Java动态修改Enum实例
众所周知,enum类型实例数量是固定的,甚至还被用来设计单例。但有时候仍然存在需要动态增加Enum实例的场景,这也并非一定是设计失败,也可能是增加灵活性的实际需求,比如一些web框架,再比如HanLP 中的动态用户自定义词性。然而最大的障碍是switch语句生成的虚构类,本文参考Java Specialists第161期,提供一份可用的解决方案与实例代码。
一段有问题的代码
比如我们有一个enum类型:
public enum HumanState
{
HAPPY, SAD
}我们是这样调用的:
public class Human
{
public void sing(HumanState state)
{
switch (state)
{
case HAPPY:
singHappySong();
break;
case SAD:
singDirge();
break;
default:
new IllegalStateException("Invalid State: " + state);
}
}
private void singHappySong()
{
System.out.println("When you're happy and you know it ...");
}
private void singDirge()
{
System.out.println("Don't cry for me Argentina, ...");
}
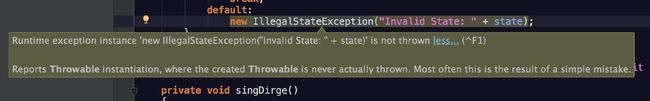
}问题在哪里?如果你使用Intelij IDEA的话,你大概会得到一个友好的提示:
不过你可能会说,这个switch分支“永远”不会被触发,就算这句有问题也无伤大雅,甚至这个default分支根本没有存在的必要。
真的吗?
触发不可能的switch分支
Enum类也是类,既然是类,就能通过反射来创建实例,我们创建一个试试。
Constructor cstr = HumanState.class.getDeclaredConstructor(
String.class, int.class
);
ReflectionFactory reflection =
ReflectionFactory.getReflectionFactory();
HumanState e =
(HumanState) reflection.newConstructorAccessor(cstr).newInstance(new Object[]{"ANGRY", 3});
System.out.printf("%s = %d\n", e.toString(), e.ordinal());
Human human = new Human();
human.sing(e);运行结果
结果出乎意料:
ANGRY = 3
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3
at com.hankcs.Human.sing(Human.java:21)
at com.hankcs.FireArrayIndexException.main(FireArrayIndexException.java:36)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:483)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMain.main(AppMain.java:144)本来指望发生IllegalStateException,怎么出了一个ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException?
探索问题
虽然我们成功地创建了一个新的Enum实例,但我们却数组越界了。stacktrace指出问题发生在:
switch (state)这一句,我们不妨看看这一句编译后是什么样子的。借助IDEA的反编译插件,我们可以看到编译后反编译回来的代码:
public class Human {
public Human() {
}
public void sing(HumanState state) {
class Human$1 {
static {
try {
$SwitchMap$com$hankcs$HumanState[HumanState.HAPPY.ordinal()] = 1;
} catch (NoSuchFieldError var2) {
;
}
try {
$SwitchMap$com$hankcs$HumanState[HumanState.SAD.ordinal()] = 2;
} catch (NoSuchFieldError var1) {
;
}
}
}
switch(Human$1.$SwitchMap$com$hankcs$HumanState[state.ordinal()]) {
case 1:
this.singHappySong();
break;
case 2:
this.singDirge();
break;
default:
new IllegalStateException("Invalid State: " + state);
}
}
private void singHappySong() {
System.out.println("When you\'re happy and you know it ...");
}
private void singDirge() {
System.out.println("Don\'t cry for me Argentina, ...");
}
}原来在switch分支前面创建了一个静态内部类(其实是synthetic类),该内部类有一个静态final数组,该数组“缓存”了编译时的所有Enum对象的ordinal。当我们通过反射新增Enum对象后,该数组并没有得到更新,所以发生了数组下标越界的异常。
解决问题
修改final static域
/**
* 修改final static域的反射工具
* @author hankcs
*/
public class ReflectionHelper
{
private static final String MODIFIERS_FIELD = "modifiers";
private static final ReflectionFactory reflection =
ReflectionFactory.getReflectionFactory();
public static void setStaticFinalField(
Field field, Object value)
throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException
{
// 获得 public 权限
field.setAccessible(true);
// 将modifiers域设为非final,这样就可以修改了
Field modifiersField =
Field.class.getDeclaredField(MODIFIERS_FIELD);
modifiersField.setAccessible(true);
int modifiers = modifiersField.getInt(field);
// 去掉 final 标志位
modifiers &= ~Modifier.FINAL;
modifiersField.setInt(field, modifiers);
FieldAccessor fa = reflection.newFieldAccessor(
field, false
);
fa.set(null, value);
}
}修改涉及Enum的switch分支
既然这个缓存数组是叫$SwitchMap$HumanState,我们需要修改所有以$SwitchMap$+Enum名称的域。
参考原作者写了一个实现类(我主要修改了虚构类的获取方法,以适应jdk8):
package com.hankcs;
import sun.reflect.*;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 动态修改Enum的对象
* @param
*/
public class EnumBuster>
{
private static final Class[] EMPTY_CLASS_ARRAY =
new Class[0];
private static final Object[] EMPTY_OBJECT_ARRAY =
new Object[0];
private static final String VALUES_FIELD = "$VALUES";
private static final String ORDINAL_FIELD = "ordinal";
private final ReflectionFactory reflection =
ReflectionFactory.getReflectionFactory();
private final Class clazz;
private final Collection switchFields;
private final Deque undoStack =
new LinkedList();
/**
* Construct an EnumBuster for the given enum class and keep
* the switch statements of the classes specified in
* switchUsers in sync with the enum values.
