springSecurity基于表单认证源码解析、认证结果如何在多个请求之间共享、获取认证用户信息
备注:此为看视频之后,自己理解总结的
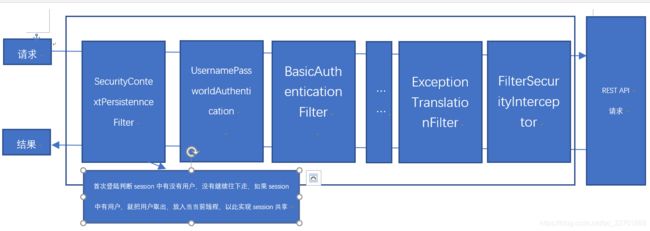
1、认证处理流程说明
首先是springSecurity的过滤器链
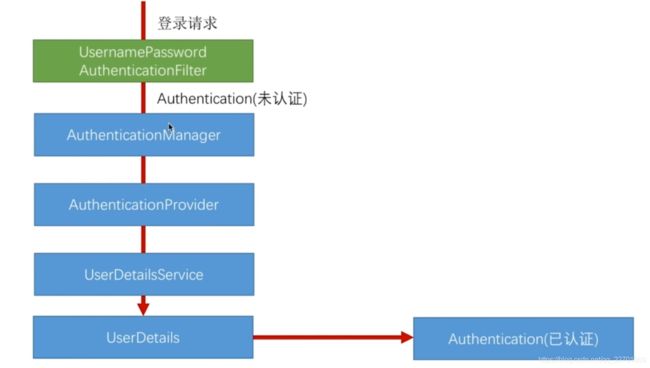
核心认证流程
我们自定义的验证用户名的逻辑MyUserDetailsService
@Component
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
logger.info("登录用户名:" + username);
// 根据用户名查找用户信息,可以冲数据库获取信息
//根据查找到的用户信息判断用户是否被冻结
String password = passwordEncoder.encode("123456");
logger.info("数据库密码是:"+password);
return new User(username, password,
true, true, true, true,
AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin"));
}
}
这里我们主要从UsernamePassworldAuthentication来跟踪源码
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
//1、调用构造方法,创建了一个还没有经过认证的token
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// 会把我们当前请求request中的session、ip等放到token中
setDetails(request, authRequest);
//2、这一句就是获取用户authention的方法
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}1、调用构造方法,创建了一个还没有经过认证的token
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials) {
//父类权限,当前为登陆,所有权限为空
super(null);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
//初始化为未认证过的token,通过认证之后,会重新调用另一个
//UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken构造方法,将其设定为true
setAuthenticated(false);
}2、接下来是this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest)中的authenticate(authRequest);
//这一句就是获取用户authention的方法return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
getAuthenticationManager这里的AuthenticationManager主要是用来管理AuthenticationProvider的,登陆方式的不同,对应的Provicder不同,比如密码登陆、第三方(qq、微信)登陆,因为对应的provider有多种,所以就有AuthernticationManager来进行管理了。
.authenticate(authRequest);有多个实现类,我们进入ProviderManager
public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware,
InitializingBean {
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Class toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
Authentication result = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
//这里就是ProviderManager管理的AuthenticationProvider,因为不同的登录对应的逻辑是不一样的。
//比如UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken、SocialAuthenticationToken,这里只讨论比如UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {//支不支持我传进来的authenticaition
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using "
+ provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
//3、跳入源码,下面会有解说
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
}
if (result == null && parent != null) {
// Allow the parent to try.
