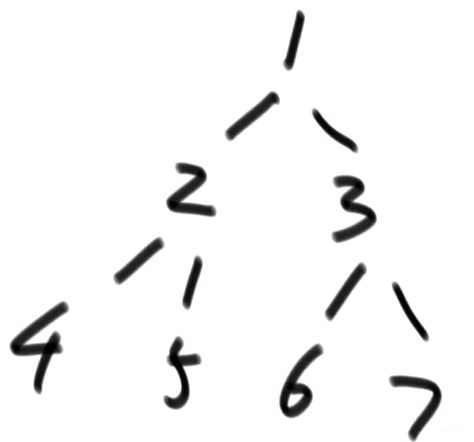数据结构与算法(二):堆,大根堆,小根堆,堆排序,比较器详解
堆
什么是堆?
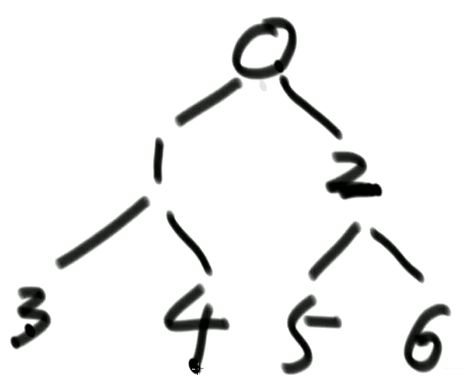
堆 是一棵 完全二叉树:即使它不是满二叉树,也是正在从左往右变满的过程中。
1)堆结构就是用数组实现的完全二叉树结构
2)完全二叉树中,如果每棵子树的 最大值都在顶部,是 大根堆
3)完全二叉树中,如果每棵子树的 最小值都在顶部,是 小根堆
4)堆结构的 heapInsert 与 heapify 操作
5)堆结构的增大和减少
6)优先级队列结构,就是堆结构
7)特点:由 N 个数 组成的堆,高度是 log(n)
如何用数组存放堆?
如果从 0 位置开始:
i 层,则
- 左孩子:2 * i + 1
- 右孩子:2 * i + 2
- 父节点:(i - 1) / 2
如果从 1 位置开始:
正是由于可以使用 位运算 来代替 算数运算,效率更高,所以有时候让下标从 1 开始。
- 左孩子:2 * i (i << 1)
- 右孩子:2 * i + 1 (i << 1 | 1)
- 父节点:i / 2 (i >> 1)
如何将数组转化成大根堆?—— heapInsert 操作
每在 i 位置加入一个新的节点,都与它的 (i - 1) / 2 位置的父节点比较,如果比父节点大,则交换(并while比较父节点与父父节点)
private void heapInsert(int[] arr, int index) {
while (arr[index] > arr[(index - 1) / 2]) {
swap(arr, index, (index - 1) / 2);
index = (index - 1) / 2;
}
}
private void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
如何返回并删除大根堆的最大值,剩余数字依然保持大根堆?—— heapify 操作
- 将顶部元素取出
- 将大根堆的最后位置上的元素覆盖到顶部
- while 循环
- 如果左右孩子中较大的数比当前节点更大,则交换当前节点和较大的孩子节点
- 如果左孩子下标越界,或左右孩子都不比当前节点大,就停止
// 返回最大值,并在大根堆中把最大值删掉,剩下的数依然保持大根堆形态
public int pop() {
int ans = heap[0];
swap(heap, 0, --heapSize);
heapify(heap, 0, heapSize);
return ans;
}
// 从index位置开始,不断的下沉,直到我的孩子都不再比我大,或者我已经没孩子了,就停止
private void heapify(int[] arr, int index, int heapSize) {
int left = index * 2 + 1;
while (left < heapSize) {
// largest存储左右孩子 较大者 的下标
int largest = left + 1 < heapSize && arr[left + 1] > arr[left] ? left + 1 : left;
// largest存储两个孩子与父节点 较大者 的下标
largest = arr[largest] > arr[index] ? largest : index;
if (largest == index) { // 不需要交换的情况
break;
}
swap(arr, largest, index);
index = largest;
left = index * 2 + 1;
}
}
堆排序
- 先让整个数组都变成大根堆结构,建立堆的过程:
- 从上到下的方法,时间复杂度为O(N*logN)
- 从下到上的方法,时间复杂度为O(N)
- 把堆的最大值和堆末尾的值交换,然后减少堆的大小之后,再去调整堆,一直周而复始,时间复杂度为O(N*logN)
- 堆的大小减小成0之后,排序完成!
