一、概念
限流的目的是通过对并发访问/请求进行限速,或者对一个时间窗口内的请求进行限速来保护系统,一旦达到限制速率则可以拒绝服务、排队或等待、降级等处理。
常用的限流算法有两种:漏桶算法和令牌桶算法:
漏桶算法的思路很简单,水(请求)先进入到漏桶里,漏桶以一定的速度出水,当水流入速度过大会直接溢出,可以看出漏桶算法能强行限制数据的传输速率。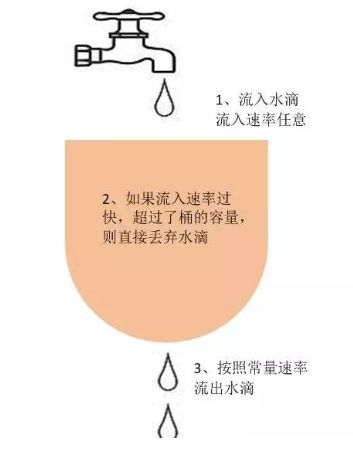
对于很多应用场景来说,除了要求能够限制数据的平均传输速率外,还要求允许某种程度的突发传输。这时候漏桶算法可能就不合适了,令牌桶算法更为适合。
令牌桶算法的原理是系统会以一个恒定的速度往桶里放入令牌,而如果请求需要被处理,则需要先从桶里获取一个令牌,当桶里没有令牌可取时,则拒绝服务。
二、应用
Google 开源工具包 Guava 提供了限流工具类 RateLimiter,该类基于令牌桶算法来完成限流,非常易于使用。RateLimiter api 可以查看并发编程网 Guava RateLimiter 的介绍。
我们用 MVC 的拦截器 + Guava RateLimiter 实现我们的限流方案:
@Slf4j
public class RequestLimitInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter implements BeanPostProcessor {
private static final Integer GLOBAL_RATE_LIMITER = 10;
private static Map URL_RATE_MAP;
private Properties urlProperties;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
if (URL_RATE_MAP != null) {
String lookupPath = new UrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
for (PatternsRequestCondition patternsRequestCondition : URL_RATE_MAP.keySet()) {
//使用spring DispatcherServlet的匹配器PatternsRequestCondition进行匹配
//spring 3.x 版本
//Set matches = patternsRequestCondition.getMatchingCondition(request).getPatterns();
//spring 4.x 版本
List matches = patternsRequestCondition.getMatchingPatterns(lookupPath);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(matches)){
continue;
}
//尝试获取令牌
if (!URL_RATE_MAP.get(patternsRequestCondition).tryAcquire(1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
log.info(" 请求'{}'匹配到 mathes {},超过限流速率,获取令牌失败。", lookupPath, Joiner.on(",").join(patternsRequestCondition.getPatterns()));
return false;
}
log.info(" 请求'{}'匹配到 mathes {} ,成功获取令牌,进入请求。", lookupPath, Joiner.on(",").join(patternsRequestCondition.getPatterns()));
}
}
return super.preHandle(request, response, handler);
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class.isAssignableFrom(bean.getClass())) {
if (URL_RATE_MAP == null) {
URL_RATE_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
}
log.info("we get all the controllers's methods and assign it to urlRateMap");
RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping = (RequestMappingHandlerMapping) bean;
Map handlerMethods = requestMappingHandlerMapping.getHandlerMethods();
for (RequestMappingInfo mappingInfo : handlerMethods.keySet()) {
PatternsRequestCondition requestCondition = mappingInfo.getPatternsCondition();
// 默认的 url 限流方案设定
URL_RATE_MAP.put(requestCondition, RateLimiter.create(GLOBAL_RATE_LIMITER));
}
// 自定义的限流方案设定
if (urlProperties != null) {
for (String urlPatterns : urlProperties.stringPropertyNames()) {
String limit = urlProperties.getProperty(urlPatterns);
if (!limit.matches("^-?\\d+$")){
log.error("the value {} for url patterns {} is not a number ,please check it ", limit, urlPatterns);
}
URL_RATE_MAP.put(new PatternsRequestCondition(urlPatterns), RateLimiter.create(Integer.parseInt(limit)));
}
}
}
return bean;
}
/**
* 限流的 URL与限流值的 K/V 值
*
* @param urlProperties
*/
public void setUrlProperties(Properties urlProperties) {
this.urlProperties = urlProperties;
}
} @Configuration
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public RequestLimitInterceptor requestLimitInterceptor(){
RequestLimitInterceptor limitInterceptor = new RequestLimitInterceptor();
// 设置自定义的 url 限流方案
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("/admin/**", "10");
limitInterceptor.setUrlProperties(properties);
return limitInterceptor;
}
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
// 限流方案
registry.addInterceptor(requestLimitInterceptor());
}
}tips: 这边自定义限流列表 urlProperties 的方案不太合理,可以考虑放在配置中心(Nacos、Spring Cloud Config 等)去动态的更新需要限流的 url。
参考博文:
- https://blog.csdn.net/Lili429/article/details/79236819
- https://blog.csdn.net/valleychen1111/article/details/78038366