pjlib系列之非动态内存pool
pool简介
pjlib的pool实现了内存池,使得可以不必频繁地创建释放内存,避免由此引起的内存碎片。官方文档为pjlib内存池pool
pool共有这么几个组件:
pool factory内存池工厂:用来管理内存池的
policy:管理策略,工厂只是用来管理内存池对象,对于如何分配内存(使用malloc还是new),则由策略组件来实现。
pool object:内存池对象,使用内存池对象可以alloc和free内存,但实际上如果超过设置的块大小才malloc,没有超过的时候只是移动一下指针而已。
caching pool factory:系统实现的默认工厂,一般我们没有必要自己实现一个工厂,使用pjlib提供的默认工厂就可以。
使用示例
官方文档提供了使用示例
#include
#define THIS_FILE "pool_sample.c"
static void my_perror(const char *title, pj_status_t status)
{
PJ_PERROR(1,(THIS_FILE, status, title));
}
static void pool_demo_1(pj_pool_factory *pfactory)
{
unsigned i;
pj_pool_t *pool;
// Must create pool before we can allocate anything
pool = pj_pool_create(pfactory, // the factory
"pool1", // pool's name
4000, // initial size
4000, // increment size
NULL); // use default callback.
if (pool == NULL) {
my_perror("Error creating pool", PJ_ENOMEM);
return;
}
// Demo: allocate some memory chunks
for (i=0; i<1000; ++i) {
void *p;
p = pj_pool_alloc(pool, (pj_rand()+1) % 512);
// Do something with p
...
// Look! No need to free p!!
}
// Done with silly demo, must free pool to release all memory.
pj_pool_release(pool);
}
int main()
{
pj_caching_pool cp;
pj_status_t status;
// Must init PJLIB before anything else
status = pj_init();
if (status != PJ_SUCCESS) {
my_perror("Error initializing PJLIB", status);
return 1;
}
// Create the pool factory, in this case, a caching pool,
// using default pool policy.
pj_caching_pool_init(&cp, NULL, 1024*1024 );
// Do a demo
pool_demo_1(&cp.factory);
// Done with demos, destroy caching pool before exiting app.
pj_caching_pool_destroy(&cp);
return 0;
} 流程伪代码如下:
1、pjlib初始化
2、初始化caching pool factioy
3、创建内存池
4、使用和释放内存
5、销毁内存池
6、清理caching pool factory
7、pjlib退出
其中1、2、6、7这个应用程序只需要调用一次。
下面通过代码分别解释内存池的实现细节
内存池对象
内存池对象定义在pool.h文件
/**
* This class, which is used internally by the pool, describes a single
* block of memory from which user memory allocations will be allocated from.
*/
typedef struct pj_pool_block
{
PJ_DECL_LIST_MEMBER(struct pj_pool_block); /**< List's prev and next. */
unsigned char *buf; /**< Start of buffer. */
unsigned char *cur; /**< Current alloc ptr. */
unsigned char *end; /**< End of buffer. */
} pj_pool_block;
/**
* This structure describes the memory pool. Only implementors of pool factory
* need to care about the contents of this structure.
*/
struct pj_pool_t
{
PJ_DECL_LIST_MEMBER(struct pj_pool_t); /**< Standard list elements. */
/** Pool name */
char obj_name[PJ_MAX_OBJ_NAME];
/** Pool factory. */
pj_pool_factory *factory;
/** Data put by factory */
void *factory_data;
/** Current capacity allocated by the pool. */
pj_size_t capacity;
/** Size of memory block to be allocated when the pool runs out of memory */
pj_size_t increment_size;
/** List of memory blocks allcoated by the pool. */
pj_pool_block block_list;
/** The callback to be called when the pool is unable to allocate memory. */
pj_pool_callback *callback;
};内存池有名字obj_name,工厂指针factory,capacity表示当前内存池已经申请的内存空间,increment_size表示当空间不足时,再申请的空间增量。内存池实际上是有多个内存块组成,用链表连接block_list,每个内存块有三个指针,起始地址,结束地址,当前使用地址。
创建内存池时,会传入两个重要参数,初始化大小和增量大小,也比较好理解,就是第一次申请initial_size大的内存,当不够时,再申请increment_size大的内存。pj_pool_create函数内部会调用到pj_pool_create_int,看下这个函数做了哪些事。
PJ_DEF(pj_pool_t*) pj_pool_create_int( pj_pool_factory *f, const char *name,
pj_size_t initial_size,
pj_size_t increment_size,
pj_pool_callback *callback)
{
pj_pool_t *pool;
pj_pool_block *block;
pj_uint8_t *buffer;
PJ_CHECK_STACK();
/* Size must be at least sizeof(pj_pool)+sizeof(pj_pool_block) */
PJ_ASSERT_RETURN(initial_size >= sizeof(pj_pool_t)+sizeof(pj_pool_block),
NULL);
/* If callback is NULL, set calback from the policy */