*/
public EnumBuster(Class clazz, Class... switchUsers)
{
try
{
this.clazz = clazz;
switchFields = findRelatedSwitchFields(switchUsers);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Could not create the class", e);
}
}
/**
* Make a new enum instance, without adding it to the values
* array and using the default ordinal of 0.
*/
public E make(String value)
{
return make(value, 0,
EMPTY_CLASS_ARRAY, EMPTY_OBJECT_ARRAY);
}
/**
* Make a new enum instance with the given ordinal.
*/
public E make(String value, int ordinal)
{
return make(value, ordinal,
EMPTY_CLASS_ARRAY, EMPTY_OBJECT_ARRAY);
}
/**
* Make a new enum instance with the given value, ordinal and
* additional parameters. The additionalTypes is used to match
* the constructor accurately.
*/
public E make(String value, int ordinal,
Class[] additionalTypes, Object[] additional)
{
try
{
undoStack.push(new Memento());
ConstructorAccessor ca = findConstructorAccessor(
additionalTypes, clazz);
return constructEnum(clazz, ca, value,
ordinal, additional);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Could not create enum", e);
}
}
/**
* This method adds the given enum into the array
* inside the enum class. If the enum already
* contains that particular value, then the value
* is overwritten with our enum. Otherwise it is
* added at the end of the array.
*
* In addition, if there is a constant field in the
* enum class pointing to an enum with our value,
* then we replace that with our enum instance.
*
* The ordinal is either set to the existing position
* or to the last value.
*
* Warning: This should probably never be called,
* since it can cause permanent changes to the enum
* values. Use only in extreme conditions.
*
* @param e the enum to add
*/
public void addByValue(E e)
{
try
{
undoStack.push(new Memento());
Field valuesField = findValuesField();
// we get the current Enum[]
E[] values = values();
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++)
{
E value = values[i];
if (value.name().equals(e.name()))
{
setOrdinal(e, value.ordinal());
values[i] = e;
replaceConstant(e);
return;
}
}
// we did not find it in the existing array, thus
// append it to the array
E[] newValues =
Arrays.copyOf(values, values.length + 1);
newValues[newValues.length - 1] = e;
ReflectionHelper.setStaticFinalField(
valuesField, newValues);
int ordinal = newValues.length - 1;
setOrdinal(e, ordinal);
addSwitchCase();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Could not set the enum", ex);
}
}
/**
* We delete the enum from the values array and set the
* constant pointer to null.
*
* @param e the enum to delete from the type.
* @return true if the enum was found and deleted;
* false otherwise
*/
public boolean deleteByValue(E e)
{
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
try
{
undoStack.push(new Memento());
// we get the current E[]
E[] values = values();
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++)
{
E value = values[i];
if (value.name().equals(e.name()))
{
E[] newValues =
Arrays.copyOf(values, values.length - 1);
System.arraycopy(values, i + 1, newValues, i,
values.length - i - 1);
for (int j = i; j < newValues.length; j++)
{
setOrdinal(newValues[j], j);
}
Field valuesField = findValuesField();
ReflectionHelper.setStaticFinalField(
valuesField, newValues);
removeSwitchCase(i);
blankOutConstant(e);
return true;
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Could not set the enum", ex);
}
return false;
}
/**
* Undo the state right back to the beginning when the
* EnumBuster was created.
*/
public void restore()
{
while (undo())
{
//
}
}
/**
* Undo the previous operation.
*/
public boolean undo()
{
try
{
Memento memento = undoStack.poll();
if (memento == null) return false;
memento.undo();
return true;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not undo", e);
}
}
private ConstructorAccessor findConstructorAccessor(
Class[] additionalParameterTypes,
Class clazz) throws NoSuchMethodException
{
Class[] parameterTypes =
new Class[additionalParameterTypes.length + 2];
parameterTypes[0] = String.class;
parameterTypes[1] = int.class;
System.arraycopy(
additionalParameterTypes, 0,
parameterTypes, 2,
additionalParameterTypes.length);
Constructor cstr = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(
parameterTypes
);
return reflection.newConstructorAccessor(cstr);
}
private E constructEnum(Class clazz,
ConstructorAccessor ca,
String value, int ordinal,
Object[] additional)
throws Exception
{
Object[] parms = new Object[additional.length + 2];
parms[0] = value;
parms[1] = ordinal;
System.arraycopy(
additional, 0, parms, 2, additional.length);
return clazz.cast(ca.newInstance(parms));
}
/**
* The only time we ever add a new enum is at the end.