public static void heapSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
// 方法1:对数组进行堆排序 O(N*logN)
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { // O(N)
heapInsert(arr, i); // O(logN)
}
// 方法2:仅将数组转化成大顶堆 O(n)
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(arr, i, arr.length);
}
}
语言提供的堆结构 vs 手写的堆结构,怎么选择?
取决于你有没有 动态改信息 的需求!
-
语言提供的堆结构,如果你动态改数据,不保证依然有序
-
手写堆结构,因为增加了对象的位置表,所以能够满足动态改信息的 resign 需求(以后我们的 Dijskra 会用到),而系统自带的堆结构即使是实现了对数据的修改,时间复杂度也不会好,因为它没有 hashmap,只能从顶部开始,遍历每个元素进行 heapify
public static class MyHeap<T> { private ArrayList<T> heap; // 用动态数组存堆 private HashMap<T, Integer> indexMap; // 对象的位置表 private int heapSize; // 堆大小 private Comparator<? super T> comparator; // 自定义比较器 /*...省略push,pop,heapInsert,heapify等...*/ public void resign(T value) { // resign操作不需要全量遍历整个堆 int valueIndex = indexMap.get(value); heapInsert(valueIndex); // 这个heapInsert和下面的heapify,只会命中一个,另一个直接返回 heapify(valueIndex, heapSize); } } public static void main(String[] args) { myHeap = new MyHeap<>(new StudentComparator()); /*...省略s1, s2等new对象过程...*/ myHeap.push(s1); myHeap.push(s2); myHeap.push(s3); myHeap.push(s4); myHeap.push(s5); s2.age = 6; myHeap.resign(s2); }
PriorityQueue 底层就是用堆实现的,默认是小根堆
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 小根堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>();
heap.add(5);
heap.add(7);
heap.add(3);
heap.add(0);
heap.add(2);
heap.add(5);
while (!heap.isEmpty()) { // 排序输出
System.out.println(heap.poll());
}
}
与堆有关的题目
已知一个几乎有序的数组。
几乎有序是指,如果把数组排好顺序的话,每个元素移动的距离一定不超过k(假设k=5),并且k相对于数组长度来说是比较小的。
请选择一个合适的排序策略,对这个数组进行排序。
思路:维护一个大小为 k 的小根堆,每加入一个新数字,先将小根堆的最小值弹出,再把新值放入小根堆中去。
public static void sortedArrDistanceLessK(int[] arr, int k) {
if (k == 0) {
return;
}
// 默认小根堆,复杂度:log(k)
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>();
int index = 0;
for (; index <= Math.min(arr.length - 1, k - 1); index++) {
heap.add(arr[index]);
}
int i = 0;
for (; index < arr.length; i++, index++) {
heap.add(arr[index]);
arr[i] = heap.poll();
}
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
arr[i++] = heap.poll();
}
}
比较器 Comparator
1)比较器的实质就是重载比较运算符
2)比较器可以很好的应用在特殊标准的排序上
3)比较器可以很好的应用在根据特殊标准排序的结构上
4)写代码变得异常容易,还用于范型编程
public static class IdAscendingComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
// 返回负数,第一个参数排在前面
// 返回正数,第二个参数排在前面
// 返回0的时候,谁在前面无所谓
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.id - o2.id;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student("A", 2, 20);
Student student2 = new Student("B", 3, 21);
Student student3 = new Student("C", 1, 22);
Student[] students = new Student[]{student1, student2, student3};
Arrays.sort(students, new IdAscendingComparator());
}
用 Comparator 排序:
public static class HeapComp implements Comparator<Integer> {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] arr = {5, 4, 3, 2, 7, 9, 1, 0};
Arrays.sort(arr, new HeapComp());
}