MATLAB教程(五):绘图进阶
**1. Advanced 2D plots
spacial plots:
logarithm plots:
x = logspace(-1,1,100); %设置变量空间
y = x.^2;
subplot(2,2,1);
plot(x,y);
title('plot');
subplot(2,2,2);
semilogx(x,y); %半对数坐标系
title('Semilogx');
subplot(2,2,3);
semilogy(x,y);
title('Semilogy');
subplot(2,2,4);
loglog(x,y); %双对数坐标系
title('LogLog');
set(gca,'XGrid','on')
x = 0:0.01:20;
y1 = 200*exp(-0.05*x).*sin(x);
y2 = 0.8*exp(-0.5x).*sin(10*x);
y2 = 0.8*exp(-0.5*x).*sin(10*x);
[AX,H1,H2]=plotyy(x,y1,x,y2);
set(AX(1),'Ylabel'),'String','Left Y-axis')
set(get(AX(2),'Ylabel'),'String','Right Y-axis')
title('Labeling plotyy');
set(H1,'LineStyle','--');
set(H2,'Linestyle',':');
Histogram:统计整体的情况
y = randn(1,1000);
subplot(2,1,1);
hist(y,10);
title('bins = 10');
subplot(2,1,2);
hist(y,50);
title('bins = 50');
>> x = [1 2 5 4 8];
>> y = [x;1:5];
>> subplot(1,3,1);
>> bar(x);
>> title('A bargraph of vector x');
>> subplot(1,3,2);
>> bar(y);
>> title('A bargraph of vector y');
>> subplot(1,3,3);
>> bar3(y);
>> title('A 3D bargraph');
Pie charts:
>> a = [10 5 20 30];
>> subplot(1,3,1);
>> pie(a);
>> subplot(1,3,2);
>> pie(a,[0,0,0,1]);
>> subplot(1,3,3);
>> pie3(a,[0,0,0,1]);
>> x = 1:100; theta = x/10; r = log10(x);
>> subplot(1,4,1);
>> polar(theta,r);
>> theta = linspace(0,2*pi); r = cos(4*theta);
>> subplot(1,4,2); polar(theta,r);
>> theta = linspace(0,2*pi,6);r = ones(1,length(theta));
>> subplot(1,4,3);polar(theta,r);
>> theta = linspace(0,2*pi); r = 1-sin(theta);
>> subplot(1,4,4); polar(theta,r);
Stairs and Stem Charts:
>> x = linspace(0 ,4*pi, 40);
>> y = sin(x);
>> subplot(1,2,1);
>> stairs(y);
>> subplot(1,2,2);
>> stem(y);
load carsmall
boxplot(MPG,Origin);
>> x = 0:pi/10:pi; y=sin(x);
>> e=std(y)*ones(size(x));
>> errorbar(x,y,e);
t = (1:2:15)'*pi/8;
>> x = sin(t);
>> y = cos(t);
>> fill(0,0,'STOP','Color','w','FontSize',80,...
>> fill(x,y,'r');
>> axis square off
>> text(0,0,'STOP','Color','w','FontSize',80,...
