一.rsync介绍
rsync全称remote sync,是一种更高效、可以本地或远程同步的命令,之所以高效是因为rsync会对需要同步的源和目的进度行对比,只同步有改变的部分,所以比scp命令更高效,但是rsync本身是一种非加密的传输,可以借助-e选项来设置具备加密功能的承载工具进行加密传输
二.rsync的工作模式
1、shell模式,也称作本地模式
如:rsync -av dir1 /tmp/
2、远程shell模式,此时可以利用ssh协议承载其数据传输过程
如:rsync -av dir1 root@server0:/root
注:shell模式默认不需要配置
3、服务器模式(daemon模式),此时,rsync可以工作在守护进程,能够接收客户端的数据请求;在使用时,可以在客户端使用rsync命令把文件发送到守护进程,也可以像服务器请求获取文件
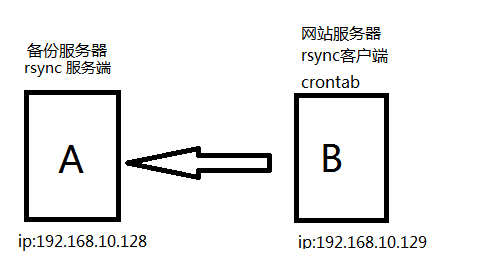
三.企业案列: 搭建远程容灾备份系统
为了保证数据安全,需要建立一个远程容灾系统,将网站数据在每天凌晨2点备份到远程的容灾服务器上,由于数量很大,每天只能进行增量备份,仅仅备份当天增加的数据,当网站出现故障后,可以通过备份最大程度的恢复数据。
1.解决方案(rsync+crontab定时备份)
1)服务端A配置
[root@server ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS release 6.6 (Final)
[root@server ~]# /etc/init.d/iptables stop
[root@server ~]# setenforce 0
[root@server ~]# yum install -y rsync
[root@server ~]# cat /etc/rsyncd.conf
######全局参数
uid = rsync########这里也可以用其它用户uid,后面将创建这个用户
gid = rsync
use chroot = no
max connections = 10
timeout = 300
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock
######模块,类似于nfs中的共享目录
[fengxiaoli]
path = /cx/####备份路径最好和模块名一致,这里只是为了测试一下路径名和模块名区别
ignore errors
read only = false ##可写
list = false ##是否允许列出模块内容
hosts allow = 192.168.10.0/24
hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32
auth users = rsyncuser #虚拟的用户
secrets file = /etc/rsync.password####用户对应的密码文件
注意:我做的时候里面的中文好不删的话同步文件的时候会出错
创建rsync用户且指定/cx/目录所属
[root@server ~]# useradd rsync -s /sbin/nologin
[root@server ~]# mkdir /cx
[root@server ~]# chown -R rsync.rsync /cx/
创建rsync密码文件
[root@server ~]# echo "rsyncuser:pass" >/etc/rsync.password#将用户名和密码输入rsync密码文件rsync虚拟用户名:密码
[root@server ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password 注意这里的密码文件权限必须给600
2)rsync客户端B配置
[root@client ~]# rpm -qa rsync只需下载该软件,不需要其它配置
rsync-3.0.6-12.el6.x86_64
[root@client ~]# echo "pass" >/etc/rsync.password
[root@client ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password
3)编写脚本创建定时任务
[root@client ~]# cat 002.sh
#!/bin/bash
rsync -avz --delete /data1/ [email protected]::fengxiaoli --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
[root@client ~]# crontab -e
0 2 * * * /bin/bash /root/002.sh
到此该企业案例rsync+crontab结束
四.Rsync备注
1.无差异同步--delete
1)把文件从服务器拉到客户端(应用场景:代码发布,下载)
[root@client ~]# rsync -avz --delete [email protected]::fengxiaoli /data1 --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
2)把文件从客户端推服务器(应用场景:备份)
[root@client data1]#rsync -avz --delete /data1/ [email protected]::fengxiaoli --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
2.--delete参数说明(慎用)
如果把文件从服务器拉到客户端时不加--delete参数,客户端原有文件不会改变,加了--delete后变成无差异同步,服务器有什么客户端就有什么,本地客户端目录数据可能丢失,有一定风险
如果把文件从客户端推服务器不加--delete参数,服务器原有文件不会改变,加了--delete后变成无差异同步,客户端有什么服务器就有什么,服务器端的目录数据可能丢失,有一定风险
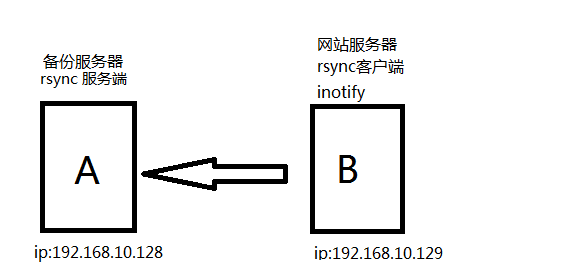
五.Rsync+inotify(实现实时备份)
1.inotify简介
Inotify 是基于inode级别的文件系统监控技术,是一种强大的、细粒度的、异步的机制,它满足各种各样的文件监控需要,不仅限于安全和性能,内核要求2.6.13以上,inotify能监控非常多的文件系统事件,通过监控这些事件来监控文件是否发生变更,然后通过rsync来更新发生变更的文件