if (callback == NULL)
callback = f->policy.callback;
/* Allocate initial block */
buffer = (pj_uint8_t*) (*f->policy.block_alloc)(f, initial_size); //创建一块initial_size大的内存,也就是第一个内存块
if (!buffer)
return NULL;
/* Set pool administrative data. */
pool = (pj_pool_t*)buffer; //第一个内存块首先存储pj_pool_t结构体,也就是本内存池的对象
pj_bzero(pool, sizeof(*pool));
pj_list_init(&pool->block_list);
pool->factory = f;
/* Create the first block from the memory. */
block = (pj_pool_block*) (buffer + sizeof(*pool)); //pj_pool_t之后是pj_pool_blockj结构图,也就是第一个内存块的对象
block->buf = ((unsigned char*)block) + sizeof(pj_pool_block);//第三部分开始才是真正可用的内存
block->end = buffer + initial_size;
/* Set the start pointer, aligning it as needed */
block->cur = ALIGN_PTR(block->buf, PJ_POOL_ALIGNMENT);
pj_list_insert_after(&pool->block_list, block);//把第一个内存块添加到内存链表
pj_pool_init_int(pool, name, increment_size, callback);
/* Pool initial capacity and used size */
pool->capacity = initial_size; //当前的内存空间就是初始化大小
LOG((pool->obj_name, "pool created, size=%u", pool->capacity));
return pool;
}上面的流程简化描述,先申请一块increment_size的内存块,这块内存先用来存内存池本身的信息pj_pool_t,接着是第一个内存块本身信息pj_pool_block,最后才是真正可使用的内存。
创建和内存池后,就可以使用内存池申请释放内存,当申请的内存不足时,就要再申请一个内存块,看看代码如何实现。
PJ_IDEF(void*) pj_pool_alloc_from_block( pj_pool_block *block, pj_size_t size )
{
/* The operation below is valid for size==0.
* When size==0, the function will return the pointer to the pool
* memory address, but no memory will be allocated.
*/
if (size & (PJ_POOL_ALIGNMENT-1)) {
size = (size + PJ_POOL_ALIGNMENT) & ~(PJ_POOL_ALIGNMENT-1);
}
if ((pj_size_t)(block->end - block->cur) >= size) {
void *ptr = block->cur;
block->cur += size;
return ptr;
}
return NULL;
}
/*
* Allocate memory chunk for user from available blocks.
* This will iterate through block list to find space to allocate the chunk.
* If no space is available in all the blocks, a new block might be created
* (depending on whether the pool is allowed to resize).
*/
PJ_DEF(void*) pj_pool_allocate_find(pj_pool_t *pool, pj_size_t size)
{
pj_pool_block *block = pool->block_list.next;
void *p;
pj_size_t block_size;
PJ_CHECK_STACK();
//遍历当前内存块,如果有一块够大,则更新指针后直接返回
while (block != &pool->block_list) {
p = pj_pool_alloc_from_block(block, size);
if (p != NULL)
return p;
block = block->next;
}
/* No available space in all blocks. */
/* If pool is configured NOT to expand, return error. */
if (pool->increment_size == 0) {
LOG((pool->obj_name, "Can't expand pool to allocate %u bytes "
"(used=%u, cap=%u)",
size, pj_pool_get_used_size(pool), pool->capacity));
(*pool->callback)(pool, size);
return NULL;
}
/* If pool is configured to expand, but the increment size
* is less than the required size, expand the pool by multiple
* increment size. Also count the size wasted due to aligning
* the block.
*/
if (pool->increment_size <
size + sizeof(pj_pool_block) + PJ_POOL_ALIGNMENT)
{
pj_size_t count;
count = (size + pool->increment_size + sizeof(pj_pool_block) +
PJ_POOL_ALIGNMENT) /
pool->increment_size;
block_size = count * pool->increment_size;
} else {
block_size = pool->increment_size;
}
LOG((pool->obj_name,
"%u bytes requested, resizing pool by %u bytes (used=%u, cap=%u)",
size, block_size, pj_pool_get_used_size(pool), pool->capacity));
//到这里所有内存块都不足了,因此要再申请一个新的内存块
block = pj_pool_create_block(pool, block_size);
if (!block)
return NULL;
p = pj_pool_alloc_from_block(block, size);
pj_assert(p != NULL);
#if PJ_DEBUG
if (p == NULL) {
PJ_UNUSED_ARG(p);
}
#endif
return p;
}首先检查当前的内存块是否有一块够大,如果存在,更新一下那一块的指针,就返回了。说明大部分情况,并没有真正去malloc内存,而是在内存块上更新指针,提升了效率。如果不够大,再申请新的内存块。申请新内存块的代码如下:
/*
* Create new block.
