【FPGA】FIFO的Verilog设计之同步FIFO的设计
这个同步FIFO的设计方法是调用异步读写双端口RAM来实现的。
关于异步读写双端口RAM的设计,前面博文已经讲到过了:【FPGA】双端口RAM的设计(异步读写)
此时使用双端口RAM来设计FIFO,可以使用一套端口进行写操作,一套端口进行读操作的方式来实现,例如例化方式大概是这样的:
ram_dp_ar_aw #(DATA_WIDTH,ADDR_WIDTH) DP_RAM (
.address_0 (wr_pointer) , // address_0 input
.data_0 (data_in) , // data_0 bi-directional
.cs_0 (wr_cs) , // chip select
.we_0 (wr_en) , // write enable
.oe_0 (1'b0) , // output enable
.address_1 (rd_pointer) , // address_q input
.data_1 (data_ram) , // data_1 bi-directional
.cs_1 (rd_cs) , // chip select
.we_1 (1'b0) , // Read enable
.oe_1 (rd_en) // output enable
);
这样就可以同时读写。
其原理大概如此:
FIFO uses a dual port memory and there will be two pointers to point read and write addresses. Here is a generalized block diagram of FIFO.
![]()
Generally fifos are implementedusing rotating pointers. We can call write and read pointers of a FIFO as headand tail of data area. Initially read and write pointers of the FIFO will pointto the same location
Here is an example to explain howFIFO uses the memory. This is a fifo of length 8, WP and RP are the locationswhere write pointer and read pointer points. Shaded area in the diagram isfilled with data.
![]()
When ever FIFO counter becomes zeroor BUF_LENGTH, empty or full flags will be set.
使用fifo_counter记录FIFO RAM中的数据个数,等于0时,给出empty信号,等于BUF_LENGTH时,给出full信号
fifo_counter is incremented ifwrite takes place and buffer is not full and will be decremented id read takesplace and buffer is not empty. If both read and write takes place, counter willremain the same.
fifo_counter写而未满时增加1,读而未空时减1。同时发生读写操作时,fifo_counter不变。
rd_ptr and wr_ptr are read andwrite pointers. Since we selected the bits in these registers same as addresswidth of buffer, when buffer overflows, values will overflow and become 0.
读写指针宽度与地址宽度相当,地址增加而溢出后,自动变成0。
给出同步FIFO的Verilog描述:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
//-----------------------------------------------------
// Design Name : syn_fifo
// File Name : syn_fifo.v
// Function : Synchronous (single clock) FIFO
//-----------------------------------------------------
module syn_fifo (
clk , // Clock input
rst , // Active high reset
wr_cs , // Write chip select
rd_cs , // Read chipe select
data_in , // Data input
rd_en , // Read enable
wr_en , // Write Enable
data_out , // Data Output
empty , // FIFO empty
full // FIFO full
);
// FIFO constants
parameter DATA_WIDTH = 8;
parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 8;
parameter RAM_DEPTH = (1 << ADDR_WIDTH);
// Port Declarations
input clk ;
input rst ;
input wr_cs ;
input rd_cs ;
input rd_en ;
input wr_en ;
input [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] data_in ;
output full ;
output empty ;
output [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] data_out ;
//-----------Internal variables-------------------
reg [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] wr_pointer;
reg [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] rd_pointer;
reg [ADDR_WIDTH :0] status_cnt;
reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] data_out ;
wire [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] data_ram ;
//-----------Variable assignments---------------
assign full = (status_cnt == (RAM_DEPTH));
assign empty = (status_cnt == 0);
//-----------Code Start---------------------------
always @ (posedge clk or posedge rst)
begin : WRITE_POINTER
if (rst) begin
wr_pointer <= 0;
end
else if (wr_cs && wr_en ) begin
wr_pointer <= wr_pointer + 1;
end
end
always @ (posedge clk or posedge rst)
begin : READ_POINTER
if (rst) begin
rd_pointer <= 0;
end else if (rd_cs && rd_en ) begin
rd_pointer <= rd_pointer + 1;
end
end
always @ (posedge clk or posedge rst)
begin : READ_DATA
if (rst) begin
data_out <= 0;
end
else if (rd_cs && rd_en ) begin
data_out <= data_ram;
end
end
always @ (posedge clk or posedge rst)
begin : STATUS_COUNTER
if (rst) begin
status_cnt <= 0;
// Read but no write.
end
else if ((rd_cs && rd_en) && !(wr_cs && wr_en)
&& (status_cnt != 0)) begin
status_cnt <= status_cnt - 1;
// Write but no read.
