Spring Cloud Eureka 配置原理详解
导语:
首先对于Eureka注册中心默认大家都有所了解,这篇博客主要就是来通过Eureka的配置源码来了解一下关于Eureka配置中心都有那些详细的配置内容。对于Eureka 客户端的配置主要分为两个方面
- 服务注册相关的配置信息,包括服务注册中心的地址、服务获取的时间间隔、可用区域等
- 服务实例相关配置信息,包括服务的实例名、IP地址、端口号、健康检查路径等等。
文章目录
- 配置文件详解
- eureka.client
- enable
- registryFetchIntervalSeconds
- instanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds
- initialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds
- eurekaServiceUrlPollIntervalSeconds
- eurekaServerReadTimeoutSeconds
- eurekaServerConnectTimeoutSeconds
- eurekaServerTotalConnections
- eurekaServerTotalConnectionsPerHost
- eurekaConnectionIdleTimeoutSeconds
- heartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize
- heartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound
- cacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize
- cacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound
- registerWithEureka
- preferSameZoneEureka
- filterOnlyUpInstances
- fetchRegistry
- 配置原理
- 总结
配置文件详解
对于Eureka来说作为注册中心既要有服务端还要有客户端。这样的话就需要它既要有服务器端的配置也要有客户端的配置。当然服务端以eureka.server前缀,客户端以eureka.client为前缀,下面就来介绍一下客户端的配置。
关于客户端的配置类主要是来自于一个配置文件,通过对于SpringBoot自动配置机制的了解可以知道,SpringBoot的自动配置实现通过的是一个配置类,而在SpringCloud中对于这个配置类的支持如下
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientConfigBean
eureka.client
在这个类中提供了很多的配置属性,对应于配置文件中的配置项。下面就通过源码来详细看一下其中的配置
public static final String PREFIX = "eureka.client";
public static final String DEFAULT_URL = "http://localhost:8761" + DEFAULT_PREFIX
+ "/";
public static final String DEFAULT_ZONE = "defaultZone";
private static final int MINUTES = 60;
首先会看到在配置类中为所有的配置都设置了一个统一的客户端前缀 “eureka.client”,表示这是一个客户端的配置,并且指定了默认的服务注册中心地址。那么这个是怎么实现的呢?
在配置文件中是通过如下的方式进行配置的
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
在代码中是怎么实现呢?
/**
* Map of availability zone to list of fully qualified URLs to communicate with eureka
* server. Each value can be a single URL or a comma separated list of alternative
* locations.
*
* Typically the eureka server URLs carry protocol,host,port,context and version
* information if any. Example:
* http://ec2-256-156-243-129.compute-1.amazonaws.com:7001/eureka/
*
* The changes are effective at runtime at the next service url refresh cycle as
* specified by eurekaServiceUrlPollIntervalSeconds.
*/
private Map<String, String> serviceUrl = new HashMap<>();
{
this.serviceUrl.put(DEFAULT_ZONE, DEFAULT_URL);
}
会看到这个serviceURL其实是一个Map,也就是说可以有多个对应的关系。当需要构建高可用的服务注册中心集群的时候,可以为参数的Value配置多个注册中心地址通过逗号进行分隔。当然有的时候为了注册中心的安全考虑,会为注册中心加上安全校验,这个时候配置serviceURL的时候就需要增加对应的安全校验信息,例如加上用户名或者密码等等。
enable
/**
* Flag to indicate that the Eureka client is enabled.
*/
private boolean enabled = true;
判断是否是一个客户端实例
registryFetchIntervalSeconds
/**
* Indicates how often(in seconds) to fetch the registry information from the eureka
* server.
*/
private int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = 30;
从Eureka服务端获取注册信息的时间间隔单位是秒
instanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds
/**
* Indicates how often(in seconds) to replicate instance changes to be replicated to
* the eureka server.
*/
private int instanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds = 30;
更新实例信息的变化到Eureka服务端的时间间隔,单位为秒
initialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds
/**
* Indicates how long initially (in seconds) to replicate instance info to the eureka
* server
*/
private int initialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds = 40;
初始化实例信息到Eureka服务端的时间间隔,单位为秒
eurekaServiceUrlPollIntervalSeconds
/**
* Indicates how often(in seconds) to poll for changes to eureka server information.
