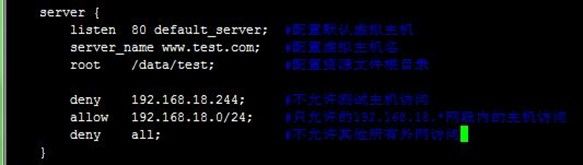
配置第二台虚拟主机只允许的192.168.18.*网段内的主机访问,但除测试主机192.168.18.244外,注意,多个规则是自上而下进行匹配的,所以不允许测试主机访问得在最上面;测试访问www.test.com可以看到返回403禁止访问页面,而访问www.tjiyu.com是正常的,过程如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# vim nginx.conf [root@node2 nginx]# service nginx reload
server { listen 80 default_server; server_name www.test.com; root /data/test; deny 192.168.18.244; #不允许测试主机访问 allow 192.168.18.0/24; #只允许的192.168.18.*网段内的主机访问 deny all; #不允许其他所有外网访问 }
3-4、基于用户认证的访问控制
基于用户认证的访问控制是ngx_http_auth_basic_module模块的功能,只有配置名称(或者off)选项auth_basic和配置文件选项auth_basic_user_file,文件由htpasswd生成,包括用户和密码。
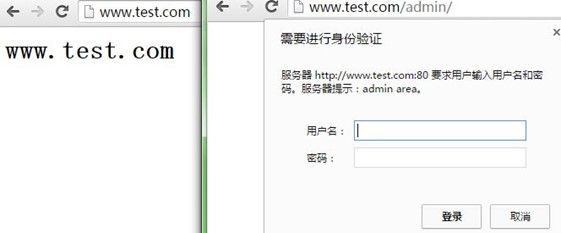
先创建需要用户认证的目录/data/test/admin,提供一个测试页面;然后用htpasswd生成认证文件;编辑配置文件,用location匹配/data/test/admin目录,接着在里面配置访问控制配置的名称字符串和访问控制配置的文件,过程如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# mkdir /data/test/admin [root@node2 nginx]# echo "admin area
" > /data/test/admin/index.html [root@node2 nginx]# htpasswd -c -m /etc/nginx/.htpasswd admin [root@node2 nginx]# vim nginx.conf [root@node2 nginx]# service nginx reloadserver { listen 80 default_server; #配置默认虚拟主机 server_name www.test.com; #配置虚拟主机名 root /data/test; #配置资源文件根目录 #deny 192.168.18.244; #不允许测试主机访问 allow 192.168.18.0/24; #只允许的192.168.18.*网段内的主机访问 deny all; #不允许其他所有外网访问 location /admin/ { #匹配基于用户认证的访问控制 auth_basic "admin area"; #访问控制配置的名称字符串,或者off关闭 auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd; #访问控制配置的文件,htpasswd生成,包含用户名用密码 } }
测试访问www.test.com正常,访问www.test.com/admin/需要用户和密码认证,也就实现了目录/data/test/admin里的资源需要用户认证,如下:
3-5、建立下载站点下载列表
下载站点下载列表是ngx_http_autoindex_module模块的功能,有几个选项,最基本就是开关选项autoindex on | off和显示时间选项autoindex_localtime on | off。
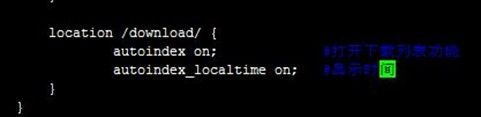
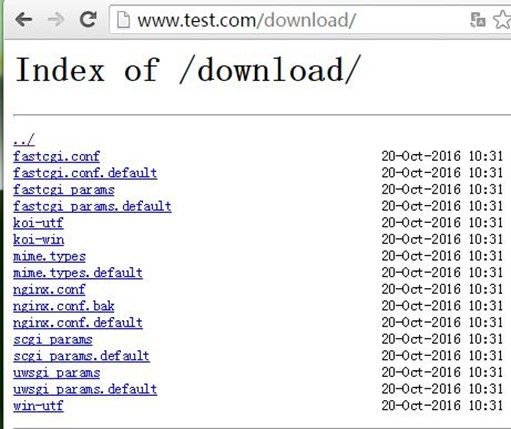
先创建存放下载资源的目录/data/test/download,复制一些文件进去提供测试;然后编辑配置文件,用location匹配/data/test/download目录,接着在里面配置打开下载列表功能;测试访问www.test.com/download可以看到下载列表,过程如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# mkdir /data/test/download [root@node2 nginx]# cp /etc/nginx/* /data/test/download/ [root@node2 nginx]# vim nginx.conf [root@node2 nginx]# service nginx reloadserver { listen 80 default_server; server_name www.test.com; root /data/test; location /download/ { autoindex on; #打开下载列表功能 autoindex_localtime on; #显示时间 } }
3-6、URL地址重写/重定向
URL地址重写/重定向是ngx_http_rewrite_module模块的功能,通过正则匹配,把匹配的URL重写为指定的URL,以重写的URL来请求响应。主要应用在实现URL跳转、域名跳转、站点镜像等,比如网站改版,目录结构发生改变,但不希望不改变页面中的URL,用URL地址重写来实现。
