一 CSS介绍
层叠样式表(英文全称:Cascading Style Sheets)是一种用来表现HTML(超文本标记语言)或XML(标准通用标记语言的一个子集)等文件样式的计算机语言。CSS不仅可以静态地修饰网页,还可以配合各种脚本语言动态地对网页各元素进行格式化。
CSS 能够对网页中元素位置的排版进行像素级精确控制,支持几乎所有的字体字号样式,拥有对网页对象和模型样式编辑的能力,CSS也称为级联样式表。
二 CSS语法
1.CSS实例与注释
1.1 注释乃代码之母
/*单行注释*/ /* 这是多行注释 这是多行注释 */
1.2 CSS实例
选择器 {属性:属性值;属性:属性值;属性:属性值;}
/*举个例子,比如将html中div标签的字体样式都设置为红色、24像素大小且加粗*/ div { color: red; font-size: 24px; font-weight: bold; }
1.3 引入CSS的三种方式
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>引入CSS的三种方式title>
<style>
div {
color: red;
}
style>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="mycss.css">
head>
<body>
<div style="color:red;">this is testdiv>
body>
html>
2. CSS选择器
要修改样式,就需要先找到要被修改的对象,这就需要用到选择器。
选择器优先级:
行内样式 > id选择器 > 类选择器 > 标签选择器
2.1 基本选择器
基本选择器
div1
div2
div3
div4
p1
2.2 组合选择器
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>组合选择器title>
<style>
/*组合选择器分为四种:后代选择器、儿子选择器、毗邻选择器、弟弟选择器*/
/*后代选择器*/
div span {
color:red;
}
/*儿子选择器*/
div>span {
color:red;
}
/*毗邻选择器*/
div+span {
color:red;
}
/*弟弟选择器*/
div~span {
color:red;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<span>我是div上面的第一个spanspan>
<div>
<span>我是div里面的第一个spanspan>
<p>我是div里面的第一个p
<span>
我是p里面的span
span>
p>
<span>我是div里面的第二个spanspan>
div>
<span>我是div下的第一个spanspan>
<span>我是div下的第二个spanspan>
body>
html>
2.3 属性选择器
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>属性选择器title>
<style>
/*样式对所有属性为xxx的元素生效*/
[xxx] {
color:red;
}
/*样式对所有属性为xxx且值为'2'的元素生效*/
[xxx='2'] {
color:red;
}
/*样式对所有属性为xxx且值为'2',并且标签为div的元素生效*/
div[xxx='3'] {
color:red;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div xxx="1">div1div>
<div xxx="2">div2div>
<div xxx="3">div3div>
<p xxx="3">p1p>
body>
html>
2.4 伪类选择器
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伪类选择器title>
<style>
/*a标签自带下划线,用decoration去掉会好看点*/
a {
text-decoration: none;
}
/*未访问的链接颜色设置为红色*/
a:link {
color: red;
}
/*鼠标移动到链接上时的链接的颜色设置为黄色*/
a:hover {
color: yellow;
}
/*标点击链接时链接的颜色设置为蓝色*/
a:active {
color: blue;
}
/*已访问的链接颜色设置为绿色*/
a:visited {
color: green;
}
/*input输入框获取焦点时的颜色设置为红色*/
input:focus {
background-color:red;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<a href="https://www.baidu.com">这是百度a>
<a href="https://www.sogo.com">这是搜狗a>
<a href="https://www.cnblogs.com/linhaifeng">博客园a>
<a href="https://hao.360.com/?a1004">点我a>
<input type="text">
body>
html>
2.5 伪元素选择器
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伪元素选择器title>
<style>
/*伪元素可以用于清除浮动带来的影响*/
/*修改p标签中内容的第一个元素的样式*/
p:first-letter {
color:red;
font-size: 24px;
}
/*在p标签内容前加16px大小'*'*/
p:before {
content: '*';
font-size: 16px;
}
/*在p标签内容后面加24px大小的红色'?'*/
p:after {
content: '?';
color:red;