* Thus all we need to do is expand the switch map arrays
* by one empty slot.
*/
private void addSwitchCase()
{
try
{
for (Field switchField : switchFields)
{
int[] switches = (int[]) switchField.get(null);
switches = Arrays.copyOf(switches, switches.length + 1);
ReflectionHelper.setStaticFinalField(
switchField, switches
);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Could not fix switch", e);
}
}
private void replaceConstant(E e)
throws IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException
{
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields)
{
if (field.getName().equals(e.name()))
{
ReflectionHelper.setStaticFinalField(
field, e
);
}
}
}
private void blankOutConstant(E e)
throws IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException
{
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields)
{
if (field.getName().equals(e.name()))
{
ReflectionHelper.setStaticFinalField(
field, null
);
}
}
}
private void setOrdinal(E e, int ordinal)
throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException
{
Field ordinalField = Enum.class.getDeclaredField(
ORDINAL_FIELD);
ordinalField.setAccessible(true);
ordinalField.set(e, ordinal);
}
/**
* Method to find the values field, set it to be accessible,
* and return it.
*
* @return the values array field for the enum.
* @throws NoSuchFieldException if the field could not be found
*/
private Field findValuesField()
throws NoSuchFieldException
{
// first we find the static final array that holds
// the values in the enum class
Field valuesField = clazz.getDeclaredField(
VALUES_FIELD);
// we mark it to be public
valuesField.setAccessible(true);
return valuesField;
}
private Collection findRelatedSwitchFields(
Class[] switchUsers)
{
Collection result = new LinkedList();
try
{
for (Class switchUser : switchUsers)
{
String name = switchUser.getName();
int i = 0;
while (true)
{
try
{
Class suspect = Class.forName(String.format("%s$%d", name, ++i));
Field[] fields = suspect.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields)
{
String fieldName = field.getName();
if (fieldName.startsWith("$SwitchMap$") && fieldName.endsWith(clazz.getSimpleName()))
{
field.setAccessible(true);
result.add(field);
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException e)
{
break;
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Could not fix switch", e);
}
return result;
}
private void removeSwitchCase(int ordinal)
{
try
{
for (Field switchField : switchFields)
{
int[] switches = (int[]) switchField.get(null);
int[] newSwitches = Arrays.copyOf(
switches, switches.length - 1);
System.arraycopy(switches, ordinal + 1, newSwitches,
ordinal, switches.length - ordinal - 1);
ReflectionHelper.setStaticFinalField(
switchField, newSwitches
);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Could not fix switch", e);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private E[] values()
throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException
{
Field valuesField = findValuesField();
return (E[]) valuesField.get(null);
}
private class Memento
{
private final E[] values;
private final Map savedSwitchFieldValues =
new HashMap();
private Memento() throws IllegalAccessException
{
try
{
values = values().clone();
for (Field switchField : switchFields)
{
int[] switchArray = (int[]) switchField.get(null);
savedSwitchFieldValues.put(switchField,
switchArray.clone());
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Could not create the class", e);
}
}
private void undo() throws
NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException
{
Field valuesField = findValuesField();
ReflectionHelper.setStaticFinalField(valuesField, values);
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++)
{
setOrdinal(values[i], i);
}
// reset all of the constants defined inside the enum
Map valuesMap =
new HashMap();
for (E e : values)
{
valuesMap.put(e.name(), e);
}
Field[] constantEnumFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field constantEnumField : constantEnumFields)
{
E en = valuesMap.get(constantEnumField.getName());
if (en != null)
{
ReflectionHelper.setStaticFinalField(
constantEnumField, en
);
}
}
for (Map.Entry entry :
savedSwitchFieldValues.entrySet())
{
Field field = entry.getKey();
int[] mappings = entry.getValue();
ReflectionHelper.setStaticFinalField(field, mappings);
}
}
}
} 调用方式
EnumBuster buster =
new EnumBuster(HumanState.class,
Human.class);
HumanState ANGRY = buster.make("ANGRY");
buster.addByValue(ANGRY);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(HumanState.values()));
Human human = new Human();
human.sing(ANGRY); 输出
[HAPPY, SAD, ANGRY]switch分支完美了。
没有发生异常,其实这才是最大的异常,那个default分支明明进去了,可就是没有抛异常。为什么?因为我们忘了加throw啊,朋友。
Reference
http://www.javaspecialists.eu/archive/Issue161.html