基于Netty的JT/T 809-2011车辆定位数据交换协议的服务端开发记录
1.写在前面
九月初接到任务,负责开发xx区交通局接收车辆定位数据模块。当时对于socket的了解并不是太多,过往的工作和学习中对这一块也没有太过涉猎,吃了知识面过窄的亏。
pm给的时间也不是很长,当时就感觉要原地螺旋上天。资深的程序猿能在短时间内将一项新技能掌握个七七八八并迅速运行到项目中,完美掌控bug出现率。很明显我离这个境界差的不是一点点啊。所以面对是选择原生socket还是通信框架进行开发的时候,我只能选择直接上网google+度娘试图抓住几根救命稻草。
感谢这个信息爆炸的时代,弊端暂且不谈,互联网带给我们的好处还是大大的。
不知道是哪位大佬以前接过这样的任务,并无私地将半成品的代码发到网上供后来者参考,虽然漏洞也有但似乎已经足够了啊,喝水不忘挖井人,还是要感谢这位大佬奉献的精神,不然绩效被扣完就要吃土了啊!
佚名大佬选择的框架是netty,当时就着代码和几篇netty从入门到入土的博客直接开始啃,超硬
2.开始搞
public class JTServer implements Runnable{
private static Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JTServer.class);
private static Properties prop = new PropFileManagerImpl().load("socketParam.properties");
@Override
public void run() {
ChannelFactory factory = new NioServerSocketChannelFactory(Executors.newCachedThreadPool(),
Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(factory);
bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory() {
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = Channels.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("loging", new LoggingHandler(InternalLogLevel.INFO));
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new Decoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new Encoder());
pipeline.addLast("busiHandler", new BusiHandler());
return pipeline;
}
});
bootstrap.setOption("child.tcpNoDelay", true);
bootstrap.setOption("child.keepAlive", true);
bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(Integer.parseInt(prop.getProperty("mastersocket.port"))));
System.out.println("Netty服务启动!!!");
}
}public class NettyServerStart implements ServletContextListener{
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent arg0){
new Thread(new JTServer()).start();
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent arg0){
// waiting....
}
}2.1 服务端初建立
服务类直接继承了Runnable接口,我的处理是:通过启动tomcat的时候,初始化自定义的继承ServletContextListener的类,在contextInitialized()方法中启动netty服务类,并在web.xml中配置监听器监听tomcat的启动和销毁。至于什么tomcat热部署的时候会提示netty已经绑定当前的接口的异常不必理会,这种情况发生个鬼啊
那么这个服务启动类做了啥?
- ChannelFactory配置bossExecutor和workerExecutor,装进ServerBootstrap实例中
- 设置各种业务的handler,长连接配置
- 绑定服务器监听接口
2.2 Handler:Decoder
抛开logingHandler不谈,这货只是用来调试的,调试稳定之后就可以去除了啊。
Decoder这个Handler,继承了FrameDecoder这个抽象类,这个抽象类可以帮忙调整收到的数据包整理成需要的帧,看起来很不错的样子。那么按照JT-T809-2011的文件格式,逐步进行解析。
@Override
protected Object deocde(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,Channel channel,ChannelBuffer buffer) throws Exception{
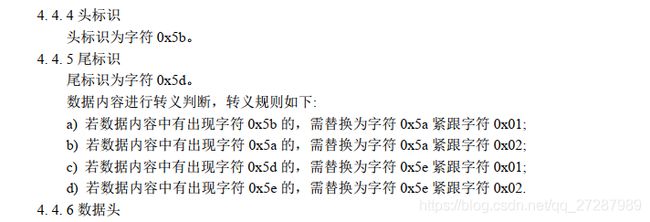
int head = buffer.getByte(0);//头标识 0x5b
int tail = buffer.getByte(buffer.capacity()-1); //尾标识 0x5d
if (!(head == Message.MSG_HEAD && tail == Message.MSG_TAIL)) { //确保收到的是完整的流
return null;
}
ChannelBuffer buffers = ChannelBuffers.dynamicBuffer(buffer.capacity());
byte[] bytes = ChannelBuffers.copiedBuffer(buffer).array();
//开始转义
ChannelBuffer newbuffer = reFormatBuffer(bytes,buffers);//转义后
buffer.setBytes(0, newbuffer, newbuffer.array().length);
//跳过头标识
buffer.skipBytes(1);
Message msg1 = this.buildMessage(buffer,bytes);
return msg1;
}佚名大佬忘记写针对流的反转义过程,这一点我是在测试接收车辆定位数据流的发现的,根据console中打印的日志可以清晰的观察到流中是否包含需要反转义的数据,log真tm是个节约时间的好东西
以下是自己写的反转义的过程:
private ChannelBuffer reFormatBuffer(byte[] bytes,ChannelBuffer buffers){