font-size: 24px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<p>23333333p>
<p>23333333p>
<p>23333333p>
<p>23333333p>
body>
html>
2.6 分组与嵌套
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>分组与嵌套title>
<style>
/*让div、span、p标签元素读使用同一样式*/
div,p,span {
color: red;
}
/*也可以组合选择器与基本选择器混用*/
div p,span {
color: red;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div>div0div>
<p>p0p>
<span>s0span>
body>
html>
这里提一下CSS的继承,继承是CSS的一个主要特征,它是依赖于祖先-后代的关系的。继承是一种机制,它允许样式不仅可以应用于某个特定的元素,还可以应用于它的后代。例如一个body定义了的字体颜色值也会应用到段落的文本中。
body { color: red; }
此时页面上所有标签都会继承body的字体颜色。然而CSS继承性的权重是非常低的,是比普通元素的权重还要低的0。
我们只要给对应的标签设置字体颜色就可覆盖掉它继承的样式。
p { color: green; }
此外,继承是CSS重要的一部分,我们甚至不用去考虑它为什么能够这样,但CSS继承也是有限制的。有一些属性不能被继承,如:border, margin, padding, background等。
3.CSS文本属性、颜色
CSS可以给为元素设置高度(height)和宽度(width),当然是针对块级标签而言,内联标签(行内标签)的大小由内容来决定。
3.1 文字字体
font-family可以把多个字体名称作为一个“回退”系统来保存。如果浏览器不支持第一个字体,则会尝试下一个。浏览器会使用它可识别的第一个值。
body { font-family: "Microsoft Yahei", "微软雅黑", "Arial", sans-serif }
3.2 文字大小
/*如果设置成inherit表示继承父元素的字体大小值。*/ p { font-size: 14px; }
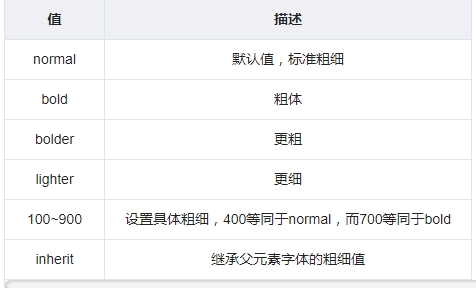
3.3 字重(粗细)
font-weight用来设置字体的字重(粗细)。
3.4 文本颜色
颜色属性被用来设置文字的颜色。
颜色是通过CSS最经常的指定:
- 十六进制值 - 如: #FF0000
- 一个RGB值 - 如: RGB(255,0,0)
- 颜色的名称 - 如: red
还有rgba(255,0,0,0.3),第四个值为alpha, 指定了色彩的透明度/不透明度,它的范围为0.0到1.0之间(0.0为全透明,1.0为正常)。
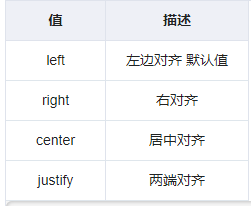
3.5 文字对齐
text-align 属性规定元素中的文本的水平对齐方式。
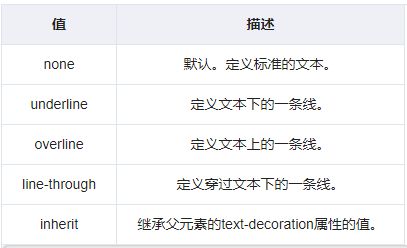
3.6 文字装饰
text-decoration 属性用来给文字添加特殊效果。常配合a标签使用来去除a标签默认的下划线。
3.7 首行缩进
/*首行缩进32像素*/ p { text-indent: 32px; }
4. 背景属性
/*背景颜色*/ background-color: red; /*背景图片*/ background-image: url('1.jpg'); /* 背景重复 repeat(默认):背景图片平铺排满整个网页 repeat-x:背景图片只在水平方向上平铺 repeat-y:背景图片只在垂直方向上平铺 no-repeat:背景图片不平铺 */ background-repeat: no-repeat; /*背景位置*/ background-position: left top; /*background-position: 200px 200px;*/
支持简写:
background:#336699 url('1.png') no-repeat left top;
使用背景图片的一个常见案例就是很多网站会把很多小图标放在一张图片上,然后根据位置去显示图片。减少频繁的图片请求。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>滚动背景图示例title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
}
.box {
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
background: url("http://gss0.baidu.com/94o3dSag_xI4khGko9WTAnF6hhy/zhidao/wh%3D450%2C600/sign=e9952f4a6f09c93d07a706f3aa0dd4ea/4a36acaf2edda3cc5c5bdd6409e93901213f9232.jpg") center center;
background-attachment: fixed;
}
.d1 {
height: 500px;
background-color: tomato;
}
.d2 {
height: 500px;
background-color: steelblue;
}
.d3 {
height: 500px;
background-color: mediumorchid;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="d1">div>
<div class="box">div>
<div class="d2">div>
<div class="d3">div>
body>
html>
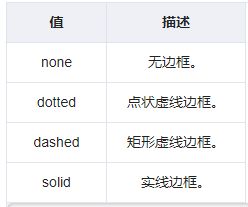