'FontWeight','bold','HorizontalAlignment','center');
2. Color space
G = [46 38 29 24 13]; S = [29 27 17 26 8];
B = [29 23 19 32 7] ; h = bar(1:5, [G' S' B']);
title('Medal count for top 5 countries in 2012 Olympics');
ylabel('Number of medals'); xlabel('Country');
legend('Gold', 'Silver', 'Bronze');
set(gca,'XTickLabel',['USA';'CHN';'GRE';'RUS';'KOR']);
set(h(1),'FaceColor',[0.8 0.8 0]);
set(h(2),'FaceColor',[0.6 0.6 0.6]);
set(h(3),'FaceColor',[0.6 0.4 0.2]);
display values of a matrix as an “image”
built-in Colormaps:parula,jet,hsv,spring,hot,cool,spring,summer,autumn,winter,gray,bone…
>>[x , y] = meshgrid(-3:.2:3,-3:.2:3);
>>z = x.^2 + x.*y +y.^2; surf(x,y,z); box on;
>> set(gca,'FontSize',16); zlabel('z');
>> xlim([-4 4]);xlabel('x');ylabel('y');
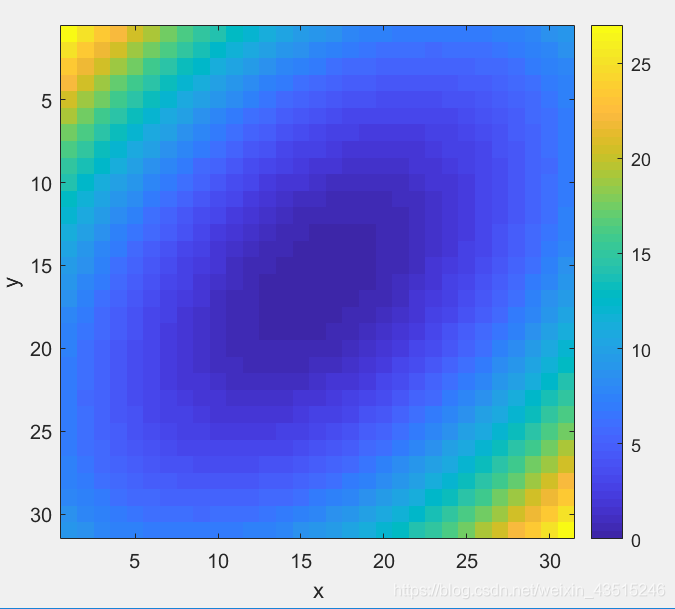
>> imagesc(z); axis square;xlabel('x');ylabel('y');
imagesc(z); axis square;xlabel('x');ylabel('y');
colorbar;
colormap(hot);
colormap(cool);
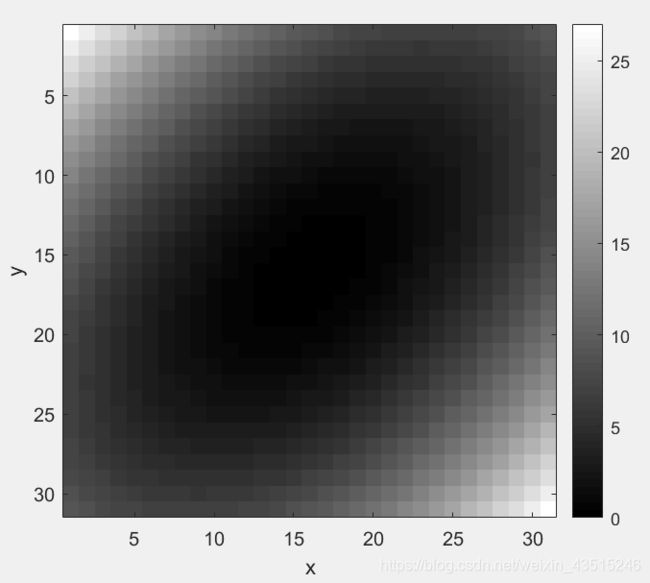
colormap(gray);
3. 3D plots
>> x = 0:0.1:3*pi; z1 = sin(x); z2 = sin(2.*x); z = sin(3.*x);
>> y1 = zeros(size(x)); y3 = ones(size(x)); y2 = y3./2;
>> plot3(x,y1,z1,'r',x,y2,z2,'b',x,y3,z,'g'); grid on;
>> xlabel('x-axis'); ylabel('y-axis'); zlabel('z-axis');
>> t = 0:pi/50:10*pi;
plot3(sin(t),cos(t),t)
>> gird on; axis aquare;
>> turns = 40*pi;
>> t = linspace(0,turns,4000);
>> x = cos(t).*(turns-t)./turns;
>> y = sin(t).*(turns-t)./turns;
>> z = t./turns;
>> plot3(x,y,z); grid on;
principles for 3D Surface Plots
- usually for plotting functions:z = f(x,y);
- need to provide MATLAB a set of (x,y,z) points;
- use meshgrid to create matrices X and Y for a given range;
- e.g. x = -2:1:2;
y = -2:1:2;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);

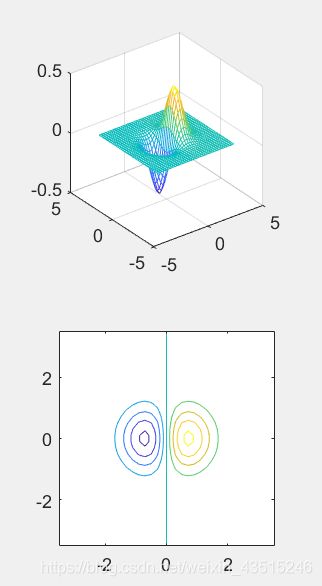
>> x = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
