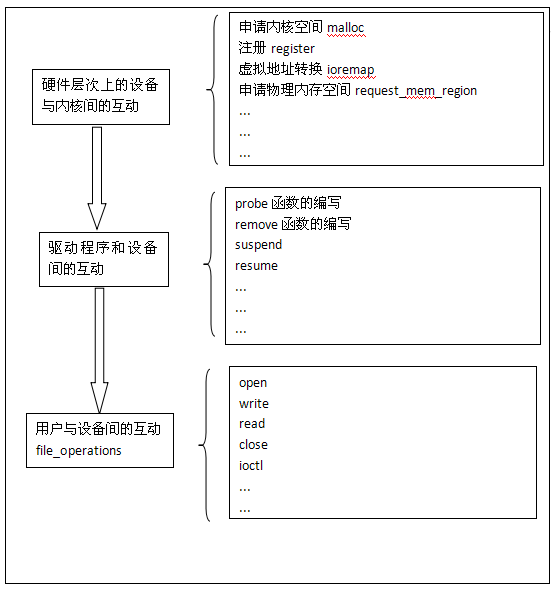
file_operations是一个对设备进行操作的抽象结构体。linux内核为设备建立一个设备文件,这样就使得对设备文件的所有操作,就相当于对设备的操作。用户程序可以用访问普通文件的方法访问设备文件,进而访问设备。
对普通文件的访问,常常使用open(), write(), read(), close(), ioctl()等方法。同样,对设备文件的访问,也可以使用这些方法。于是,对设备驱动的编写,就编程了对不同操作函数的编写。
file_operations结构体如下:(include\linux\fs.h)
1 struct file_operations { 2 struct module *owner; 3 loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int); 4 ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); 5 ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); 6 ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t); 7 ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t); 8 int (*readdir) (struct file *, void *, filldir_t); 9 unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *); 10 int (*ioctl) (struct inode *, struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); 11 long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); 12 long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); 13 int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *); 14 int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *); 15 int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id); 16 int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *); 17 int (*fsync) (struct file *, struct dentry *, int datasync); 18 int (*aio_fsync) (struct kiocb *, int datasync); 19 int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int); 20 int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *); 21 ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int); 22 unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long); 23 int (*check_flags)(int); 24 int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *); 25 ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int); 26 ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int); 27 int (*setlease)(struct file *, long, struct file_lock **); 28 };
注:1.指向结构体struct file_operations的指针通常命名为fops;
2.owner成员根本不是一个函数;它是一个指向拥有这个结构模块的指针。这个成员用来维持模块的引用计数,当模块还在使用时,不能用rmmod卸载模块。几乎所有时刻,它被简单初始化为THIS_MODULE,一个在linux\module.h中定义的宏;
在frame_buffer驱动程序一节,有这些结构体,在这里区分一下:
struct file_operations fb_fops;
struct fb_ops *fb=info->fbops;
fb_ops是自己定义的struct, 它是在编写probe, ioctl, ...可能会涉及到的函数
而驱动的编写就是对上要实现open()...ioctl()...read()...write()...等函数的编写;对下要实现probe()...remove()...等函数的编写;