Intel Thread Building Blocks (TBB) 入门篇
一、什么是TBB
TBB(Thread Building Blocks)是英特尔发布的一个库,全称为 Threading Building Blocks。TBB 获得过 17 届 Jolt Productivity Awards,是一套 C++ 模板库,和直接利用 OS API 写程序的 raw thread 比,在并行编程方面提供了适当的抽象,当然还包括更多其他内容,比如 task 概念,常用算法的成熟实现,自动负载均衡特 性还有不绑定 CPU 数量的灵活的可扩展性等等。STL 之父,Alexander Stepanov 对此评价不错,他说“Threading Building Blocks… could become a basis for the concurrency dimension of the C++ standard library”。其他 TBB 的早期用户,包括 Autodesk,Sun,Red Hat, Turbo Linux 等亦然。现在 O’Reilly 已经出版了一本 Intel Threading Building Blocks: Outfitting C++ for Multi-core Processor Parallelism。
二、为什么要TBB
在多核的平台上开发并行化的程序,必须合理地利用系统的资源 - 如与内核数目相匹配的线程,内存的合理访问次序,最大化重用缓存。有时候用户使用(系统)低级的应用接口创建、管理线程,很难保证是否程序处于最佳状态。
而 Intel Thread Building Blocks (TBB) 很好地解决了上述问题:
1)TBB提供C++模版库,用户不必关注线程,而专注任务本身。
2)抽象层仅需很少的接口代码,性能上毫不逊色。
3)灵活地适合不同的多核平台。
4)线程库的接口适合于跨平台的移植(Linux, Windows, Mac)
5)支持的C++编译器 – Microsoft, GNU and Intel
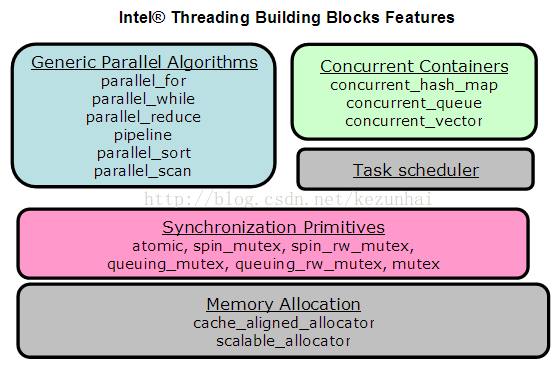
三、TBB库包含的内容
TBB包含了 Algorithms、Containers、Memory Allocation、Synchronization、Timing、Task Scheduling这六个模块。TBB的结构:
1) 循环的并行:
① parallel_for
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace tbb;
typedef vector::iterator IntVecIt;
struct body
{
void operator()(const blocked_range&r)const
{
for(auto i = r.begin(); i!=r.end(); i++)
cout<<*i<<' ';
}
};
int main()
{
vector vec;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
vec.push_back(i);
parallel_for(blocked_range< IntVecIt>(vec.begin(), vec.end())
, body());
return 0;
}
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace tbb;
int main()
{
vector vec;
for(int i=0; i<100; i++)
vec.push_back(i);
int result = parallel_reduce(blocked_range::iterator>(vec.begin(), vec.end()),
0,[](const blocked_range::iterator>& r, int init)->int{
for(auto a = r.begin(); a!=r.end(); a++)
init+=*a;
return init;
},
[](int x, int y)->int{
return x+y;
}
);
cout<<"result:"< 并行计算前束(prefix)的函数模板。即输入一个数组,生成一个数组,其中每个元素的值都是原数组中在此元素之前的元素的某个运算符的结果的累积。比如求和:
输入:[2, 8, 9, -4, 1, 3, -2, 7]
生成:[0, 2, 10, 19, 15, 16, 19, 17]
例子:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace tbb;
using namespace std;
template
class Body
{
T _sum;
T* const _y;
const T* const _x;
public:
Body(T y[], const T x[]):_sum(0), _x(x), _y(y){}
T get_sum() const
{
return _sum;
}
template
void operator()(const blocked_range& r, Tag)
{
T temp = _sum;
for(int i = r.begin(); i< r.end(); i++)
{
temp+=_x[i];
if(Tag::is_final_scan())
_y[i] = temp;
}
_sum = temp;
}
Body(Body&b, split):_x(b._x), _y(b._y), _sum(0){}
void reverse_join(Body& a)
{
_sum+=a._sum;
}
void assign(Body& b)
{
_sum = b._sum;
}
};
int main()
{
int x[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int y[10];
Body body(y,x);
parallel_scan(blocked_range(0, 10), body);
cout<<"sum:"< 并行处理工作项的模板函数。
