深度学习_目标检测(二)——SSD(二)复现-为了更好的理解
目录
复现ssd网络
Step 1/x 网络构建部分——命名空间scope【block】输入x+计算*(卷积)
Step 2/x 网络构建部分——命名空间scope【loc和cls】输出
Step 3/x 先验框部分——先验框生成
第一步:anchor_size和Sk的计算过程:
第二步:ar计算-自己设定
Step 4/x 先验框部分——解码网络得 box[x0, y0, x1, y1]
Step 5/x 先验框部分——筛选
Step 6/x 检测部分——检测,使用预训练模型进行网络测试
Step 7/x 训练部分——数据转换voc转tfrecords
Step 8/x 训练部分——Trainer
Step 9/x 预测部分——整合1-7步的code
参考
复现ssd网络
几个关键点理解透
如何计算Anchor和Proposal:https://blog.csdn.net/as472780551/article/details/81227408。
Step 1/x 网络构建部分——命名空间scope【block】输入x+计算*(卷积)
需要材料,
基本功:卷积模块+池化模块+填补模块(block8和block9需要而用)
import tensorflow as tf
class ssd(object):
# step 2/x 卷积模块创建,池化模块,随意丢弃模块。
'''
tf.layers.conv2d() 经典输入参数:
f(w*x+b):
x = 输入input;
w = 卷积核个数filter_num,尺寸k_size;
b = 默认,use_bias=True;
* = 卷积步长stride,填充方式padding,卷积模式dilation(标准,扩张等),等等一系列;
f = 激活函数。
'''
def conv2d(self,x,filter,k_size,stride=[1,1],padding='same',dilation=[1,1],activation=tf.nn.relu,scope='conv2d'):
return tf.layers.conv2d(inputs=x, filters=filter, kernel_size=k_size,
strides=stride, dilation_rate=dilation, padding=padding,
name=scope, activation=activation, use_bias=True)
#
'''
tf.layers.max_pooling2d(),经典输入参数:
p*x:
p = 尺寸pool_size
x = 输入input
'''
def max_pool2d(self,x, pool_size, stride, scope='max_pool2d'):
return tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=x, pool_size=pool_size, strides=stride, name=scope, padding='same')
#
'''
tf.pad() 对原图进行填充,为了匹配输入输出尺寸
'''
def pad2d(self,x, pad):
return tf.pad(x, paddings=[[0, 0], [pad, pad], [pad, pad], [0, 0]])
def set_net(self,x=None):
# 列表放FM
check_points = {}
with tf.variable_scope('ssd_300_vgg'):
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[None,300,300,3])
#b1
net = self.conv2d(x,filter=64,k_size=[3,3],scope='conv1_1')
net = self.conv2d(net,64,[3,3],scope='conv1_2')
net = self.max_pool2d(net,pool_size=[2,2],stride=[2,2],scope='pool1')
#b2
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=128, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv2_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2_2')
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool2')
#b3
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=256, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv3_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_3')
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool3')
#b4
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=512, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv4_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4_3')
print("block4_output", net)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------4
check_points['block4'] = net
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool4')
#print('pool4', net)
#b5
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=512, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv5_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5_3')
#print('conv5_3',net)
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[3, 3], stride=[1, 1], scope='pool5')
#print('pool5',net)
#b6
net = self.conv2d(net,1024,[3,3],dilation=[6,6],scope='conv6')
#print('conv6',net)
#b7
net = self.conv2d(net,1024,[1,1],scope='conv7')
print("block7_output", net)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------7
check_points['block7'] = net
#b8],scope='conv8_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [1, 1], scope='conv8_1x1')
#print('conv8_3',net)
# 该层要进行填补
net = self.pad2d(net, 1)
#print('pad2d',net)
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], [2, 2], scope='conv8_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------8
print("block8_output", net)
check_points['block8'] = net
#b9
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv9_1x1')
net = self.pad2d(net, 1)
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], [2, 2], scope='conv9_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------9
print("block9_output", net)
check_points['block9'] = net
#b10
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv10_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv10_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------10
print("block10_output", net)
check_points['block10'] = net
#b11
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv11_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv11_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------11
print("block11_output", net)
check_points['block11'] = net
print(check_points)
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = ssd()
model.set_net()模型FM(feature map)输出结果
pad模块处理结果
![]()
Step 2/x 网络构建部分——命名空间scope【loc和cls】输出
import tensorflow as tf
class ssd(object):
def __init__(self):
# FM、cls和loc设置
self.feature_map_size = [[38, 38], [19, 19], [10, 10], [5, 5], [3, 3], [1, 1]]
self.classes = ["aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat", "bottle",
"bus", "car", "cat", "chair", "cow", "diningtable",
"dog", "horse", "motorbike", "person", "pottedplant",
"sheep", "sofa", "train", "tvmonitor"]
self.feature_layers = ['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11']
self.img_size = (300,300)
self.num_classes = 21
self.boxes_len = [4,6,6,6,4,4]
self.isL2norm = [True,False,False,False,False,False]
# 先验框
self.anchor_sizes = [[21., 45.], [45., 99.], [99., 153.],[153., 207.],[207., 261.], [261., 315.]]
self.anchor_ratios = [[2, .5], [2, .5, 3, 1. / 3], [2, .5, 3, 1. / 3],
[2, .5, 3, 1. / 3], [2, .5], [2, .5]]
# self.anchor_steps = [8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300]
self.anchor_steps = [8, 16, 30, 60, 100, 300]
self.prior_scaling = [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2] #特征图先验框缩放比例
self.n_boxes = [5776,2166,600,150,36,4] #8732个
self.threshold = 0.25
# step 2/x 卷积模块创建,池化模块,随意丢弃模块。
'''
tf.layers.conv2d() 经典输入参数:
f(w*x+b):
x = 输入input;
w = 卷积核个数filter_num,尺寸k_size;
b = 默认,use_bias=True;
* = 卷积步长stride,填充方式padding,卷积模式dilation(标准,扩张等),等等一系列;
f = 激活函数。
'''
def conv2d(self,x,filter,k_size,stride=[1,1],padding='same',dilation=[1,1],activation=tf.nn.relu,scope='conv2d'):
return tf.layers.conv2d(inputs=x, filters=filter, kernel_size=k_size,
strides=stride, dilation_rate=dilation, padding=padding,
name=scope, activation=activation, use_bias=True)
#
'''
tf.layers.max_pooling2d(),经典输入参数:
p*x:
p = 尺寸pool_size
x = 输入input
'''
def max_pool2d(self,x, pool_size, stride, scope='max_pool2d'):
return tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=x, pool_size=pool_size, strides=stride, name=scope, padding='same')
#
'''
tf.pad() 对原图进行填充,为了匹配输入输出尺寸
'''
def pad2d(self,x, pad):
return tf.pad(x, paddings=[[0, 0], [pad, pad], [pad, pad], [0, 0]])
# 对第四层模块的卷积进行L2归一化,只对通道数进行归一化,因为比较靠前。。。。???
def l2norm(self, x, trainable=True, scope='L2Normalization'):
n_channels = x.get_shape().as_list()[-1] # 通道数
l2_norm = tf.nn.l2_normalize(x, dim=[3], epsilon=1e-12) # 只对每个像素点在channels上做归一化
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
gamma = tf.get_variable("gamma", shape=[n_channels, ], dtype=tf.float32,
trainable=trainable)
return l2_norm * gamma
# loc 和 cls 通过卷积进行计算
def ssd_prediction(self, x, num_classes, box_num, isL2norm, scope='multibox'):
reshape = [-1] + x.get_shape().as_list()[1:-1] # 去除第一个和最后一个得到shape
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
if isL2norm:
x = self.l2norm(x) # 进行
print(x)
# 预测位置 --》 坐标和大小 回归
location_pred = self.conv2d(x, filter=box_num * 4, k_size=[3,3], activation=None,scope='conv_loc')
location_pred = tf.reshape(location_pred, reshape + [box_num, 4])
# 预测类别 --> 分类 sofrmax
class_pred = self.conv2d(x, filter=box_num * num_classes, k_size=[3,3], activation=None, scope='conv_cls')
class_pred = tf.reshape(class_pred, reshape + [box_num, num_classes])
print(location_pred, class_pred)
return location_pred, class_pred
def set_net(self,x=None):
# 列表放FM
check_points = {} # 字典存储{'key':value}
predictions = [] # 列表存储[value]
locations = [] # 列表存储[value]
with tf.variable_scope('ssd_300_vgg'):
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[None,300,300,3])
#b1
net = self.conv2d(x,filter=64,k_size=[3,3],scope='conv1_1')
net = self.conv2d(net,64,[3,3],scope='conv1_2')
net = self.max_pool2d(net,pool_size=[2,2],stride=[2,2],scope='pool1')
#b2
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=128, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv2_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2_2')
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool2')
#b3
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=256, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv3_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_3')
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool3')
#b4
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=512, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv4_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4_3')
print("block4_output", net)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------4
check_points['block4'] = net
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool4')
#print('pool4', net)
#b5
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=512, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv5_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5_3')
#print('conv5_3',net)
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[3, 3], stride=[1, 1], scope='pool5')
#print('pool5',net)
#b6
net = self.conv2d(net,1024,[3,3],dilation=[6,6],scope='conv6')
#print('conv6',net)
#b7
net = self.conv2d(net,1024,[1,1],scope='conv7')
print("block7_output", net)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------7
check_points['block7'] = net
#b8],scope='conv8_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [1, 1], scope='conv8_1x1')
#print('conv8_3',net)
# 该层要进行填补
print('pad2d-start',net)
net = self.pad2d(net, 1)
print('pad2d-end',net)
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], [2, 2], scope='conv8_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------8
print("block8_output", net)
check_points['block8'] = net
#b9
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv9_1x1')
net = self.pad2d(net, 1)
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], [2, 2], scope='conv9_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------9
print("block9_output", net)
check_points['block9'] = net
#b10
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv10_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv10_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------10
print("block10_output", net)
check_points['block10'] = net
#b11
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv11_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv11_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------11
print("block11_output", net)
check_points['block11'] = net
print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
for i,j in enumerate(self.feature_layers):
loc, cls = self.ssd_prediction(
x = check_points[j],
num_classes = self.num_classes,
box_num = self.boxes_len[i],
isL2norm = self.isL2norm[i],
scope = j + '_box'
)
predictions.append(tf.nn.softmax(cls))
locations.append(loc)
print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
print(locations, predictions)
print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
print(check_points)
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = ssd()
model.set_net()Step 3/x 先验框部分——先验框生成
引用:SSD在6个特征图上使用2组3x3的卷积核分别做分类和boundingbox回归,所以SSD是一个全卷积神经网络。我们知道每个特征图上每个像素点对应一个理论感受野,所以SSD相当于对原图中所有的理论感受野作分类和回归,由于有效感受野在理论感受野中有重要的影响,其他区域的影响可以忽略,所以这里我们认为SSD是对有效感受野作分类和回归,那么问题来了,既然是对所有的有效感受野做分类和回归,那每个有效感受野的分类的label和回归的label是如何确定的呢?default box就是用来干这个的。
先验框干嘛用:https://blog.csdn.net/qianqing13579/article/details/82106664
先验框计算流程:
第一步:先计算![]() ,即(scale),通过该系数计算每张FM映射原图的尺寸大小
,即(scale),通过该系数计算每张FM映射原图的尺寸大小![]() 。
。
第二步:计算![]() ,即(anchor_ratios),该值是自定义的,取值范围为:
,即(anchor_ratios),该值是自定义的,取值范围为:![]() 。
。
第三步:
-
第一步:anchor_size和Sk的计算过程:
![]() 得到每一层FM的和原图的映射比例值;
得到每一层FM的和原图的映射比例值;
![]() 得到每一层FM对应原图映射的min_size和max_size;
得到每一层FM对应原图映射的min_size和max_size;
![]() 和
和![]() 如果按照理论公式计算:
如果按照理论公式计算:
![]()
理论计算结果:
![]() 和
和![]() 论文实际计算:【因为作者将第一层S1, 单独拿出来设置了.】
论文实际计算:【因为作者将第一层S1, 单独拿出来设置了.】
![]()
在SSD中一共有6个用于分类和回归的特征层(feature map),
分别是feat_layers=['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11'],
m是就是特征层的个数,按理说分母应该是6-1=5,但是这里是5-1=4, 因为作者将第一层S1, 单独拿出来设置了.