* Create a new big chunk of memory block, from which user allocation will be
* taken from.
*/
static pj_pool_block *pj_pool_create_block( pj_pool_t *pool, pj_size_t size)
{
pj_pool_block *block;
PJ_CHECK_STACK();
pj_assert(size >= sizeof(pj_pool_block));
LOG((pool->obj_name, "create_block(sz=%u), cur.cap=%u, cur.used=%u",
size, pool->capacity, pj_pool_get_used_size(pool)));
/* Request memory from allocator. */
block = (pj_pool_block*)
(*pool->factory->policy.block_alloc)(pool->factory, size);
if (block == NULL) {
(*pool->callback)(pool, size);
return NULL;
}
/* Add capacity. */
pool->capacity += size;
/* Set start and end of buffer. */
block->buf = ((unsigned char*)block) + sizeof(pj_pool_block);
block->end = ((unsigned char*)block) + size;
/* Set the start pointer, aligning it as needed */
block->cur = ALIGN_PTR(block->buf, PJ_POOL_ALIGNMENT);
/* Insert in the front of the list. */
pj_list_insert_after(&pool->block_list, block);
LOG((pool->obj_name," block created, buffer=%p-%p",block->buf, block->end));
return block;
}申请一块increment_size大的新块,头部是块信息pj_pool_block,块的起始使用位置是在此结构体之后,并且做了对其处理。
下面用一张图来总结内存池当中内存的结构。
策略policy
库默认实现了三个策略,pool_policy_kmalloc.c、pool_policy_malloc.c、pool_policy_new.cpp只需要编译一个即可,一般c语言使用malloc版,每种策略都实现了默认策略。
PJ_DEF_DATA(pj_pool_factory_policy) pj_pool_factory_default_policy =
{
&default_block_alloc,
&default_block_free,
&default_pool_callback,
0
};
PJ_DEF(const pj_pool_factory_policy*) pj_pool_factory_get_default_policy(void)
{
return &pj_pool_factory_default_policy;
}默认工厂caching_pool
caching初始化时传入两个重要参数,策略,可以为空,则使用默认策略;最大内存空间大小,即所有管理的内存池的总和。先看下caching_pool结构体
/**
* Declaration for caching pool. Application doesn't normally need to
* care about the contents of this struct, it is only provided here because
* application need to define an instance of this struct (we can not allocate
* the struct from a pool since there is no pool factory yet!).
*/
struct pj_caching_pool
{
/** Pool factory interface, must be declared first. */
pj_pool_factory factory;
/** Current factory's capacity, i.e. number of bytes that are allocated
* and available for application in this factory. The factory's
* capacity represents the size of all pools kept by this factory
* in it's free list, which will be returned to application when it
* requests to create a new pool.
*/
pj_size_t capacity;
/** Maximum size that can be held by this factory. Once the capacity
* has exceeded @a max_capacity, further #pj_pool_release() will
* flush the pool. If the capacity is still below the @a max_capacity,
* #pj_pool_release() will save the pool to the factory's free list.
*/
pj_size_t max_capacity;
/**
* Number of pools currently held by applications. This number gets
* incremented everytime #pj_pool_create() is called, and gets
* decremented when #pj_pool_release() is called.
*/
pj_size_t used_count;
/**
* Total size of memory currently used by application.
*/
pj_size_t used_size;
/**
* The maximum size of memory used by application throughout the life
* of the caching pool.
*/
pj_size_t peak_used_size;
/**
* Lists of pools in the cache, indexed by pool size.
*/
pj_list free_list[PJ_CACHING_POOL_ARRAY_SIZE];
/**
* List of pools currently allocated by applications.
*/
pj_list used_list;
/**
* Internal pool.
*/
char pool_buf[256 * (sizeof(size_t) / 4)];
/**
* Mutex.
