JPEG原理分析及解码调试
JPEG是国际标准化组织制定的一种压缩标准,用于图像,后缀为.jpg或.jpeg
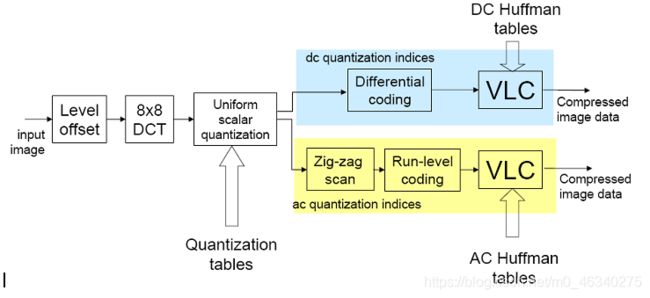
JPEG编解码原理
- 零电平偏置:将所有像素的值减去128
- DCT变化:将经过偏置的图像分成8*8的块进行处理,直流系数在该块的左上角,该操作能实现能量集中化(能量主要集中在低频,高频能量很小)和去相关
- 量化:根据人眼视觉特性来设计量化矩阵,对低频分量人眼较为敏感,故量化较为细致;对高频分量人眼不敏感,故粗量化,此举可以有效降低视觉冗余
- DC系数:通常两个相邻块的DC系数有一定相关性即两个块的变化不大,并且本身数值较大,针对此特性采用了DPCM编码
- AC系数:之字形扫描(zigzag)后进行游程编码并在结束加上EOB即结束码
文件格式
Segment 的组织形式
JPEG 在文件中以Segment 的形式组织,它具有以下特点:
- 均以 0xFF 开始,后跟 1 byte 的 Marker 和 2 byte 的 Segment length(包含表示Length 本身所占用的 2 byte,不含“0xFF” + “Marker” 所占用的 2 byte);
- 采用 Motorola 序(相对于Intel 序),即保存时高位在前,低位在后;
- Data 部分中,0xFF 后若为 0x00,则跳过此字节不予处理;
JPEG 的 Segment Marker
个别marker下字段的一些解释
APP0
- 数据长度(2bytes),即该segment总长度
- 标识符(5bytes),为固定值,字符串“JFIF0”
- 版本号(2bytes)
- 密度单位(1byte)只有0(无单位),1(点数/英寸),2(点数/厘米)三中取值
- x方向像素密度(2bytes)
- y方向像素密度(2bytes)
- 缩略图水平像素数目(1byte)
- 缩略图垂直像素数目(1byte)
- 缩略图RGB位图(3*nbytes):缩略图的rgb数据
DQT
- 数据长度(2bytes),即该segment总长度
- 精度以及量化表ID(1byte):高4位表示精度,0代表8bit,1代表16bit;低4位表示表ID,取值范围0~3,即最多有4张量化表
- 数据(length-2-1 bytes)
SOF0
- 数据长度(2bytes),即该segment总长度
- 精度(1byte)
- 高(2bytes)
- 宽(2bytes)
- 颜色分量数(1byte):三个可选值,但JFIF中使用YCbCr,所以这里取3
- 颜色分量信息(颜色分量数*3bytes,即9bytes):每个分量的三个字节分别依次表示,颜色分量(1byte),水平垂直采样因子(高4水平,低4垂直,共1byte),量化表id(1byte)
DHT
- 数据长度(2bytes),即该segment总长度
- huffman表(length-2 bytes):内容如下
- Huffman 表 ID 号和类型(1byte):高 4 位为表的类型,0:DC 直流;1:AC 交流 可以看出这里是直流表;低四位为 Huffman 表 ID。
- 不同长度 Huffman 的码字数量(16bytes):每个字节代表从长度为 1 到长度为 16 的码字的个数
- 编码内容
SOS
- 数据长度(2bytes),即该segment总长度
- 颜色分量数(1byte)
- 颜色分量信息(颜色分量数*2bytes):颜色分量ID(1byte),使用的huffman树的ID(高4位为DC,低4位AC,共1byte)
- 压缩图像数据: 谱选择开始 (1byte) 固定值 0x00,谱选择结束 (1byte) 固定值 0x3F,谱选择 (1byte) 在基本 JPEG 中总为 00
huffman码表的储存说明
1 在标记段DHT内,包含了一个或者多个的哈夫曼表。对于单一个哈夫曼表,应该包括了三部分:
- 哈夫曼表ID和表类型
这个字节的值为一般只有四个0x00、0x01、0x10、0x11。
0x00表示DC直流0号表;
0x01表示DC直流1号表;
0x10表示AC交流0号表;
0x11表示AC交流1号表。 - 不同位数的码字数量
JPEG文件的哈夫曼编码只能是116位。这个字段的16个字节分别表示116位的编码码字在哈夫曼树中的个数。 - 编码内容
这个字段记录了哈夫曼树中各个叶子结点的权。所以,上一字段(不同位数的码字数量)的16个数值之和就应该是本字段的长度,也就是哈夫曼树中叶子结点个数。
举个栗子(来自老师)

JPEG 的解码流程
- 读取文件
- 解析 Segment Marker
- 解析 SOI
- 解析APP0
(1)检查标识“JFIF”及版本
(2) 得到一些参数 - 解析DQT
(1)得到量化表长度(可能包含多张量化表)
(2)得到量化表的精度
(3)得到及检查量化表的序号(只能是 0 —— 3)
