实验五-jpg解码
一、实验原理
1.jpg编码
JPEG(Joint Photographic Experts Group),文件后缀名为.jpg,.jpeg,是一种常用的图像文件格式。采用有损压缩方式去除冗余的图像和彩色数据,在获得极高压缩率的同时能展现十分丰富生动的图像。
编码过程如图示:
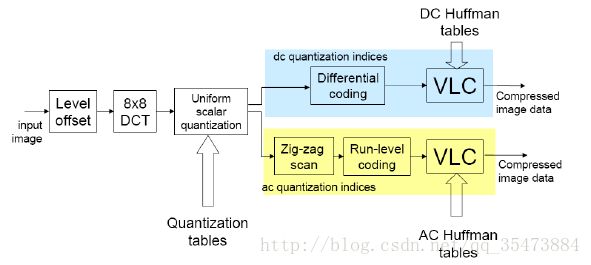
解码为编码的逆过程。
2.jpg文件格式
jpeg文件以Segment的形式组织,均以0xFF开始,后面跟1字节的Marker和2字节的Segment Length(包含Length本身长度,不包括Marker和0xFF)。
常用的Marker有:
1)SOI(start of image)0xFFDB
所有的jpeg文件必须以SOI开始。
2)APPn(reserved for application use)0xFFE0-0xFFEF
eg:FFE0 运用程序保留标记0
FF E0 00 10 4A 46 49 46 00 01 01 01 00 48 00 48 00 00
length 2byte:0X0010=16
标识符:4A 46 49 46 00 –JFIF
Version 2byte:0101
Units 1byte:01 –X,Y are dots per inch
Xdensity 2byte:0x0048 –水平方向点密度
Ydensity 2byte:0x0048 –垂直方向点密度
缩略图水平像素数目 1byte :0x00
缩略图垂直像素数目 1byte :0x00
缩略图24bitRGB 数据:没有缩略图
3)DQT(Define Quantization Table) 0xFFDB

length 2byte:0x 00 43
QT信息 1byte 0-3位:QT号(0-3,可能有4张量化表,亮度,色度,可能会有rgb各一张量化表) 4-7位:QT精度(0:8bit,1:16bit)
QT实际数据:nbyte n=64*QT精度的字节数。(对于8*8的宏块来说,共有8*8=64个量化系数)
需要注意的是,jpeg文件中的量化表是按之字形扫描的格式存的,要得到真正的量化表还需要反之字形扫描;
static const unsigned char zigzag[64] =
{
0, 1, 5, 6, 14, 15, 27, 28,
2, 4, 7, 13, 16, 26, 29, 42,
3, 8, 12, 17, 25, 30, 41, 43,
9, 11, 18, 24, 31, 40, 44, 53,
10, 19, 23, 32, 39, 45, 52, 54,
20, 22, 33, 38, 46, 51, 55, 60,
21, 34, 37, 47, 50, 56, 59, 61,
35, 36, 48, 49, 57, 58, 62, 63
};
static void build_quantization_table(float *qtable, const unsigned char *ref_table)
{
/* Taken from libjpeg. Copyright Independent JPEG Group's LLM idct.
* For float AA&N IDCT method, divisors are equal to quantization
* coefficients scaled by scalefactor[row]*scalefactor[col], where
* scalefactor[0] = 1
* scalefactor[k] = cos(k*PI/16) * sqrt(2) for k=1..7
* We apply a further scale factor of 8.
* What's actually stored is 1/divisor so that the inner loop can
* use a multiplication rather than a division.