2.inotify配置之前准备
在rsync daemon服务器模式配置成功,可以进行客户端推送拉取数据(也就上面第三步配置成功),然后才能配置inotify,注意在rsync客户端配置inotify(内核达到2.6.13)
[root@client ~]# uname -r
2.6.32-504.el6.x86
[root@client ~]# ls -l /proc/sys/fs/inotify/(查看一下是否有这三个文件)
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jul 17 22:47 max_queued_events
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jul 17 22:47 max_user_instances
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jul 17 22:47 max_user_watches
3.inotify配置
[root@client tools]# wget http://github.com/downloads/rvoicilas/inotify-tools/inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
[root@client tools]# tar xvf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
[root@client tools]# cd inotify-tools-3.14
[root@client inotify-tools-3.14]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/inotify-tools-3.14
[root@client inotify-tools-3.14]# make && make install
[root@client tools]# ln -s /usr/local/inotify-tools-3.14/ /usr/local/inotify
[root@client tools]# ll /usr/local/inotify
4.测试inotify
终端1:
[root@client data1]# /usr/local/inotify/bin/inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%d/%m/%y %H:%M' --format '%T %w%f' -e create,delete /data1/
终端2:
[root@client ~]# cd /data1
[root@client data1]# mkdir file
终端1显示:
[root@client data1]# /usr/local/inotify/bin/inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%d/%m/%y %H:%M' --format '%T %w%f' -e create,delete /data1/
20/07/17 08:24 /data1/file
5.inotify监控脚本
#!/bin/bash
#para
host01=192.168.10.128 #inotify-slave的ip地址
src=/data 1 #本地监控的目录
dst=fengxiaoli #inotify-slave的rsync服务的模块名
user=rsyncuser #inotify-slave的rsync服务的虚拟用户
rsync_passfile=/etc/rsync.password #本地调用rsync服务的密码文件
inotify_home=/usr/local/inotify/ #inotify的安装目录
#judge
if [ ! -e "$src" ] \
|| [ ! -e "${rsync_passfile}" ] \
|| [ ! -e "${inotify_home}/bin/inotifywait" ] \
|| [ ! -e "/usr/bin/rsync" ];
then
echo "Check File and Folder"
exit 9
fi
${inotify_home}/bin/inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%d/%m/%y %H:%M' --format '%T %w%f' -e close_write,delete,create,attrib $src \
| while read file
do
# rsync -avzP --delete --timeout=100 --password-file=${rsync_passfile} $src $user@$host01::$dst >/dev/null 2>&1
cd $src && rsync -aruz -R --delete ./ --timeout=100 $user@$host01::$dst --password-file=${rsync_passfile} >/dev/null 2>&1
done
exit 0
6.测试inotify+rsync
[root@client ~]# sh -x 001.sh
[root@client ~]# cd /data1
[root@client data1]# touch {1..1000}
[root@client ~]# cd /data1
[root@client data1]# rm -rf {1..1000}
7.生产环境中可以将这几个参数调大一点
[root@client ~]# ll /proc/sys/fs/inotify/
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jul 20 02:30 max_queued_events
327679
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jul 20 02:30 max_user_instances
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jul 20 02:30 max_user_watches
50000000
8.inotify缺点
并发不能大于200(10-100K)个文件
前面的脚本每次都是全部推送一次