int index = 0; //是否跳过的标志位
int del = 0; //需要减少的数组个数
for(int i=0;i < bytes.length-1;i++){
if(index > 0){
index -- ;
continue;
}
byte begin = bytes[i];
byte next = bytes[i+1];
if(begin == 0x5a && next == 0x01){
index ++;
buffers.writeByte(0x5a);
del++;
}else if(begin == 0x5a && next == 0x02){
index ++;
buffers.writeByte(0x5a);
del++;
}else if(begin == 0x5e && next == 0x01){
index ++;
buffers.writeByte(0x5d);
del++;
}else if(begin == 0x5e && next == 0x02){
index ++;
buffers.writeByte(0x5b);
del++;
}else{
buffers.writeByte(begin);
}
}
buffers.writeByte(0x5d);
//反转义了多少字符,就在后面添加多少个0
for(int i=0;i针对转义的过程进行反转义,写的比较糙,空出的位数在后面补充0x00,确保buffers的容量填满。所以说写成这样是会过多久连自己都不认识然后大骂是哪个沙雕写的啊啊啊啊啊
校验和反转义完成后,然后就是开始解析数据头了啊
private Message buildMessage(ChannelBuffer bufferFinal,byte[] bytes){
Message msg = new Message();
msg.setMsgLength(bufferFinal.readUnsignedInt());
msg.setMsgSn(bufferFinal.readInt());//4 byte
msg.setMsgId(bufferFinal.readUnsignedShort());//2 byte
msg.setMsgGesscenterId(bufferFinal.readUnsignedInt());//4 byte
msg.setVersionFlag(bufferFinal.readBytes(3).array());//3 byte
msg.setEncryptFlag(bufferFinal.readUnsignedByte());//1 byte
msg.setEncryptKey(bufferFinal.readUnsignedInt());//4 byte
ChannelBuffer bodyBytes = bufferFinal.readBytes(bufferFinal.readableBytes() - 2 -1);//数据体为变长字节
msg.setMsgBody(bodyBytes);
msg.setCrcCode(bufferFinal.readUnsignedShort());//2 byte
//跳过尾标识
bufferFinal.skipBytes(1);//1 byte
//跳过剩余的字节0,考虑到有转义的字符
if(bufferFinal.readable()){
int nums = bufferFinal.readableBytes();
bufferFinal.skipBytes(nums);
}
return msg;
}读入除了头标识之外的剩余的数据结构部分。对比原来的部分,要考虑是否有字符被反转义然后读取尾标识之后的填充的0x00,将处理完毕后的消息继续传递给下个Handler
2.3 Handler:BusiHandler
这个处理器继承SImpleChannelHandler,为上下游事件向下转换
messageReceived方法开搞
@Override
public void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) throws Exception {
Message msg = (Message) e.getMessage(); //封装的数据体
switch (msg.getMsgId()) {
case 0x1001:
login(msg, ctx, e);
break;
case 0x1005:
heartBeat(msg, ctx, e);
break;
case 0x1200:
parseGPS(msg, ctx, e);
break;
case 0x1003:
cancellation(msg, ctx, e);
break;
case 0x1007:
disConnect(msg, ctx, e);
break;
case 0x1008:
closeLink(msg, ctx, e);
break;
default:
break;
}
}将消息转型成封装的数据体,那么针对业务类型进行不同的业务处理方法,先看看下级平台的登录请求接收处理
private void login(Message msg, ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) throws Exception {
final Channel channel = ctx.getChannel();
int userId = msg.getMsgBody().readInt();
String passWord = msg.getMsgBody().readBytes(8).toString(Charset.forName("GBK")).trim();
final String ip = msg.getMsgBody().readBytes(32).toString(Charset.forName("GBK")).trim();
final int port = msg.getMsgBody().readUnsignedShort();
msg.getMsgBody().clear();
Message msgRep = new Message(0x1002);
ChannelBuffer buffer = ChannelBuffers.buffer(5);
buffer.writeByte(0x00);
// 校验码
buffer.writeInt(1111);
msgRep.setMsgBody(buffer);
ChannelFuture f = e.getChannel().write(msgRep);
f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
// 开始建立从链路并发送登录请求
login2YinZhouGov(ip, port, 1111);
// 连接状态判断是否重连
boolean flag = TcpClient809.isFlag();
if (false == flag) {
// 客户端的ip和端口连接不上,发送消息进行通知
Message msgdis = new Message(0x9007);