5. 边框
边框border有三个属性,border-width(边框宽度)、border-style(边框样式)、border-color(边框颜色)。
#i1 { border-width: 2px; border-style: solid; border-color: red; } /*通常简写为以下形式,且不分先后顺序*/ #i1 { border: 2px solid red; }
设置border-radius可以得到一个圆形
div { height: 400px; width: 400px; /*border-color: black;*/ /*border-style: solid;*/ /*border-width: 3px;*/ /*以上三步合并为一步*/ border:3px black solid; background-color: burlywood; /*画圆,建议写50%而不是长或宽一半的像素, 当长宽不一样时得到的是一个椭圆 */ border-radius: 50%; }
边框样式
6. display属性
用于控制HTML元素的显示效果。
display:"none"与visibility:hidden的区别:
visibility:hidden: 可以隐藏某个元素,但隐藏的元素仍需占用与未隐藏之前一样的空间。也就是说,该元素虽然被隐藏了,但仍然会影响布局。
display:none: 可以隐藏某个元素,且隐藏的元素不会占用任何空间。也就是说,该元素不但被隐藏了,而且该元素原本占用的空间也会从页面布局中消失。
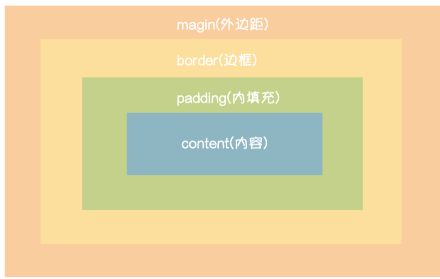
三. CSS盒子模型
- margin: 用于控制元素与元素之间的距离;margin的最基本用途就是控制元素周围空间的间隔,从视觉角度上达到相互隔开的目的。
- padding: 用于控制内容与边框之间的距离;
- Border(边框): 围绕在内边距和内容外的边框。
- Content(内容): 盒子的内容,显示文本和图像。
如果把一个元素比喻成一个盒子的话,margin就是一个盒子与另一个盒子之间的距离;border是盒子的厚度;content是装在盒子里的东西;padding就是盒子与装在它里面的东西的间隙大小。
1. margin和padding
/*padding的话只需把margin改成padding即可*/
.margin-test { margin-top:5px; margin-right:10px; margin-bottom:15px; margin-left:20px; } /*以上可以简写为以下形式,padding也是*/ .margin-test { margin: 5px 10px 15px 20px; }
margin和padding的简写根据参数个数不同有以下四种情况:
- 一个参数:用于四边
- 两个参数:第一个用于上下,第二个用于左右
- 三个参数:第一个用于上,第二个用于左右,第三个用于下
- 四个参数:按上右下左的顺序作用于四边(即顺时针)
注意:两个参数时可以实现居中
/* 第一个参数0作用于上下,第二个参数auto作用于左右 而且auto用在上和下时没有意义,因为auto居中只能实现水平方向的居中 */ .mycenter { margin: 0 auto; }
四. 浮动
在CSS中,任何元素都可以浮动。不论本身是何种元素,只要浮动了就会生成一个块级框。
CSS中存在X轴和Y轴,浮动相当于元素在Z轴的方向上变高了(抽象来说,就是离用户更近了,贞子从电视里爬出来,爬的就是Z轴,怕不怕)。
关于浮动的两个特点:
- 浮动的框可以向左或向右移动,直到它的外边缘碰到包含框或另一个浮动框的边框为止。
- 由于浮动框不在文档的普通流中,所以文档的普通流中的块框表现得就像浮动框不存在一样。
.c1 { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: burlywood; /*left向左浮动,right向右浮动,none默认值不浮动*/ loat:left; }
浮动常用于页面的布局,而浮动带来的影响就是会造成父标签的塌陷(如果说父标签是一个气球,浮动相当于里面的气都浮出去了,然后带来的结果就是气球扁了。)
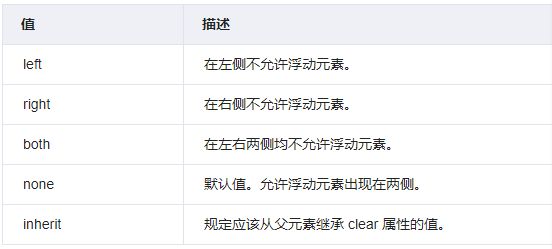
1. 清除浮动带来的影响
这里要用到clear属性,它规定元素的哪一侧不能有其他浮动元素。
注意:clear属性只会对自身起作用,而不会影响其他元素。
清除浮动的方式:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>浮动清除方式一title>
<style>
/*浏览器自带8像素的margin,这里将其去除以更好展示浮动效果*/
body {
margin:0;
}
.c1 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: burlywood;
float:left;
}
.c2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
float:left;
}
.c3 {
border: 3px solid black;
}
/*定义一个与浮动元素等宽的元素来撑起父标签*/
.c4 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="c3">
<div class="c1">div>
<div class="c2">div>
<div class="c4">div>
div>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>浮动title>
<style>
body {
margin:0;
}
.c1 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: burlywood;
float:left;