k是第几个特征层的意思,注意k的范围是1~m, 也就是1~6.
由于![]() , 就是0.1, 再乘以300, 就是30.
, 就是0.1, 再乘以300, 就是30.
anchor_sizes=[
(30., 60.),
(60., 111.),
(111., 162.),
(162., 213.),
(213., 264.),
(264., 315.)
]https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42450404/article/details/92800381
https://blog.csdn.net/gbyy42299/article/details/81235891
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36735489/article/category/9196814
https://www.jianshu.com/p/b4fa2f4ee6ee
-
第二步:ar计算-自己设定
![]() ,即
,即![]() ,得到每层每种默认框的比例值,和上面计算的
,得到每层每种默认框的比例值,和上面计算的![]() 直接决定默认框宽w高h尺寸实际取值。
直接决定默认框宽w高h尺寸实际取值。
self.anchor_ratios = [
[2, .5],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5],
[2, .5]
]第一步得到了,min_size、max_size;第二步得到了ratio;那么每层的默认框就可以按照如下图的计算方法计算默认框的宽和高。
def ssd_anchor_layer(self,img_size,feature_map_size,anchor_size,anchor_ratio,anchor_step,box_num,offset=0.5):
# 提取FM的每个坐标
y, x = np.mgrid[0:feature_map_size[0],0:feature_map_size[1]]
# 映射回原图,映射到原图 anchor_step = SRC[300*300]/FM1[38*38] = 7.89 = 8
# 返回FM1每个像素点坐标对于的原图坐标,归一化值(0-1)之间的比例值。
y = (y.astype(np.float32) + offset) * anchor_step /img_size[0]
x = (x.astype(np.float32) + offset) * anchor_step /img_size[1]
y = np.expand_dims(y,axis=-1)
x = np.expand_dims(x,axis=-1)
# 有两个默认的长宽比为1,但是大小不同的正方形先验框:计算两个长宽比为1的h、w。——根据先验框个数来确定的,多少个先验框就有多少个长宽。
h = np.zeros((box_num,), np.float32)
w = np.zeros((box_num,), np.float32)
# 第一个:h[0]、w[0]: 30/300, ....
h[0] = anchor_size[0] /img_size[0]
w[0] = anchor_size[0] /img_size[0]
# 第二个:h[1]、w[1]:sqrt(30*60)/300, ....
h[1] = (anchor_size[0] * anchor_size[1]) ** 0.5 / img_size[0] # **0.5相当于sqrt开根号,
w[1] = (anchor_size[0] * anchor_size[1]) ** 0.5 / img_size[1]
# 剩下的长宽比按公式来计算。
for i, j in enumerate(anchor_ratio):
h[i + 2] = anchor_size[0] / img_size[0] / (j ** 0.5)
w[i + 2] = anchor_size[0] / img_size[1] * (j ** 0.5)
return y, x, h, wStep 4/x 先验框部分——解码网络得 box[x0, y0, x1, y1]
为什么需要解码,解码是个啥?https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/31426458
因为先验框是![]() 表示,上节已经计算出;实际原图对应边界框用
表示,上节已经计算出;实际原图对应边界框用![]() 表示;
表示;
(边界框编码encode)边界框的预测值 ![]() 是
是 ![]() 相对于
相对于 ![]() 的转换值:
的转换值:
(边界框解码decode)预测时,需要反向该过程,从预测值 ![]() 中得到边界框的真实值
中得到边界框的真实值 ![]() :
:
( ![]() 为需要学习的量,使得
为需要学习的量,使得 ![]() )
)
原caffe增加variance:{0.1,0.1,0.2,0.2}来调整检测值。prior_scaling人称先验框缩放比例。
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33544892
# 解码网络返回box[x0, y0, x1, y1] -》先验框通过平移和缩放接近真实框。其中 prior_scaling 为平移、尺度因子
def ssd_decode(self, location, box, prior_scaling):
y_a, x_a, h_a, w_a = box
# 平移
cx = location[:, :, :, :, 0] * w_a * prior_scaling[0] + x_a #location最后一个维度有4,表示4个值:x,y,w,h
cy = location[:, :, :, :, 1] * h_a * prior_scaling[1] + y_a
# 缩放
w = w_a * tf.exp(location[:, :, :, :, 2] * prior_scaling[2])
h = h_a * tf.exp(location[:, :, :, :, 3] * prior_scaling[3])
# 计算框的左上和右下坐标:box[x0, y0, x1, y1]
bboxes = tf.stack(
[
cy - h / 2.0,
cx - w / 2.0,
cy + h / 2.0,
cx + w / 2.0
],
axis=-1
)
print(bboxes)
return bboxesimport tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class ssd(object):
def __init__(self):
# 初始化一:FM、cls和loc设置
self.feature_map_size = [[38, 38], [19, 19], [10, 10], [5, 5], [3, 3], [1, 1]]
self.classes = ["aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat", "bottle",
"bus", "car", "cat", "chair", "cow", "diningtable",
"dog", "horse", "motorbike", "person", "pottedplant",
"sheep", "sofa", "train", "tvmonitor"]
self.feature_layers = ['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11']
self.img_size = (300, 300)
self.num_classes = 21
self.boxes_len = [4, 6, 6, 6, 4, 4] # FM1每个像素点取4个尺度框,FM2每个像素点取6个尺度框,。。。
self.isL2norm = [True, False, False, False, False, False]
# 初始化二:先验框
# 计算得到:sk:6组min_size和max_size [[h0, w0],[h1, w1],[h2, w2],[h3, w3]]每次取一组两个:[21., 45.]
'''
# 官方:60, 111, 162, 213, 264, 315.》》》6组min_size和max_size
anchor_sizes=[
(30., 60.),
(60., 111.),
(111., 162.),
(162., 213.),
(213., 264.),
(264., 315.)]
'''
# 初始化二:先验框
self.anchor_sizes = [
[21., 45.],
[45., 99.],
[99., 153.],
[153., 207.],
[207., 261.],
[261., 315.]
]
# 取ar:{1, 2, 1/2, 3, 1/3},对应每层的ar=[[1,2,1/2]]
self.anchor_ratios = [
[2, .5],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5],
[2, .5]
]
# 初始化二:先验框实现FM像素点映射到原图300*300的中心点扩张步长。
self.anchor_steps = [8, 16, 30, 60, 100, 300]
# 初始化三:先验框先验框解码用的缩放比例。
self.prior_scaling = [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2] #特征图先验框缩放比例
# 每层FM的默认框个数值,可计算。
self.n_boxes = [5776, 2166, 600, 150, 36, 4] #8732个
# IOU阈值设置
self.threshold = 0.25
# step 2/x 卷积模块创建,池化模块,随意丢弃模块。
'''
tf.layers.conv2d() 经典输入参数:
f(w*x+b):
x = 输入input;
w = 卷积核个数filter_num,尺寸k_size;
b = 默认,use_bias=True;
* = 卷积步长stride,填充方式padding,卷积模式dilation(标准,扩张等),等等一系列;
f = 激活函数。
'''
def conv2d(self,x,filter,k_size,stride=[1,1],padding='same',dilation=[1,1],activation=tf.nn.relu,scope='conv2d'):
return tf.layers.conv2d(inputs=x, filters=filter, kernel_size=k_size,
strides=stride, dilation_rate=dilation, padding=padding,
name=scope, activation=activation, use_bias=True)
#
'''
tf.layers.max_pooling2d(),经典输入参数:
p*x:
p = 尺寸pool_size
x = 输入input
'''
def max_pool2d(self,x, pool_size, stride, scope='max_pool2d'):
return tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=x, pool_size=pool_size, strides=stride, name=scope, padding='same')
#
'''
tf.pad() 对原图进行填充,为了匹配输入输出尺寸
'''
def pad2d(self,x, pad):
return tf.pad(x, paddings=[[0, 0], [pad, pad], [pad, pad], [0, 0]])
