链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/5278/K
来源:牛客网
题目描述
SuperSodaSea 在玩一个走迷宫的游戏。迷宫是一个大小为 n×m的矩阵,从上到下依次给行编号为 0,1,…n−1,从左到右依次给列编号为 0,1,…,m−1。
游戏规则很简单:从起点出发,每步操作可以移动到上、下、左、右四个方向的空地上,直到终点。
为了增加游戏的难度,在这个游戏中,从起点到终点并不一定会有直接的通路。当然,相对应地,玩家可以使用名为“穿越”的技能:从一块空地移动到距离至多为 d 另一片空地上(起点和终点也视为空地),无论中间是否有障碍。
在使用技能时的距离是指“切比雪夫距离”,即如果从 (x1,y1)穿越到(x2,y2)需要满足 max{∣x1−x2∣,∣y1−y2∣}≤d。“穿越”只能最多使用一次,使用时算一步操作。
现在你需要帮 SuperSodaSea 计算出给定的迷宫,他最少需要多少步才能到达终点,并给出一个方案。
输入描述:
第一行包含 3 个整数 n, m, d (1≤n,m≤2 0001≤n,m≤2000, 0≤d≤2 0000≤d≤2000),中间以空格分隔,分别表示地图的行数、列数和穿越的最大距离。
接下来 n 行,每行包含一个长度为 m 的字符串,表示地图。
其中,. 表示空地,X 表示障碍,S 表示起点,T表示终点。
输入保证有且仅有一个起点和一个终点。
输出描述:
第一行输出一个整数 t 表示最少所需要的步骤。
接下来 t + 1 行,每行输出两个整数 xi,yixi,yi,中间以空格分隔, 表示每一步所经过的坐标。其中,第一行和最后一行应分别对应起点和终点。
特别地,如果没有可以走到终点的方案,则在一行输出 -1。
答案不唯一,任何符合要求的答案都会被判为正确。
首先,先想一下暴力的其中之一个解法,我们可以枚举使用“穿越”的那条边的起点和终点。所以我们可以bfs从起点S跑,和终点T跑,然后取枚举的最小值,然后输出答案就是了。
上述做法的时间复杂度为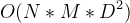 。
。
但是,我们可以想办法去把这个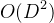 给优化掉,这里就要引入单调栈和单调队列了。
给优化掉,这里就要引入单调栈和单调队列了。
我们想知道这个点出去的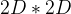 的面积块的最小值(从T到点的最短距离),尽管可以用四叉树等数据结构来
的面积块的最小值(从T到点的最短距离),尽管可以用四叉树等数据结构来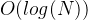 的维护这个信息,但是能多优化就多优化一下。
的维护这个信息,但是能多优化就多优化一下。
我们可以跑一个单调递增的单调队列/栈,先从左往右跑,再从右往左,如此,就可以确定每一行的在范围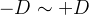 这个范围的最值了,用一个二维数组进行存储,然后就是我们对现在这个存储的一维信息再从上到下和从下到上的再来跑两次这样的单调队列/栈,我们就可以确定每个点的在范围
这个范围的最值了,用一个二维数组进行存储,然后就是我们对现在这个存储的一维信息再从上到下和从下到上的再来跑两次这样的单调队列/栈,我们就可以确定每个点的在范围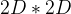 的“穿越”能到的最小值了。
的“穿越”能到的最小值了。
然后就是各种维护了,代码较长,慎读。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
![]() 。
。![]() 给优化掉,这里就要引入单调栈和单调队列了。
给优化掉,这里就要引入单调栈和单调队列了。![]() 的面积块的最小值(从T到点的最短距离),尽管可以用四叉树等数据结构来
的面积块的最小值(从T到点的最短距离),尽管可以用四叉树等数据结构来![]() 的维护这个信息,但是能多优化就多优化一下。
的维护这个信息,但是能多优化就多优化一下。![]() 这个范围的最值了,用一个二维数组进行存储,然后就是我们对现在这个存储的一维信息再从上到下和从下到上的再来跑两次这样的单调队列/栈,我们就可以确定每个点的在范围
这个范围的最值了,用一个二维数组进行存储,然后就是我们对现在这个存储的一维信息再从上到下和从下到上的再来跑两次这样的单调队列/栈,我们就可以确定每个点的在范围![]() 的“穿越”能到的最小值了。
的“穿越”能到的最小值了。