(4)得到量化表内容(64 个数据) - 解析 SOF0
(1) 得到每个 sample 的比特数、长宽、颜色分量数
(2)得到每个颜色分量的 ID、水平采样因子、垂直采样因子、使用的量化表序号(与DQT 中序号对应) - 解析DHT
(1) 得到Huffman 表的类型(AC、DC)、序号
(2)依据数据重建Huffman 表 - 解析 SOS
(1) 得到解析每个颜色分量的DC、AC 值所使用的Huffman 表序号(与 DHT
中序号对应)
-
依据每个分量的水平、垂直采样因子计算 MCU 的大小,并得到每个 MCU 中 8*8
宏块的个数 -
对每个 MCU 解码(依照各分量水平、垂直采样因子对 MCU 中每个分量宏块解码)
- 对每个宏块进行 Huffman 解码,得到 DCT 系数
- 对每个宏块的DCT 系数进行 IDCT,得到Y、Cb、Cr
- 遇到 Segment Marker RST 时,清空之前的 DC DCT 系数
- 解析到 EOI,解码结束
- 将 Y、Cb、Cr 转化为需要的色彩空间并保存。
代码分析
主函数如下
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int output_format = TINYJPEG_FMT_YUV420P;
char *output_filename, *input_filename;
clock_t start_time, finish_time;
unsigned int duration;
int current_argument;
int benchmark_mode = 0;//上面都是一些定义和初始化
#if TRACE
p_trace=fopen(TRACEFILE,"w");
if (p_trace==NULL)
{
printf("trace file open error!");
}
#endif//当trace为真时运行上面的if
if (argc < 3)
usage();
current_argument = 1;
while (1)
{
if (strcmp(argv[current_argument], "--benchmark")==0)
benchmark_mode = 1;
else
break;
current_argument++;
}
if (argc < current_argument+2)
usage();
input_filename = argv[current_argument];
if (strcmp(argv[current_argument+1],"yuv420p")==0)
output_format = TINYJPEG_FMT_YUV420P;
else if (strcmp(argv[current_argument+1],"rgb24")==0)
output_format = TINYJPEG_FMT_RGB24;
else if (strcmp(argv[current_argument+1],"bgr24")==0)
output_format = TINYJPEG_FMT_BGR24;
else if (strcmp(argv[current_argument+1],"grey")==0)
output_format = TINYJPEG_FMT_GREY;
else
exitmessage("Bad format: need to be one of yuv420p, rgb24, bgr24, grey\n");
output_filename = argv[current_argument+2];
start_time = clock();
if (benchmark_mode)
load_multiple_times(input_filename, output_filename, output_format);
else//不是benchmarkmode的时候,运行下面这行代码
convert_one_image(input_filename, output_filename, output_format);
finish_time = clock();
duration = finish_time - start_time;
snprintf(error_string, sizeof(error_string),"Decoding finished in %u ticks\n", duration);
#if TRACE
fclose(p_trace);
#endif
return 0;
}
不难看出,convert_one_image这个函数起到了关键的作用,代码如下
/*
* Load one jpeg image, and decompress it, and save the result.