# 对第四层模块的卷积进行L2归一化,只对通道数进行归一化,因为比较靠前。。。。???
def l2norm(self, x, trainable=True, scope='L2Normalization'):
n_channels = x.get_shape().as_list()[-1] # 通道数
l2_norm = tf.nn.l2_normalize(x, dim=[3], epsilon=1e-12) # 只对每个像素点在channels上做归一化
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
gamma = tf.get_variable("gamma", shape=[n_channels, ], dtype=tf.float32,
trainable=trainable)
return l2_norm * gamma
# loc 和 cls 通过卷积进行计算 【num_classes和box_num】
def ssd_prediction(self, x, num_classes, box_num, isL2norm, scope='multibox'):
reshape = [-1] + x.get_shape().as_list()[1:-1] # 去除第一个和最后一个得到shape
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
if isL2norm:
x = self.l2norm(x) # 进行
print(x)
# 预测位置loc --》 坐标和大小 回归
location_pred = self.conv2d(x, filter=box_num * 4, k_size=[3,3], activation=None,scope='conv_loc')
location_pred = tf.reshape(location_pred, reshape + [box_num, 4])
# 预测类别cls --> 分类 sofrmax
class_pred = self.conv2d(x, filter=box_num * num_classes, k_size=[3,3], activation=None, scope='conv_cls')
class_pred = tf.reshape(class_pred, reshape + [box_num, num_classes])
print(location_pred, class_pred)
return location_pred, class_pred
def set_net(self,x=None):
# 列表放FM
check_points = {} # 字典存储{'key':value}
predictions = [] # 列表存储[value]
locations = [] # 列表存储[value]
with tf.variable_scope('ssd_300_vgg'):
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[None,300,300,3])
#b1
net = self.conv2d(x,filter=64,k_size=[3,3],scope='conv1_1')
net = self.conv2d(net,64,[3,3],scope='conv1_2')
net = self.max_pool2d(net,pool_size=[2,2],stride=[2,2],scope='pool1')
#b2
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=128, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv2_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2_2')
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool2')
#b3
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=256, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv3_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_3')
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool3')
#b4
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=512, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv4_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4_3')
print("block4_output", net)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------4
check_points['block4'] = net
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool4')
#print('pool4', net)
#b5
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=512, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv5_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5_3')
#print('conv5_3',net)
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[3, 3], stride=[1, 1], scope='pool5')
#print('pool5',net)
#b6
net = self.conv2d(net,1024,[3,3],dilation=[6,6],scope='conv6')
#print('conv6',net)
#b7
net = self.conv2d(net,1024,[1,1],scope='conv7')
print("block7_output", net)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------7
check_points['block7'] = net
#b8],scope='conv8_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [1, 1], scope='conv8_1x1')
#print('conv8_3',net)
# 该层要进行填补
print('pad2d-start',net)
net = self.pad2d(net, 1)
print('pad2d-end',net)
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], [2, 2], scope='conv8_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------8
print("block8_output", net)
check_points['block8'] = net
#b9
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv9_1x1')
net = self.pad2d(net, 1)
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], [2, 2], scope='conv9_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------9
print("block9_output", net)
check_points['block9'] = net
#b10
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv10_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv10_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------10
print("block10_output", net)
check_points['block10'] = net
#b11
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv11_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv11_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------11
print("block11_output", net)
check_points['block11'] = net
print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
for i,j in enumerate(self.feature_layers):
loc, cls = self.ssd_prediction(
x = check_points[j],
num_classes = self.num_classes,
box_num = self.boxes_len[i],
isL2norm = self.isL2norm[i],
scope = j + '_box'
)
predictions.append(tf.nn.softmax(cls))
locations.append(loc)
print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
print(locations, predictions)
return locations, predictions, x
#print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
#print(check_points)
########## 先验框部分开始
# 先验框生成
def ssd_anchor_layer(self,img_size,feature_map_size,anchor_size,anchor_ratio,anchor_step,box_num,offset=0.5):
# 提取FM的每个坐标
y, x = np.mgrid[0:feature_map_size[0],0:feature_map_size[1]]
# 映射回原图,映射到原图 anchor_step = SRC[300*300]/FM1[38*38] = 7.89 = 8
# 返回FM1每个像素点坐标对于的原图坐标,归一化值(0-1)之间的比例值。
y = (y.astype(np.float32) + offset) * anchor_step /img_size[0]
x = (x.astype(np.float32) + offset) * anchor_step /img_size[1]
y = np.expand_dims(y,axis=-1)
x = np.expand_dims(x,axis=-1)
# 有两个默认的长宽比为1,但是大小不同的正方形先验框:计算两个长宽比为1的h、w。——根据先验框个数来确定的,多少个先验框就有多少个长宽。
h = np.zeros((box_num,), np.float32)
w = np.zeros((box_num,), np.float32)
# 第一个:h[0]、w[0]:先验框
h[0] = anchor_size[0] /img_size[0]
w[0] = anchor_size[0] /img_size[0]
# 第二个:h[1]、w[1]
h[1] = (anchor_size[0] * anchor_size[1]) ** 0.5 / img_size[0] # **0.5相当于sqrt开根号,
w[1] = (anchor_size[0] * anchor_size[1]) ** 0.5 / img_size[1]
# 剩下的长宽比按公式来计算。
for i, j in enumerate(anchor_ratio):
h[i + 2] = anchor_size[0] / img_size[0] / (j ** 0.5)
w[i + 2] = anchor_size[0] / img_size[1] * (j ** 0.5)
return y, x, h, w
# 解码网络返回box[x0, y0, x1, y1] -》先验框通过平移和缩放接近真实框。其中 prior_scaling 为平移、尺度因子
def ssd_decode(self, location, box, prior_scaling):
y_a, x_a, h_a, w_a = box
# 平移
cx = location[:, :, :, :, 0] * w_a * prior_scaling[0] + x_a #location最后一个维度有4,表示4个值:x,y,w,h
cy = location[:, :, :, :, 1] * h_a * prior_scaling[1] + y_a
# 缩放
w = w_a * tf.exp(location[:, :, :, :, 2] * prior_scaling[2])
h = h_a * tf.exp(location[:, :, :, :, 3] * prior_scaling[3])
# 计算框的左上和右下坐标:box[x0, y0, x1, y1]
bboxes = tf.stack(
[
cy - h / 2.0,
cx - w / 2.0,
cy + h / 2.0,
cx + w / 2.0
],
axis=-1
)
print(bboxes)
return bboxes
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = ssd()
locations, predictions, x = model.set_net()
x, y, h, w = model.ssd_anchor_layer(model.img_size, (38,38), (21.,45.), [2.,.5], 8, 4)
print(x, y, h, w)
print(x.shape, y.shape, h.shape, w.shape)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
box = model.ssd_anchor_layer(model.img_size, (10,10), (60, 111), [2.,.5,3.,1/3], 32, 6)
print("________________________________________________________________")
print('box',box)
# 解码网络打印
bboxes = model.ssd_decode(locations[2],box,model.prior_scaling)
print(bboxes)![]()
Step 5/x 先验框部分——筛选
由于在进行box提取时,SSD网络提出太多的box(8732个),这么多的box需要进行筛选。才能输出进行最后的输出。
关于8732个box怎么保留,训练和测试的筛选方法不一样。(https://www.jianshu.com/p/5b3ca7201fae)
# 先验框筛选_由于先验框太多了,需要进行减少——将总8732的6层,每层n_box
def choose_anchor_boxes(self, predictions, anchor_box, n_box):
anchor_box = tf.reshape(anchor_box, [n_box, 4])
prediction = tf.reshape(predictions, [n_box, 21])
prediction = prediction[:, 1:]
classes = tf.argmax(prediction, axis=1) + 1 # 20+1
scores = tf.reduce_max(prediction, axis=1) # 当得分大于阈值,保留锚框,一个先验框对应一个类别
filter_mask = scores > self.threshold
# tf.boolean_mask(a,b)用来过滤概率值比较低的锚盒,b为过来条件【filter_mask = scores > self.threshold】
classes = tf.boolean_mask(classes, filter_mask)
scores = tf.boolean_mask(scores, filter_mask)
anchor_box = tf.boolean_mask(anchor_box, filter_mask)
return classes, scores, anchor_boximport tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class ssd(object):
def __init__(self):
# 初始化一:FM、cls和loc设置
self.feature_map_size = [[38, 38], [19, 19], [10, 10], [5, 5], [3, 3], [1, 1]]
self.classes = ["aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat", "bottle",
"bus", "car", "cat", "chair", "cow", "diningtable",
"dog", "horse", "motorbike", "person", "pottedplant",
"sheep", "sofa", "train", "tvmonitor"]
self.feature_layers = ['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11']
self.img_size = (300, 300)
self.num_classes = 21
self.boxes_len = [4, 6, 6, 6, 4, 4] # FM1每个像素点取4个尺度框,FM2每个像素点取6个尺度框,。。。
self.isL2norm = [True, False, False, False, False, False]
# 初始化二:先验框
# 计算得到:sk:6组min_size和max_size [[h0, w0],[h1, w1],[h2, w2],[h3, w3]]每次取一组两个:[21., 45.]
'''
# 官方:60, 111, 162, 213, 264, 315.》》》6组min_size和max_size
anchor_sizes=[
(30., 60.),
(60., 111.),
(111., 162.),
(162., 213.),
(213., 264.),
(264., 315.)]
'''
# 初始化二:先验框
self.anchor_sizes = [
[21., 45.],
[45., 99.],
[99., 153.],
[153., 207.],
[207., 261.],
[261., 315.]