* Eureka servers could be added or removed and this setting controls how soon the
* eureka clients should know about it.
*/
private int eurekaServiceUrlPollIntervalSeconds = 5 * MINUTES;
轮询Eureka服务端地址更改的时间间隔,单位为秒,当与Spring Cloud Config配合,动态刷新Eureka的serviceURL地址是需要关注这个参数
eurekaServerReadTimeoutSeconds
/**
* Indicates how long to wait (in seconds) before a read from eureka server needs to
* timeout.
*/
private int eurekaServerReadTimeoutSeconds = 8;
读取Eureka Server信息的超时时间,单位为秒
eurekaServerConnectTimeoutSeconds
/**
* Indicates how long to wait (in seconds) before a connection to eureka server needs
* to timeout. Note that the connections in the client are pooled by
* org.apache.http.client.HttpClient and this setting affects the actual connection
* creation and also the wait time to get the connection from the pool.
*/
private int eurekaServerConnectTimeoutSeconds = 5;
连接Eureka Server的超时时间,单位为秒
eurekaServerTotalConnections
/**
* Gets the total number of connections that is allowed from eureka client to all
* eureka servers.
*/
private int eurekaServerTotalConnections = 200;
从Eureka客户端到所有Eureka服务端的连接总数
eurekaServerTotalConnectionsPerHost
/**
* Gets the total number of connections that is allowed from eureka client to a eureka
* server host.
*/
private int eurekaServerTotalConnectionsPerHost = 50;
从Eureka客户端到每个Eureka服务端主机的连接总数
eurekaConnectionIdleTimeoutSeconds
/**
* Indicates how much time (in seconds) that the HTTP connections to eureka server can
* stay idle before it can be closed.
*
* In the AWS environment, it is recommended that the values is 30 seconds or less,
* since the firewall cleans up the connection information after a few mins leaving
* the connection hanging in limbo
*/
private int eurekaConnectionIdleTimeoutSeconds = 30;
Eureka服务端连接的空闲关闭时间,单位为秒
heartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize
/**
* The thread pool size for the heartbeatExecutor to initialise with
*/
private int heartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize = 2;
心跳连接池的初始化线程数
heartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound
/**
* Heartbeat executor exponential back off related property. It is a maximum
* multiplier value for retry delay, in case where a sequence of timeouts occurred.
*/
private int heartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound = 10;
心跳超时重试延迟时间的最大乘数值
cacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize
/**
* The thread pool size for the cacheRefreshExecutor to initialise with
*/
private int cacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize = 2;
缓存刷新线程池的初始化线程数
cacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound
/**
* Cache refresh executor exponential back off related property. It is a maximum
* multiplier value for retry delay, in case where a sequence of timeouts occurred.
*/
private int cacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound = 10;
缓存刷新重试延迟时间的最大乘数值
registerWithEureka
/**
* Indicates whether or not this instance should register its information with eureka
* server for discovery by others.
*
* In some cases, you do not want your instances to be discovered whereas you just
* want do discover other instances.
*/
private boolean registerWithEureka = true;
是否要将自身注册到Eureka服务端
preferSameZoneEureka
/**
* Indicates whether or not this instance should try to use the eureka server in the
* same zone for latency and/or other reason.
*
* Ideally eureka clients are configured to talk to servers in the same zone
*
* The changes are effective at runtime at the next registry fetch cycle as specified
* by registryFetchIntervalSeconds
*/
private boolean preferSameZoneEureka = true;
是否偏好使用处于相同Zone的Eureka服务端
filterOnlyUpInstances
/**
* Indicates whether to get the applications after filtering the applications for
* instances with only InstanceStatus UP states.
*/
private boolean filterOnlyUpInstances = true;
获取实例时是否过滤,仅保留UP状态的实例
fetchRegistry
/**
* Indicates whether this client should fetch eureka registry information from eureka
* server.
