Spring生命周期以及如何在Spring启动时加入逻辑
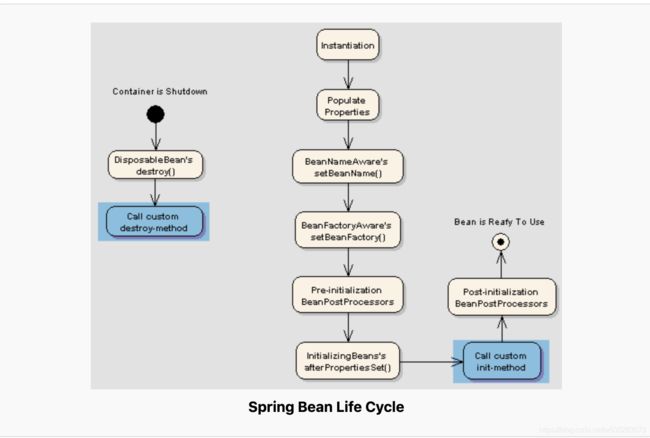
先上两张图,了解一下springbean的生命周期,对理解后面的正文有很大帮助。生命周期在面试和平时开发中也很重要。
提供三张图,大同小异,可以对比参考。
spring为在bean生命周期的不同阶段提供了丰富的可以加入逻辑的“入口”。
下面是一篇非常不错的英文文章,翻译在此,供大家参考。
-----------------------------------------------------华丽分割线-----------------------------------------------------
1、介绍
本文主要讲述如何在Spring 应用启动时执行逻辑。
2、启动时运行业务逻辑
我们不能简单的将逻辑代码放到bean构造器里,或者实例化完成对象后。
我们先看一个例子:
@Component
public class InvalidInitExampleBean {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
public InvalidInitExampleBean() {
env.getActiveProfiles();
}
}在构造方法中访问@autowired注解注入进来的对象。但是在spring的bean的构造方法是在还没有初始化完成时调用。这就有问题了,调用还没有初始化完成的属性当然会导致空指针异常。
Spring提供了多种解决方案。
2.1 @PostConstruct 注解
可以用在方法上,该方法将在bean初始化完成后立马调用。
需要留意的是,即使该方法中没有注入的对象也会被spring执行。
@Component
public class PostConstructExampleBean {
private static final Logger LOG
= Logger.getLogger(PostConstructExampleBean.class);
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
LOG.info(Arrays.asList(environment.getDefaultProfiles()));
}
}上面的例子,Environment实例被正确的注入到了该bean中,@PostConstruct 的方法被调用时也没报空指针。
2.2. InitializingBean接口
该接口的功能和上面的注解非常类似。需要实现InitializingBean接口并重写afterPropertiesSet() 函数。
Component
public class InitializingBeanExampleBean implements InitializingBean {
private static final Logger LOG
= Logger.getLogger(InitializingBeanExampleBean.class);
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
LOG.info(Arrays.asList(environment.getDefaultProfiles()));
}
}2.3. ApplicationListener
有些场景需要在spring上下文初始化完成后执行一些逻辑,并不需要关注任何一个具体的bean,但是还需要等待他们初始化完成。
这种情况,我们可以实现pplicationListener
@Component
public class StartupApplicationListenerExample implements
ApplicationListener {
private static final Logger LOG
= Logger.getLogger(StartupApplicationListenerExample.class);
public static int counter;
@Override public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
LOG.info("Increment counter");
counter++;
}
}
使用 @EventListener注解也可以实现相同的效果。
@Component
public class EventListenerExampleBean {
private static final Logger LOG
= Logger.getLogger(EventListenerExampleBean.class);
public static int counter;
@EventListener
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
LOG.info("Increment counter");
counter++;
}
}2.4 @Bean initMethod
bean的initMethod方法可以用在bean初始化完成后。
Bean长这样:
public class InitMethodExampleBean {
private static final Logger LOG = Logger.getLogger(InitMethodExampleBean.class);
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
public void init() {
LOG.info(Arrays.asList(environment.getDefaultProfiles()));
}
}可以通过注解方式实现
Bean(initMethod="init")
public InitMethodExampleBean exBean() {
return new InitMethodExampleBean();
}也可以通过xml方式
2.5. Constructor 构造方法注入
可以通过构造方法注入,在构造方法中加上逻辑。
@Component
public class LogicInConstructorExampleBean {
private static final Logger LOG
= Logger.getLogger(LogicInConstructorExampleBean.class);
private final Environment environment;
@Autowired
public LogicInConstructorExampleBean(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
LOG.info(Arrays.asList(environment.getDefaultProfiles()));
}
}2.6. Spring Boot CommandLineRunner
springboot提供 CommanLineRunner 接口,提供了run() 回调方法,spirng上下文初始化完成后应用启动后将会调用。
@Component
public class CommandLineAppStartupRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
private static final Logger LOG =
LoggerFactory.getLogger(CommandLineAppStartupRunner.class);
public static int counter;
@Override
public void run(String...args) throws Exception {
LOG.info("Increment counter");
counter++;
}
}完整代码在这里:https://github.com/eugenp/tutorials/tree/master/spring-boot
如果有多个CommanLineRunner 实现类,可以实现 Ordered 接口或者@Order注解指定执行顺序。
2.7. Spring Boot ApplicationRunner
和CommandLineRunner非常相似,ApplicationRunner 接口也体用了run()方法,当应用启动时会调用。
但是参数不同,它的参数是ApplicationArguments 。
@Component
public class AppStartupRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
private static final Logger LOG =
LoggerFactory.getLogger(AppStartupRunner.class);
public static int counter;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
LOG.info("Application started with option names : {}",
args.getOptionNames());
LOG.info("Increment counter");
counter++;
}
}3. 多种机制一起用
执行顺序是
- 构造方法
- @PostConstruct注解的方法
- InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet() 方法
- xml定义的init-method 初始化方法
@Component
@Scope(value = "prototype")
public class AllStrategiesExampleBean implements InitializingBean {
private static final Logger LOG
= Logger.getLogger(AllStrategiesExampleBean.class);
public AllStrategiesExampleBean() {
LOG.info("Constructor");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
LOG.info("InitializingBean");
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
LOG.info("PostConstruct");
}
public void init() {
LOG.info("init-method");
}
}运行时的输出:
[main] INFO o.b.startup.AllStrategiesExampleBean - Constructor
[main] INFO o.b.startup.AllStrategiesExampleBean - PostConstruct
[main] INFO o.b.startup.AllStrategiesExampleBean - InitializingBean
英文原文:https://www.baeldung.com/running-setup-logic-on-startup-in-spring