]
# 取ar:{1, 2, 1/2, 3, 1/3},对应每层的ar=[[1,2,1/2]]
self.anchor_ratios = [
[2, .5],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5],
[2, .5]
]
# 初始化二:先验框实现FM像素点映射到原图300*300的中心点扩张步长。
self.anchor_steps = [8, 16, 30, 60, 100, 300]
# 初始化三:先验框先验框解码用的缩放比例。
self.prior_scaling = [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2] #特征图先验框缩放比例
# 每层FM的默认框个数值,可计算。
self.n_boxes = [5776, 2166, 600, 150, 36, 4] #8732个
# IOU阈值设置
self.threshold = 0.25
# step 2/x 卷积模块创建,池化模块,随意丢弃模块。
'''
tf.layers.conv2d() 经典输入参数:
f(w*x+b):
x = 输入input;
w = 卷积核个数filter_num,尺寸k_size;
b = 默认,use_bias=True;
* = 卷积步长stride,填充方式padding,卷积模式dilation(标准,扩张等),等等一系列;
f = 激活函数。
'''
def conv2d(self,x,filter,k_size,stride=[1,1],padding='same',dilation=[1,1],activation=tf.nn.relu,scope='conv2d'):
return tf.layers.conv2d(inputs=x, filters=filter, kernel_size=k_size,
strides=stride, dilation_rate=dilation, padding=padding,
name=scope, activation=activation, use_bias=True)
#
'''
tf.layers.max_pooling2d(),经典输入参数:
p*x:
p = 尺寸pool_size
x = 输入input
'''
def max_pool2d(self,x, pool_size, stride, scope='max_pool2d'):
return tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=x, pool_size=pool_size, strides=stride, name=scope, padding='same')
#
'''
tf.pad() 对原图进行填充,为了匹配输入输出尺寸
'''
def pad2d(self,x, pad):
return tf.pad(x, paddings=[[0, 0], [pad, pad], [pad, pad], [0, 0]])
# 对第四层模块的卷积进行L2归一化,只对通道数进行归一化,因为比较靠前。。。。???
def l2norm(self, x, trainable=True, scope='L2Normalization'):
n_channels = x.get_shape().as_list()[-1] # 通道数
l2_norm = tf.nn.l2_normalize(x, dim=[3], epsilon=1e-12) # 只对每个像素点在channels上做归一化
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
gamma = tf.get_variable("gamma", shape=[n_channels, ], dtype=tf.float32,
trainable=trainable)
return l2_norm * gamma
# loc 和 cls 通过卷积进行计算 【num_classes和box_num】
def ssd_prediction(self, x, num_classes, box_num, isL2norm, scope='multibox'):
reshape = [-1] + x.get_shape().as_list()[1:-1] # 去除第一个和最后一个得到shape
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
if isL2norm:
x = self.l2norm(x) # 进行
print(x)
# 预测位置loc --》 坐标和大小 回归
location_pred = self.conv2d(x, filter=box_num * 4, k_size=[3,3], activation=None,scope='conv_loc')
location_pred = tf.reshape(location_pred, reshape + [box_num, 4])
# 预测类别cls --> 分类 sofrmax
class_pred = self.conv2d(x, filter=box_num * num_classes, k_size=[3,3], activation=None, scope='conv_cls')
class_pred = tf.reshape(class_pred, reshape + [box_num, num_classes])
print(location_pred, class_pred)
return location_pred, class_pred
def set_net(self,x=None):
# 列表放FM
check_points = {} # 字典存储{'key':value}
predictions = [] # 列表存储[value]
locations = [] # 列表存储[value]
with tf.variable_scope('ssd_300_vgg'):
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[None,300,300,3])
#b1
net = self.conv2d(x,filter=64,k_size=[3,3],scope='conv1_1')
net = self.conv2d(net,64,[3,3],scope='conv1_2')
net = self.max_pool2d(net,pool_size=[2,2],stride=[2,2],scope='pool1')
#b2
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=128, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv2_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2_2')
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool2')
#b3
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=256, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv3_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_3')
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool3')
#b4
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=512, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv4_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4_3')
print("block4_output", net)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------4
check_points['block4'] = net
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool4')
#print('pool4', net)
#b5
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=512, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv5_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5_3')
#print('conv5_3',net)
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[3, 3], stride=[1, 1], scope='pool5')
#print('pool5',net)
#b6
net = self.conv2d(net,1024,[3,3],dilation=[6,6],scope='conv6')
#print('conv6',net)
#b7
net = self.conv2d(net,1024,[1,1],scope='conv7')
print("block7_output", net)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------7
check_points['block7'] = net
#b8],scope='conv8_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [1, 1], scope='conv8_1x1')
#print('conv8_3',net)
# 该层要进行填补
print('pad2d-start',net)
net = self.pad2d(net, 1)
print('pad2d-end',net)
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], [2, 2], scope='conv8_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------8
print("block8_output", net)
check_points['block8'] = net
#b9
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv9_1x1')
net = self.pad2d(net, 1)
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], [2, 2], scope='conv9_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------9
print("block9_output", net)
check_points['block9'] = net
#b10
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv10_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv10_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------10
print("block10_output", net)
check_points['block10'] = net
#b11
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv11_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv11_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------11
print("block11_output", net)
check_points['block11'] = net
print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
for i,j in enumerate(self.feature_layers):
loc, cls = self.ssd_prediction(
x = check_points[j],
num_classes = self.num_classes,
box_num = self.boxes_len[i],
isL2norm = self.isL2norm[i],
scope = j + '_box'
)
predictions.append(tf.nn.softmax(cls))
locations.append(loc)
print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
print(locations, predictions)
return locations, predictions, x
#print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
#print(check_points)
########## 先验框部分开始
# 先验框生成
def ssd_anchor_layer(self,img_size, feature_map_size, anchor_size, anchor_ratio, anchor_step, box_num, offset=0.5):
# 提取FM的每个坐标
y, x = np.mgrid[0:feature_map_size[0],0:feature_map_size[1]]
# 映射回原图,映射到原图 anchor_step = SRC[300*300]/FM1[38*38] = 7.89 = 8
# 返回FM1每个像素点坐标对于的原图坐标,归一化值(0-1)之间的比例值。
y = (y.astype(np.float32) + offset) * anchor_step /img_size[0]
x = (x.astype(np.float32) + offset) * anchor_step /img_size[1]
y = np.expand_dims(y,axis=-1)
x = np.expand_dims(x,axis=-1)
# 有两个默认的长宽比为1,但是大小不同的正方形先验框:计算两个长宽比为1的h、w。——根据先验框个数来确定的,多少个先验框就有多少个长宽。
h = np.zeros((box_num,), np.float32)
w = np.zeros((box_num,), np.float32)
# 第一个:h[0]、w[0]:先验框
h[0] = anchor_size[0] /img_size[0]
w[0] = anchor_size[0] /img_size[0]
# 第二个:h[1]、w[1]
h[1] = (anchor_size[0] * anchor_size[1]) ** 0.5 / img_size[0] # **0.5相当于sqrt开根号,
w[1] = (anchor_size[0] * anchor_size[1]) ** 0.5 / img_size[1]
# 剩下的长宽比按公式来计算。
for i, j in enumerate(anchor_ratio):
h[i + 2] = anchor_size[0] / img_size[0] / (j ** 0.5)
w[i + 2] = anchor_size[0] / img_size[1] * (j ** 0.5)
return x, y, h, w
# 解码网络返回box[x0, y0, x1, y1] -》先验框通过平移和缩放接近真实框。其中 prior_scaling 为平移、尺度因子
def ssd_decode(self, location, box, prior_scaling):
y_a, x_a, h_a, w_a = box
# 平移
cx = location[:, :, :, :, 0] * w_a * prior_scaling[0] + x_a #location最后一个维度有4,表示4个值:x,y,w,h
cy = location[:, :, :, :, 1] * h_a * prior_scaling[1] + y_a
# 缩放
w = w_a * tf.exp(location[:, :, :, :, 2] * prior_scaling[2])
h = h_a * tf.exp(location[:, :, :, :, 3] * prior_scaling[3])
# 计算框的左上和右下坐标:box[x0, y0, x1, y1]
bboxes = tf.stack(
[
cy - h / 2.0,
cx - w / 2.0,
cy + h / 2.0,
cx + w / 2.0
],