>> y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
>> [X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
>> Z = X.*exp(-x.^2-Y.^2);
>> subplot(1,2,1); mesh(X,Y,Z);
>> subplot(1,2,2); surf(X,Y,Z);
>> x = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
>> y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
>> [X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
>> Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
>> subplot(2,1,1);
>> mesh(X,Y,Z);
>> axis square
>> subplot(2,1,2);
>> contour(X,Y,Z);
>> axis square;
>> x = -3.5:0.2:3.5; y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
>> [X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y); Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
>> subplot(1,3,1); contour(Z,[-.45:.05:.45]);
>> subplot(1,3,2); [C,h] = contour(Z);
>> clabel(C,h); axis square;
>> subplot(1,3,3); contourf(Z); axis square;
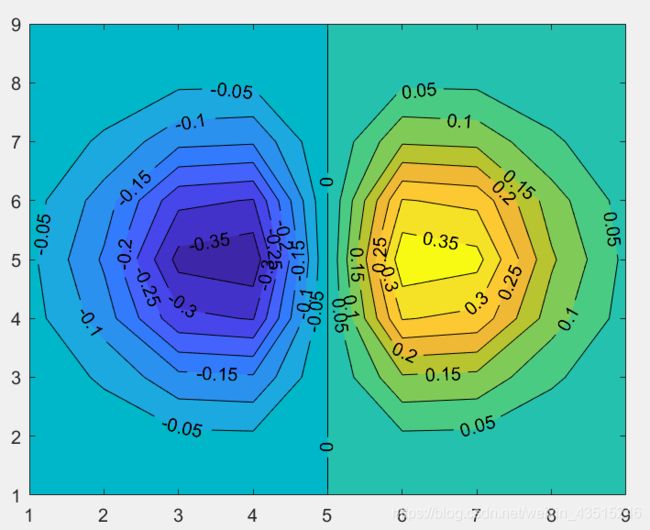
Exercise:conbine the contour techniques to generate a figure as shown below
卖家秀

买家秀
>> x = -2:0.5:2; y = -2:0.5:2;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y); Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
>> contourf(Z,[-0.4:0.05:0.4]);
[C,h] = contourf(Z,[-0.4:0.05:0.4]);
clabel(C,h);
meshc() and surfc():conbination of surface/mesh and conours
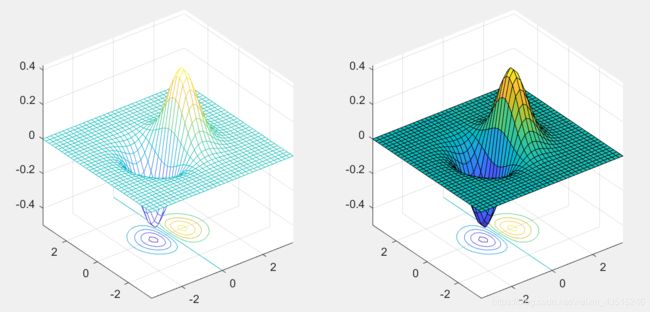
>> x = -3.5:0.2:3.5; y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
>> [X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
>> Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
>> subplot(1,2,1);meshc(X,Y,Z);
>> subplot(1,2,2);surfc(X,Y,Z);
>> sphere(50);
>> shading flat;
>> light('Position',[1,3,2]);
>> light('Position',[-3,-1,3]);
>> material shiny;
>> axis vis3d off;
>> set(gcf,'Color',[1,1,1]);
>> view(-45,20);
light()
patch()