1、if和rewrite选项
这里有两个比较重要的选项,if和rewrite:If在上面已经介绍过了,在很多地方都用到,这里用于检测条件是否成立;而rewrite regex replacement [flag],匹配regex正则表达式(可以省略,直接重写),以replacement重写代替,flag为标志位,主要有:
last:一旦被当前规则匹配并重写后立即停止检查后续饿的其他rewrite的规则,而后通过重写后的规则重新发起请求; break:一旦被当前规则匹配并重写后立即停止检查后续饿的其他rewrite的规则,而后继续由nginx进行后续的操作; redirect:返回302临时重定向代码; permanent:返回301永久重定向;
注意:当有多个rewrite规则一起使用时,可能会循环匹配,nginx最多循环10次,超出之后返回500错误;一般将rewrite写在location中时都使用break标志,或者将rewrite写if上下文中。
2、配置
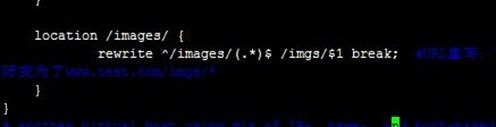
配置www.test.com虚拟主机的当目录$root_dir/images改为$root_dir /imgs时,可以通过URL重写,让www.test.com/images/*请求还能和原来一样,不过实际变为了www.test.com/imgs/*。
直接创建/data/test/imgs目录,放一些图片文件进去用来测试;然后配置文件;测试访问www.test.com/images/2.jpg可以正常看到刚才放到/data/test/imgs图片,过程如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# mkdir /data/test/imgs [root@node2 nginx]# mv /root/*.jpg /data/test/imgs/ [root@node2 nginx]# ls /data/test/imgs/ [root@node2 nginx]# vim nginx.conf [root@node2 nginx]# service nginx reload
server { listen 80 default_server; server_name www.test.com; root /data/test; location /images/ { rewrite ^/images/(.*)$ /imgs/$1 break; #URL重写:让www.test.com/images/*请求还能和原来一样,不>过实际变为了www.test.com/imgs/* } }
3-7、防盗链
防盗链基于是ngx_http_referer_module模块的功能,主要通过请求头部"Referer"字段识别,配置有两点:
(1)valid_referers选项,定义合规引用
valid_referers none |blocked |server_names|string ... none表示没有"Referer",blocked表示 "Referer" 没有没有以"http://"或"https://"开头;
(2)($invaild_referer变量,判断不合规的引用,返回一个提示
if ($invaild_referer) { rewrite ^/.*$ http://www.a.com/403.html }
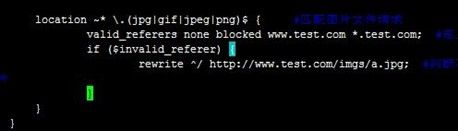
下面配置当www.tjiyu.com虚拟主机页面引用www.test.com虚拟主机上的图片时,返回一个"图片仅供内部交流使用的图片"。www.test.com虚拟主机上配置location匹配图片文件,valid_referers定义合规引用,包括自己的虚拟主机名称等,然后if ($invaild_referer)判断不合规的引用,用URL地址重写返回一个提示图片,操作配置如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# vim nginx.conflocation ~* \.(jpg|gif|jpeg|png)$ { #匹配图片文件请求 valid_referers none blocked www.test.com *.test.com; #定义合规引用,包括自己站主机等 if ($invalid_referer) { rewrite ^/ http://www.test.com/imgs/a.jpg; #判断不合规的引用,用URL地址重写返回一个提示>图片 } }
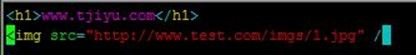
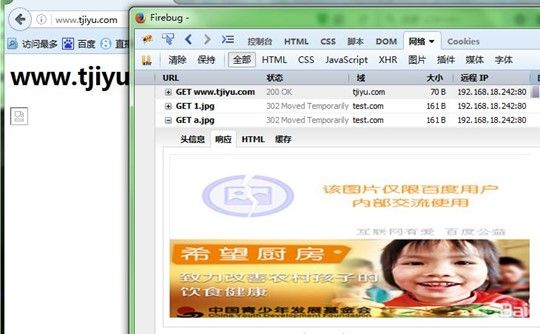
然后在www.tjiyu.com虚拟主机测试页面加入图片引用,测试访问www.tjiyu.com可以看到引用的http://www.test.com/imgs/1.jpg,但返回的是我们配置http://www.test.com/imgs/a.jpg,过程如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# vim /data/tjiyu/index.html [root@node2 nginx]# service nginx reload
3-8、提供Nginx状态页面