*/
int convert_one_image(const char *infilename, const char *outfilename, int output_format)
{
FILE *fp;
unsigned int length_of_file;
unsigned int width, height;
unsigned char *buf;
struct jdec_private *jdec;
unsigned char *components[3];//一些定义
/* Load the Jpeg into memory */
fp = fopen(infilename, "rb");//打开文件
if (fp == NULL)
exitmessage("Cannot open filename\n");
length_of_file = filesize(fp);//得到文件的长度
buf = (unsigned char *)malloc(length_of_file + 4);//分配内存
if (buf == NULL)
exitmessage("Not enough memory for loading file\n");
fread(buf, length_of_file, 1, fp);//读入数据
fclose(fp);
/* Decompress it */
jdec = tinyjpeg_init();//初始化结构体,该结构体的分析见下文
if (jdec == NULL)
exitmessage("Not enough memory to alloc the structure need for decompressing\n");
//对parseheader进行解码
if (tinyjpeg_parse_header(jdec, buf, length_of_file)<0)
exitmessage(tinyjpeg_get_errorstring(jdec));
/* Get the size of the image */
tinyjpeg_get_size(jdec, &width, &height);//获取图像的大小
snprintf(error_string, sizeof(error_string),"Decoding JPEG image...\n");
//解码
if (tinyjpeg_decode(jdec, output_format) < 0)
exitmessage(tinyjpeg_get_errorstring(jdec));
/*
* Get address for each plane (not only max 3 planes is supported), and
* depending of the output mode, only some components will be filled
* RGB: 1 plane, YUV420P: 3 planes, GREY: 1 plane
*/
tinyjpeg_get_components(jdec, components);
/* Save it */
switch (output_format)//根据想要的格式输出文件
{
case TINYJPEG_FMT_RGB24:
case TINYJPEG_FMT_BGR24:
write_tga(outfilename, output_format, width, height, components);
break;
case TINYJPEG_FMT_YUV420P:
write_yuv(outfilename, width, height, components);
break;
case TINYJPEG_FMT_GREY:
write_pgm(outfilename, width, height, components);
break;
}
/* Only called this if the buffers were allocated by tinyjpeg_decode() */
tinyjpeg_free(jdec);
/* else called just free(jdec); */
free(buf);
return 0;
}
结构体的分析
huffman table
建立一个便于查找的快速查找表,快表里找不到就用慢表
{
/* Fast look up table, using HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS bits we can have directly the symbol,
* if the symbol is <0, then we need to look into the tree table */
* 快速查找表,利用HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS我们可以直接找到符号,如果符号小于0,我们就需要取树表里找了
short int lookup[HUFFMAN_HASH_SIZE];
/* code size: give the number of bits of a symbol is encoded */
给出符号对应的码长
unsigned char code_size[HUFFMAN_HASH_SIZE];
/* some place to store value that is not encoded in the lookup table
* FIXME: Calculate if 256 value is enough to store all values
*/
储存一些快速表里没有存的码字
uint16_t slowtable[16-HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS][256];
};
component
用来储存每一个8*8块的信息,会不断更新,但是会保留一些数据便于解码
struct component
{
unsigned int Hfactor;//水平采样因子
unsigned int Vfactor;//垂直采样因子
float *Q_table; /* Pointer to the quantisation table to use */指向量化表的指针
struct huffman_table *AC_table;指向交流表的指针
struct huffman_table *DC_table;指向直流表的指针
short int previous_DC; /* Previous DC coefficient */上以块的dc系数
