Response
就是对于响应报文的封装。
HttpServletResponse----父子接口。
既然response就代表了将来的响应报文
响应报文:
响应行:版本、状态码(setStatus)、描述
响应头(response.setHeader(key,value))
响应体(response.getWriter().println())
1.1输出数据到客户端
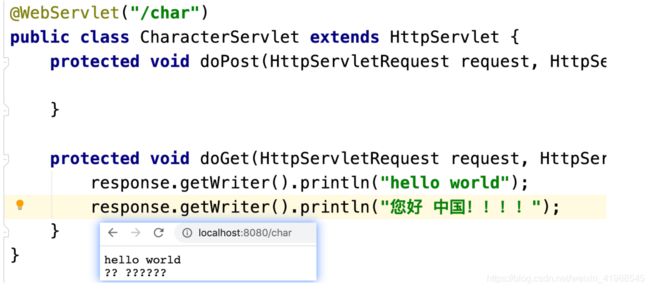
Response.getWriter().println
输出中文?
乱码的原因去分析?
编解码不一致。
服务器构建响应报文的时候,中文用哪种编码格式?不清楚。ISO-8859-1。
响应报文到达客户端之后,客户端怎么去处理的?客户端使用的是GBK。
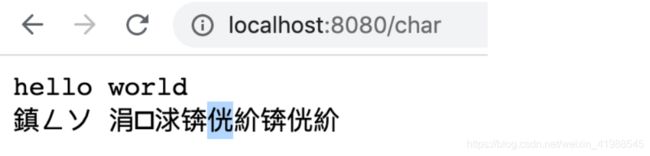
锟斤拷烫烫烫
此时乱码发生了一些变化,乱码的原因在于客户端使用的不是utf-8,而是GBK。
只需要解决一个问题,怎么让客户端主动去使用utf-8?
1.1.1乱码解决方案一
1.1.2乱码解决方案二
1.1.3乱码解决方案三
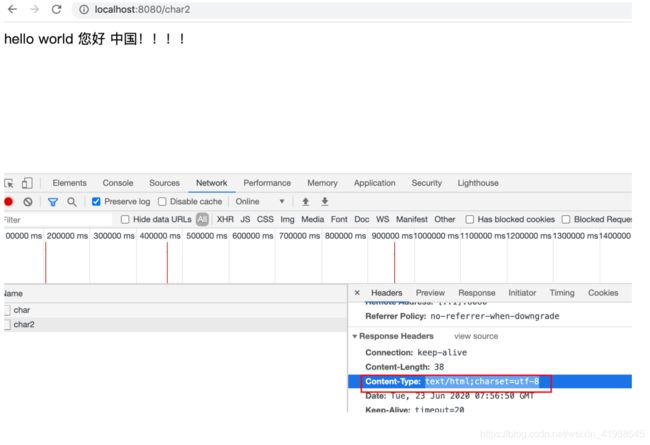
Response.setHeader(“content-type”,”text/html;charset=utf-8”)
1.2输出字节数据
文件的传输。比如显示图片、比如显示html里面的内容。
显示WEB-INF目录下的1.html内容
@WebServlet("/stream")
public class StreamServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//将WEB-INF目录下1.html显示到页面
//本质上来说不就是IO流
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
String path = getServletContext().getRealPath("WEB-INF/1.html");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File(path));
int length = 0;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while ((length = fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1){
outputStream.write(bytes, 0, length);
}
//关闭流 request提供的输入流以及response提供的输出流可以关 也可以不关
//不关的话,tomcat也会在响应结束时给关闭
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
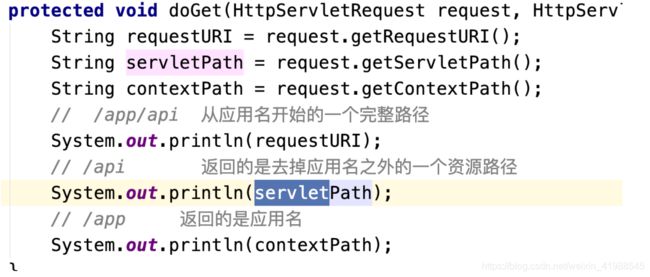
requestURI = contextPath + servletPath
1.3定时刷新
refresh响应头
@WebServlet("/refresh")
public class RefreshServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//使用方式一 每隔指定秒数刷新一下当前页面
response.getWriter().println(new Date());
//response.setHeader("refresh","1");
//使用方式二 后面会带着一个url,表示的是经过指定秒数之后,跳转至url
//response.setHeader("refresh","2;url=stream");
// /应用名/资源名路径写法
//response.setHeader("refresh","2;url=" + request.getContextPath() + "/stream");
//可以跳转至外部
response.setHeader("refresh","2;url=http://www.cskaoyan.com");
}
}定时刷新也可以用来进行页面跳转。
1.4重定向
访问某一个地址,服务器返回一个302或者307的状态码,表示需要重定向,响应头还包含一个Location头,指明了下次重定向的路径。
自己利用现有的API来实现。
方式1:
@WebServlet("/redirect")
public class RedirectServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setStatus(302);
response.setHeader("Location",request.getContextPath() + "/stream");
}
}方式2:也可以利用服务器提供的api
@WebServlet("/redirect2")
public class RedirectServlet2 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// response.setStatus(302);
// response.setHeader("Location",request.getContextPath() + "/stream");
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/stream");
}
}
1.5转发,定时刷新,重定向区别联系
共同点:都可以用来进行页面跳转
不同点:
1.转发只有一次请求;刷新和重定向发起两次请求
2.转发是request介导的;刷新和重定向是response介导的
3.转发可以共享request域;刷新和重定向不可以
4.转发只能应用内跳转;刷新和重定向没有限制
5.转发是服务器介导;刷新和重定向是浏览器介导(/开头路径写法不同)
6.重定向状态码302、307;其他是2001.6下载
比如导出数据到excel。最后一步会利用该API。
对于浏览器来说,浏览器可以打开的文件,默认会执行打开操作,对于无法打开的文件,默认会执行下载操作。
但是,对于那些可以打开的文件,如果不想让它打开,可以设置一个响应头,直接让文件下载下来。
@WebServlet("/download")
public class DownloadServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename=1.jpg");//这条
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
String path = getServletContext().getRealPath("1.jpg");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File(path));
int length = 0;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while ((length = fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1){
outputStream.write(bytes, 0, length);
}
//关闭流 request提供的输入流以及response提供的输出流可以关 也可以不关
//不关的话,tomcat也会在响应结束时给关闭
fileInputStream.close();
}
}用servlet显示图片
@WebServlet("/view")
public class ViewServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename=1.jpg");
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
String path = getServletContext().getRealPath("1.jpg");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File(path));
int length = 0;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while ((length = fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1){
outputStream.write(bytes, 0, length);
}
//关闭流 request提供的输入流以及response提供的输出流可以关 也可以不关
//不关的话,tomcat也会在响应结束时给关闭
fileInputStream.close();
}
}