axis=-1
)
print(bboxes)
return bboxes
# 先验框筛选_由于先验框太多了,需要进行减少——将总8732的6层,每层n_box
def choose_anchor_boxes(self, predictions, anchor_box, n_box):
anchor_box = tf.reshape(anchor_box, [n_box, 4])
prediction = tf.reshape(predictions, [n_box, 21])
prediction = prediction[:, 1:]
classes = tf.argmax(prediction, axis=1) + 1 # 20+1
scores = tf.reduce_max(prediction, axis=1) # 当得分大于阈值,保留锚框,一个先验框对应一个类别
filter_mask = scores > self.threshold
# tf.boolean_mask(a,b)用来过滤概率值比较低的锚盒,b为过来条件【filter_mask = scores > self.threshold】
classes = tf.boolean_mask(classes, filter_mask)
scores = tf.boolean_mask(scores, filter_mask)
anchor_box = tf.boolean_mask(anchor_box, filter_mask)
return classes, scores, anchor_box
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 类ssd实例化object:model
model = ssd()
# 类ssd实例的对象:model —— 构建网络,返回loc、cls、x
# 索引:locations[i],predictions[i]; {i=0,1,...}
locations, predictions, x = model.set_net()
# FM4层:--------------------------------
# 类ssd实例的对象:model —— FM4层的锚框生成 可以输出:'box=',也可以输出:'x, y, h, w='
# ssd_anchor_layer(self,img_size, feature_map_size, anchor_size, anchor_ratio, anchor_step, box_num, offset=0.5)
# FM4
box = model.ssd_anchor_layer(model.img_size, (38, 38), (21.,45.), [2.,.5], 8, 4)
# 类ssd实例的对象:model —— FM8层的锚框解码生成 bboxes
# 解码网络打印
bboxes = model.ssd_decode(locations[0], box, model.prior_scaling)
print(bboxes)
# 类ssd实例的对象:model —— 先验框进行筛选剔除。
# 先验框筛选测试 predictions类别得分,先验框传入,
classes, scores, anchor_box = model.choose_anchor_boxes(predictions[0], bboxes, model.n_boxes[0])
print(classes, scores, anchor_box)
# FM8层:--------------------------------
# x, y, h, w = ssd_anchor_layer(self,img_size, feature_map_size, anchor_size, anchor_ratio, anchor_step, box_num, offset=0.5)
x, y, h, w = model.ssd_anchor_layer(model.img_size, (10, 10), (99., 153.), [2, 0.5, 3, 1/3], 30, 6)
box = [x, y, h, w]
# bboxes = ssd_decode(self, location, box, prior_scaling)
bboxes = model.ssd_decode(locations[2], box, model.prior_scaling)
# classes, scores, anchor_box = choose_anchor_boxes(self, predictions, anchor_box, n_box)
classes, scores, anchor_box = model.choose_anchor_boxes(predictions[2], bboxes, model.n_boxes[2])
print(classes, scores, anchor_box)![]()
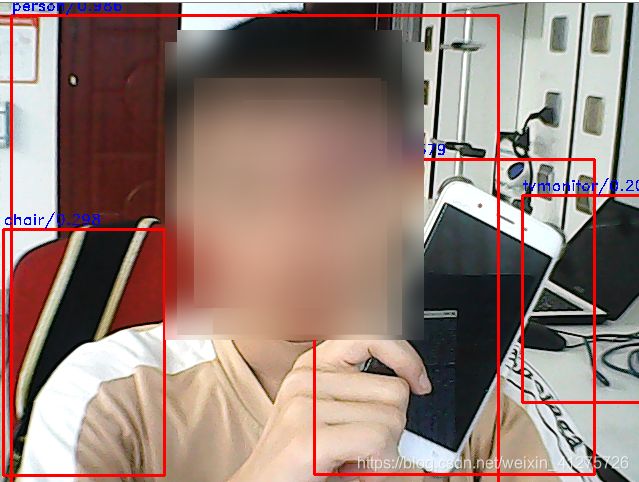
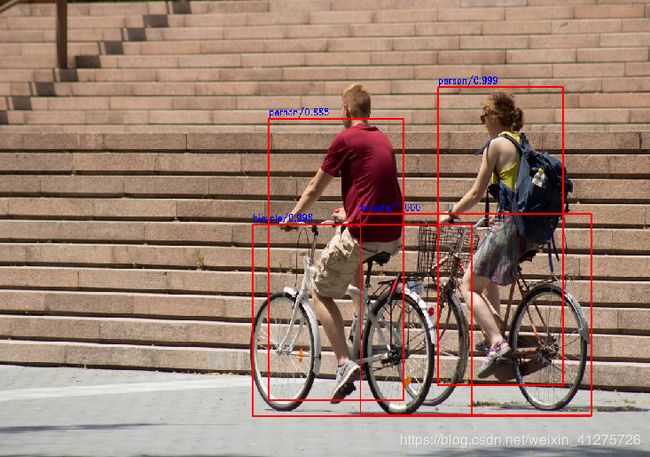
Step 6/x 检测部分——检测,使用预训练模型进行网络测试
opencv-python==4.1.1.26
matplotlib==3.1.1
numpy==1.17.3
tensorflow-gpu==1.14.0import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
class ssd(object):
def __init__(self):
# 初始化一:FM、cls和loc设置
self.feature_map_size = [[38, 38], [19, 19], [10, 10], [5, 5], [3, 3], [1, 1]]
self.classes = ["aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat", "bottle",
"bus", "car", "cat", "chair", "cow", "diningtable",
"dog", "horse", "motorbike", "person", "pottedplant",
"sheep", "sofa", "train", "tvmonitor"]
self.feature_layers = ['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11']
self.img_size = (300, 300)
self.num_classes = 21
self.boxes_len = [4, 6, 6, 6, 4, 4] # FM1每个像素点取4个尺度框,FM2每个像素点取6个尺度框,。。。
self.isL2norm = [True, False, False, False, False, False]
# 初始化二:先验框
# 计算得到:sk:6组min_size和max_size [[h0, w0],[h1, w1],[h2, w2],[h3, w3]]每次取一组两个:[21., 45.]
# 初始化二:先验框
self.anchor_sizes = [[21., 45.], [45., 99.], [99., 153.],[153., 207.],[207., 261.], [261., 315.]]
# 取ar:{1, 2, 1/2, 3, 1/3},对应每层的ar=[[1,2,1/2]]
self.anchor_ratios = [[2, .5], [2, .5, 3, 1. / 3], [2, .5, 3, 1. / 3], [2, .5, 3, 1. / 3], [2, .5], [2, .5]]
# 初始化二:先验框实现FM像素点映射到原图300*300的中心点扩张步长。
# self.anchor_steps = [8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300]
self.anchor_steps = [8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300]
# 初始化三:先验框先验框解码用的缩放比例。
self.prior_scaling = [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2] #特征图先验框缩放比例
# 每层FM的默认框个数值,可计算。
self.n_boxes = [5776, 2166, 600, 150, 36, 4] #8732个
# IOU阈值设置
self.threshold = 0.2
# step 2/x 卷积模块创建,池化模块,随意丢弃模块。
'''
tf.layers.conv2d() 经典输入参数:
f(w*x+b):
x = 输入input;
w = 卷积核个数filter_num,尺寸k_size;
b = 默认,use_bias=True;
* = 卷积步长stride,填充方式padding,卷积模式dilation(标准,扩张等),等等一系列;
f = 激活函数。
'''
def conv2d(self,x,filter,k_size,stride=[1,1],padding='same',dilation=[1,1],activation=tf.nn.relu,scope='conv2d'):
return tf.layers.conv2d(inputs=x, filters=filter, kernel_size=k_size,
strides=stride, dilation_rate=dilation, padding=padding,
name=scope, activation=activation)
#
'''
tf.layers.max_pooling2d(),经典输入参数:
p*x:
p = 尺寸pool_size
x = 输入input
'''
def max_pool2d(self,x, pool_size, stride, scope='max_pool2d'):
return tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=x, pool_size=pool_size, strides=stride, name=scope, padding='same')
#
'''
tf.pad() 对原图进行填充,为了匹配输入输出尺寸
'''
def pad2d(self,x, pad):
return tf.pad(x, paddings=[[0, 0], [pad, pad], [pad, pad], [0, 0]])
# 对第四层模块的卷积进行L2归一化,只对通道数进行归一化,因为比较靠前。。。。???
def l2norm(self, x, trainable=True, scope='L2Normalization'):
n_channels = x.get_shape().as_list()[-1] # 通道数
l2_norm = tf.nn.l2_normalize(x, dim=[3], epsilon=1e-12) # 只对每个像素点在channels上做归一化
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
gamma = tf.get_variable("gamma", shape=[n_channels, ], dtype=tf.float32,
trainable=trainable)
return l2_norm * gamma
# loc 和 cls 通过卷积进行计算 【num_classes和box_num】
def ssd_prediction(self, x, num_classes, box_num, isL2norm, scope='multibox'):
reshape = [-1] + x.get_shape().as_list()[1:-1] # 去除第一个和最后一个得到shape
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
if isL2norm:
x = self.l2norm(x) # 进行
print(x)
# 预测位置loc --》 坐标和大小 回归
location_pred = self.conv2d(x, filter=box_num * 4, k_size=[3,3], activation=None,scope='conv_loc')
location_pred = tf.reshape(location_pred, reshape + [box_num, 4])
# 预测类别cls --> 分类 sofrmax
class_pred = self.conv2d(x, filter=box_num * num_classes, k_size=[3,3], activation=None, scope='conv_cls')
class_pred = tf.reshape(class_pred, reshape + [box_num, num_classes])
print(location_pred, class_pred)
return location_pred, class_pred
# 第一步:网络构建
def set_net(self,x=None):
# 列表放FM
check_points = {} # 字典存储{'key':value}
predictions = [] # 列表存储[value]
locations = [] # 列表存储[value]
with tf.variable_scope('ssd_300_vgg'):
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[None,300,300,3])
#b1
net = self.conv2d(x,filter=64,k_size=[3,3],scope='conv1_1')
net = self.conv2d(net,64,[3,3],scope='conv1_2')
net = self.max_pool2d(net,pool_size=[2,2],stride=[2,2],scope='pool1')
#b2
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=128, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv2_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2_2')
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool2')
#b3
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=256, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv3_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_3')
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool3')
#b4
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=512, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv4_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4_3')
print("block4_output", net)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------4
check_points['block4'] = net
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool4')
#print('pool4', net)
#b5
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=512, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv5_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5_3')
#print('conv5_3',net)
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[3, 3], stride=[1, 1], scope='pool5')
#print('pool5',net)
#b6
net = self.conv2d(net,1024,[3,3],dilation=[6,6],scope='conv6')
#print('conv6',net)
#b7
net = self.conv2d(net,1024,[1,1],scope='conv7')
print("block7_output", net)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------7
