(二)基于Netty的高性能Websocket服务器(netty-websocket-spring-boot)
@toc
Netty是一款基于NIO(Nonblocking I/O,非阻塞IO)开发的网络通信框架,对比于BIO(Blocking I/O,阻塞IO),他的并发性能得到了很大提高。
1、Netty为什么传输快
Netty的传输快其实也是依赖了NIO的一个特性——零拷贝。我们知道,Java的内存有堆内存、栈内存和字符串常量池等等,其中堆内存是占用内存空间最大的一块,也是Java对象存放的地方,一般我们的数据如果需要从IO读取到堆内存,中间需要经过Socket缓冲区,也就是说一个数据会被拷贝两次才能到达他的的终点,如果数据量大,就会造成不必要的资源浪费。
Netty针对这种情况,使用了NIO中的另一大特性——零拷贝,当他需要接收数据的时候,他会在堆内存之外开辟一块内存,数据就直接从IO读到了那块内存中去,在netty里面通过ByteBuf可以直接对这些数据进行直接操作,从而加快了传输速度。
2、Netty和Tomcat有什么区别?
Netty和Tomcat最大的区别就在于通信协议,Tomcat是基于Http协议的,他的实质是一个基于http协议的web容器,但是Netty不一样,他能通过编程自定义各种协议,因为netty能够通过codec自己来编码/解码字节流,完成类似redis访问的功能,这就是netty和tomcat最大的不同。
3、Netty-websocket-spring-boot-starter
这是个开源的框架。通过它,我们可以像spring-boot-starter-websocket一样使用注解进行开发,只需关注需要的事件(如OnMessage)。并且底层是使用Netty,netty-websocket-spring-boot-starter其他配置和spring-boot-starter-websocket完全一样,当需要调参的时候只需要修改配置参数即可,无需过多的关心handler的设置。
Maven配置:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.yeautygroupId>
<artifactId>netty-websocket-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>0.7.6version>
dependency>
new一个ServerEndpointExporter对象,交给Spring IOC容器,表示要开启WebSocket功能,样例如下:
@Configuration
public class WebSocketConfig {
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}
在端点类上加上@ServerEndpoint、@Component注解,并在相应的方法上加上@OnOpen、@OnClose、@OnError、@OnMessage、@OnBinary、OnEvent注解,样例如下:
@ServerEndpoint
@Component
public class MyWebSocket {
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session, HttpHeaders headers, ParameterMap parameterMap) throws IOException {
System.out.println("new connection");
String paramValue = parameterMap.getParameter("paramKey");
System.out.println(paramValue);
}
@OnClose
public void onClose(Session session) throws IOException {
System.out.println("one connection closed");
}
@OnError
public void onError(Session session, Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(Session session, String message) {
System.out.println(message);
session.sendText("Hello Netty!");
}
@OnBinary
public void onBinary(Session session, byte[] bytes) {
for (byte b : bytes) {
System.out.println(b);
}
session.sendBinary(bytes);
}
@OnEvent
public void onEvent(Session session, Object evt) {
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
IdleStateEvent idleStateEvent = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
switch (idleStateEvent.state()) {
case READER_IDLE:
System.out.println("read idle");
break;
case WRITER_IDLE:
System.out.println("write idle");
break;
case ALL_IDLE:
System.out.println("all idle");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
打开WebSocket客户端,连接到ws://127.0.0.1:80
4、注解
4.1 @ServerEndpoint
当ServerEndpointExporter类通过Spring配置进行声明并被使用,它将会去扫描带有@ServerEndpoint注解的类
被注解的类将被注册成为一个WebSocket端点
所有的配置项都在这个注解的属性中 ( 如:@ServerEndpoint("/ws") )
4.2 @OnOpen
当有新的WebSocket连接进入时,对该方法进行回调
注入参数的类型:Session、HttpHeaders、ParameterMap
4.3 @OnClose
当有WebSocket连接关闭时,对该方法进行回调
注入参数的类型:Session
4.4 @OnError
当有WebSocket抛出异常时,对该方法进行回调
注入参数的类型:Session、Throwable
4.5 @OnMessage
当接收到字符串消息时,对该方法进行回调
注入参数的类型:Session、String
4.6 @OnBinary
当接收到二进制消息时,对该方法进行回调
注入参数的类型:Session、byte[]
4.7 @OnEvent
当接收到Netty的事件时,对该方法进行回调
注入参数的类型:Session、Object
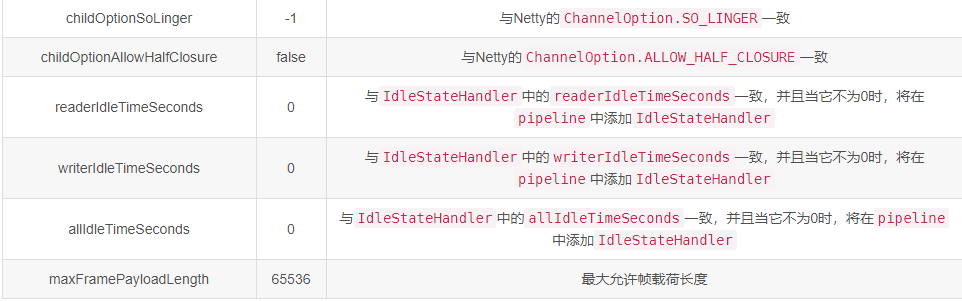
5、配置
6、通过application.properties进行配置
对注解中的prefix进行设置后,即可在application.properties中进行配置。如下:
- 首先在ServerEndpoint注解中设置prefix的值
@ServerEndpoint(prefix = "netty-websocket")
@Component
public class MyWebSocket {
...
}
- 接下来即可在application.properties中配置
netty-websocket.host=0.0.0.0
netty-websocket.path=/
netty-websocket.port=80
application.properties中的key与注解@ServerEndpoint中属性的对应关系如下:
7、自定义Favicon
配置favicon的方式与spring-boot中完全一致。只需将favicon.ico文件放到classpath的根目录下即可。如下:
src/
+- main/
+- java/
| + <source code>
+- resources/
+- favicon.ico
8、自定义错误页面
配置自定义错误页面的方式与spring-boot中完全一致。你可以添加一个 /public/error 目录,错误页面将会是该目录下的静态页面,错误页面的文件名必须是准确的错误状态或者是一串掩码,如下:
src/
+- main/
+- java/
| + <source code>
+- resources/
+- public/
+- error/
| +- 404.html
| +- 5xx.html
+- <other public assets>
9、多端点服务
- 在快速启动的基础上,在多个需要成为端点的类上使用@ServerEndpoint、@Component注解即可
- 可通过ServerEndpointExporter.getInetSocketAddressSet()获取所有端点的地址
- 当地址不同时(即host不同或port不同),使用不同的ServerBootstrap实例
- 当地址相同,路径(path)不同时,使用同一个ServerBootstrap实例
- 当多个端点服务的port为0时,将使用同一个随机的端口号
- 当多个端点的port和path相同时,host不能设为"0.0.0.0",因为"0.0.0.0"意味着绑定所有的host