}
.c2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
float:left;
}
.c3 {
border: 3px solid black;
}
/*clearfix是约定俗成的用来清除浮动带来的影响的类的名字
运用伪元素来撑起空间,推荐该方式
*/
.clearfix:after {
content: '';
display:block;
clear:both;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="c3 clearfix">
<div class="c1">div>
<div class="c2">div>
div>
body>
html>
五. 溢出
当一个元素长宽设置好时,如果里面的元素比它大,就会造成溢出效果。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>溢出title>
<style>
/*定义一个长宽均为50像素的元素*/
.c2 {
height: 50px;
width: 50px;
border:3px solid white;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="c2">
nioasf;awejfafuahefefnaius
hdfsandjfhauirgha;ndfj;kanfdja
div>
body>
html>
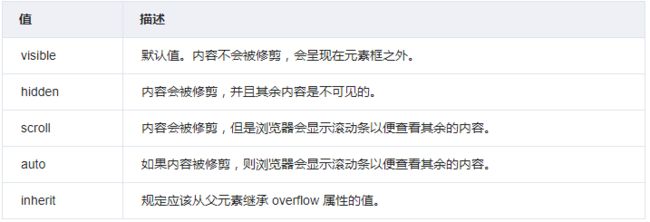
可以通过overflow属性来设置对溢出的处理
.c2 { height: 50px; width: 50px; border:3px solid white; overflow:hidden;
/*具体overflow参数见下图*/ }
可以运用溢出的处理以及border-radius画圆来实现圆形头像。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>溢出title>
<style>
body {
background-color: darkgray;
}
.c1 {
height: 150px;
width: 150px;
border:3px solid white;
border-radius: 50%;
overflow:hidden;
}
img {
width: 100%;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="c1">
<img src="1.jpg" alt="">
div>
body>
html>
六. 定位
static
static 默认值,无定位,不能当作绝对定位的参照物,并且设置标签对象的left、top等值是不起作用的的。
relative(相对定位)
相对定位是相对于该元素在文档流中的原始位置,即以自己原始位置为参照物。有趣的是,即使设定了元素的相对定位以及偏移值,元素还占有着原来的位置,即占据文档流空间。对象遵循正常文档流,但将依据top,right,bottom,left等属性在正常文档流中偏移位置。而其层叠通过z-index属性定义。
注意:position:relative的一个主要用法:方便绝对定位元素找到参照物。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>相对定位title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
.c1 {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background: red;
position:relative;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="c1">div>
body>
html>
absolute(绝对定位)
定义:设置为绝对定位的元素框从文档流完全删除,并相对于最近的已定位祖先元素定位,如果元素没有已定位的祖先元素,那么它的位置相对于最初的包含块(即body元素)。元素原先在正常文档流中所占的空间会关闭,就好像该元素原来不存在一样。元素定位后生成一个块级框,而不论原来它在正常流中生成何种类型的框。
重点:如果父级设置了position属性,例如position:relative;,那么子元素就会以父级的左上角为原始点进行定位。这样能很好的解决自适应网站的标签偏离问题,即父级为自适应的,那我子元素就设置position:absolute;父元素设置position:relative;,然后Top、Right、Bottom、Left用百分比宽度表示。
另外,对象脱离正常文档流,使用top,right,bottom,left等属性进行绝对定位。而其层叠通过z-index属性定义。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位title>
<style>
.c1 {
width:100px;
height:100px;
background-color: red;
position:relative;
}
.c2 {
width:100px;
height:100px;
background-color: blue;
position:absolute;
top:100px;
left:100px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="c1">
<div class="c2">div>
div>
body>
html>
fixed(固定)
fixed:对象脱离正常文档流,使用top,right,bottom,left等属性以窗口为参考点进行定位,当出现滚动条时,对象不会随着滚动。而其层叠通过z-index属性 定义。 注意点: 一个元素若设置了 position:absolute | fixed; 则该元素就不能设置float。这 是一个常识性的知识点,因为这是两个不同的流,一个是浮动流,另一个是“定位流”。但是 relative 却可以。因为它原本所占的空间仍然占据文档流。