end
else if ((wr_cs && wr_en) && !(rd_cs && rd_en)
&& (status_cnt != RAM_DEPTH)) begin
status_cnt <= status_cnt + 1;
end
end
ram_dp_ar_aw #(DATA_WIDTH,ADDR_WIDTH) DP_RAM (
.address_0 (wr_pointer) , // address_0 input
.data_0 (data_in) , // data_0 bi-directional
.cs_0 (wr_cs) , // chip select
.we_0 (wr_en) , // write enable
.oe_0 (1'b0) , // output enable
.address_1 (rd_pointer) , // address_q input
.data_1 (data_ram) , // data_1 bi-directional
.cs_1 (rd_cs) , // chip select
.we_1 (1'b0) , // Read enable
.oe_1 (rd_en) // output enable
);
endmodule给出异步读写双端口RAM的Verilog描述代码:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Create Date: 2019/05/29 21:11:08
// Design Name:
// Module Name: ram_dp_ar_aw
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
module ram_dp_ar_aw #(
parameter DATA_WIDTH = 8,
parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 8,
parameter RAM_DEPTH = 1 << ADDR_WIDTH
)(
input [ADDR_WIDTH - 1 : 0] address_0,
inout [DATA_WIDTH - 1 : 0] data_0,
input cs_0,
input we_0,
input oe_0,
input [ADDR_WIDTH - 1 : 0] address_1,
inout [DATA_WIDTH - 1 : 0] data_1,
input cs_1,
input we_1,
input oe_1
);
reg [DATA_WIDTH - 1 : 0] mem [RAM_DEPTH - 1 : 0];
integer i;
// initialization
initial begin
for(i = 0; i < RAM_DEPTH; i = i + 1) begin
mem[i] = 0;
end
end
//write
always@(*) begin
if(cs_0 && we_0) begin
mem[address_0] = data_0;
end
else if(cs_1 && we_0) begin
mem[address_1] = data_1;
end
else;
end
//read
reg [DATA_WIDTH - 1 : 0] data_out0;
assign data_0 = (cs_0 && !we_0 && oe_0) ? data_out0 : 'hz;
always@(*) begin
if(cs_0 && !we_0 && oe_0) begin
data_out0 = mem[address_0];
end
else begin
data_out0 = 0;
end
end
reg [DATA_WIDTH - 1 : 0] data_out1;
assign data_1 = (cs_1 && !we_1 && oe_1) ? data_out1 : 'hz;
always@(*) begin
if(cs_1 && !we_1 && oe_1) begin
data_out1 = mem[address_1];
end
else begin
data_out1 = 0;
end
end
endmodule
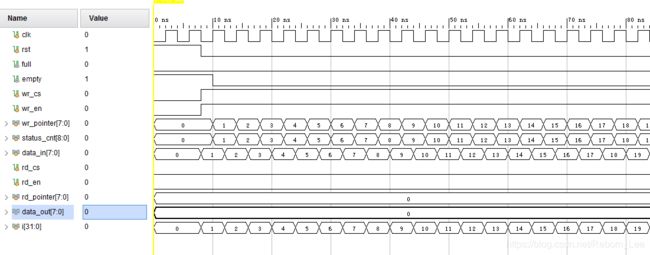
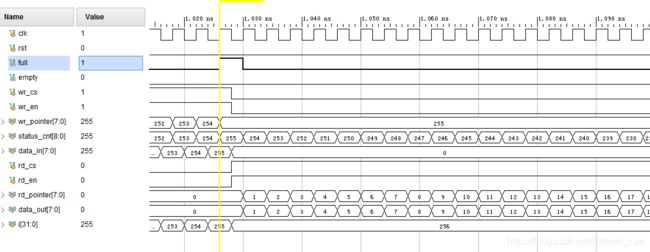
简单测试下:
测试代码:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Create Date: 2019/05/29 22:01:38
// Design Name:
// Module Name: syn_fifo_tb
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
module syn_fifo_tb(
);
reg clk ;
reg rst ;
reg wr_cs ;
reg rd_cs ;
reg rd_en ;
reg wr_en ;
reg [7:0] data_in ;
wire full ;
wire empty ;
wire [7:0] data_out ;
initial begin
clk = 0;
forever
#2 clk = ~clk;
end
integer i=0;
initial begin
rst = 1;
wr_cs = 0;
rd_cs = 0;
wr_en = 0;
rd_en = 0;
data_in = 0;
#8
rst = 0;
//write
wr_cs = 1;
wr_en = 1;
for(i = 0; i < 256; i = i + 1) begin
@(negedge clk) begin
data_in = data_in + 1;
end
end
//read
//#8
wr_cs = 0;
wr_en = 0;
rd_cs = 1;
rd_en = 1;
end
syn_fifo u_syn_fifo(
.clk(clk),
.rst(rst),
.wr_cs(wr_cs),
.rd_cs(rd_cs),
.rd_en(rd_en),
.wr_en(wr_en),
.data_in(data_in),
.full(full),
.empty(empty),
.data_out(data_out)
);
endmodule
当然测试代码并没有测试同时读写的情况,但至少验证了,先进先出的事实,且读写数据都符合预期。
下一篇:异步FIFO的设计