*/
pj_lock_t *lock;
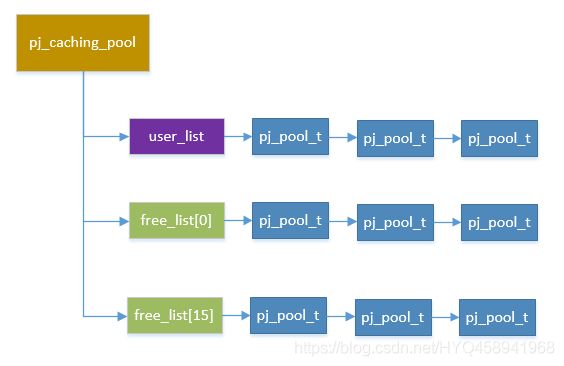
};其中比较重要的一个使用链表,和一组空闲链表。当创建一个内存池时,就把它添加到使用链表,并更新内存池个数,总的使用空间等参数。当释放内存池时,并不是真的释放,如果大小没有超过分类的最大值,则移动到空闲列表,下次再复用。这里要先解释一下大小分类。工厂按内存大小分了16个等级,看代码。
#define PJ_CACHING_POOL_ARRAY_SIZE 16
static pj_size_t pool_sizes[PJ_CACHING_POOL_ARRAY_SIZE] =
{
256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 12288, 16384,
20480, 24576, 28672, 32768, 40960, 49152, 57344, 65536
};每一个等级有一个空闲回收链表。比如我第一次申请了200字节,则释放时回收到第1个等级free_list,如果第2次申请1000个字节,则释放时回收到第3个等级free_list。第3次我又一次申请200个字节,则把第一次的内存池对象从free_list移到used_list就行。用图来表示caching_pool如何管理内存池对象
static pj_pool_t* cpool_create_pool(pj_pool_factory *pf,
const char *name,
pj_size_t initial_size,
pj_size_t increment_sz,
pj_pool_callback *callback)
{
pj_caching_pool *cp = (pj_caching_pool*)pf;
pj_pool_t *pool;
int idx;
PJ_CHECK_STACK();
pj_lock_acquire(cp->lock);
/* Use pool factory's policy when callback is NULL */
if (callback == NULL) {
callback = pf->policy.callback;
}
/* Search the suitable size for the pool.
* We'll just do linear search to the size array, as the array size itself
* is only a few elements. Binary search I suspect will be less efficient
* for this purpose.
*/
if (initial_size <= pool_sizes[START_SIZE]) {
for (idx=START_SIZE-1;
idx >= 0 && pool_sizes[idx] >= initial_size;
--idx)
;
++idx;
} else {
for (idx=START_SIZE+1;
idx < PJ_CACHING_POOL_ARRAY_SIZE &&
pool_sizes[idx] < initial_size;
++idx)
;
}
/* Check whether there's a pool in the list. */
if (idx==PJ_CACHING_POOL_ARRAY_SIZE || pj_list_empty(&cp->free_list[idx])) {
/* No pool is available. */
/* Set minimum size. */
if (idx < PJ_CACHING_POOL_ARRAY_SIZE)
initial_size = pool_sizes[idx];
/* Create new pool */
pool = pj_pool_create_int(&cp->factory, name, initial_size,
increment_sz, callback);
if (!pool) {
pj_lock_release(cp->lock);
return NULL;
}
} else {
/* Get one pool from the list. */
pool = (pj_pool_t*) cp->free_list[idx].next;
pj_list_erase(pool);
/* Initialize the pool. */
pj_pool_init_int(pool, name, increment_sz, callback);
/* Update pool manager's free capacity. */
if (cp->capacity > pj_pool_get_capacity(pool)) {
cp->capacity -= pj_pool_get_capacity(pool);
} else {
cp->capacity = 0;
}
PJ_LOG(6, (pool->obj_name, "pool reused, size=%u", pool->capacity));
}
/* Put in used list. */
pj_list_insert_before( &cp->used_list, pool );
/* Mark factory data */
pool->factory_data = (void*) (pj_ssize_t) idx;
/* Increment used count. */
++cp->used_count;
pj_lock_release(cp->lock);
return pool;
}先根据内存池的创建初始化大小,计算它属于哪个等级,再看看该等级有没有回收的内存池,如果有就把它从free_list[]移动到used_list,如果没有再创建,并添加到used_list。
这样,pjlib的非动态内存的重点就分析完了。其中不仅内存池不用频繁malloc、free,内存工厂还可以回收内存池对象,并且统一在最后释放,不会引入内存泄漏。在做音视频流接收时,由于要频繁地接收包添加到队列,供播放线程来取,这时候就需要频繁地申请释放,使用pjlib则可以极大地提高内存的使用效率。