*/
int i, j;
static const double aanscalefactor[8] = {
1.0, 1.387039845, 1.306562965, 1.175875602,
1.0, 0.785694958, 0.541196100, 0.275899379
};
const unsigned char *zz = zigzag;
for (i=0; i<8; i++) {
for (j=0; j<8; j++) {
*qtable++ = ref_table[*zz++] * aanscalefactor[i] * aanscalefactor[j];
}
}
}解析到的量化表为
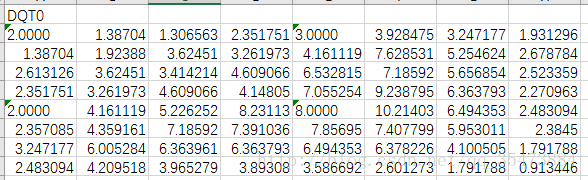
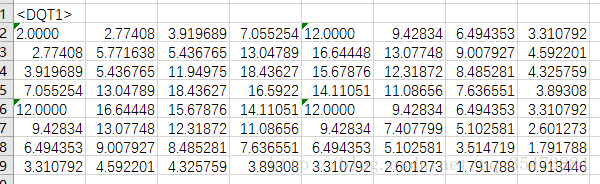
4)SOF(start of Frame)0xFFC0
eg:FF C0 00 11 08 0F C0 0B D0 03 01 22 00 02 11 01 03 11 01
length 2byte :0x11—17byte
图像精度(每个数据样本的位数)1byte:0x08
图像高度 2byte:0x0FC0=4032
图像宽度 2byte : 0X0BD0=3024
颜色分量数 1byte:03(ycrcb)
颜色分量id 1byte:01—-y
采样率 1byte :4-7位水平采样率:2 0-3位垂直采样率:2
量化表号 1byte:00
颜色分量id 1byte:02—-U
采样率 1byte :位水平采样率:1 垂直采样率:1
量化表号 1byte:01
颜色分量id 1byte:03—–V
采样率 1byte :水平采样率:1 垂直采样率:1
量化表号 1byte:01
5)DHT,define Huffman Table 0xFFC4
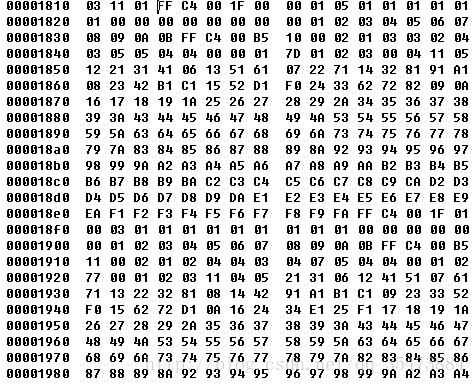
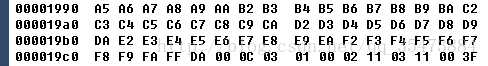
length 2byte:0x001f—31byte
huffman表信息 1byte:4-7位huffman表类型(0:Dc,1:Ac):0
0-3位huffman表id:0
huffmanTableIndex:16byte 1-16位码长的码字各有多少个
huffman权值信息:nbyte(n为huffmanTableIndex的和,表示每个码字的权值)
6)SOS(start of Scan)0xFFDA
eg:FF DA 00 0C 03 01 00 02 11 03 11 03 3F 00
length 2byte:0x000c—12
颜色分量数 1byte:0x03 –和SOF中的颜色分量数相同
颜色分量信息 6byte:每个颜色分量占2byte
颜色分量id 1byte:0x01
颜色分量使用的huffman编号:0-3位直流分量使用的表号;4-7位交流分量使用的表号
y: 01 dc–0 ac–0
cb:02 dc–1 ac–1
cr: 03 dc–1 ac–1
压缩图像数据 3byte:
谱选择开始 1byte 固定值0x00
谱选择结束 1byte 固定值0x3f
谱选择 1byte 在基本jpeg中总为00
7)EOI end of image 0xFFD9
结束符,jpeg文件中固定为EOI。
3.解码数据结构
struct component
{
unsigned int Hfactor; //水平采样因子
unsigned int Vfactor;
float *Q_table; /* Pointer to the quantisation table to use */
struct huffman_table *AC_table;
struct huffman_table *DC_table;
short int previous_DC; /* Previous DC coefficient */
short int DCT[64]; /* DCT coef */
#if SANITY_CHECK
unsigned int cid;
#endif
};struct jdec_private
{
/* Public variables */
uint8_t *components[COMPONENTS];
unsigned int width, height; /* Size of the image */
unsigned int flags;
/* Private variables */
const unsigned char *stream_begin, *stream_end;
unsigned int stream_length;
const unsigned char *stream; /* Pointer to the current stream */
unsigned int reservoir, nbits_in_reservoir;
struct component component_infos[COMPONENTS];
float Q_tables[COMPONENTS][64]; /* quantization tables */
struct huffman_table HTDC[HUFFMAN_TABLES]; /* DC huffman tables */
struct huffman_table HTAC[HUFFMAN_TABLES]; /* AC huffman tables */
int default_huffman_table_initialized;
int restart_interval;
int restarts_to_go; /* MCUs left in this restart interval */
int last_rst_marker_seen; /* Rst marker is incremented each time */
/* Temp space used after the IDCT to store each components */
uint8_t Y[64*4], Cr[64], Cb[64];
jmp_buf jump_state;
/* Internal Pointer use for colorspace conversion, do not modify it !!! */
uint8_t *plane[COMPONENTS];