*/
private boolean fetchRegistry = true;
是否从Eureka服务端获取注册信息。
配置原理
上面所描述的是一些常用的配置属性,在配置文件中可以进行配置,当然在EurekaClientConfigBean配置类中还提供了其他配置属性,有兴趣的可以查看源码根据自己的业务需求进行配置。
这里会有个疑问,既然是使用了SpringBoot的自动配置原理,那么为什么这里的配置属性不是xxxProperties结尾的呢?
在这里我们首先需要关注一个接口
@ImplementedBy(DefaultEurekaClientConfig.class)
public interface EurekaClientConfig {
这里我们关注一个注解@ImplementedBy,要知道在其他的配置类上都是通过@Import进行组件注入的为什么这里使用的这个注解,这个注解打破了传统的DI。
首先会注意到在这个注解上标注了一个配置类,可以进入到这个配置类
@Singleton
@ProvidedBy(DefaultEurekaClientConfigProvider.class)
public class DefaultEurekaClientConfig implements EurekaClientConfig {
会看到这个配置其实是实现了刚刚那个配置接口。在这个配置类上标注了另一个注解@ProvidedBy ,这里继续深入这个注解
package com.google.inject;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.TYPE;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* A pointer to the default provider type for a type.
*
* @author [email protected] (Bob Lee)
*/
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Target(TYPE)
public @interface ProvidedBy {
/**
* The implementation type.
*/
Class<? extends javax.inject.Provider<?>> value();
}
public class DefaultEurekaClientConfigProvider implements Provider<EurekaClientConfig> {
@Inject(optional = true)
@EurekaNamespace
private String namespace;
private DefaultEurekaClientConfig config;
@Override
public synchronized EurekaClientConfig get() {
if (config == null) {
config = (namespace == null)
? new DefaultEurekaClientConfig()
: new DefaultEurekaClientConfig(namespace);
// TODO: Remove this when DiscoveryManager is finally no longer used
DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setEurekaClientConfig(config);
}
return config;
}
}
通过上面的代码,会注意到其实绕了一大圈,最终还是没有使用到EurekaClientConfigBean类进行注入操作,那么它是怎么进行属性绑定呢?通过下面的类图,就可以清楚的看到
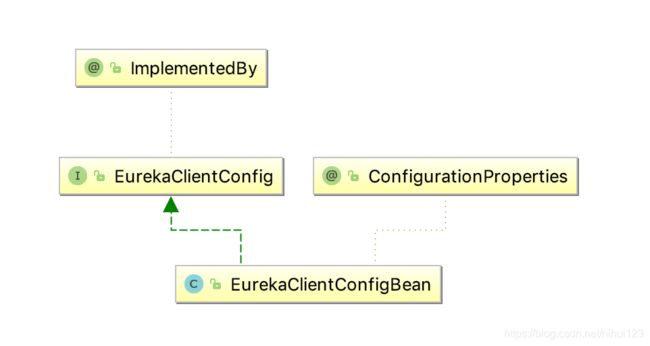
会看看到对于它的属性绑定操作其实是通过另外的方式。一方面要支持自动配置,另一方面还要支持Config的动态配置
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties
@ConditionalOnClass(EurekaClientConfig.class)
@Import(DiscoveryClientOptionalArgsConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration.Marker.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "eureka.client.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@AutoConfigureBefore({ NoopDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration.class,
CommonsClientAutoConfiguration.class, ServiceRegistryAutoConfiguration.class })
@AutoConfigureAfter(name = {"org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.RefreshAutoConfiguration",
"org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration",
"org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationAutoConfiguration"})
public class EurekaClientAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EurekaClientConfig.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public EurekaClientConfigBean eurekaClientConfigBean(ConfigurableEnvironment env) {
EurekaClientConfigBean client = new EurekaClientConfigBean();
if ("bootstrap".equals(this.env.getProperty("spring.config.name"))) {
// We don't register during bootstrap by default, but there will be another
// chance later.
client.setRegisterWithEureka(false);
}
return client;
}
到这里就会看到如果在容器中没有EurekaClientConfig的时候才会有自动配置生效。
总结
通过代码的跟踪会发现在SpringCloud Eureka配置中利用了两个注解来动态的注入配置,让Eureka既可以实现SpringBoot的自动配置功能也可以实现基于配置模块Config的动态配置,当然后面的博客中还会对他的动态代理模式进行详细分析。