check_points['block7'] = net
#b8],scope='conv8_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [1, 1], scope='conv8_1x1')
#print('conv8_3',net)
# 该层要进行填补
print('pad2d-start',net)
net = self.pad2d(net, 1)
print('pad2d-end',net)
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], [2, 2], scope='conv8_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------8
print("block8_output", net)
check_points['block8'] = net
#b9
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv9_1x1')
net = self.pad2d(net, 1)
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], [2, 2], scope='conv9_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------9
print("block9_output", net)
check_points['block9'] = net
#b10
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv10_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv10_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------10
print("block10_output", net)
check_points['block10'] = net
#b11
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv11_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv11_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------11
print("block11_output", net)
check_points['block11'] = net
print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
for i,j in enumerate(self.feature_layers):
loc, cls = self.ssd_prediction(
x = check_points[j],
num_classes = self.num_classes,
box_num = self.boxes_len[i],
isL2norm = self.isL2norm[i],
scope = j + '_box'
)
predictions.append(tf.nn.softmax(cls))
locations.append(loc)
print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
print(locations, predictions)
return locations, predictions, x
#print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
#print(check_points)
########## 先验框部分开始
# 第二步:分点:锚框
# 先验框生成
def ssd_anchor_layer(self,img_size, feature_map_size, anchor_size, anchor_ratio, anchor_step, box_num, offset=0.5):
# 提取FM的每个坐标
y, x = np.mgrid[0:feature_map_size[0],0:feature_map_size[1]]
# 映射回原图,映射到原图 anchor_step = SRC[300*300]/FM1[38*38] = 7.89 = 8
# 返回FM1每个像素点坐标对于的原图坐标,归一化值(0-1)之间的比例值。
y = (y.astype(np.float32) + offset) * anchor_step /img_size[0]
x = (x.astype(np.float32) + offset) * anchor_step /img_size[1]
y = np.expand_dims(y, axis=-1)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=-1)
# 有两个默认的长宽比为1,但是大小不同的正方形先验框:计算两个长宽比为1的h、w。——根据先验框个数来确定的,多少个先验框就有多少个长宽。
h = np.zeros((box_num,), np.float32) #类型统一,才可以相乘相除——————修改一
w = np.zeros((box_num,), np.float32)
# 第一个:h[0]、w[0]:先验框
h[0] = anchor_size[0] /img_size[0]
w[0] = anchor_size[0] /img_size[0]
# 第二个:h[1]、w[1]
h[1] = (anchor_size[0] * anchor_size[1]) ** 0.5 / img_size[0] # **0.5相当于sqrt开根号,
w[1] = (anchor_size[0] * anchor_size[1]) ** 0.5 / img_size[1]
# 剩下的长宽比按公式来计算。
for i, j in enumerate(anchor_ratio):
h[i + 2] = anchor_size[0] / img_size[0] / (j ** 0.5)
w[i + 2] = anchor_size[0] / img_size[1] * (j ** 0.5)
return y, x, h, w
# 第二步:分点:解码
# 解码网络返回box[x0, y0, x1, y1] -》先验框通过平移和缩放接近真实框。其中 prior_scaling 为平移、尺度因子
def ssd_decode(self, location, box, prior_scaling):
y_a, x_a, h_a, w_a = box
# 平移
cx = location[:, :, :, :, 0] * w_a * prior_scaling[0] + x_a #location最后一个维度有4,表示4个值:x,y,w,h
cy = location[:, :, :, :, 1] * h_a * prior_scaling[1] + y_a
# 缩放
w = w_a * tf.exp(location[:, :, :, :, 2] * prior_scaling[2])
h = h_a * tf.exp(location[:, :, :, :, 3] * prior_scaling[3])
# 计算框的左上和右下坐标:box[x0, y0, x1, y1]
bboxes = tf.stack([cy - h / 2.0, cx - w / 2.0, cy + h / 2.0, cx + w / 2.0], axis=-1)
print(bboxes)
return bboxes
# 第二步:分点:筛选
# 先验框筛选_由于先验框太多了,需要进行减少——将总8732的6层,每层n_box
def choose_anchor_boxes(self, predictions, anchor_box, n_box):
anchor_box = tf.reshape(anchor_box, [n_box, 4])
prediction = tf.reshape(predictions, [n_box, 21])
prediction = prediction[:, 1:]
classes = tf.argmax(prediction, axis=1) + 1 # 20+1
scores = tf.reduce_max(prediction, axis=1) # 当得分大于阈值,保留锚框,一个先验框对应一个类别
filter_mask = scores > self.threshold
# tf.boolean_mask(a,b)用来过滤概率值比较低的锚盒,b为过来条件【filter_mask = scores > self.threshold】b的制作规则是要用逻辑表达式(>或者<)生成布尔值
classes = tf.boolean_mask(classes, filter_mask)
scores = tf.boolean_mask(scores, filter_mask)
anchor_box = tf.boolean_mask(anchor_box, filter_mask)
return classes, scores, anchor_box
######### 训练部分开始
# 第四步:先验框分数排序,取top_k个
# 先验框分数排序,取前400
def bboxes_sort(self,classes, scores, bboxes, top_k=400):
idxes = np.argsort(-scores)
classes = classes[idxes][:top_k]
scores = scores[idxes][:top_k]
bboxes = bboxes[idxes][:top_k]
return classes, scores, bboxes
# 计算IOU
# 第五步:先验框NMS+IOU去重二
# IOU
def bboxes_iou(self,bboxes1, bboxes2):
bboxes1 = np.transpose(bboxes1)
bboxes2 = np.transpose(bboxes2)
# 计算两个box的交集:交集左上角的点取两个box的max,交集右下角的点取两个box的min
int_ymin = np.maximum(bboxes1[0], bboxes2[0])
int_xmin = np.maximum(bboxes1[1], bboxes2[1])
int_ymax = np.minimum(bboxes1[2], bboxes2[2])
int_xmax = np.minimum(bboxes1[3], bboxes2[3])
# 计算两个box交集的wh:如果两个box没有交集,那么wh为0(按照计算方式wh为负数,跟0比较取最大值)
int_h = np.maximum(int_ymax - int_ymin, 0.)
int_w = np.maximum(int_xmax - int_xmin, 0.)
# 计算IOU
int_vol = int_h * int_w # 交集面积
vol1 = (bboxes1[2] - bboxes1[0]) * (bboxes1[3] - bboxes1[1]) # bboxes1面积
vol2 = (bboxes2[2] - bboxes2[0]) * (bboxes2[3] - bboxes2[1]) # bboxes2面积
iou = int_vol / (vol1 + vol2 - int_vol) # IOU=交集/并集
return iou
# 第五步:先验框NMS+IOU去重一
# NMS
def bboxes_nms(self,classes, scores, bboxes, nms_threshold=0.5):
keep_bboxes = np.ones(scores.shape, dtype=np.bool)
for i in range(scores.size - 1):
if keep_bboxes[i]:
overlap = self.bboxes_iou(bboxes[i], bboxes[(i + 1):])
keep_overlap = np.logical_or(overlap < nms_threshold, classes[(i + 1):] != classes[i])
keep_bboxes[(i + 1):] = np.logical_and(keep_bboxes[(i + 1):], keep_overlap)
idxes = np.where(keep_bboxes)
return classes[idxes], scores[idxes], bboxes[idxes]
######## 训练部分结束
#________________________________________________________________
# 第三步:图像预处理
# 图像预处理——均值处理
def handle_img(self, img_path):
means = np.array((123., 117., 104.))
self.img = cv2.imread(img_path)
# img = self.img
# img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) - means
# img = cv2.resize(img,self.img_size)
# img = np.expand_dims(img,axis=0)
img = np.expand_dims(cv2.resize(cv2.cvtColor(self.img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) - means,self.img_size),axis=0)
return img
def video_handle_img(self, image):
means = np.array((123., 117., 104.))
self.img = image
# img = self.img
# img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) - means
# img = cv2.resize(img,self.img_size)
# img = np.expand_dims(img,axis=0)
img = np.expand_dims(cv2.resize(cv2.cvtColor(self.img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) - means,self.img_size),axis=0)
return img
# 第六步:画出结果
# 画框
def draw_rectangle(self,img, classes, scores, bboxes, colors, thickness=2):
shape = img.shape
for i in range(bboxes.shape[0]):
bbox = bboxes[i]
# color = colors[classes[i]]
p1 = (int(bbox[0] * shape[0]), int(bbox[1] * shape[1]))
p2 = (int(bbox[2] * shape[0]), int(bbox[3] * shape[1]))
cv2.rectangle(img, p1[::-1], p2[::-1], colors[0], thickness)
# Draw text...
s = '%s/%.3f' % (self.classes[classes[i] - 1], scores[i])
p1 = (p1[0] - 5, p1[1])
cv2.putText(img, s, p1[::-1], cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 0.5, colors[1], 1)
cv2.namedWindow("img", 0)
cv2.resizeWindow("img", 640, 480)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def video_draw_rectangle(self,img, classes, scores, bboxes, colors, thickness=2):
shape = img.shape
for i in range(bboxes.shape[0]):
bbox = bboxes[i]
# color = colors[classes[i]]
p1 = (int(bbox[0] * shape[0]), int(bbox[1] * shape[1]))
p2 = (int(bbox[2] * shape[0]), int(bbox[3] * shape[1]))
cv2.rectangle(img, p1[::-1], p2[::-1], colors[0], thickness)