在理论上,被设置为fixed的元素会被定位于浏览器窗口的一个指定坐标,不论窗口是否滚动,它都会固定在这个位置。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>返回顶部示例title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
}
.d1 {
height: 1000px;
background-color: #eeee;
}
.scrollTop {
background-color: darkgrey;
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
position: fixed;
right: 10px;
bottom: 20px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="d1">111div>
<div class="scrollTop">返回顶部div>
body>
html>
是否脱离文档流
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<style>
.c1 {
height: 50px;
width: 100px;
background-color: dodgerblue;
}
.c2 {
height: 100px;
width: 50px;
background-color: orange;
position: relative;
left: 100px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="c1">div>
<div class="c2">div>
<div style="height: 100px;width: 200px;background-color: black">div>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<style>
.c1 {
height: 50px;
width: 100px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
}
.c2 {
height: 50px;
width: 200px;
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
left: 50px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="c1">购物车
<div class="c2">空空如也~div>
<div style="height: 50px;width: 100px;background-color: deeppink">div>
div>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
head>
<body>
<div class="c1" style="height: 50px;width: 500px;background-color: black">div>
<div class="c2" style="height: 50px;width: 100px;background-color: deeppink;position: fixed;right: 10px;bottom: 20px">div>
<div class="c3" style="height: 10px;width: 100px;background-color: green">div>
body>
html>
上述例子可知:
脱离文档流:
绝对定位
固定定位
不脱离文档流:
相对定位
七. z-index
#i2 { z-index: 999; }
设置对象的层叠顺序。
- z-index 值表示谁压着谁,数值大的压盖住数值小的,
- 只有定位了的元素,才能有z-index,也就是说,不管相对定位,绝对定位,固定定位,都可以使用z-index,而浮动元素不能使用z-index
- z-index值没有单位,就是一个正整数,默认的z-index值为0如果大家都没有z-index值,或者z-index值一样,那么谁写在HTML后面,谁在上面压着别人,定位了元素,永远压住没有定位的元素。
- 从父现象:父亲怂了,儿子再牛逼也没用
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>自定义模态框title>
<style>
.cover {
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.65);
position: fixed;
top: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
z-index: 998;
}
.modal {
background-color: white;
position: fixed;
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
margin: -200px 0 0 -300px;
z-index: 1000;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="cover">div>
<div class="modal">div>
body>
html>
八. opacity
用来定义透明效果。取值范围是0~1,0是完全透明,1是完全不透明。
九. 模拟一个简单的博客页面
HTML和CSS代码分开写是一个规范,而且一般是先HTML将页面骨架搭建好,然后再去写CSS来增加样式,最重要的事要多写注释!!!