提供Nginx状态页面指的是ngx_http_stub_status_module模块的功能,还有一个可以提供更详细信息的ngx_http_status_module模块,配置都很简单,不过编译nginx时需要指定包含进来。
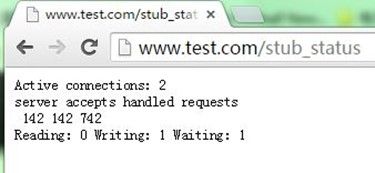
可以看到的信息有:
当下处于活动状态的总数;
接受的总数,已经建立和处理总数,请求的总数;
正在接受的并发请求个数,正在读取的个数或发往客户端的,长连接中的处于活动状态的值;
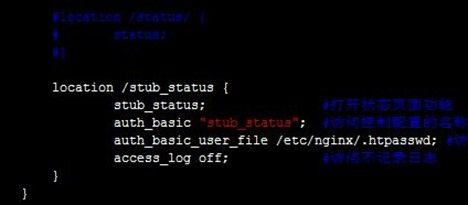
配置一个location匹配访问,里面"stub_status;"就可以打开状态页面功能,注意1.7.5版本前需要"stub_status on;",然后加入用户认证和不记录日志,以防信息泄露,过程如下:
[root@node2 nginx]# vim nginx.conf [root@node2 nginx]# service nginx reload
location /stub_status { stub_status; #打开状态页面功能 auth_basic "stub_status"; #访问控制配置的名称字符串,或者off关闭 auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd; #访问控制配置的文件,htpasswd生成,包含用户名用密码 access_log off; #访问不记录日志 }
3-9、配置gzip压缩
提供gzip压缩指的是ngx_http_gzip_module模块的功能,nginx默认会附带gzip压缩的功能,而ngx_http_gzip_static_module模块是提供gzip预压缩功能,需要编译指定。
配置选项有:
gzip on|off gzip_buffer 使用的缓存大小 gzip_comp_level 压缩的级别 gzip_disable 不压缩的类型或浏览器 gzip_min_length 最少压缩的大小 gzip_http_version 压缩完成以后发送http的版本 gzip_types:只压缩的格式
nginx将响应报文发送至客户端之前可以启用压缩功能,这能够有效地节约带宽,并提高响应至客户端的速度。可以在http块或server块中配置,一般在http块中配置,配置如下:
gzip on; #打开gzip压缩功能 gzip_http_version 1.0; #使用1.0版本 gzip_comp_level 4; #压缩级别为4 gzip_min_length 64; #内容超过最少长度后才开启压缩:64k gzip_types text/plain text/css application/x-javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript application/javascript application/json; #压缩的文件类型:文本压 gzip_disable msie6; #不压缩的浏览器类型:ie6不支持
3-10、配置日志
Nginx常用的日志分为:错误日志error_log,这是nginx核心模块ngx_core_module提供的,前面《nginx详解》已有详细的说明;http访问日志access_log,这是ngx_http_log_module模块提供的。
这两种日志默认都是打开记录的,而我们configure配置编译的时候已经指定了日志存放的目录,我们可以看到目录下已经存在这两个日志文件,如下:
下面就来配置http访问日志,配置选项有:
access_log off | path [format [buffer=size] [gzip[=level]] [flush=time] [if=condition]]; #设置存放路径、(引用)日志格式、缓存区大小、压缩等级、缓存时间等; log_format name string ...; #定义日志格式,access_log引用 open_log_file_cache max=N [inactive=time] [min_uses=N] [valid=time]; #设置日志文件缓存注意,默认access_log logs/access.log combined; log_format combined "...";也就是说日志格式为combined,如下:
log_format combined '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] ' '"$request" $status $body_bytes_sent ' '"$http_referer" "$http_user_agent"';
格式定义中可以使用公共变量和仅日志格式中的变量。
典型应用配置:如果请求经过nginx反向代理服务器,后端web服务器无法直接获取到客户端真实的IP地址(因为$remote_addr获取到的是反向代理IP地址)。可以配置反向代理服务器在转发请求的http头信息中增加"x-Forwarded-For"行信息,该信息中记录客户端IP地址和客户端请求的服务器地址;而后在后端服务器就配置重新定义日志格式,增加"$http_x_forwarded_for"变量信息到格式,就如原来配置文件中存在的配置(已注释,后面介绍nginx负载均衡再配置),如下:
3-11、配置基于SSL提供https服务