try {
result = parent.authenticate(authentication);
}
}
if (result != null) {
if (eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication
&& (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
// Authentication is complete. Remove credentials and other secret data
// from authentication
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
return result;
}
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
throw lastException;
}
}
3、result = provider.authenticate(authentication);源码跟踪
public abstract class AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider implements
AuthenticationProvider, InitializingBean, MessageSourceAware {
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
// Determine username
String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED"
: authentication.getName();
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
//4、源码跟踪。这一句就会调用我们自己定义的MyUsesrDetailService,从数据库获取用户的逻辑
//我们进入当前类的实现类DaoAuthenticationProvider查看源码
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
}
try {
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
//5、跟踪检查用户是否过期超时等
postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
//这里对passwordEncoder密码的一些检查
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
}
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
}
//6源码进入
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}
}//4、源码跟踪。这一句就会调用我们自己定义的MyUsesrDetailService,从数据库获取用户的逻辑
//我们进入当前类的实现类DaoAuthenticationProvider查看源码
user = retrieveUser(username, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
UserDetails loadedUser;
try {
//调用我们自己的MyUserDetailService的loadUserByUsername
loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
}
return loadedUser;
}5、跟踪检查用户是否过期超时等postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
public void check(UserDetails user) {
if (!user.isAccountNonLocked()) {//检查是否被锁定
throw new LockedException(messages.getMessage(
"AccountStatusUserDetailsChecker.locked", "User account is locked"));
}
if (!user.isEnabled()) {//检查是否是有效的
throw new DisabledException(messages.getMessage(
"AccountStatusUserDetailsChecker.disabled", "User is disabled"));
}
if (!user.isAccountNonExpired()) {//检查是否超时
throw new AccountExpiredException(
messages.getMessage("AccountStatusUserDetailsChecker.expired",
"User account has expired"));
}
if (!user.isCredentialsNonExpired()) {
throw new CredentialsExpiredException(messages.getMessage(
"AccountStatusUserDetailsChecker.credentialsExpired",
"User credentials have expired"));
}
}6、源码进入 return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
这里就已经返回一个经过认证的authentication,然后我们返回到最开始的代码
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter的return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal,
Authentication authentication, UserDetails user) {
//这里就是最开始说的,认证成功之后,重新new一个token,这里的权限都有了
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken result = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
principal, authentication.getCredentials(),
authoritiesMapper.mapAuthorities(user.getAuthorities()));
result.setDetails(authentication.getDetails());
return result;
}接下来就会进入到springsecurity的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter前面的过滤器AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Request is to process authentication");
}
Authentication authResult;
try {
//这里调用UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.attemptAuthentication方法,
//获取到了一个authentication
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
return;
}
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
//7、源码跟踪
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}7、successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication success. Updating SecurityContextHolder to contain: "
+ authResult);
}
//认证结果如何在多个请求之间共享,把当阿倩信息存储到SecurityContextHolder 的ThreadLocal中
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
authResult, this.getClass()));
}
//这里就会调用我们自定义的成功处理器,要了解成功和失败处理器,可自行百度
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}自定义最简单的成功处理器如下
@Component
public class ImoocAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ImoocAuthenticationSuccessHandler.class);
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
logger.info("登陆成功");
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(authentication));
}
}
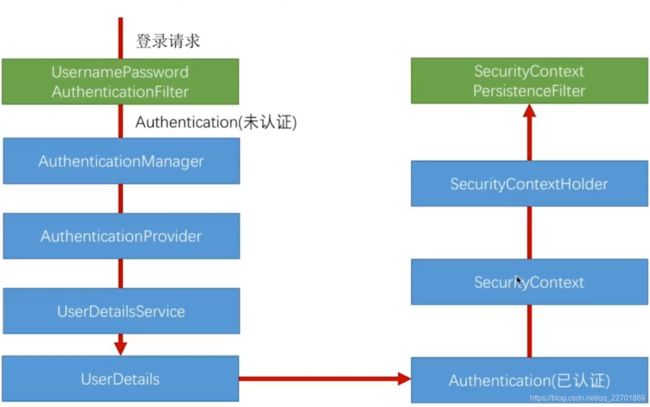
2、认证结果如何在多个请求之间共享
用户在登录成功之后,如何在后续的请求中的线程共享登录状态的呢?
在1、7中,源码如下//认证结果如何在多个请求之间共享,把当阿倩信息存储到SecurityContextHolder 的ThreadLocal变量Context中 SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication success. Updating SecurityContextHolder to contain: "
+ authResult);
}
//认证结果如何在多个请求之间共享,把当阿倩信息存储到SecurityContextHolder
//的ThreadLocal变量Context中,即放到当前线程中了,
//被SecurityContextPersistenctFilter使用
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
authResult, this.getClass()));
}
//这里就会调用我们自定义的成功处理器,要了解成功和失败处理器,可自行百度
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}被SecurityContextPersistenctFilter使用
3、获取认证用户信息
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
//方法一
@GetMapping("/getUser")
public Object getCurrentUser(){
return SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
}
//方法二
@GetMapping("/getUser2")
public Object getCurrentUser2(Authentication authentication){
return authentication;
}
}启动服务,登录之后,访问对应接口,返回结果如下,可以通过实际需要,去除多余的信息
{
"authorities": [{
"authority": "admin"
}],
"details": {
"remoteAddress": "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1",
"sessionId": null
},
"authenticated": true,
"principal": {
"password": null,
"username": "admin",
"authorities": [{
"authority": "admin"
}],
"accountNonExpired": true,
"accountNonLocked": true,
"credentialsNonExpired": true,
"enabled": true
},
"credentials": null,
"name": "admin"
}