ChannelBuffer bufferdis = ChannelBuffers.buffer(5);
bufferdis.writeByte(0x00);
msgdis.setMsgBody(bufferdis);
channel.write(msgdis);
}
}
}
});
}协议要求进行双通道通信,即所谓的上行平台和下行平台双链接。在下行平台连接成功后,获取ip和port,上行平台返回成功登录消息并添加监听器进行从链路的链接操作,login2YinZhouGov方法里面是异步的,当时low了一点直接选择Thread.sleep(算上socket重连的时间),现在想想蛮傻叉的。额,总之,繁么是繁琐了一点,为了保证消息到达的可行性才这么做,和tcp的握手挥手有异曲同工之妙。
那么来看看parseGPS方法,即下行平台传输过来的车辆定位数据处理业务逻辑。
private void parseGps(Message msg, ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException, ParseException {
Util.SysoStr("-----------------收到客户端发送的车辆业务请求!!");
MessageDomain message = new MessageDomain();
String carNum = msg.getMsgBody().readBytes(21).toString(Charset.forName("GBK")).trim();
message.setVehicleNo(carNum);
byte carColor = msg.getMsgBody().readByte();
message.setVehicleColor((int) carColor);
String dataType = "0x" + Integer.toHexString(msg.getMsgBody().readUnsignedShort()).trim();
message.setDataType(dataType);
boolean flag = dataType.trim().equals("0x1202");
if (true == flag) {
Util.SysoStr("打印是否进入车辆0x1202处理业务!!!!!");
int capacity = msg.getMsgBody().readInt(); //单纯的取出字节
byte encryptKey = msg.getMsgBody().readByte();// 加密
message.setExCrypt((int) encryptKey);
byte day = msg.getMsgBody().readByte();
byte month = msg.getMsgBody().readByte();
ChannelBuffer yearCB = msg.getMsgBody().readBytes(2);
byte[] years = yearCB.array();
String hexYear = Util.bytes2Hex(years); // 16进制字符串
String year = new BigInteger(hexYear, 16).toString();
byte hour = msg.getMsgBody().readByte();
byte minute = msg.getMsgBody().readByte();
byte second = msg.getMsgBody().readByte();
String times = addZeor(year, (int) month, (int) day, (int) hour, (int) minute, (int) second);
SimpleDateFormat simple = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmss");
message.setTimes(simple.parse(times)); // 年月日时分秒
int lon = msg.getMsgBody().readInt();
message.setLon(lon);
int lat = msg.getMsgBody().readInt();
message.setLat(lat);
int vec1 = msg.getMsgBody().readUnsignedShort();
message.setVec1(vec1);
int vec2 = msg.getMsgBody().readUnsignedShort();
message.setVec2(vec2);
int vec3 = msg.getMsgBody().readInt();
message.setVec3(vec3);
int direction = msg.getMsgBody().readUnsignedShort();
message.setDirection(direction);
int altitude = msg.getMsgBody().readUnsignedShort();
message.setAltitude(altitude);
int state = msg.getMsgBody().readInt();
message.setState(state);
int alarm = msg.getMsgBody().readInt();
message.setAlarm(alarm);
// 入库
ApplicationContext context = SpringContextUtils.getApplicationContext();
if (null == context) {
Util.SysoStr("当前环境为测试环境不包括spring框架,或者未在applicationContext配置文件中进行配置,入库操作取消");
} else {
MessageService messageService = (MessageService) context.getBean(MessageService.class);
messageService.inserts(message);
Util.SysoStr("--------车辆信息入库->" + message.toString());
}
} else if (dataType.trim().equals("0x1203")) {
// 车辆定位信息自动补报,判断条数
Util.SysoStr("打印是否进入车辆0x1203处理业务!!!!!");
prescribedCar(msg, message);//车辆自动补报业务
return;
}
}关于车辆定位自动补报和其它的业务,就不再详叙了,和0x1202的业务差不多。关于一条数据消息在整个处理链中的传递的步骤处理,处理速度能有多快就有多块,看了下数据库相邻数据的的入库时间,就只差几秒而已,一天的话差不多就有几万条数据入库,酌情保留N天的数据。目前项目部署在服务器上跑了将近1个月了,还没发现出现什么大问题,如果崩溃的话需要结合线上的日志和其他工具分析可能引起的问题。
3.总结
知识面过窄是致命的缺陷,尽量避免叫天不应叫地不灵的局面,不然还指望能有凹凸曼从天而降拯救世界嘛