提供基于SSL提供https服务的是ngx_mail_ssl_module模块,需要编译指定。
1、创建CA自签证书
[root@node2 ~]# cd /etc/pki/CA/ [root@node2 CA]# ls certs crl newcerts private [root@node2 CA]# cd private/ [root@node2 private]# ls [root@node2 private]# (umask 077; openssl genrsa 2048 > cakey.pem) Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus ....+++ ..........................................................+++ e is 65537 (0x10001) [root@node2 private]# openssl req -new -x509 -key ./cakey.pem -out ../cacert.pem You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN State or Province Name (full name) []:HZ Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:ZJ Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:TJIYU Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:TEST Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:ca.tjiyu.com Email Address []:[email protected] [root@node2 private]# ll 总用量 4 -rw-------. 1 root root 1675 10月 20 17:18 cakey.pem [root@node2 private]# cd .. [root@node2 CA]# touch serial [root@node2 CA]# echo 01 > serial [root@node2 CA]# touch index.txt [root@node2 CA]# ll 总用量 24 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1383 10月 20 17:25 cacert.pem drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 9月 27 20:30 certs drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 9月 27 20:30 crl -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 20 17:26 index.txt drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 9月 27 20:30 newcerts drwx------. 2 root root 4096 10月 20 17:18 private -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 3 10月 20 17:26 serial
2、生成证书申请
[root@node2 CA]# mkdir /etc/nginx/ssl [root@node2 CA]# cd /etc/nginx/ssl/ [root@node2 ssl]# (umask 077; openssl genrsa 1024 > nginx.key) Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus ....................................................++++++ ..............++++++ e is 65537 (0x10001) [root@node2 ssl]# openssl req -new -key nginx.key -out nginx.csr You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN State or Province Name (full name) []:HZ Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:ZJ Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:TJIYU Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:TEST Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:www.test.com Email Address []: Please enter the following 'extra' attributes to be sent with your certificate request A challenge password []: An optional company name []:
3、让CA签名并颁发证书
[root@node2 ssl]# openssl ca -in nginx.csr -out nginx.crt -days 3650 Using configuration from /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf Check that the request matches the signature Signature ok Certificate Details: Serial Number: 1 (0x1) Validity Not Before: Oct 20 09:31:01 2016 GMT Not After : Oct 18 09:31:01 2026 GMT Subject: countryName = CN stateOrProvinceName = HZ organizationName = TJIYU organizationalUnitName = TEST commonName = www.test.com X509v3 extensions: X509v3 Basic Constraints: CA:FALSE Netscape Comment: OpenSSL Generated Certificate X509v3 Subject Key Identifier: AD:3D:C4:0D:11:A0:68:51:1B:CE:5E:45:B3:7C:A0:A8:2C:01:A8:27 X509v3 Authority Key Identifier: keyid:5B:22:1A:8A:67:E6:C2:8A:CA:DA:F5:5C:97:86:76:5B:09:94:88:48 Certificate is to be certified until Oct 18 09:31:01 2026 GMT (3650 days) Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y 1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y Write out database with 1 new entries Data Base Updated [root@node2 ssl]# ll 总用量 12 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 3736 10月 20 17:33 nginx.crt -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 635 10月 20 17:30 nginx.csr -rw-------. 1 root root 887 10月 20 17:27 nginx.key
4、修改配置文件
使用另外一个server配置SSL监听433端口,注意,配置如下:
server { listen 443 ssl; #打开SSL,监听433端口 server_name localhost; ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt; #证书文件 ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key; #证书key文件 ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; #所有worker进程共享会话缓存 ssl_session_timeout 5m; #会话超时时间:5分钟 ssl_protocols SSLv2 SSLv3 TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; #支持SSL协议,从1.1.13和1.0.12版本开始支持TLSv1.1和TLSv1.2 ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; #加密方法 ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; #由服务器选择加密方法 location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } }
5、测试
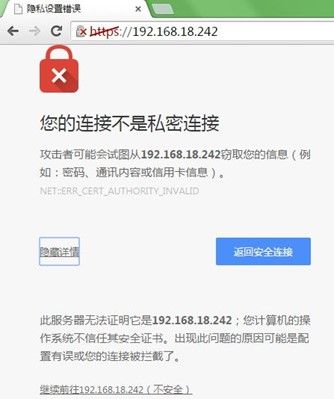
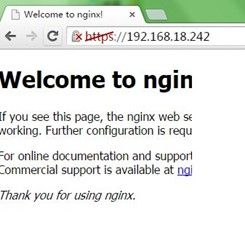
重新加载配置后,查看网络状态,可以看到nginx监听了433端口;访问可以看到警告提示,因为我们的证书不是正规机构申请的,无法认证;继续访问可以看到正常页面 ,如下:
到这里,我们成功对nginx进行了编译安装以及配置WEB服务相关内容,后面将进行nginx的反向代理、负载均衡、后端健康检测和缓存等相关功能配置……
【参考资料】
1、nginx官网文档:http://nginx.org/en/docs/
2、nginx详解:http://blog.csdn.net/tjiyu/article/details/53027619
3、Web服务器之Nginx详解:http://freeloda.blog.51cto.com/2033581/1285722