//add by zhn
int tempY[4];
int tempU,tempV;
//end add
};struct huffman_table
{
/* Fast look up table, using HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS bits we can have directly the symbol,
* if the symbol is <0, then we need to look into the tree table */
short int lookup[HUFFMAN_HASH_SIZE];
/* code size: give the number of bits of a symbol is encoded */
unsigned char code_size[HUFFMAN_HASH_SIZE];
/* some place to store value that is not encoded in the lookup table
* FIXME: Calculate if 256 value is enough to store all values
*/
uint16_t slowtable[16-HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS][256];
};4.typedef指向函数的用法
typedef void (*decode_MCU_fct) (struct jdec_private *priv);
decode_MCU_fct decode_MCU;
decode_MCU=decode_MCU_2x2_1plane;
decode_MCU(priv);
decode_MCU_fct是一个函数指针,用它来声明的decode_MCU也是一个函数指针,并用它指向decode_MCU_2x2_1plane函数,传入参数即可调用。
二、实验步骤
1)读取文件;
2)解析Segment Marker;
3)根据每个分量的水平和垂直采样因子计算MCU的大小,得到每个MCU中宏块的个数;
4)对每个MCU解码,知道解析到EOI,解码结束;
5)将y,cb,cr转化为需要的彩色空间并保存。
三、关键代码分析
int convert_one_image(const char *infilename, const char *outfilename, int output_format)
{
FILE *fp;
unsigned int length_of_file;
unsigned int width, height;
unsigned char *buf;
struct jdec_private *jdec;
unsigned char *components[3];
//add by zhn
unsigned char *yBuffer;
unsigned char *uBuffer;
unsigned char *vBuffer;
//end add
/* Load the Jpeg into memory */
fp = fopen(infilename, "rb");
if (fp == NULL)
exitmessage("Cannot open filename\n");
length_of_file = filesize(fp);
buf = (unsigned char *)malloc(length_of_file + 4);
if (buf == NULL)
exitmessage("Not enough memory for loading file\n");
fread(buf, length_of_file, 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
/* Decompress it */
jdec = tinyjpeg_init();
if (jdec == NULL)
exitmessage("Not enough memory to alloc the structure need for decompressing\n");
if (tinyjpeg_parse_header(jdec, buf, length_of_file)<0)
exitmessage(tinyjpeg_get_errorstring(jdec));
/* Get the size of the image */
tinyjpeg_get_size(jdec, &width, &height);
snprintf(error_string, sizeof(error_string),"Decoding JPEG image...\n");
if (tinyjpeg_decode(jdec, output_format) < 0)
exitmessage(tinyjpeg_get_errorstring(jdec));
/*
* Get address for each plane (not only max 3 planes is supported), and
* depending of the output mode, only some components will be filled
* RGB: 1 plane, YUV420P: 3 planes, GREY: 1 plane
*/
tinyjpeg_get_components(jdec, components);
/* Save it */
switch (output_format)
{
case TINYJPEG_FMT_RGB24:
case TINYJPEG_FMT_BGR24:
write_tga(outfilename, output_format, width, height, components);
break;
case TINYJPEG_FMT_YUV420P:
write_yuv_onefile(outfilename, width, height, components);
break;
case TINYJPEG_FMT_GREY:
write_pgm(outfilename, width, height, components);
break;
}
/* Only called this if the buffers were allocated by tinyjpeg_decode() */