# Draw text...
s = '%s/%.3f' % (self.classes[classes[i] - 1], scores[i])
p1 = (p1[0] - 5, p1[1])
cv2.putText(img, s, p1[::-1], cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 0.5, colors[1], 1)
cv2.namedWindow("img", 0)
cv2.resizeWindow("img", 640, 480)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
# 第二步:综合:锚框+解码+筛选
def predict(self, locations, predictions):
layers_anchors = []
classes_list = []
scores_list = []
bboxes_list = []
# 锚框
for i, s in enumerate(self.feature_map_size):
anchor_bboxes = self.ssd_anchor_layer(self.img_size, s,
self.anchor_sizes[i],
self.anchor_ratios[i],
self.anchor_steps[i],
self.boxes_len[i])
layers_anchors.append(anchor_bboxes)
for i in range(len(predictions)):
# 解码
d_box = self.ssd_decode(locations[i], layers_anchors[i], self.prior_scaling)
# 筛选
cls, sco, box = self.choose_anchor_boxes(predictions[i], d_box, self.n_boxes[i])
classes_list.append(cls)
scores_list.append(sco)
bboxes_list.append(box)
# tf.concat拼接张量
classes = tf.concat(classes_list, axis=0)
scores = tf.concat(scores_list, axis=0)
bboxes = tf.concat(bboxes_list, axis=0)
return classes, scores, bboxes
import datetime
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 类ssd实例化object:model —— 建立一个类
model = ssd() # 实例类ssd的对象:model
locations, predictions, x = model.set_net() #
classes, scores, bboxes = model.predict(locations, predictions) #
sess = tf.Session() #
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) #
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.restore(sess, 'ssd_vgg_300_weights.ckpt') #
VIDEO = True #
if VIDEO == False:
start_time = datetime.datetime.now()
print(start_time)
img = model.handle_img("image4.jpg") # -------------------------------- -------------
rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = sess.run([classes, scores, bboxes], feed_dict={x: img})
rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = model.bboxes_sort(rclasses, rscores, rbboxes)
rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = model.bboxes_nms(rclasses, rscores, rbboxes)
print(datetime.datetime.now() - start_time)
print(datetime.datetime.now())
model.draw_rectangle(model.img,rclasses,rscores,rbboxes,[[0,0,255],[255,0,0]])
else:
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
if cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = cap.read()
start_time = datetime.datetime.now()
img = model.video_handle_img(frame)
rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = sess.run([classes, scores, bboxes], feed_dict={x: img})
rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = model.bboxes_sort(rclasses, rscores, rbboxes)
rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = model.bboxes_nms(rclasses, rscores, rbboxes)
model.video_draw_rectangle(model.img,rclasses,rscores,rbboxes,[[0,0,255],[255,0,0]])
print(datetime.datetime.now() - start_time)
print(datetime.datetime.now())
if cv2.waitKey(10)==27:
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
'''
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
if cap.isOpened():
ret,frame = cap.read()
cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
cv2.waitKey(1000)
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
'''
Step 7/x 训练部分——数据转换voc转tfrecords
利用ssd-tensorflow的自带tf_convert_data.py及其子模块datasets进行转换。
Usage:
```shell
python tf_convert_data.py \
--dataset_name=pascalvoc \
--dataset_dir=/tmp/pascalvoc \
--output_name=pascalvoc \
--output_dir=/tmp/
```
# Window shell:
```
# 规定pascalvoc,数据集文件夹路径*/*/,指定数据集名称,指定数据集输出地址
python tf_convert_data.py --dataset_name=pascalvoc --dataset_dir=./voc2007/ --output_name=voc_2007_train --output_dir=./TFR_Data
```Step 8/x 训练部分——Trainer
模仿ssd-tensorflow的训练
>> python ssd_train.pyStep 9/x 预测部分——整合1-7步的code
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
class ssd(object):
def __init__(self):
# 初始化一:FM、cls和loc设置
self.feature_map_size = [[38, 38], [19, 19], [10, 10], [5, 5], [3, 3], [1, 1]]
self.classes = ["aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat", "bottle",
"bus", "car", "cat", "chair", "cow", "diningtable",
"dog", "horse", "motorbike", "person", "pottedplant",
"sheep", "sofa", "train", "tvmonitor"]
self.feature_layers = ['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11']
self.img_size = (300, 300)
self.num_classes = 21
self.boxes_len = [4, 6, 6, 6, 4, 4] # FM1每个像素点取4个尺度框,FM2每个像素点取6个尺度框,。。。
self.isL2norm = [True, False, False, False, False, False]
# 初始化二:先验框
# 计算得到:sk:6组min_size和max_size [[h0, w0],[h1, w1],[h2, w2],[h3, w3]]每次取一组两个:[21., 45.]
# 初始化二:先验框
self.anchor_sizes = [[21., 45.], [45., 99.], [99., 153.],[153., 207.],[207., 261.], [261., 315.]]
# 取ar:{1, 2, 1/2, 3, 1/3},对应每层的ar=[[1,2,1/2]]
self.anchor_ratios = [[2, .5], [2, .5, 3, 1. / 3], [2, .5, 3, 1. / 3], [2, .5, 3, 1. / 3], [2, .5], [2, .5]]
# 初始化二:先验框实现FM像素点映射到原图300*300的中心点扩张步长。
# self.anchor_steps = [8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300]
self.anchor_steps = [8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300]
# 初始化三:先验框先验框解码用的缩放比例。
self.prior_scaling = [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2] #特征图先验框缩放比例
# 每层FM的默认框个数值,可计算。
self.n_boxes = [5776, 2166, 600, 150, 36, 4] #8732个
# IOU阈值设置
self.threshold = 0.2
# step 2/x 卷积模块创建,池化模块,随意丢弃模块。
'''
tf.layers.conv2d() 经典输入参数:
f(w*x+b):
x = 输入input;
w = 卷积核个数filter_num,尺寸k_size;
b = 默认,use_bias=True;
* = 卷积步长stride,填充方式padding,卷积模式dilation(标准,扩张等),等等一系列;
f = 激活函数。
'''
def conv2d(self,x,filter,k_size,stride=[1,1],padding='same',dilation=[1,1],activation=tf.nn.relu,scope='conv2d'):
return tf.layers.conv2d(inputs=x, filters=filter, kernel_size=k_size,
strides=stride, dilation_rate=dilation, padding=padding,
name=scope, activation=activation)
#
'''
tf.layers.max_pooling2d(),经典输入参数:
p*x:
p = 尺寸pool_size
x = 输入input
'''
def max_pool2d(self,x, pool_size, stride, scope='max_pool2d'):
return tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=x, pool_size=pool_size, strides=stride, name=scope, padding='same')
#
'''
tf.pad() 对原图进行填充,为了匹配输入输出尺寸
'''
def pad2d(self,x, pad):
return tf.pad(x, paddings=[[0, 0], [pad, pad], [pad, pad], [0, 0]])
# 对第四层模块的卷积进行L2归一化,只对通道数进行归一化,因为比较靠前。。。。???
def l2norm(self, x, trainable=True, scope='L2Normalization'):
n_channels = x.get_shape().as_list()[-1] # 通道数
l2_norm = tf.nn.l2_normalize(x, dim=[3], epsilon=1e-12) # 只对每个像素点在channels上做归一化
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
gamma = tf.get_variable("gamma", shape=[n_channels, ], dtype=tf.float32,
trainable=trainable)
return l2_norm * gamma
# loc 和 cls 通过卷积进行计算 【num_classes和box_num】
def ssd_prediction(self, x, num_classes, box_num, isL2norm, scope='multibox'):
reshape = [-1] + x.get_shape().as_list()[1:-1] # 去除第一个和最后一个得到shape
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
if isL2norm:
x = self.l2norm(x) # 进行
print(x)
# 预测位置loc --》 坐标和大小 回归
location_pred = self.conv2d(x, filter=box_num * 4, k_size=[3,3], activation=None,scope='conv_loc')
location_pred = tf.reshape(location_pred, reshape + [box_num, 4])
# 预测类别cls --> 分类 sofrmax
class_pred = self.conv2d(x, filter=box_num * num_classes, k_size=[3,3], activation=None, scope='conv_cls')
class_pred = tf.reshape(class_pred, reshape + [box_num, num_classes])
print(location_pred, class_pred)
return location_pred, class_pred
# 第一步:网络构建
def set_net(self,x=None):
# 列表放FM
check_points = {} # 字典存储{'key':value}
predictions = [] # 列表存储[value]
locations = [] # 列表存储[value]
with tf.variable_scope('ssd_300_vgg'):
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[None,300,300,3])
#b1
net = self.conv2d(x,filter=64,k_size=[3,3],scope='conv1_1')
net = self.conv2d(net,64,[3,3],scope='conv1_2')
net = self.max_pool2d(net,pool_size=[2,2],stride=[2,2],scope='pool1')
#b2
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=128, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv2_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2_2')
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool2')
#b3
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=256, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv3_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3_3')
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool3')
#b4
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=512, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv4_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4_3')
print("block4_output", net)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------4
check_points['block4'] = net
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[2, 2], stride=[2, 2], scope='pool4')
#print('pool4', net)
#b5
net = self.conv2d(net, filter=512, k_size=[3, 3], scope='conv5_1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5_2')
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5_3')
#print('conv5_3',net)
net = self.max_pool2d(net, pool_size=[3, 3], stride=[1, 1], scope='pool5')
#print('pool5',net)
#b6
net = self.conv2d(net,1024,[3,3],dilation=[6,6],scope='conv6')
#print('conv6',net)
#b7
net = self.conv2d(net,1024,[1,1],scope='conv7')
print("block7_output", net)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------7
check_points['block7'] = net
#b8],scope='conv8_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [1, 1], scope='conv8_1x1')
#print('conv8_3',net)
# 该层要进行填补
print('pad2d-start',net)
net = self.pad2d(net, 1)
print('pad2d-end',net)
net = self.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], [2, 2], scope='conv8_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------8
print("block8_output", net)
check_points['block8'] = net
#b9
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv9_1x1')
net = self.pad2d(net, 1)
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], [2, 2], scope='conv9_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------9
print("block9_output", net)
check_points['block9'] = net
#b10
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv10_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv10_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------10
print("block10_output", net)
check_points['block10'] = net
#b11
net = self.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv11_1x1')