short int DCT[64]; /* DCT coef */dct系数组
#if SANITY_CHECK
unsigned int cid;
#endif
};
jdec_private
这个结构体在程序中的使用相当多,大部分函数里都有它的影子,它起到的作用是储存一些图像信息和表
struct jdec_private
{
/* Public variables */
uint8_t *components[COMPONENTS];//yuv分量的数组
unsigned int width, height; /* Size of the image */
unsigned int flags;
/* Private variables */
const unsigned char *stream_begin, *stream_end;
unsigned int stream_length;//文件流的长,开始,结束
const unsigned char *stream; /* Pointer to the current stream */
unsigned int reservoir, nbits_in_reservoir;
struct component component_infos[COMPONENTS];
float Q_tables[COMPONENTS][64]; /* quantization tables *///量化表
struct huffman_table HTDC[HUFFMAN_TABLES]; /* DC huffman tables */dc系数码表
struct huffman_table HTAC[HUFFMAN_TABLES]; /* AC huffman tables */ac系数码表
int default_huffman_table_initialized;
int restart_interval;
int restarts_to_go; /* MCUs left in this restart interval */剩余块
int last_rst_marker_seen; /* Rst marker is incremented each time */
/* Temp space used after the IDCT to store each components */
uint8_t Y[64*4], Cr[64], Cb[64];//反量化之后存放信息的数组
jmp_buf jump_state;
/* Internal Pointer use for colorspace conversion, do not modify it !!! */
uint8_t *plane[COMPONENTS];
};
实验结果
输出YUV文件
write_yuv函数已经修改过,可输出yuv文件
static void write_yuv(const char *filename, int width, int height, unsigned char **components)
{
FILE *F;
char temp[1024];
snprintf(temp, 1024, "%s.Y", filename);
F = fopen(temp, "wb");
fwrite(components[0], width, height, F);
fclose(F);
snprintf(temp, 1024, "%s.U", filename);
F = fopen(temp, "wb");
fwrite(components[1], width*height/4, 1, F);
fclose(F);
snprintf(temp, 1024, "%s.V", filename);
F = fopen(temp, "wb");
fwrite(components[2], width*height/4, 1, F);
fclose(F);
snprintf(temp, 1024, "%s.YUV", filename);
F = fopen(temp,"wb");
fwrite(components[0], width, height, F);
fwrite(components[1], width / 2, height / 2, F);
fwrite(components[2], width / 2, height / 2, F);
fclose(F);
}
这次用的图像如下,特别酷炫

我们输出的yuv文件预览如下,怎么调都显示不全[捂脸]

trace
首先定义trace为1
其中的内容会生成 到trace_jpeg.txt.中
可以看到,这里都是一些较为重要的信息
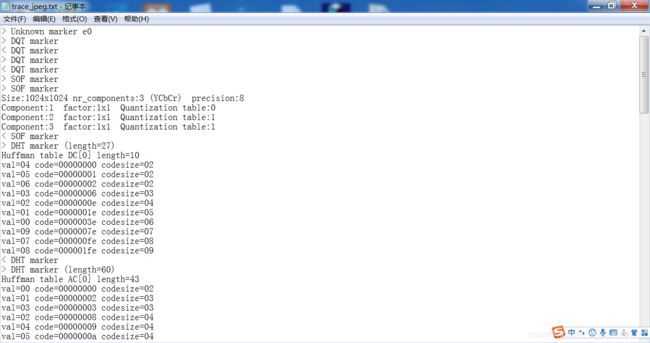
对这里的输出进行了一些小的改动,让程序不输出DHTmarker,查看一下结果
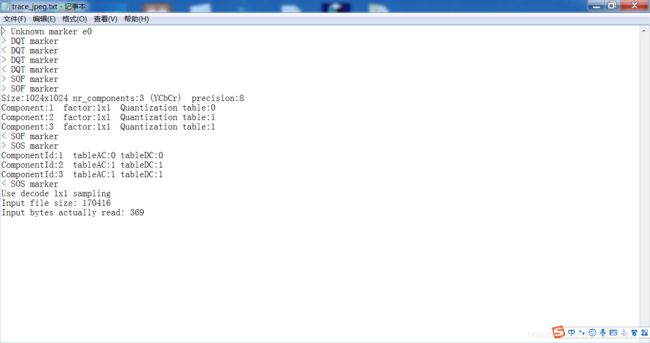
可以看到,确实没有输出,trace修改成功
输出量化矩阵和huffman码表
在主函数中添加如下代码,打开几个文件
fopen_s(&codetab, "codetab.txt", "ab");
fopen_s(&DC_ima, "DC_ima.yuv", "ab");
fopen_s(&AC_ima, "AC_ima.yuv", "ab");
fopen_s(&q_mat, "q_mat.txt", "ab");
由于要输出huffman表,在build_huffman_table()中添加如下代码
fprintf(codetab,"val=%2.2x code=%8.8x codesize=%2.2d \n",val,code,code_size);
在parse_DHT中添加
fprintf(codetab,"%s \n",(index&0xf0)?"AC":"DC");
要输出量化表,要在parse_DQT添加
fprintf(q_mat, "quantization_table: \n");
还要在build_quantization_table添加
#if TRACE
if (j == 7) { fprintf(q_mat, "\n"); fflush(q_mat); }
fprintf(q_mat, "%d\t",ref_table[*zz]);
fflush(q_mat);
#endif
输出的txt文件如下,很奇怪,明明有输出\n,但是文件中并没有换行,导致很乱

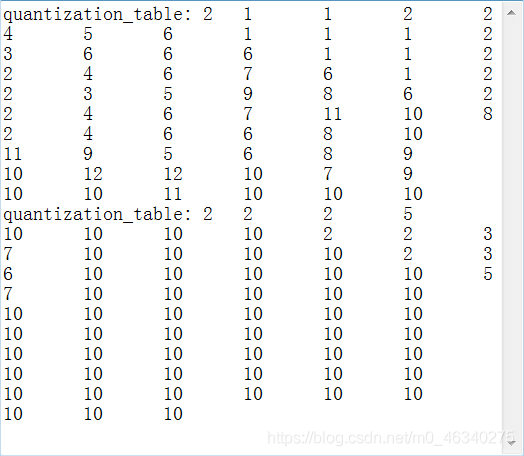
但其实huffman码表在trace_jpeg.txt里都有(嘿嘿嘿)