tinyjpeg_free(jdec);
/* else called just free(jdec); */
free(buf);
return 0;
}int tinyjpeg_decode(struct jdec_private *priv, int pixfmt)//add by zhn outdctY
{
unsigned int x, y, xstride_by_mcu, ystride_by_mcu;
unsigned int bytes_per_blocklines[3], bytes_per_mcu[3];
decode_MCU_fct decode_MCU;
const decode_MCU_fct *decode_mcu_table;
const convert_colorspace_fct *colorspace_array_conv;
convert_colorspace_fct convert_to_pixfmt;
//add by zhn
unsigned char *yBuffer;
unsigned char *uBuffer;
unsigned char *vBuffer;
int *yB,*uB,*vB;
int *ytemp,*utemp,*vtemp;
int dcSize,i,j;
FILE *O,*D;
int debug=1;
int count[256],countBefore[256];
int Q_table[3][64];
int MaxY,MaxU,MaxV;
memset(count,0,256*sizeof(int));
memset(countBefore,0,256*sizeof(int));
//end add
if (setjmp(priv->jump_state))
return -1;
/* To keep gcc happy initialize some array */
bytes_per_mcu[1] = 0;
bytes_per_mcu[2] = 0;
bytes_per_blocklines[1] = 0;
bytes_per_blocklines[2] = 0;
decode_mcu_table = decode_mcu_3comp_table;
switch (pixfmt) {
case TINYJPEG_FMT_YUV420P:
colorspace_array_conv = convert_colorspace_yuv420p;
if (priv->components[0] == NULL)
priv->components[0] = (uint8_t *)malloc(priv->width * priv->height);
if (priv->components[1] == NULL)
priv->components[1] = (uint8_t *)malloc(priv->width * priv->height/4);
if (priv->components[2] == NULL)
priv->components[2] = (uint8_t *)malloc(priv->width * priv->height/4);
bytes_per_blocklines[0] = priv->width;
bytes_per_blocklines[1] = priv->width/4;
bytes_per_blocklines[2] = priv->width/4;
bytes_per_mcu[0] = 8;
bytes_per_mcu[1] = 4;
bytes_per_mcu[2] = 4;
break;
case TINYJPEG_FMT_RGB24:
colorspace_array_conv = convert_colorspace_rgb24;
if (priv->components[0] == NULL)
priv->components[0] = (uint8_t *)malloc(priv->width * priv->height * 3);
bytes_per_blocklines[0] = priv->width * 3;
bytes_per_mcu[0] = 3*8;
break;
case TINYJPEG_FMT_BGR24:
colorspace_array_conv = convert_colorspace_bgr24;
if (priv->components[0] == NULL)
priv->components[0] = (uint8_t *)malloc(priv->width * priv->height * 3);
bytes_per_blocklines[0] = priv->width * 3;
bytes_per_mcu[0] = 3*8;
break;
case TINYJPEG_FMT_GREY:
decode_mcu_table = decode_mcu_1comp_table;
colorspace_array_conv = convert_colorspace_grey;
if (priv->components[0] == NULL)
priv->components[0] = (uint8_t *)malloc(priv->width * priv->height);
bytes_per_blocklines[0] = priv->width;
bytes_per_mcu[0] = 8;
break;
default:
#if TRACE
fprintf(p_trace,"Bad pixel format\n");
fflush(p_trace);
#endif
return -1;
}四、实验结果分析
static void write_yuv_onefile(const char *filename, int width, int height, unsigned char **components)
{
FILE *F;
F = fopen(filename, "wb");
fwrite(components[0], width, height, F);
fwrite(components[1], width*height/4, 1, F);
fwrite(components[2], width*height/4, 1, F);
fclose(F);
}/*
* Decode a 2x2
* .-------.