net = self.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv11_3x3', padding='valid')
# -------------------------------------------------------------------11
print("block11_output", net)
check_points['block11'] = net
print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
for i,j in enumerate(self.feature_layers):
loc, cls = self.ssd_prediction(
x = check_points[j],
num_classes = self.num_classes,
box_num = self.boxes_len[i],
isL2norm = self.isL2norm[i],
scope = j + '_box'
)
predictions.append(tf.nn.softmax(cls))
locations.append(loc)
print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
print(locations, predictions)
return locations, predictions, x
#print("————————————————————————————————————————————————")
#print(check_points)
########## 先验框部分开始
# 第二步:分点:锚框
# 先验框生成
def ssd_anchor_layer(self,img_size, feature_map_size, anchor_size, anchor_ratio, anchor_step, box_num, offset=0.5):
# 提取FM的每个坐标
y, x = np.mgrid[0:feature_map_size[0],0:feature_map_size[1]]
# 映射回原图,映射到原图 anchor_step = SRC[300*300]/FM1[38*38] = 7.89 = 8
# 返回FM1每个像素点坐标对于的原图坐标,归一化值(0-1)之间的比例值。
y = (y.astype(np.float32) + offset) * anchor_step /img_size[0]
x = (x.astype(np.float32) + offset) * anchor_step /img_size[1]
y = np.expand_dims(y, axis=-1)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=-1)
# 有两个默认的长宽比为1,但是大小不同的正方形先验框:计算两个长宽比为1的h、w。——根据先验框个数来确定的,多少个先验框就有多少个长宽。
h = np.zeros((box_num,), np.float32) #类型统一,才可以相乘相除——————修改一
w = np.zeros((box_num,), np.float32)
# 第一个:h[0]、w[0]:先验框
h[0] = anchor_size[0] /img_size[0]
w[0] = anchor_size[0] /img_size[0]
# 第二个:h[1]、w[1]
h[1] = (anchor_size[0] * anchor_size[1]) ** 0.5 / img_size[0] # **0.5相当于sqrt开根号,
w[1] = (anchor_size[0] * anchor_size[1]) ** 0.5 / img_size[1]
# 剩下的长宽比按公式来计算。
for i, j in enumerate(anchor_ratio):
h[i + 2] = anchor_size[0] / img_size[0] / (j ** 0.5)
w[i + 2] = anchor_size[0] / img_size[1] * (j ** 0.5)
return y, x, h, w
# 第二步:分点:解码
# 解码网络返回box[x0, y0, x1, y1] -》先验框通过平移和缩放接近真实框。其中 prior_scaling 为平移、尺度因子
def ssd_decode(self, location, box, prior_scaling):
y_a, x_a, h_a, w_a = box
# 平移
cx = location[:, :, :, :, 0] * w_a * prior_scaling[0] + x_a #location最后一个维度有4,表示4个值:x,y,w,h
cy = location[:, :, :, :, 1] * h_a * prior_scaling[1] + y_a
# 缩放
w = w_a * tf.exp(location[:, :, :, :, 2] * prior_scaling[2])
h = h_a * tf.exp(location[:, :, :, :, 3] * prior_scaling[3])
# 计算框的左上和右下坐标:box[x0, y0, x1, y1]
bboxes = tf.stack([cy - h / 2.0, cx - w / 2.0, cy + h / 2.0, cx + w / 2.0], axis=-1)
print(bboxes)
return bboxes
# 第二步:分点:筛选
# 先验框筛选_由于先验框太多了,需要进行减少——将总8732的6层,每层n_box
def choose_anchor_boxes(self, predictions, anchor_box, n_box):
anchor_box = tf.reshape(anchor_box, [n_box, 4])
prediction = tf.reshape(predictions, [n_box, 21])
prediction = prediction[:, 1:]
classes = tf.argmax(prediction, axis=1) + 1 # 20+1
scores = tf.reduce_max(prediction, axis=1) # 当得分大于阈值,保留锚框,一个先验框对应一个类别
filter_mask = scores > self.threshold
# tf.boolean_mask(a,b)用来过滤概率值比较低的锚盒,b为过来条件【filter_mask = scores > self.threshold】b的制作规则是要用逻辑表达式(>或者<)生成布尔值
classes = tf.boolean_mask(classes, filter_mask)
scores = tf.boolean_mask(scores, filter_mask)
anchor_box = tf.boolean_mask(anchor_box, filter_mask)
return classes, scores, anchor_box
######### 训练部分开始
# 第四步:先验框分数排序,取top_k个
# 先验框分数排序,取前400
def bboxes_sort(self,classes, scores, bboxes, top_k=400):
idxes = np.argsort(-scores)
classes = classes[idxes][:top_k]
scores = scores[idxes][:top_k]
bboxes = bboxes[idxes][:top_k]
return classes, scores, bboxes
# 计算IOU
# 第五步:先验框NMS+IOU去重二
# IOU
def bboxes_iou(self,bboxes1, bboxes2):
bboxes1 = np.transpose(bboxes1)
bboxes2 = np.transpose(bboxes2)
# 计算两个box的交集:交集左上角的点取两个box的max,交集右下角的点取两个box的min
int_ymin = np.maximum(bboxes1[0], bboxes2[0])
int_xmin = np.maximum(bboxes1[1], bboxes2[1])
int_ymax = np.minimum(bboxes1[2], bboxes2[2])
int_xmax = np.minimum(bboxes1[3], bboxes2[3])
# 计算两个box交集的wh:如果两个box没有交集,那么wh为0(按照计算方式wh为负数,跟0比较取最大值)
int_h = np.maximum(int_ymax - int_ymin, 0.)
int_w = np.maximum(int_xmax - int_xmin, 0.)
# 计算IOU
int_vol = int_h * int_w # 交集面积
vol1 = (bboxes1[2] - bboxes1[0]) * (bboxes1[3] - bboxes1[1]) # bboxes1面积
vol2 = (bboxes2[2] - bboxes2[0]) * (bboxes2[3] - bboxes2[1]) # bboxes2面积
iou = int_vol / (vol1 + vol2 - int_vol) # IOU=交集/并集
return iou
# 第五步:先验框NMS+IOU去重一
# NMS
def bboxes_nms(self,classes, scores, bboxes, nms_threshold=0.5):
keep_bboxes = np.ones(scores.shape, dtype=np.bool)
for i in range(scores.size - 1):
if keep_bboxes[i]:
overlap = self.bboxes_iou(bboxes[i], bboxes[(i + 1):])
keep_overlap = np.logical_or(overlap < nms_threshold, classes[(i + 1):] != classes[i])
keep_bboxes[(i + 1):] = np.logical_and(keep_bboxes[(i + 1):], keep_overlap)
idxes = np.where(keep_bboxes)
return classes[idxes], scores[idxes], bboxes[idxes]
######## 训练部分结束
#________________________________________________________________
# 第三步:图像预处理
# 图像预处理——均值处理
def handle_img(self, img_path):
means = np.array((123., 117., 104.))
self.img = cv2.imread(img_path)
# img = self.img
# img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) - means
# img = cv2.resize(img,self.img_size)
# img = np.expand_dims(img,axis=0)
img = np.expand_dims(cv2.resize(cv2.cvtColor(self.img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) - means,self.img_size),axis=0)
return img
def video_handle_img(self, image):
means = np.array((123., 117., 104.))
self.img = image
# img = self.img
# img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) - means
# img = cv2.resize(img,self.img_size)
# img = np.expand_dims(img,axis=0)
img = np.expand_dims(cv2.resize(cv2.cvtColor(self.img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) - means,self.img_size),axis=0)
return img
# 第六步:画出结果
# 画框
def draw_rectangle(self,img, classes, scores, bboxes, colors, thickness=2):
shape = img.shape
for i in range(bboxes.shape[0]):
bbox = bboxes[i]
# color = colors[classes[i]]
p1 = (int(bbox[0] * shape[0]), int(bbox[1] * shape[1]))
p2 = (int(bbox[2] * shape[0]), int(bbox[3] * shape[1]))
cv2.rectangle(img, p1[::-1], p2[::-1], colors[0], thickness)
# Draw text...
s = '%s/%.3f' % (self.classes[classes[i] - 1], scores[i])
p1 = (p1[0] - 5, p1[1])
cv2.putText(img, s, p1[::-1], cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 0.5, colors[1], 1)
cv2.namedWindow("img", 0)
cv2.resizeWindow("img", 640, 480)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def video_draw_rectangle(self,img, classes, scores, bboxes, colors, thickness=2):
shape = img.shape
for i in range(bboxes.shape[0]):
bbox = bboxes[i]
# color = colors[classes[i]]
p1 = (int(bbox[0] * shape[0]), int(bbox[1] * shape[1]))
p2 = (int(bbox[2] * shape[0]), int(bbox[3] * shape[1]))
cv2.rectangle(img, p1[::-1], p2[::-1], colors[0], thickness)
# Draw text...
s = '%s/%.3f' % (self.classes[classes[i] - 1], scores[i])
p1 = (p1[0] - 5, p1[1])
cv2.putText(img, s, p1[::-1], cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 0.5, colors[1], 1)
cv2.namedWindow("img", 0)
cv2.resizeWindow("img", 640, 480)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
# 第二步:综合:锚框+解码+筛选
def predict(self, locations, predictions):
layers_anchors = []
classes_list = []
scores_list = []
bboxes_list = []
# 锚框
for i, s in enumerate(self.feature_map_size):
anchor_bboxes = self.ssd_anchor_layer(self.img_size, s,
self.anchor_sizes[i],
self.anchor_ratios[i],
self.anchor_steps[i],
self.boxes_len[i])
layers_anchors.append(anchor_bboxes)
for i in range(len(predictions)):
# 解码
d_box = self.ssd_decode(locations[i], layers_anchors[i], self.prior_scaling)
# 筛选
cls, sco, box = self.choose_anchor_boxes(predictions[i], d_box, self.n_boxes[i])
classes_list.append(cls)
scores_list.append(sco)
bboxes_list.append(box)
# tf.concat拼接张量
classes = tf.concat(classes_list, axis=0)
scores = tf.concat(scores_list, axis=0)
bboxes = tf.concat(bboxes_list, axis=0)
return classes, scores, bboxes
import datetime
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 类ssd实例化object:model —— 建立一个类
model = ssd() # 实例类ssd的对象:model
locations, predictions, x = model.set_net() #
classes, scores, bboxes = model.predict(locations, predictions) #
sess = tf.Session() #
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) #
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.restore(sess, 'ssd_vgg_300_weights.ckpt') #
VIDEO = True #
if VIDEO == False:
start_time = datetime.datetime.now()
print(start_time)
img = model.handle_img("image4.jpg") # -------------------------------- -------------
rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = sess.run([classes, scores, bboxes], feed_dict={x: img})
rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = model.bboxes_sort(rclasses, rscores, rbboxes)
rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = model.bboxes_nms(rclasses, rscores, rbboxes)
print(datetime.datetime.now() - start_time)
print(datetime.datetime.now())
model.draw_rectangle(model.img,rclasses,rscores,rbboxes,[[0,0,255],[255,0,0]])
else:
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
if cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = cap.read()
start_time = datetime.datetime.now()
img = model.video_handle_img(frame)
rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = sess.run([classes, scores, bboxes], feed_dict={x: img})
rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = model.bboxes_sort(rclasses, rscores, rbboxes)
rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = model.bboxes_nms(rclasses, rscores, rbboxes)
model.video_draw_rectangle(model.img,rclasses,rscores,rbboxes,[[0,0,255],[255,0,0]])
print(datetime.datetime.now() - start_time)
print(datetime.datetime.now())
if cv2.waitKey(10)==27:
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
'''
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
if cap.isOpened():
ret,frame = cap.read()
cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
cv2.waitKey(1000)
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
'''
参考
视频:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av43996494/?p=1
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av45571739
https://space.bilibili.com/5462468?spm_id_from=333.788.b_765f7570696e666f.2
github:
https://github.com/bbaibowen/computer-vision
DL500问
https://github.com/bbaibowen/DeepLearning-500-questions