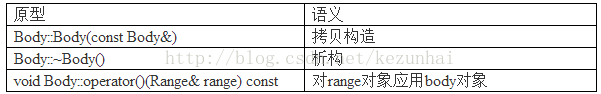
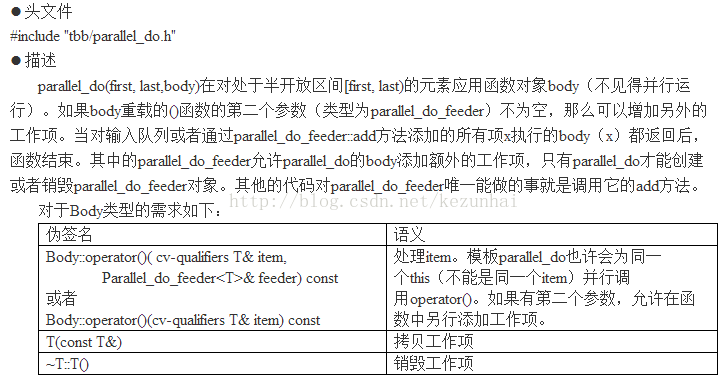
如果所有来自输入流的元素不能随机访问,那么parallel_do中的并行就不具备可扩展性。为达到可扩展性,可按如下方式之一处理:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace tbb;
struct t_test
{
string msg;
int ref;
void operator()()const
{
cout<
struct body_test
{
void operator()(T* t, parallel_do_feeder& feeder) const
{
(*t)();
if(t->ref == 0)
{
t->msg = "added msg";
feeder.add(t);
t->ref++;
}
}
};
int main()
{
t_test *pt = new t_test;
pt->ref = 0;
pt->msg = "original msg";
vector vec;
vec.push_back(pt);
parallel_do(vec.begin(), vec.end(), body_test());
delete pt;
return 0;
}
class pipeline
{
public:
pipeline();
~pipeline();
void add_filter( filter& f );
void run( size_t max_number_of_live_tokens
[,task_group_context& group] );
void clear();
};1、从filter继承类f,f的构造函数传递给基类filter的构造函数一个参数,来指定它的模式
2、重载虚方法filter::operator()来实现过滤器对元素处理,并返回一个将被下一个过滤器处理的元素指针。如果流里没有其他的要处理的元素,返回空值。最后一个过滤器的返回值将被忽略。
3、生成pipeline类的实例
4、生成过滤器f的实例,并将它们按先后顺序加给pipeline。一个过滤器的实例一次只能加给一个pipeline。同一时间,一个过滤器禁止成为多个pipeline的成员。
5、调用pipeline::run方法。参数max_number_of_live_tokens指定了能并发运行的阶段数量上限。较高的值会以更多的内存消耗为代价来增加并发性。
class filter
{
public:
enum mode
{
parallel = implementation-defined,
serial_in_order = implementation-defined,
serial_out_of_order =implementation-defined
};
bool is_serial() const;
bool is_ordered() const;
virtual void* operator()( void* item ) = 0;
virtual void finalize( void* item ) {}
virtual ~filter();
protected:
filter( mode );
};
由于parallel过滤器支持并行加速,所以推荐使用。如果必须使用serial过滤器,那么serial_out_of_order类型的过滤器是优先考虑的,因为他在处理顺序上的约束较少。
classthread_bound_filter: public filter
{
protected:
thread_bound_filter(mode filter_mode);
public:
enum result_type
{
success,
item_not_available,
end_of_stream
};
result_type try_process_item();
result_type process_item();
}; #include
#include
#include
#include
using namespacestd;
using namespacetbb;
char input[] ="abcdefg\n";
classinputfilter:public filter
{
char *_ptr;
public:
void *operator()(void *)
{
if(*_ptr)
{
cout<<"input:"<<*_ptr<run(8);
}
int main()
{
inputfilter inf;
outputfilter ouf;
pipeline p;
p.add_filter(inf);
p.add_filter(ouf);
//由于主线程服务于继承自thread_bound_filter的outputfilter,所以pipeline要运行在另一个单独的线程
thread t(run_pipeline, &p);
while(ouf.process_item()!=thread_bound_filter::end_of_stream)
continue;
t.join();
return 0;
}
3)并行排序
parallel_sort – 并行快速排序,调用了parallel_for
2)任务调度者
管理线程池,及隐藏本地线程复杂度
并行算法的实现由任务调度者的接口完成
任务调度者的设计考虑到本地线程的并行所引起的性能问题
3)并行容器
concurrent_hash_map
concurrent_vector
concurrent_queue
4)同步原语
atomic
mutex
spin_mutex – 适合于较小的敏感区域
queuing_mutex – 线程按次序等待(获得)一个锁
spin_rw_mutex
queuing_rw_mutex
说明:使用read-writer mutex允许对多线程开放”读”操作
5)高性能的内存申请
使用TBB的allocator 代替 C语言的 malloc/realloc/free 调用
使用TBB的allocator 代替 C++语言的 new/delete 操作