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>cnblogtitle>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="blog.css">
head>
<body>
<div class="blog-left">
<div class="left-avatar">
<img src="1.jpg" alt="">
div>
<div class="left_name">不愿透露姓名的博客div>
<div class="left-signature">这个人很懒,什么都没写div>
<div class="left-info">
<ul>
<li>关于我li>
<li>微博li>
<li>微信公众号li>
ul>
div>
<div class="left-lang">
<ul>
<li>#pythonli>
<li>#javali>
<li>#golangli>
ul>
div>
div>
<div class="blog-right">
<div class="right-article">
<div class="title">
<span class="tag">无题span>
<span class="date">2019-5-30span>
div>
<div class="content">两只黄鹂鸣翠柳,一行白鹭上青天div>
<div class="article-bottom">
<span>#pythonspan><span>#javascriptspan>
div>
div>
<div class="right-article">
<div class="title">
<span class="tag">无题span>
<span class="date">2019-5-30span>
div>
<div class="content">两只黄鹂鸣翠柳,一行白鹭上青天div>
<div class="article-bottom">
<span>#pythonspan><span>#javascriptspan>
div>
div>
<div class="right-article">
<div class="title">
<span class="tag">无题span>
<span class="date">2019-5-30span>
div>
<div class="content">两只黄鹂鸣翠柳,一行白鹭上青天div>
<div class="article-bottom">
<span>#pythonspan><span>#javascriptspan>
div>
div>
<div class="right-article">
<div class="title">
<span class="tag">无题span>
<span class="date">2019-5-30span>
div>
<div class="content">两只黄鹂鸣翠柳,一行白鹭上青天div>
<div class="article-bottom">
<span>#pythonspan><span>#javascriptspan>
div>
div>
<div class="right-article">
<div class="title">
<span class="tag">无题span>
<span class="date">2019-5-30span>
div>
<div class="content">两只黄鹂鸣翠柳,一行白鹭上青天div>
<div class="article-bottom">
<span>#pythonspan><span>#javascriptspan>
div>
div>
div>
body>
html>
/*通用样式*/ body { background-color: rgb(242,242,242); margin: 0; } a { text-decoration: none; } img { width: 100%; } ul { list-style-type: none; padding:0; } /*博客左侧样式开始*/ .blog-left { width:20%; height:100%; position:fixed; top:0; left:0; background-color: rgb(76,76,76); float:left; } /*圆形头像样式*/ .left-avatar { width:150px; height:150px; overflow:hidden; border: 3px solid white; border-radius: 50%; margin: 10px auto; } .left_name,.left-signature { color: white; text-align: center; } .left-info,.left-lang { text-align: center; margin-top:60px; color: darkgrey; } .left-info li:hover,.left-lang li:hover { color: white; } /*博客左侧样式结束*/ /*博客右侧样式*/ .blog-right { width:80%; float:right; } .right-article { background-color: white; box-shadow: 3px 3px 3px rgba(43,43,43, 0.4); margin:15px 20px 10px 15px; } /*文章标题样式开始*/ .title { border-left:3px solid red; } .tag { font-size: 36px; margin-left: 10px; } .date { float:right; font-size: 16px; margin-top: 20px; margin-right:10px; } /*文章标题样式结束*/ /*文章内容样式开始*/ .content { font-size: 24px; border-bottom: 1px solid black; padding: 10px 0 10px 10px; } /*文章内容样式结束*/ /*文章底部样式*/ .article-bottom { padding-bottom: 10px; padding-top: 5px; } .article-bottom span{ margin-left: 20px; /*padding: 5px;*/ }