小白入门中:TCPL习题2-1——2-10
2-1:编写程序确认signed和unsigned限定的char、short、int与long类型变量的取值范围。采用打印标准头文件中的限定值或直接计算。
#include 2-2:在不使用&&或||的条件下编写一个与下面的for循环语句等价的循环语句
for(i=0 ; i
#includeenum枚举变量,no = 0 , yes = 1;
注意末尾要加一个s[i] = '\0';,不然会多输出2~4个随机字符;
2-3:编写一个函数htoi(s),把由16进制数组组成的字符串(包含可选的前缀0x或0X) 转换为与之等价的整型值,字符串中允许包含的数字包括:0-9、a-f,A-F
#include这是我的思路,将字符串中表示16进制的字符串,以16进制的形式存储到num中,然后用(int)直接转换为整形;
运行:

hhh还是可以的,不过感觉有些作弊,这可以作为一个16转10的好办法
以下为题解所给的代码
#define yes 1
#define no 0
int htoi(char s[])
{
int hexdigit , i , inhex , n ;
i = 0;
if(s[i] == '0') //假如字符串有16进制前缀 0x 或 0X ;
i ++ ;
if(s[i] == 'x' || s[i] == 'X')
i ++ ;
n = 0 ;
inhex = yes ;
for( ; inhex == yes ; ++i)
{
if(s[i]>= '0' && s[i] <= '9')
hexdigit = s[i] - '0';
else if(s[i] >= 'a' && s[i] <= 'f')
hexdigit = s[i] - 'a' + 10 ;
else if(s[i] >= 'A' && s[i] <= 'F')
hexdigit = s[i] - 'A' + 10 ;
else inhex = no ;
if(inhex == yes)
{
n = n*16 + hexdigit ;
}
}
return n ;
}
其中最精妙的就是这一步n = n*16 + hexdigit
举例子,ABCD = 43981
ABCD分别对应10 11 12 13;
根据进制转换
sum = 13*16^0 + 12*16^1 + 11*16^2 + 10*16^4
= {[(10*16+11)*16+12]*16+13}
这就跟上面的式子是一致的
第一种思路在解决8转10,16转10较为方便%o,%x,但在其他就会出错。
第二种在解决除8,16外只需修改几个数字就可以得出答案。
2-4:重新编写squeeze(s1 , s2),将S1中任何与S2中的字符匹配的字符都删除
#include我勒个去,又忘记写s1[k] = '\0';谨记谨记,字符串的末尾必为'\0'
2-5:编写函数any(s1 , s2),返回s2任意字符第一次出现在s1的位置,若s1中没有s2的字符,则返回-1。(标准库函数strpbrk具有同样的功能,但它返回的是指向该位置的指针)**
#include2-6:编写一个函数setbits(x , p , n , y),返回对x执行操作的结果值:将x中从第p位开始的n个(二进制)位设置为y中最右边n位的值,x的其余各位保持不变**
#include 
假设最右为第0位
46:
0101110
75:
1001011
5位开始3位,即5、4、3位,101;
1001101为77
(ps.答案是真的鸡儿诡异,还是哥的思路好)
2-7:编写一个函数invert(x , p , n),返回对x执行操作的结果值:将x中从第p位开始的n个(二进制)位求反,x的其余各位保持不变**
#include (ps. 注释写得好,思路没烦恼,原本的a, b是一串诡异的表达式,写着写着自己就乱了。于是定义了c = (~(~0 << n) << (p+1-n)); //c : 00110000 ;,表明了注释,果然通透明了许多)
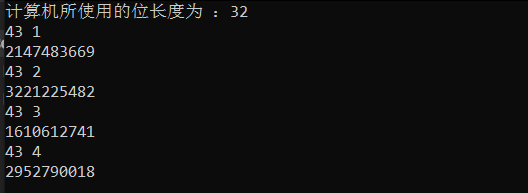
编写一个函数invert(x , p , n),返回对x执行操作的结果值: 将x右移n次,溢出的值补到高位
#include a = (x & 1) << (length() - 1)这一步确实没想到,length函数也是精妙,用>>求出所有位,学到了。
2-9:求二进制补码时,表达式 x&=(x-1)可以删除x中最右边值为1的一个二进制位,请解释原理。用这一方法重写bitscount函数,以加快执行速度
int bitscount(unsigned x)
{
int i ;
for(i = 0; x != 0; x >>= 1)
{
if(x & 1) i++ ;
}
return i ;
}
原理:x-1,二进位中最右是1的位必然要退1,即为0,在&运算中,原本的最后一位x位1,x-1为0,结果为0
即1被删去了!!!
(语言表述可能有误,但大致是这样)
#include 2-10:重新编写将大写字母转为小写字母的函数lower,用条件表达式替代if-else结构
#include 总结:类型、运算符与表达式
讲道理,这个章节是很烦人的。首先是以处理字符串问题练习关系运算符、逻辑运算符,当然,也把字符串熟悉了一下。更加深入地了解了字符串数组,'\n' , '\0'什么的我之前都是懵懵懂懂。
到后面就是烦人的位运算符了,因为书看不懂所以放弃了摸鱼了两天(实际上是在策划学院比赛,有点紧张,学不下去,对吧对吧对吧),后在4.29时候认真学习了一哈位运算符,可以说是初步掌握。特别是x &= (x-1)这个骚操作求二进制位上1的个数,属实牛逼。我想位运算符应该还有更多骚气的操作。不过我要思考的不是位运算符还能解决什么问题,而是有什么问题用位运算符解决会更加方便,不要搞花里胡哨,而要追求实际!!
明天学习第三章控制流,加油,奥利给,干就完事了!!