* | 1 | 2 |
* |---+---|
* | 3 | 4 |
* `-------'
*/
static void decode_MCU_2x2_3planes(struct jdec_private *priv)
{
int i;
// Y
process_Huffman_data_unit(priv, cY);
IDCT(&priv->component_infos[cY], priv->Y, 16);
//add by zhn
priv->tempY[0]=priv->component_infos[cY].DCT[4];
//end add
process_Huffman_data_unit(priv, cY);
IDCT(&priv->component_infos[cY], priv->Y+8, 16);
//add by zhn
priv->tempY[1]=priv->component_infos[cY].DCT[4];
#if debug_dct
for(i=0;i<64;i++)
{
if(priv->component_infos[cY].DCT[i]>=255)
printf("%4d",priv->component_infos[cY].DCT[i]);
}
#endif
//end add
process_Huffman_data_unit(priv, cY);
IDCT(&priv->component_infos[cY], priv->Y+64*2, 16);
//add by zhn
priv->tempY[2]=priv->component_infos[cY].DCT[4];
//end add
process_Huffman_data_unit(priv, cY);
IDCT(&priv->component_infos[cY], priv->Y+64*2+8, 16);
//add by zhn
priv->tempY[3]=priv->component_infos[cY].DCT[4];
//end add
// Cb
process_Huffman_data_unit(priv, cCb);
IDCT(&priv->component_infos[cCb], priv->Cb, 8);
//add by zhn
#if debug_dct
for(i=0;i<64;i++)
{
if(priv->component_infos[cCb].DCT[i]>=255)
printf("%4d",priv->component_infos[cCb].DCT[i]);
}
#endif
priv->tempU=priv->component_infos[cCb].DCT[4];
//end add
// Cr
process_Huffman_data_unit(priv, cCr);
IDCT(&priv->component_infos[cCr], priv->Cr, 8);
//add by zhn
#if debug_dct
for(i=0;i<64;i++)
{
if(priv->component_infos[cCr].DCT[i]>=255)
printf("%4d",priv->component_infos[cCr].DCT[i]);
}
#endif
priv->tempV=priv->component_infos[cCr].DCT[4];
//end add
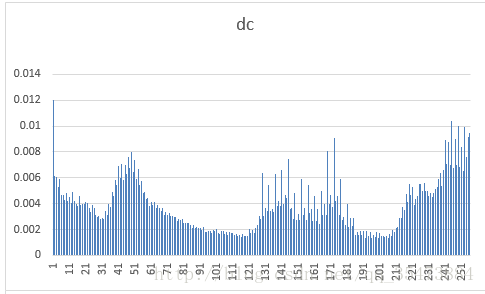
}dc系数图像

dc概率分布
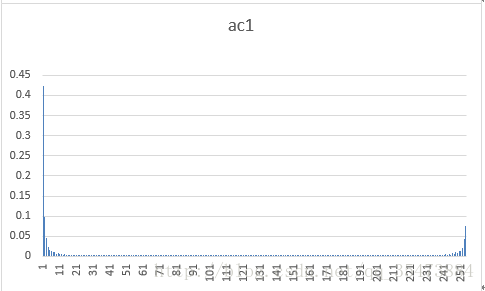
ac系数1的概率分布
ac系数3的概率分布
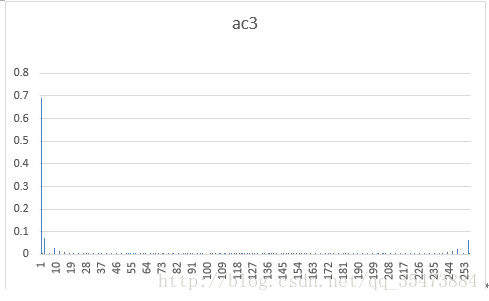
五、实验结论分析
dct的物理意义是将用各频率分量的组合来表示原图像,它的各个系数就表示该频率分量的大小。一张图片的dc系数与原图像的概率分布近似,而ac系数则服从拉普拉斯分布,且频率越高,分布越集中。
附录代码链接
http://download.csdn.net/detail/qq_35473884/9857990
